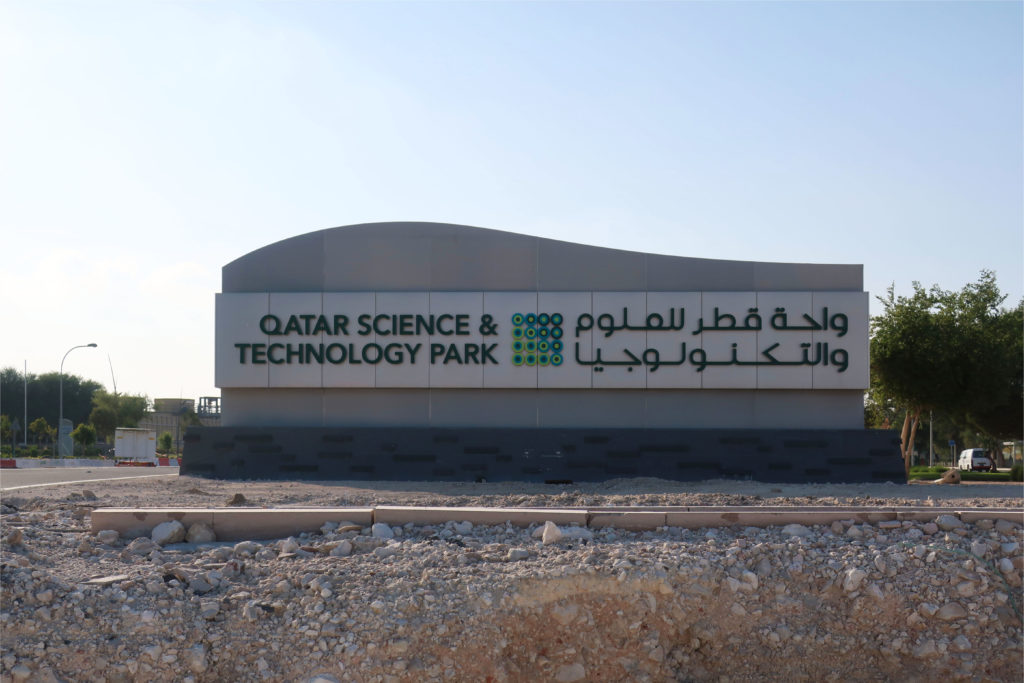
Qatar Science and Technology Park (QSTP)

Introduction
Qatar is making a large investment in education, science, research and development in recent years. Under these principles is that it has opted for a space in which companies develop and expose their new technologies, including an incubator to help new technological proposals to make their discoveries known internationally.
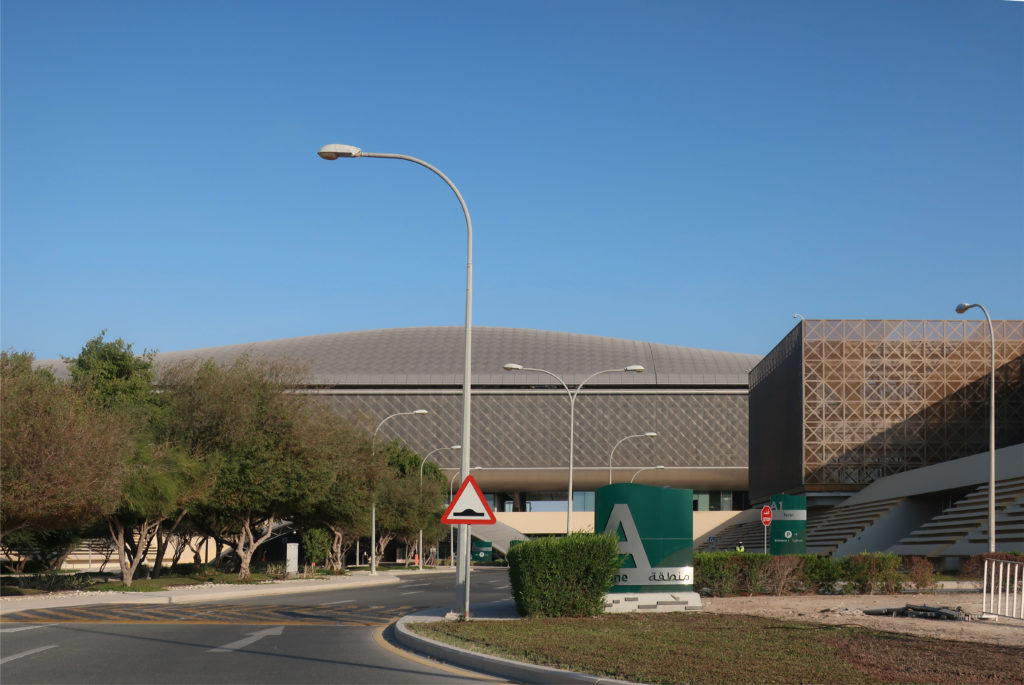
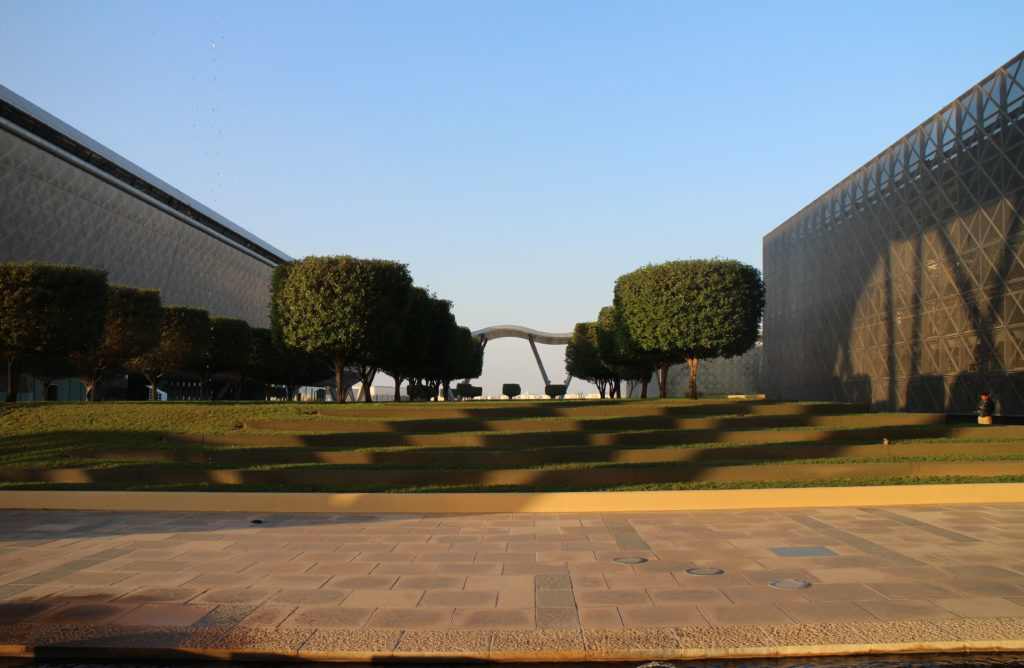
Emerging from the sand dunes, the Qatar Science and Technology Park brings together the best in design and business practices, creating an international environment for technology development. QSTP is a key initiative of the Qatar Foundation in its effort to diversify the economy, create highly qualified jobs and establish Qatar as a knowledge economy in the Middle East. The architectural aesthetic is surprising and contemporary, designed for the desert climate and respecting the Qatari culture.
Location
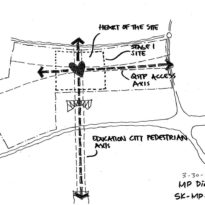
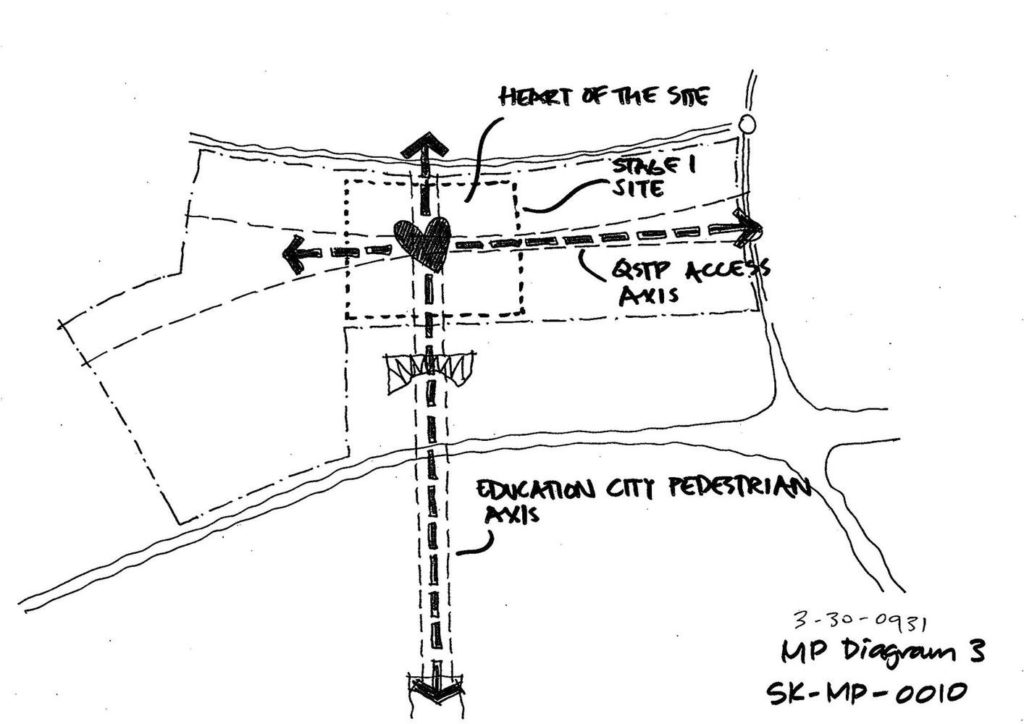
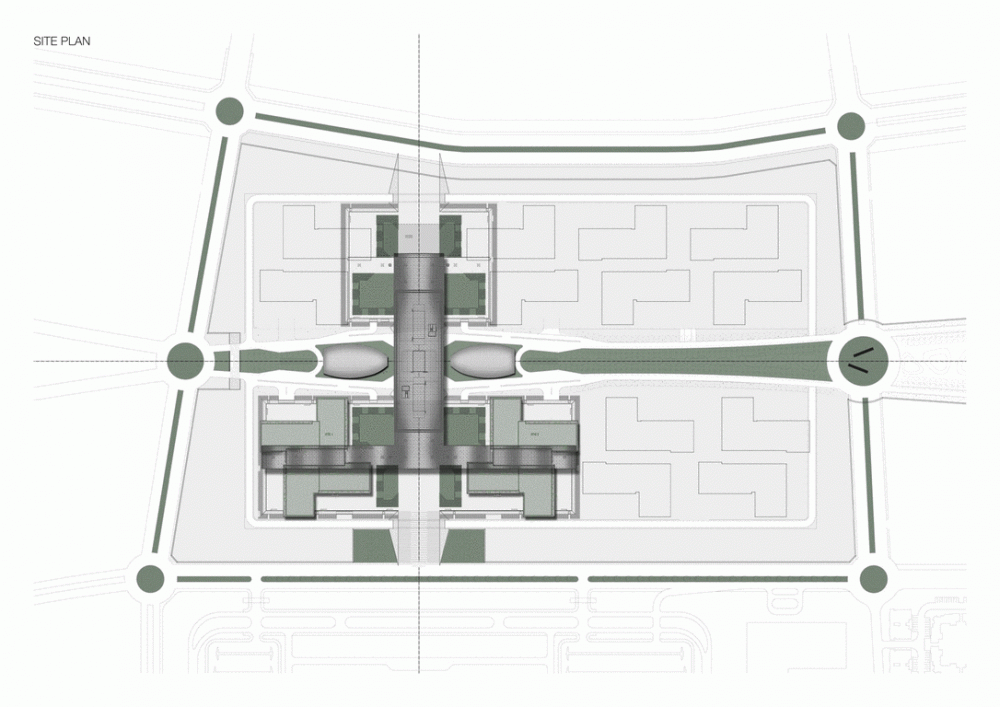
Integrated in the City of Education, the QSTP is located at the crossing point of the east-west arrival axis and the main north-south “green thorn” that joins the Campus with other enclosures of the City of Education, in the Rayan Township, Doha, Qatar.
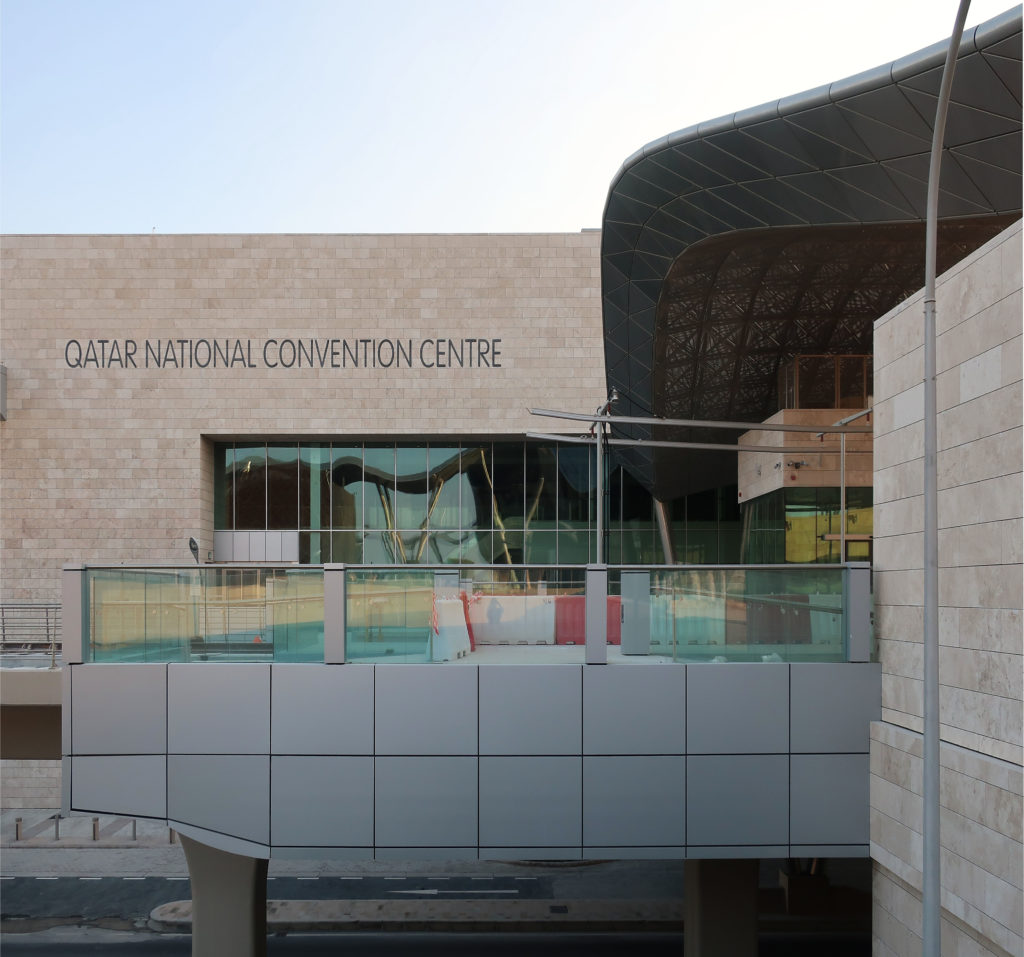
The master plan for this industrial park is developed on 123ha land and encompasses the facilities of the Qatar Foundation, Headquarters and Center for Strategic Studies, a new university hospital and the Qatar National Convention Center.
Concept
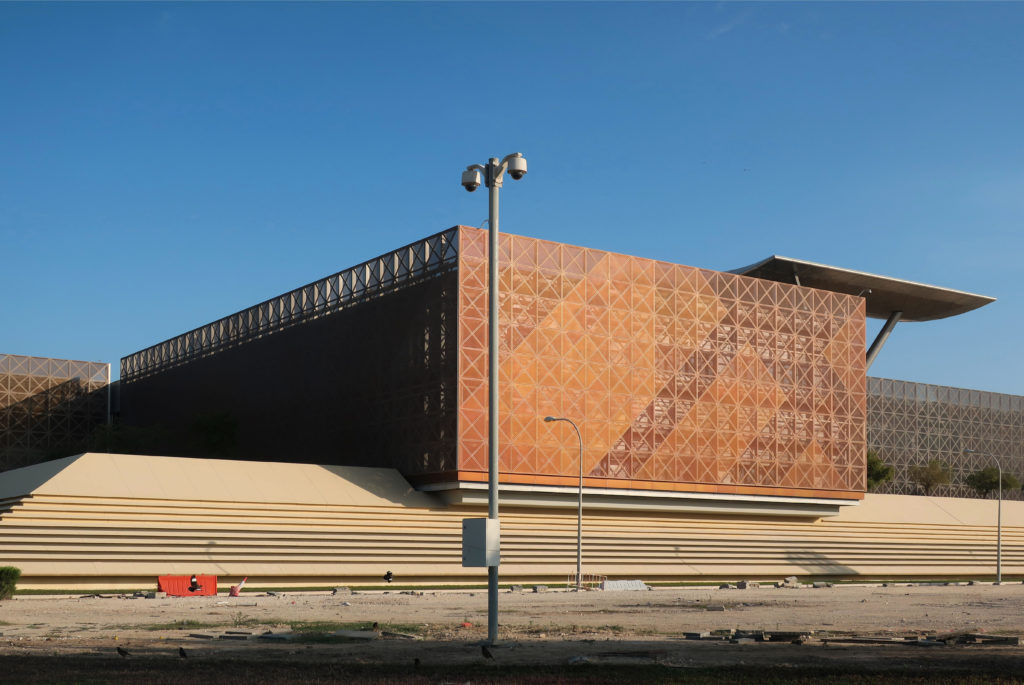
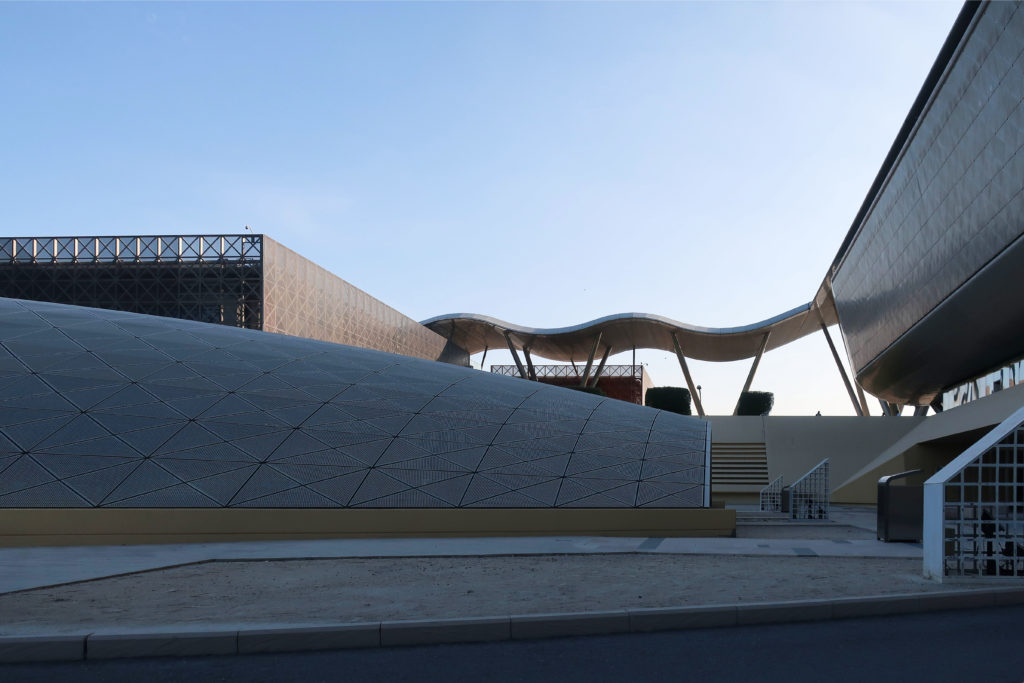
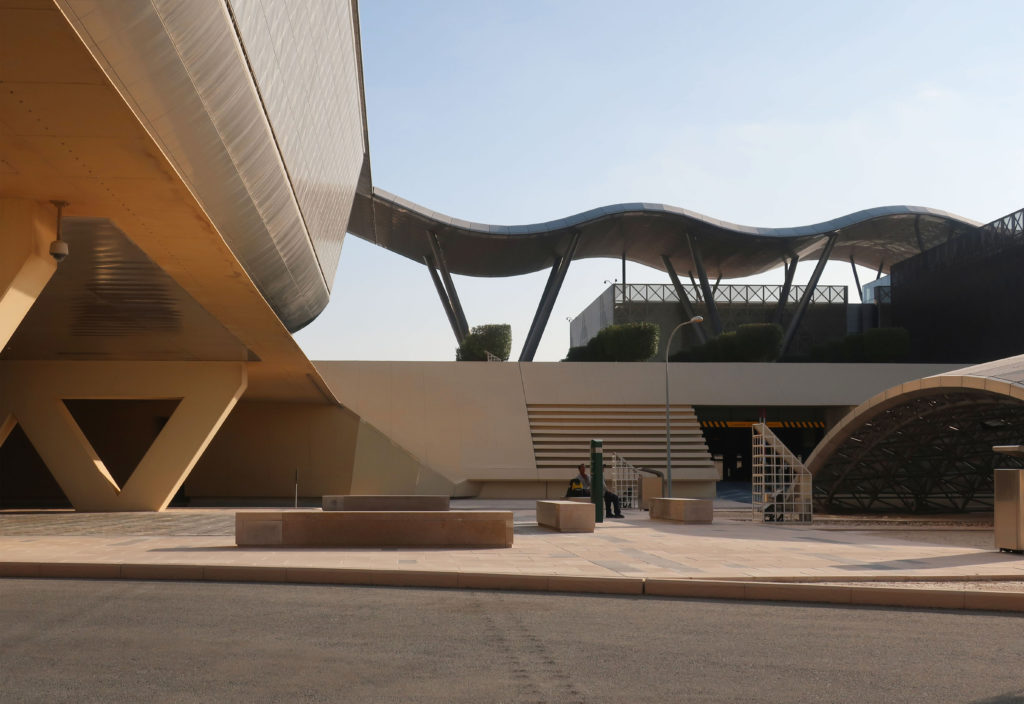
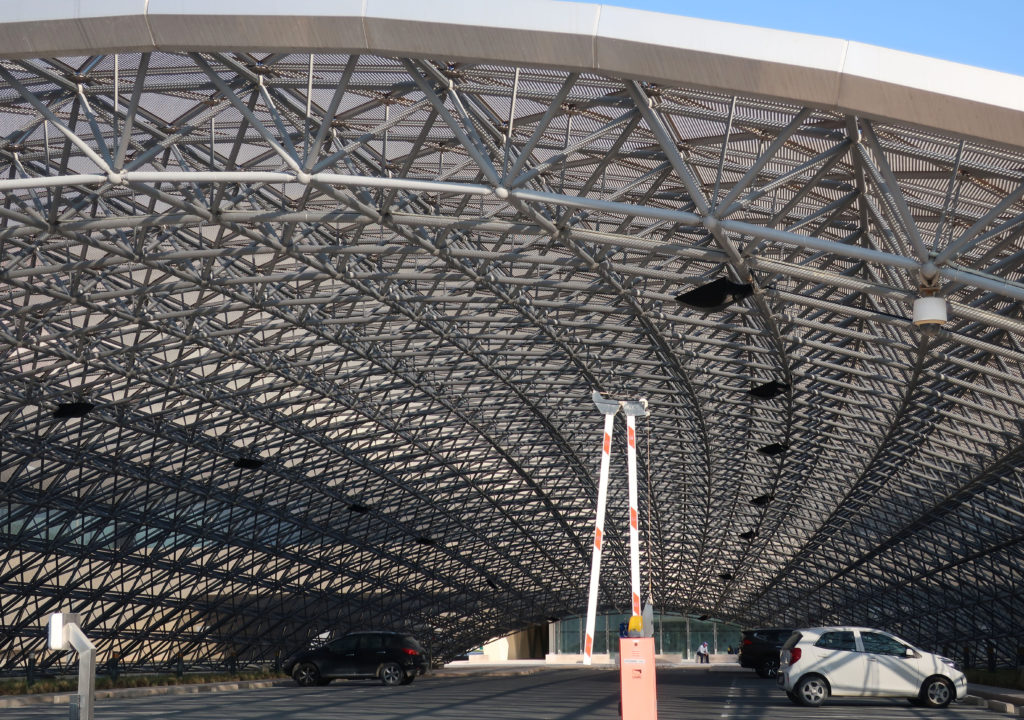
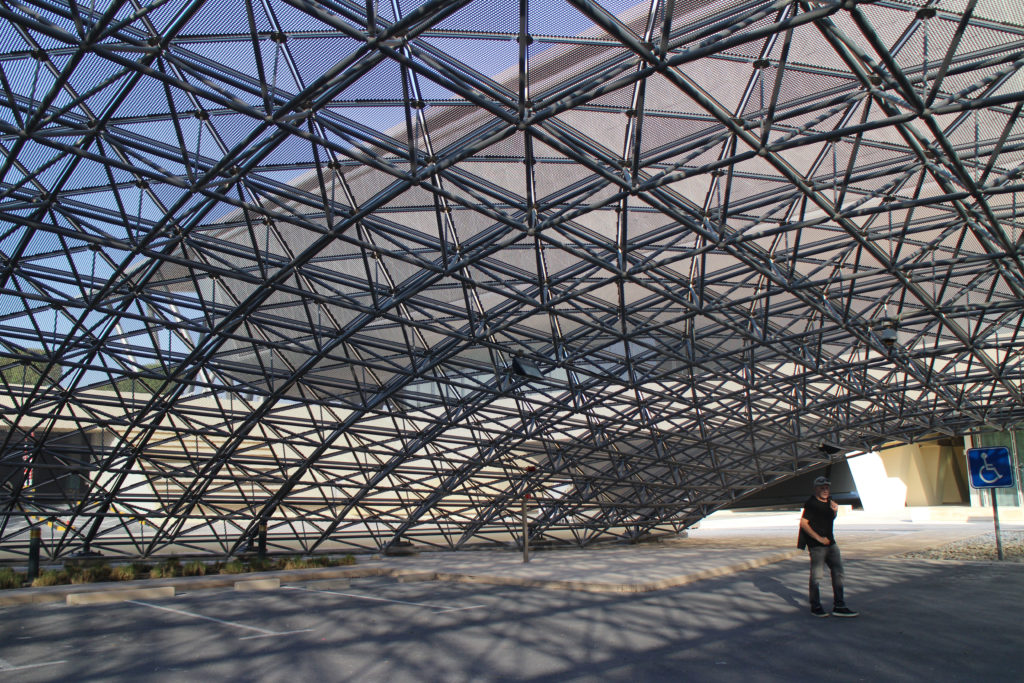
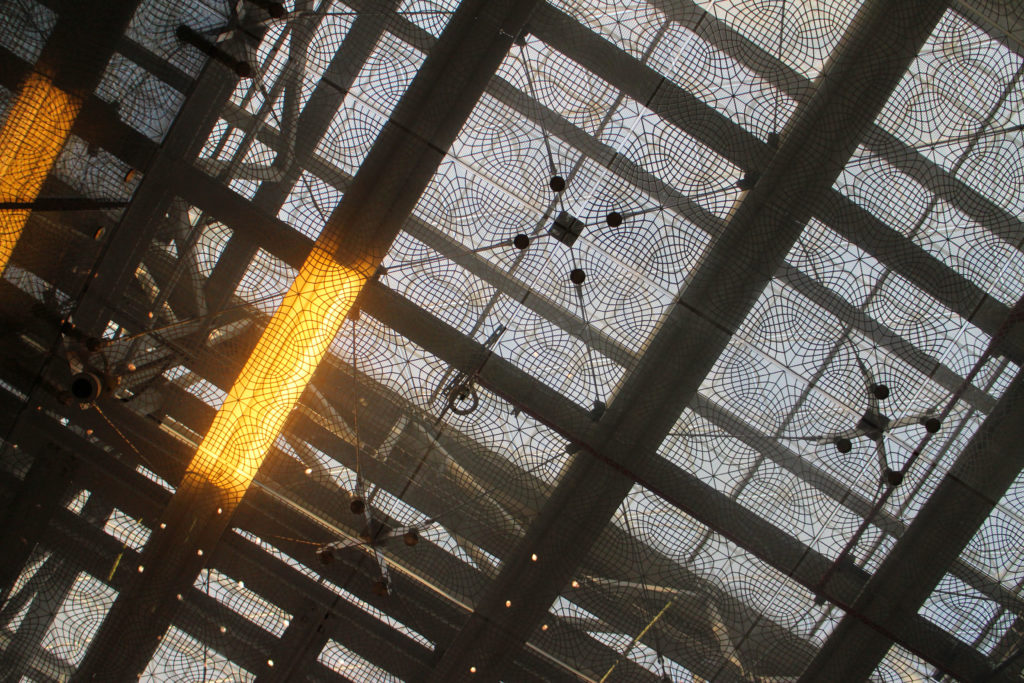
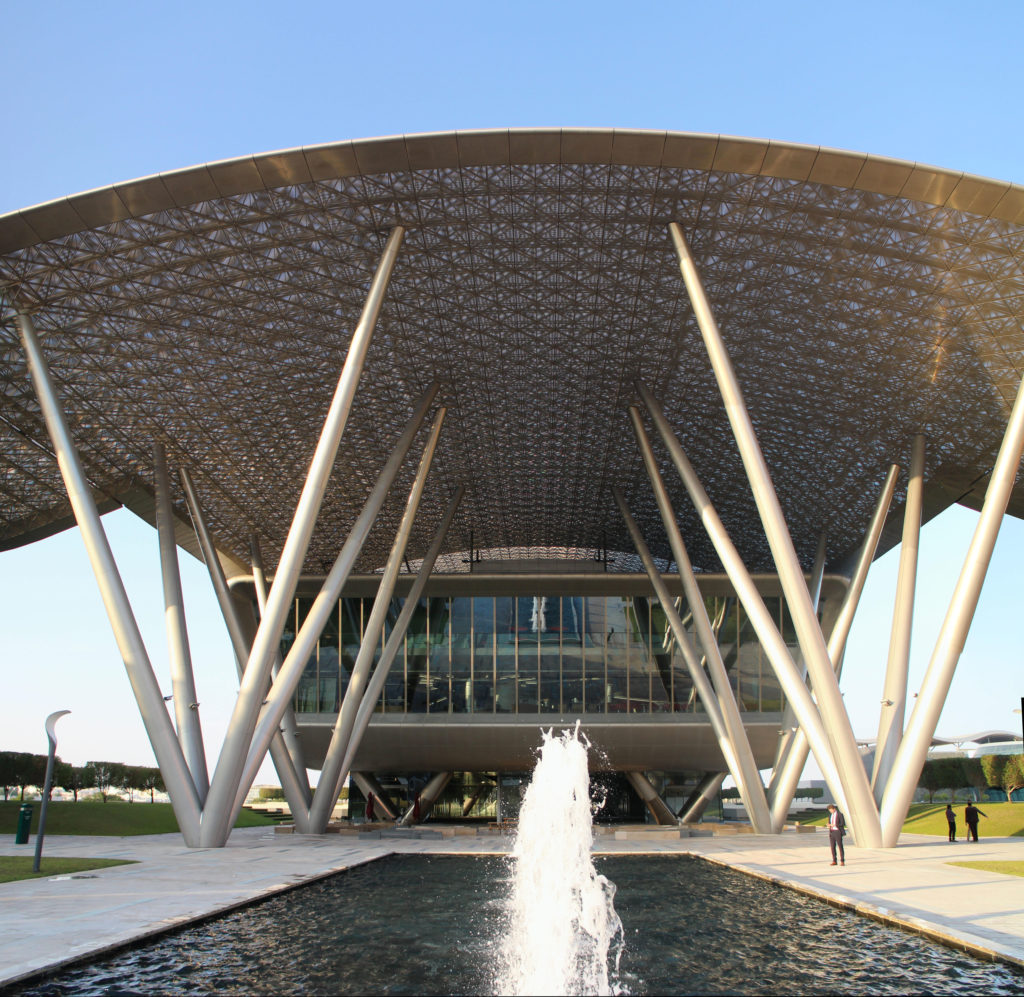
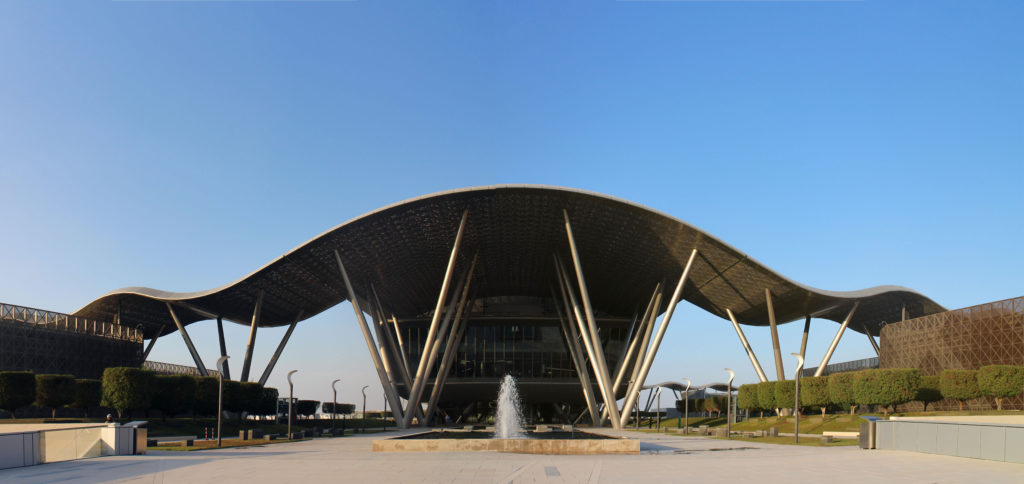
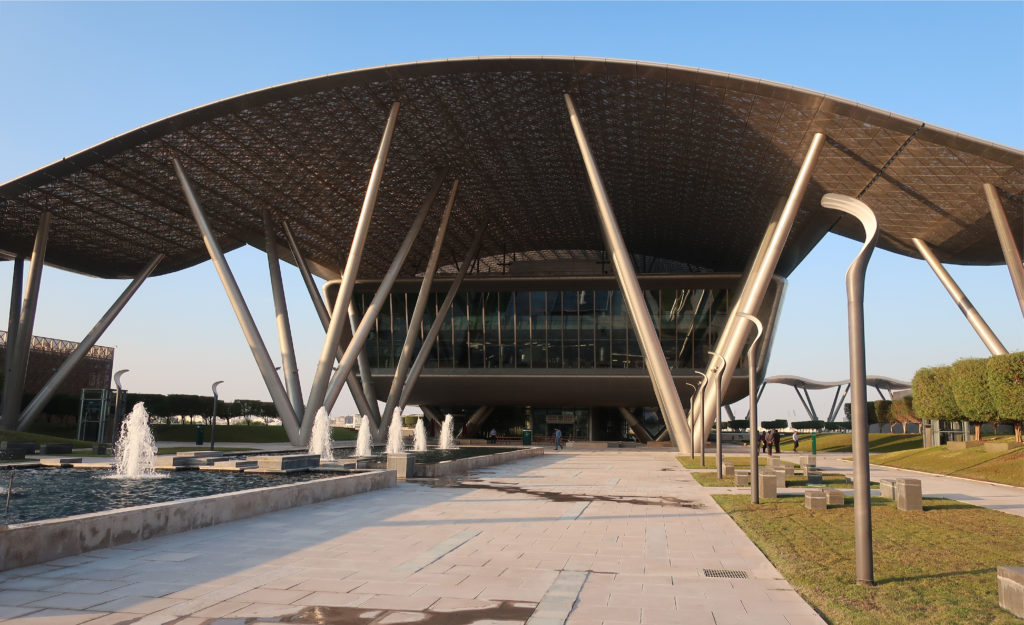
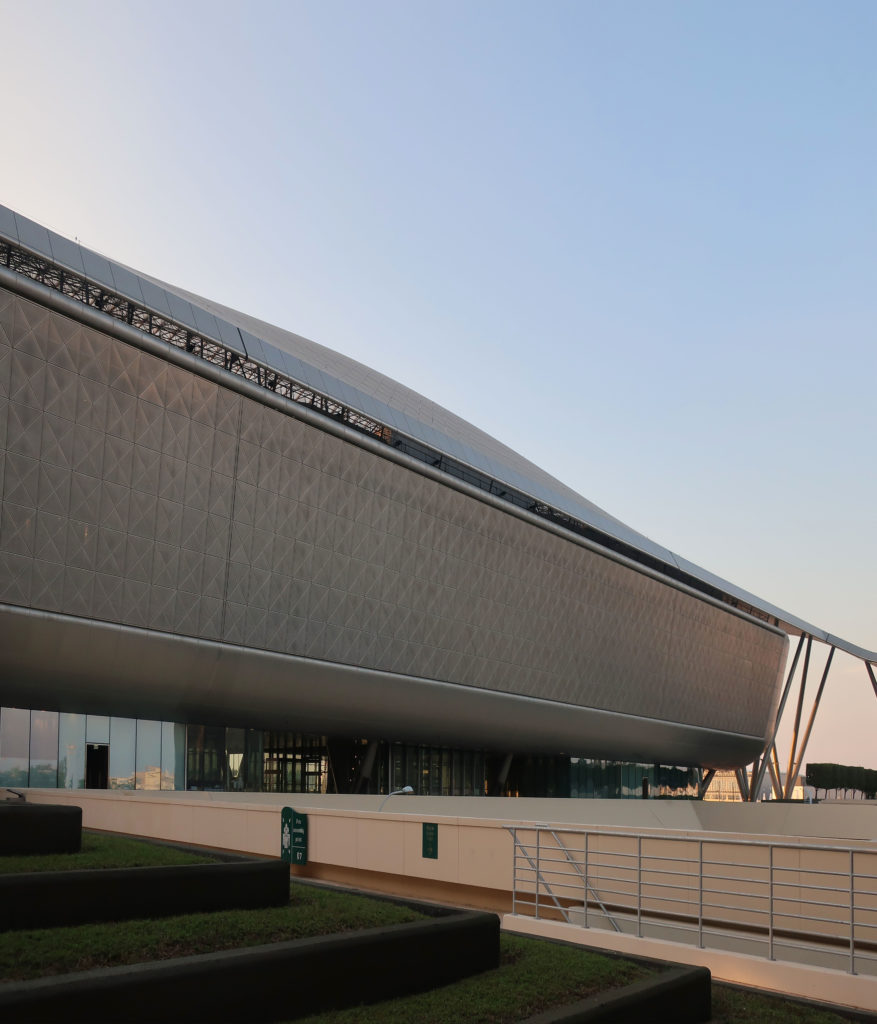
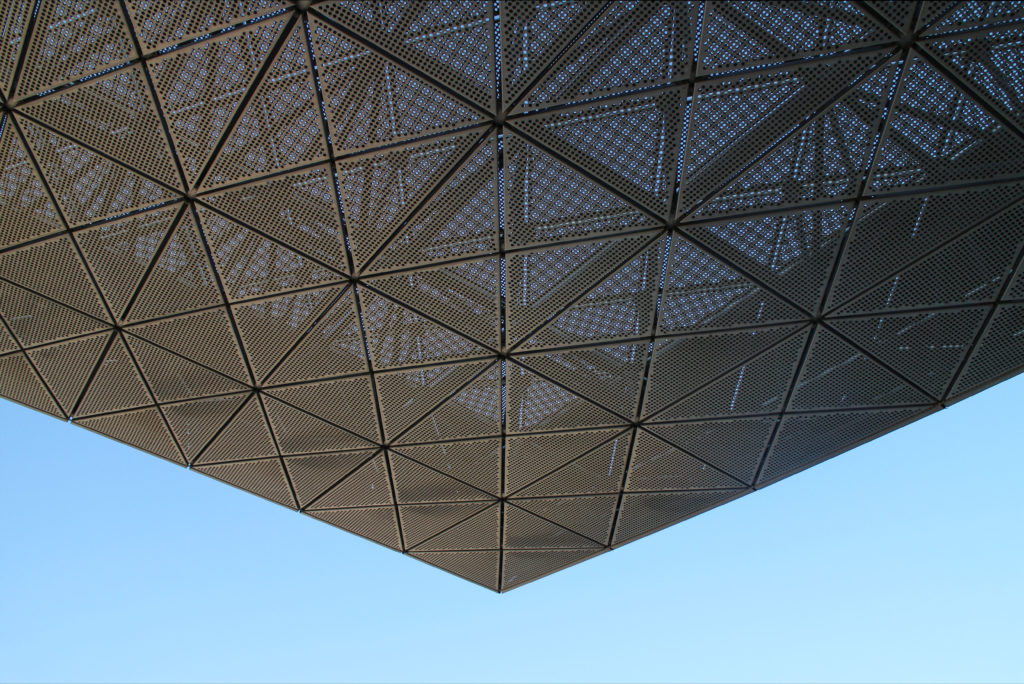
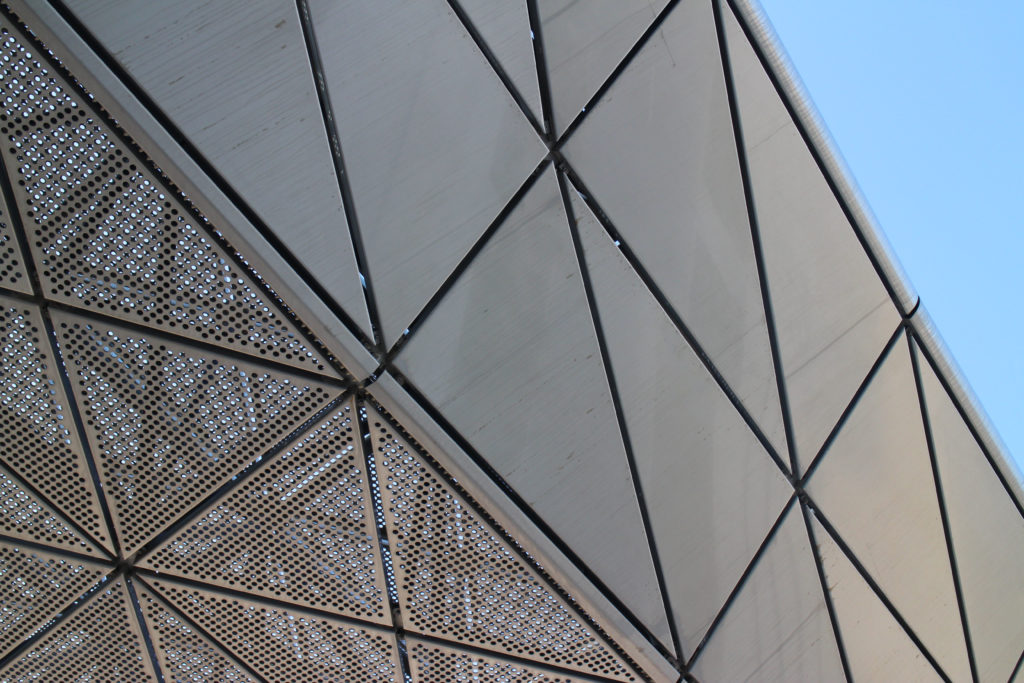
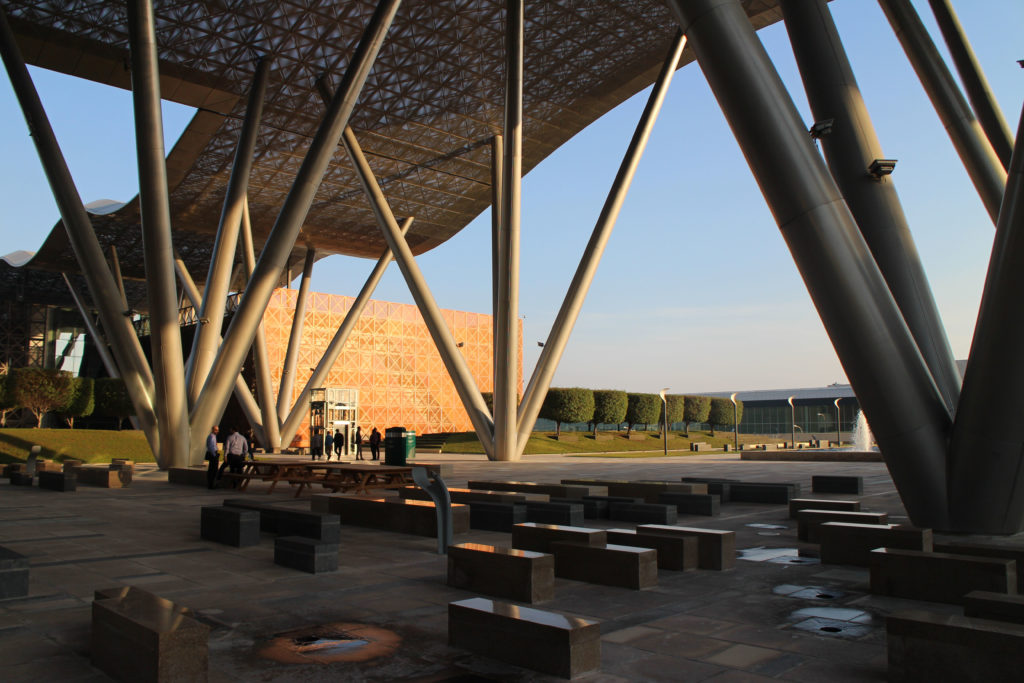
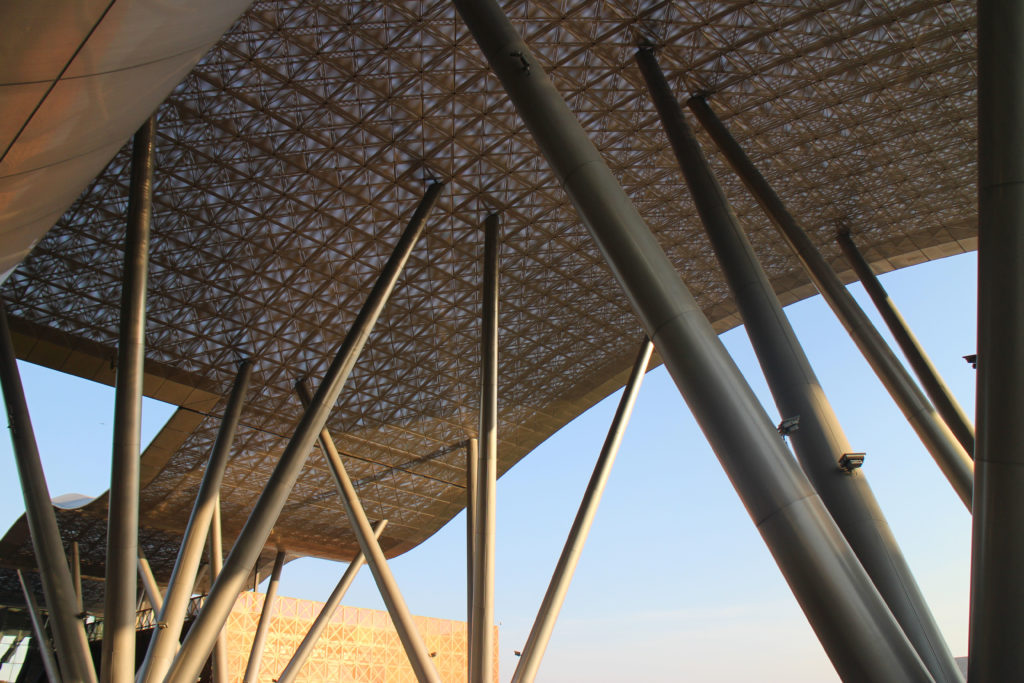
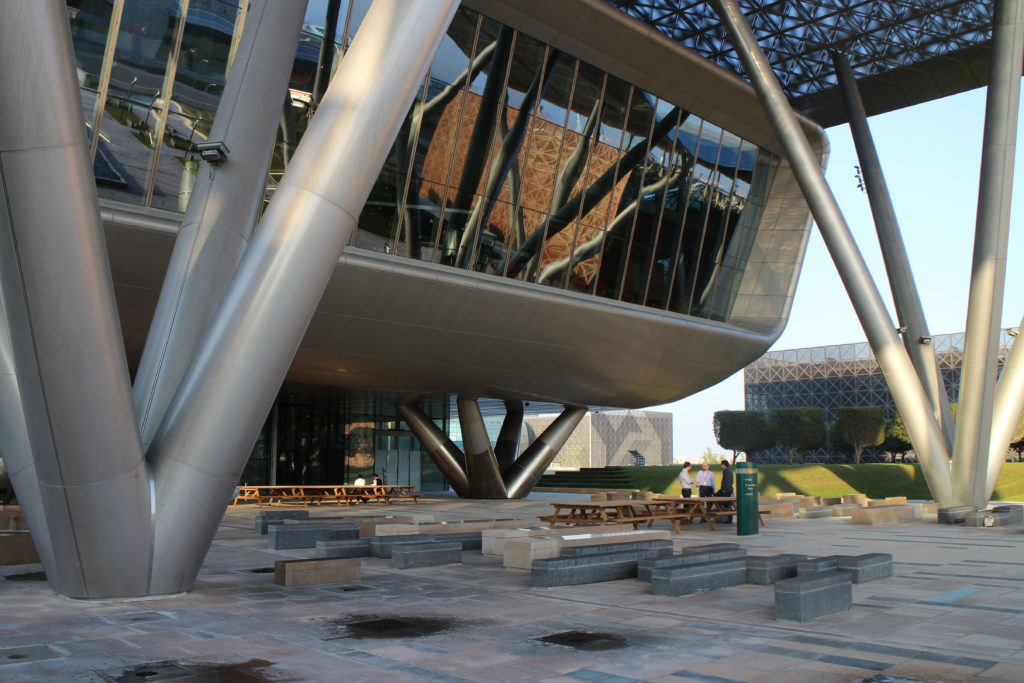
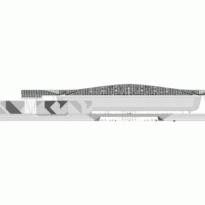
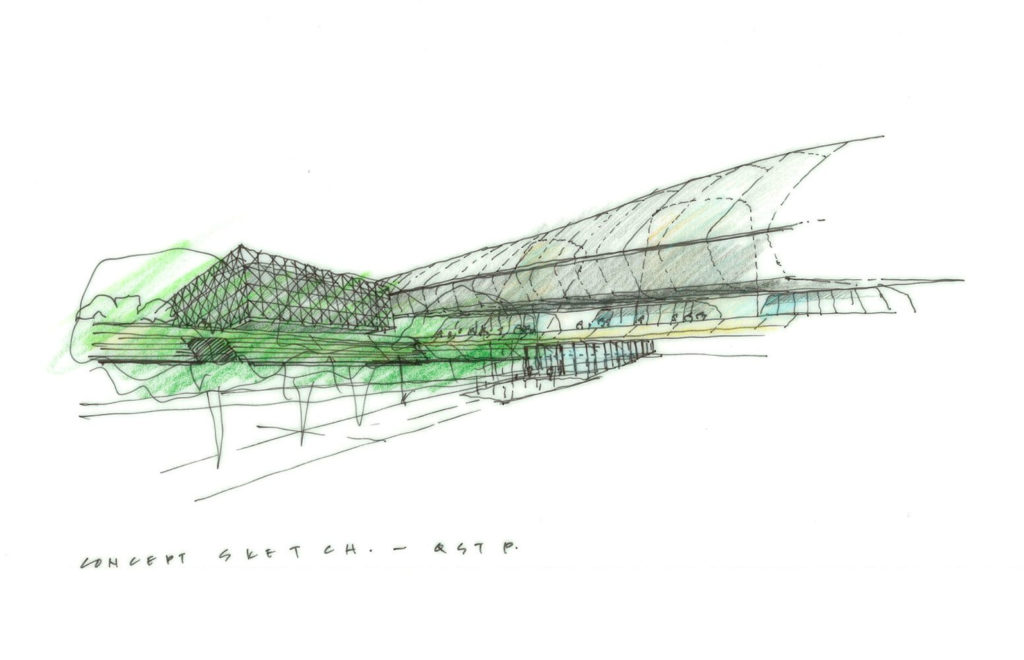
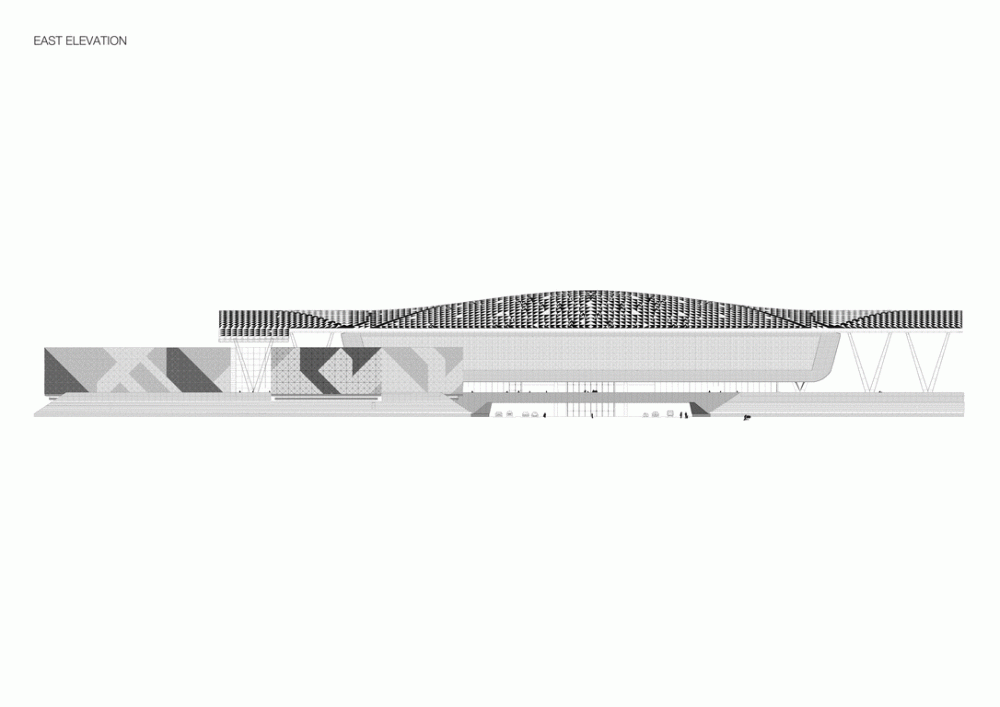
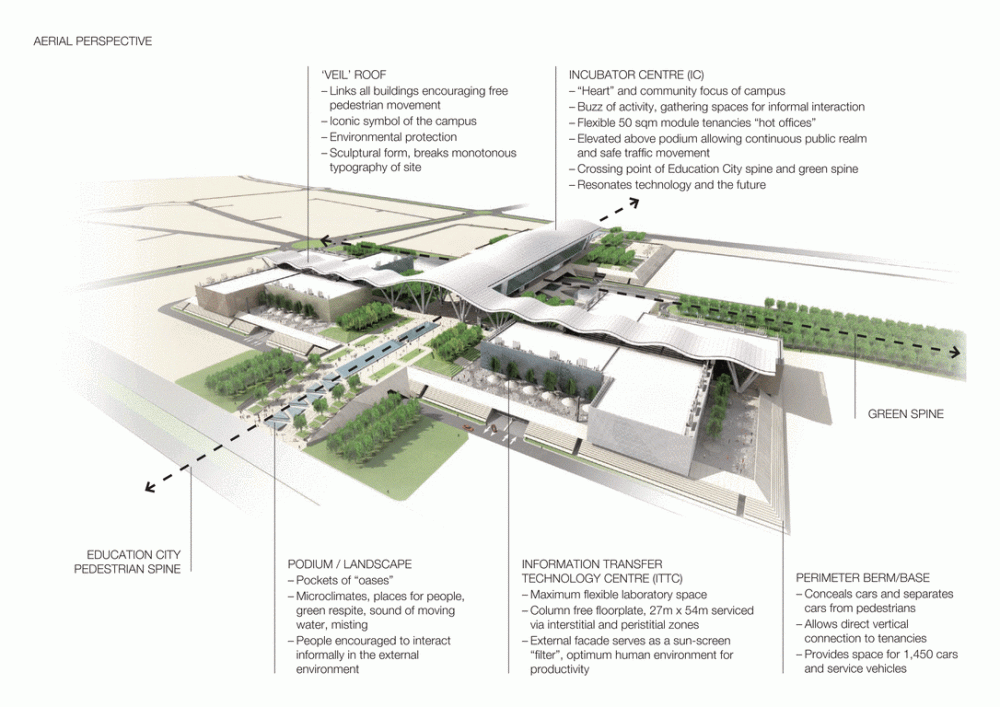
The design of the constructed form is an abstract and contemporary expression based on Islamic cultural references, using cutting-edge technology. An important feature of Islamic architecture is the focus on the interior space compared to the exterior, or the facade. The literal core of the QSTP, the Incubation Center, is located in the center of the place, on an elevated podium, just below an undulating roof structure similar to a veil. The shape of this cover has several reasons. On the one hand, the roof was built to mimic the ripple of sand dunes and the flow of a woman’s veil. On the other hand, it was designed to cover the surrounding space and reduce overall heat gain.
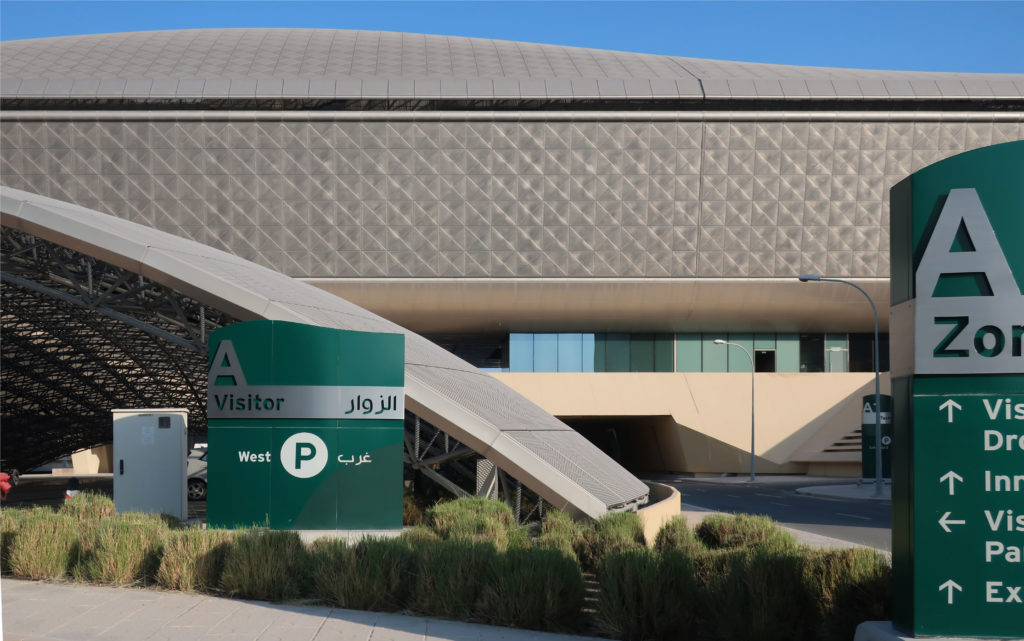
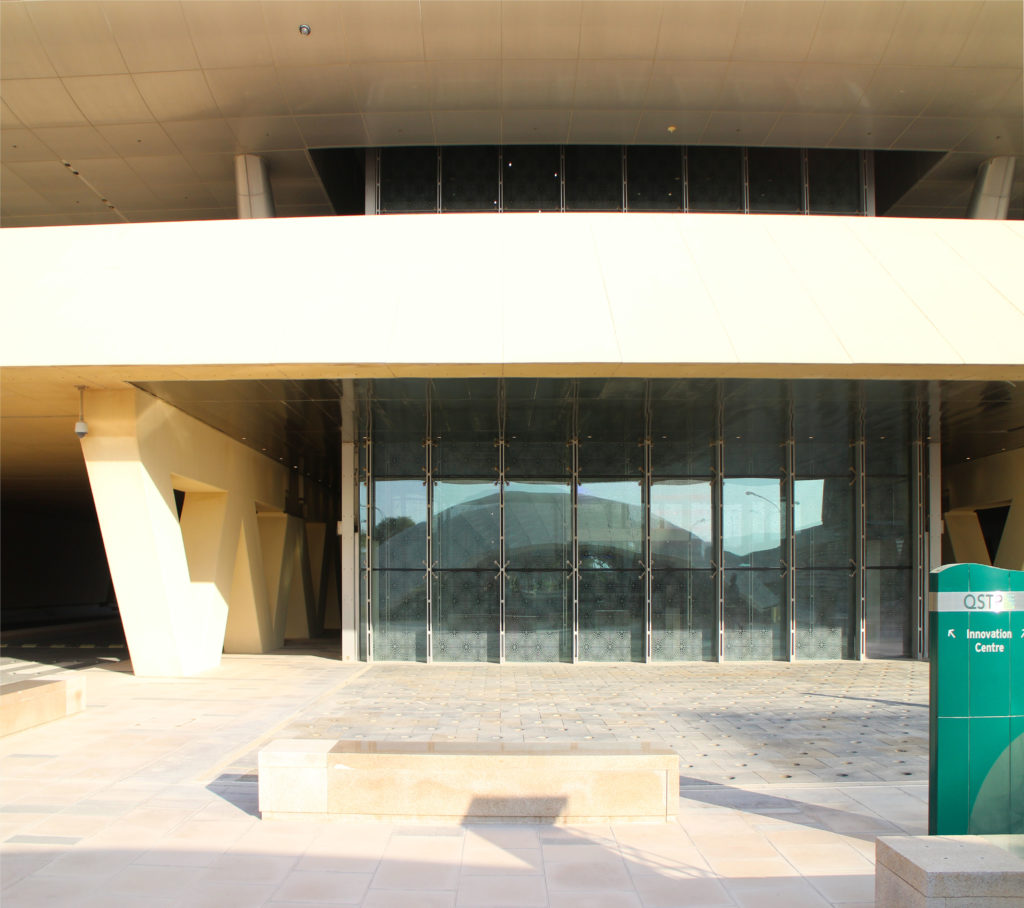
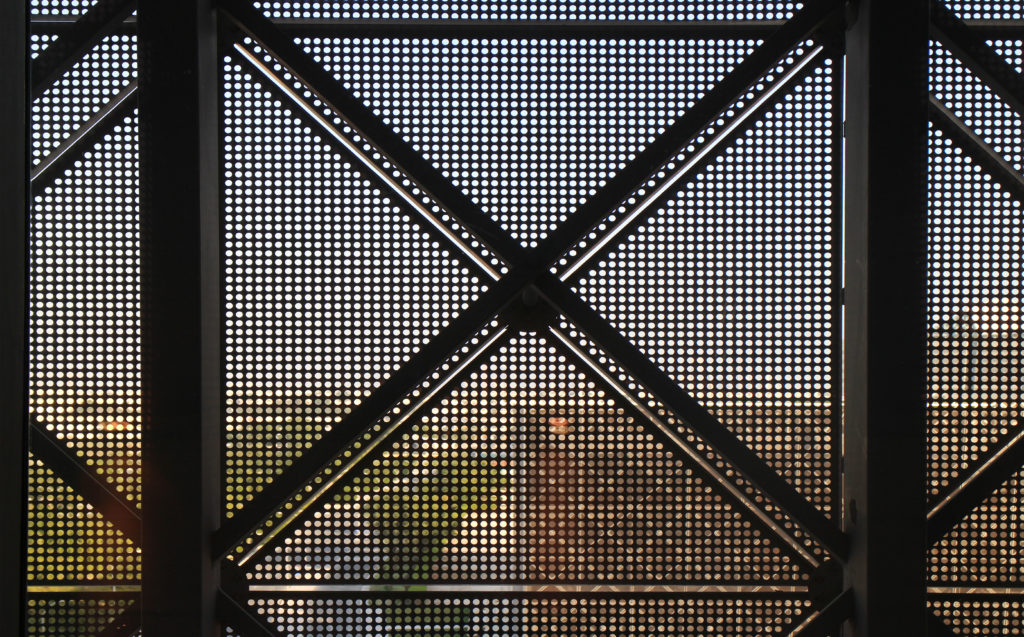
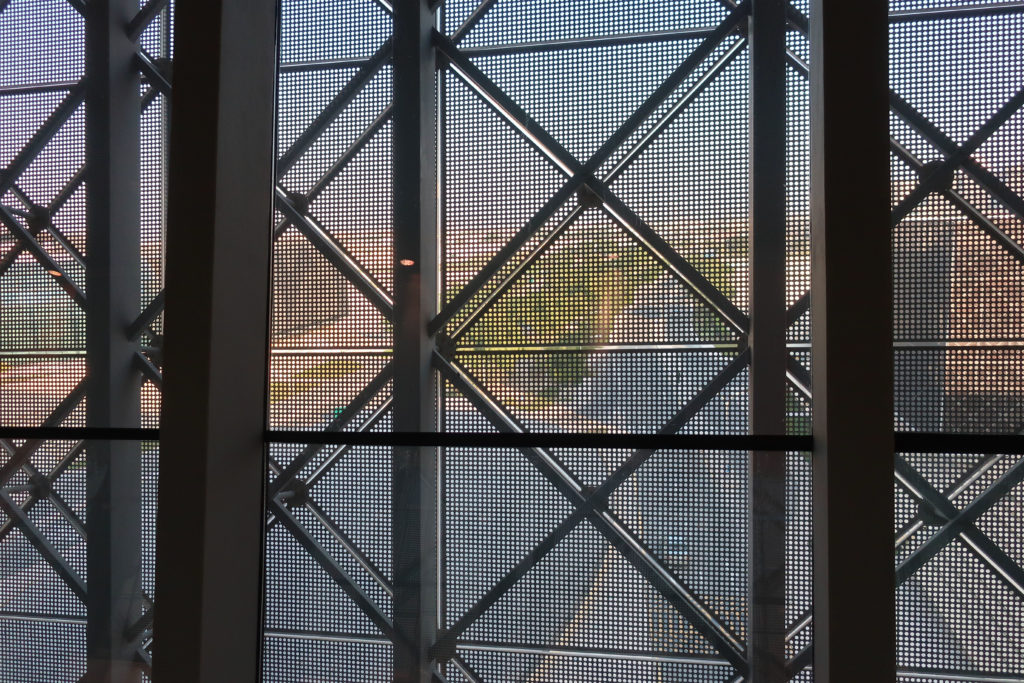
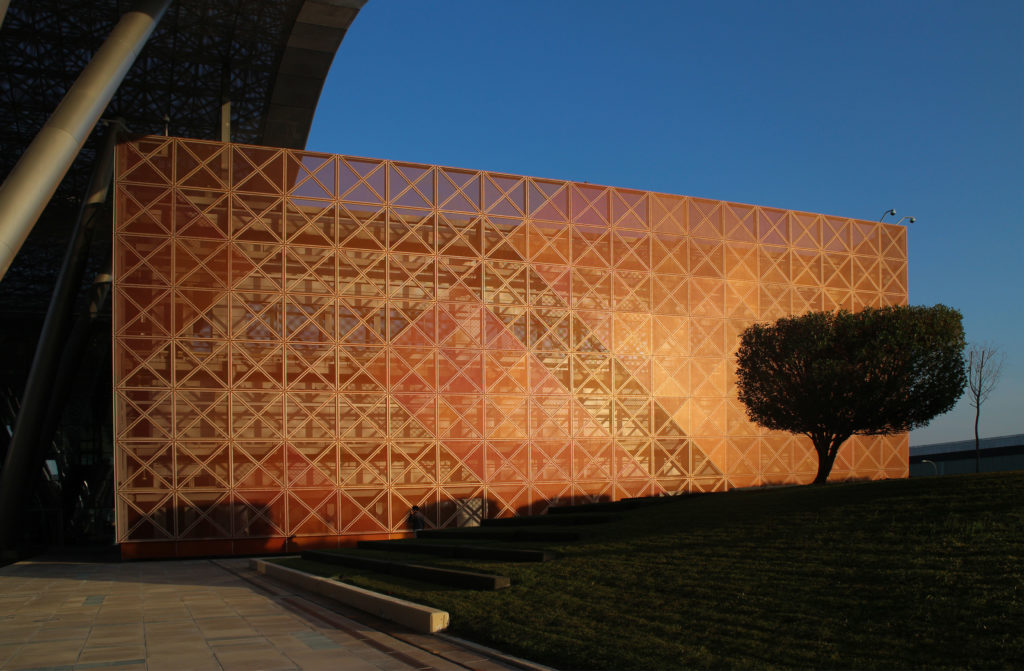
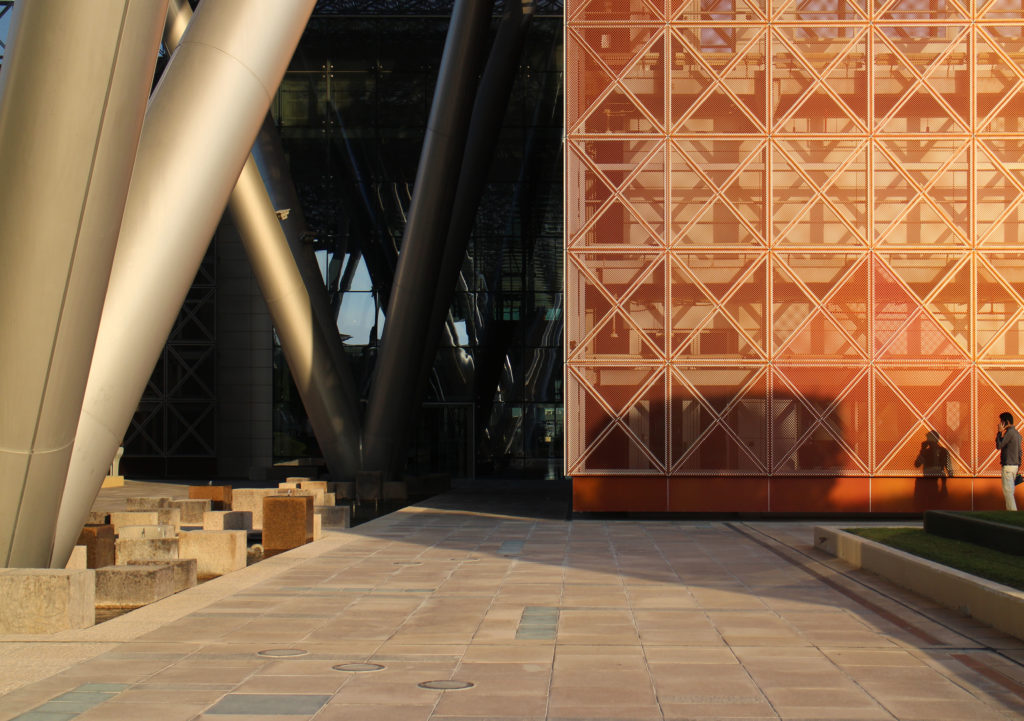
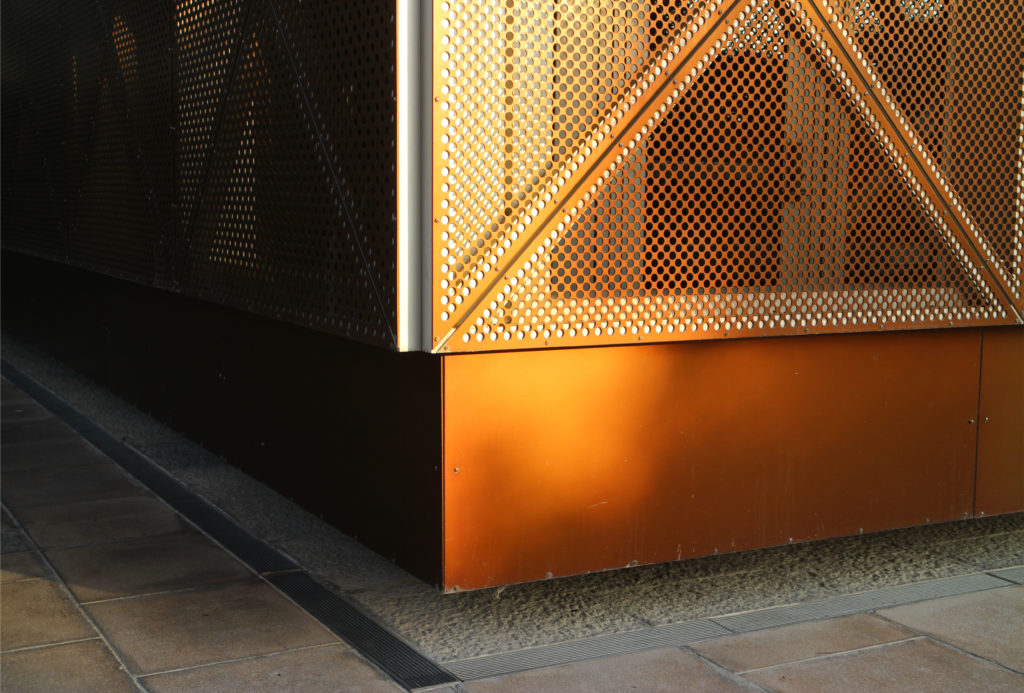
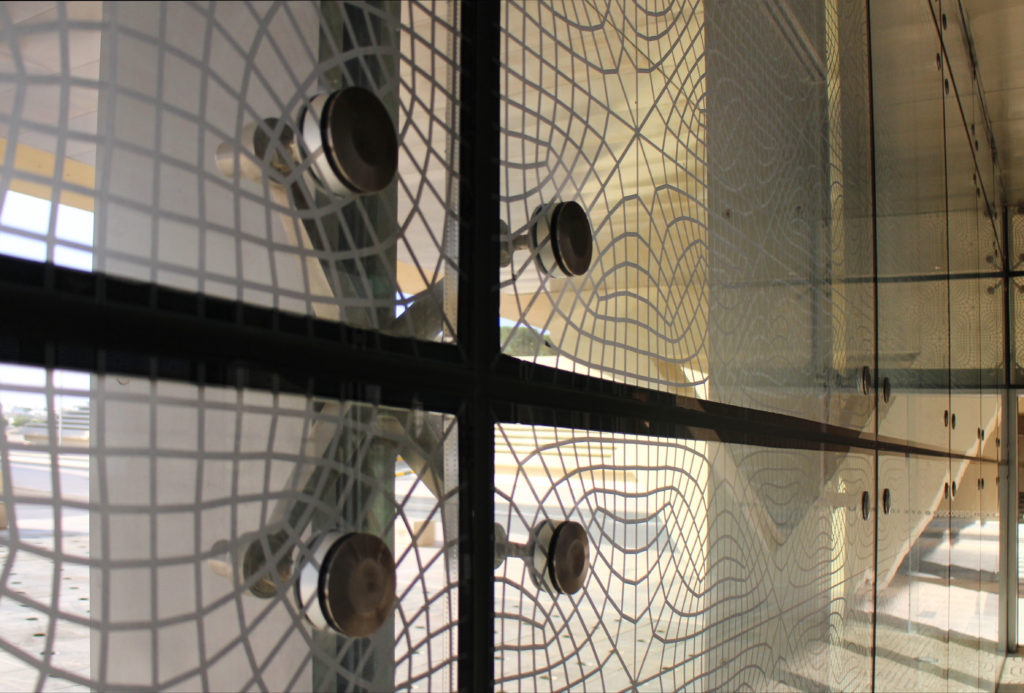
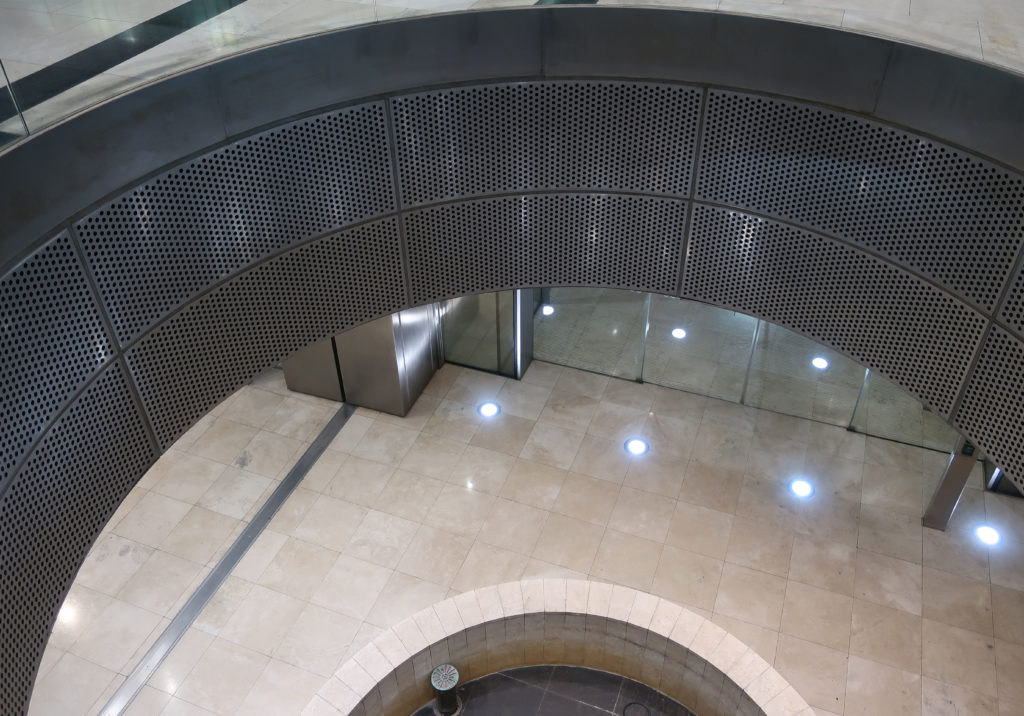
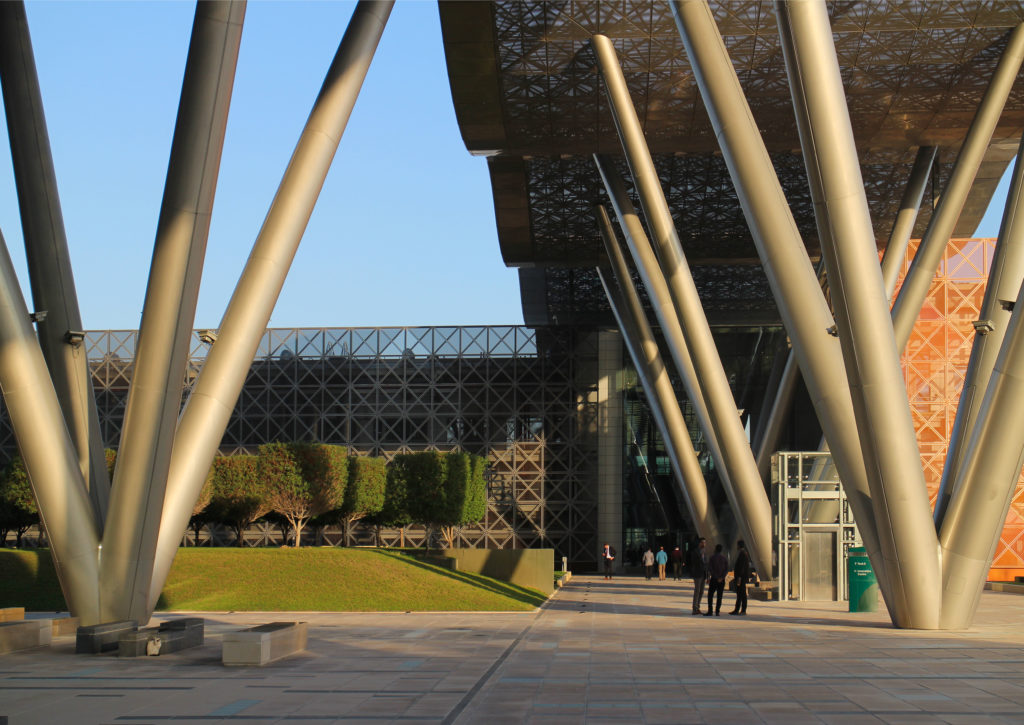
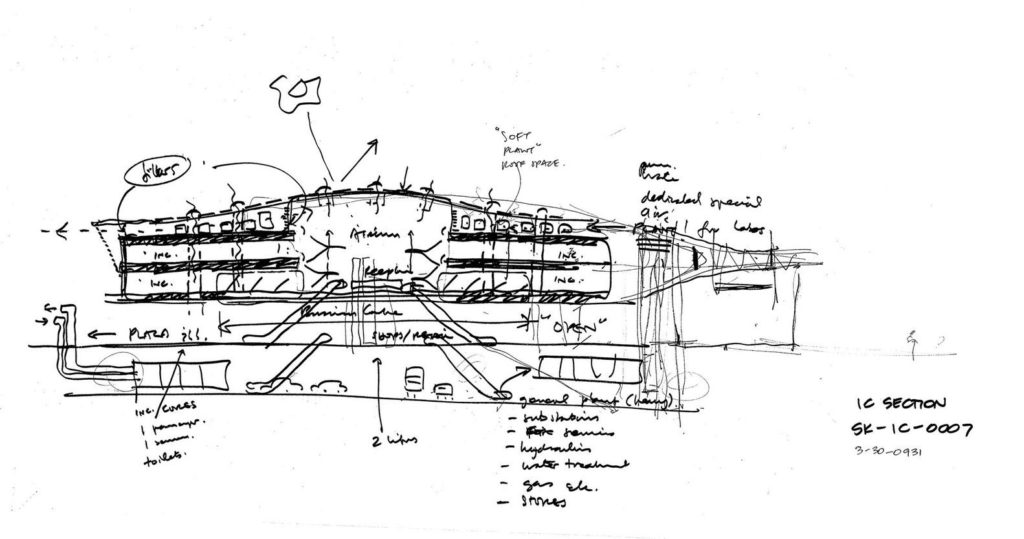
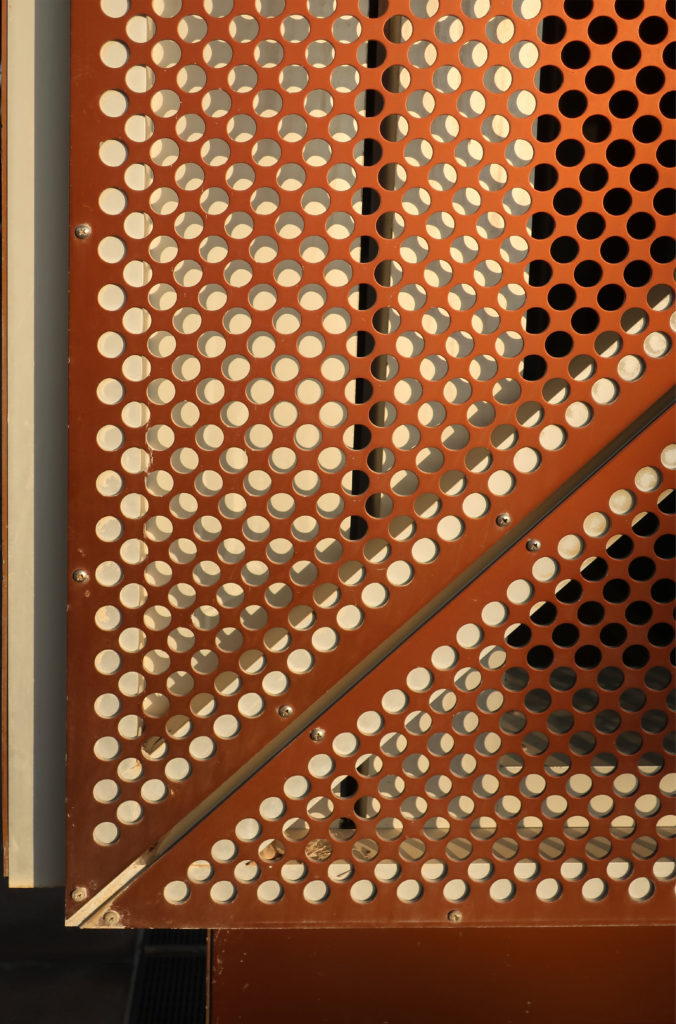
In building it is established with perforated flat screen facades and is dotted with three atriums, which reinforce the Islamic architectural notion of using “hard” exterior facades to protect “soft” internal living spaces. The buildings are surrounded by double skin facades that respond to the climate of the area with the highly elaborated and activated inner atriums, equivalent to the interior life of a traditional courtyard.
The Technology Park, QSTP, offers spaces for international technology companies while opening as an incubator for newly created technology companies, stimulating the development of the knowledge economy in the country. Micheson-Low, one of the architects involved in the design explains: “… The general idea of the Incubation Center is for people from all sectors to meet and interact in the common spaces. So, if ideas become commercially viable, there is plenty of room to diversify and develop those ideas. It is called “Incubator” because it was always planned to stimulate creativity and incubate knowledge … “.
The QSTP also became the first free trade zone in Qatar. In September 2005, the government passed a law that turns the science park into a “free zone,” allowing foreign companies to establish a 100% duty-free and duty-free entity.
Spaces
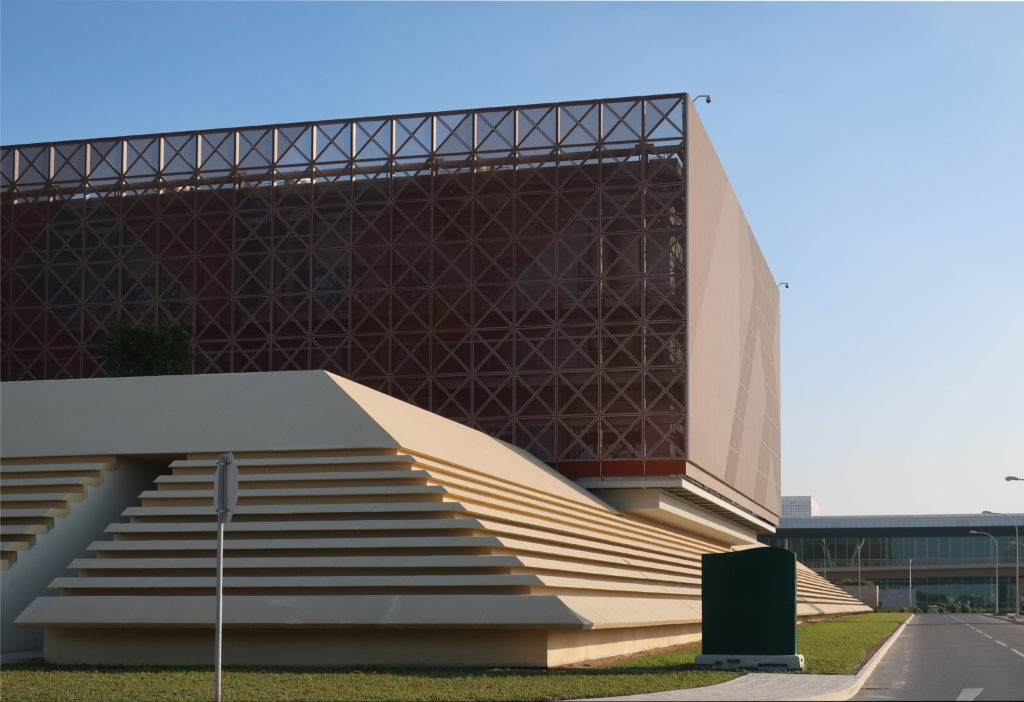
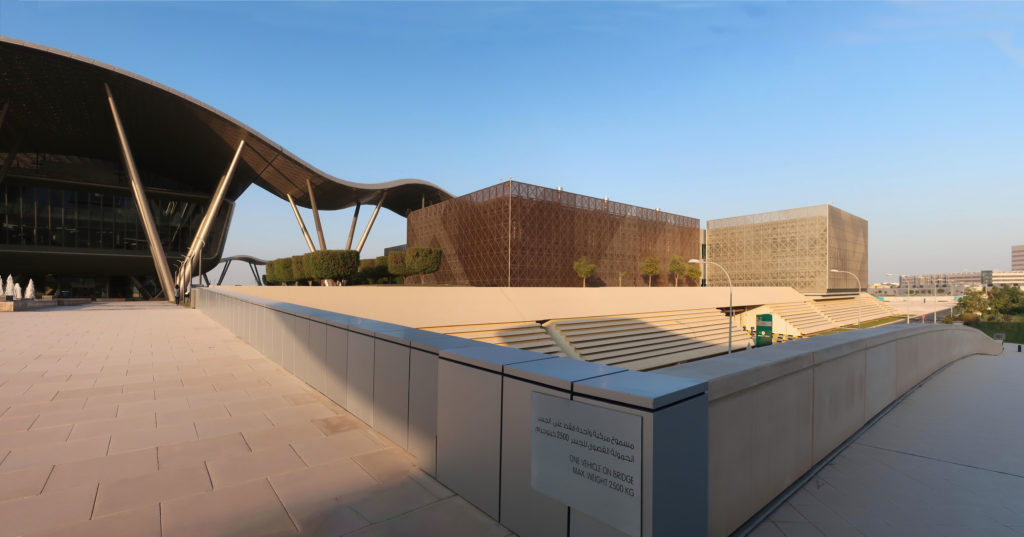
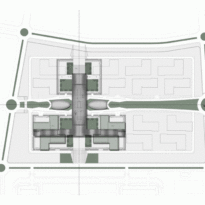
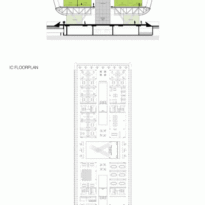
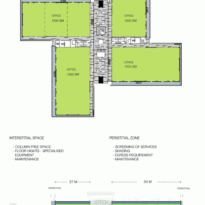
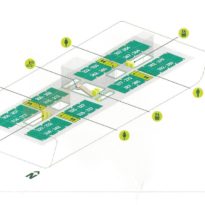
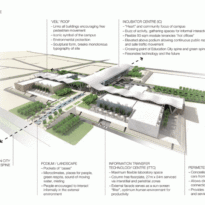
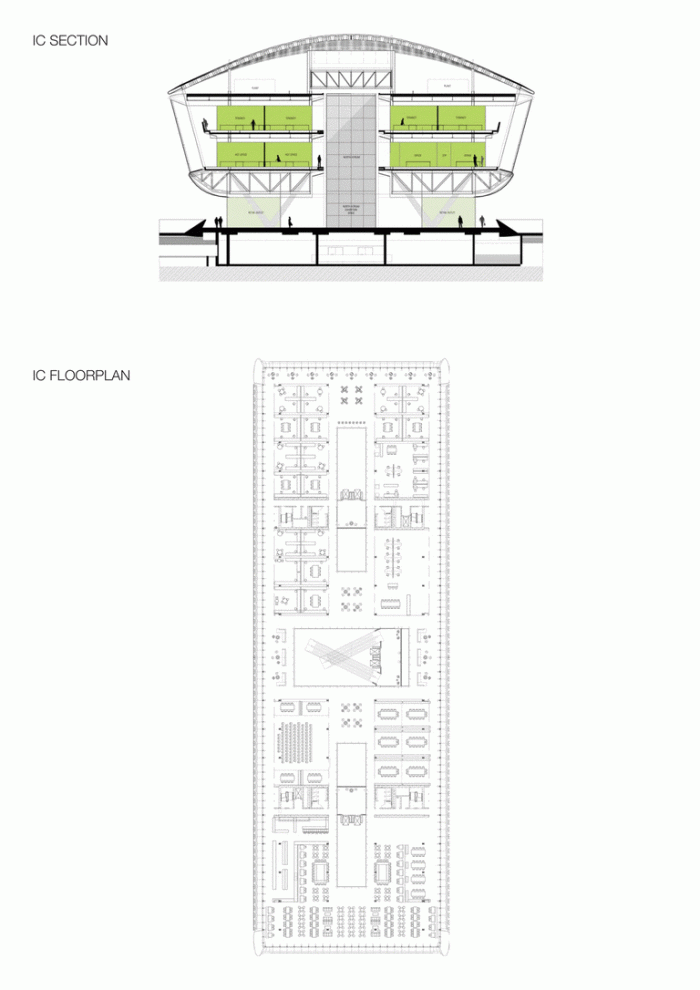
Phase one of construction covers 115,000m2, in whose heart is the Emerging Technology Center, or Incubation Center, with 12,000m2 which incorporates the Administrative Center and the Business Center, with services for small and medium enterprises. The building, raised from the ground, is flanked by the first buildings with rental spaces of the Transfer, Innovation and Technology Center, each with 20,000m2 in which large companies begin to install their R&D centers, either by leasing space in a multi-user building or one only.
The three buildings sit on a landscaped podium with pedestrian areas. The design is based on cultural references. The aesthetic diffusion of buildings reflects the symmetry of patterns in Islamic art and uses cutting-edge technology to resonate with local communities and attract international partners.
Canopy
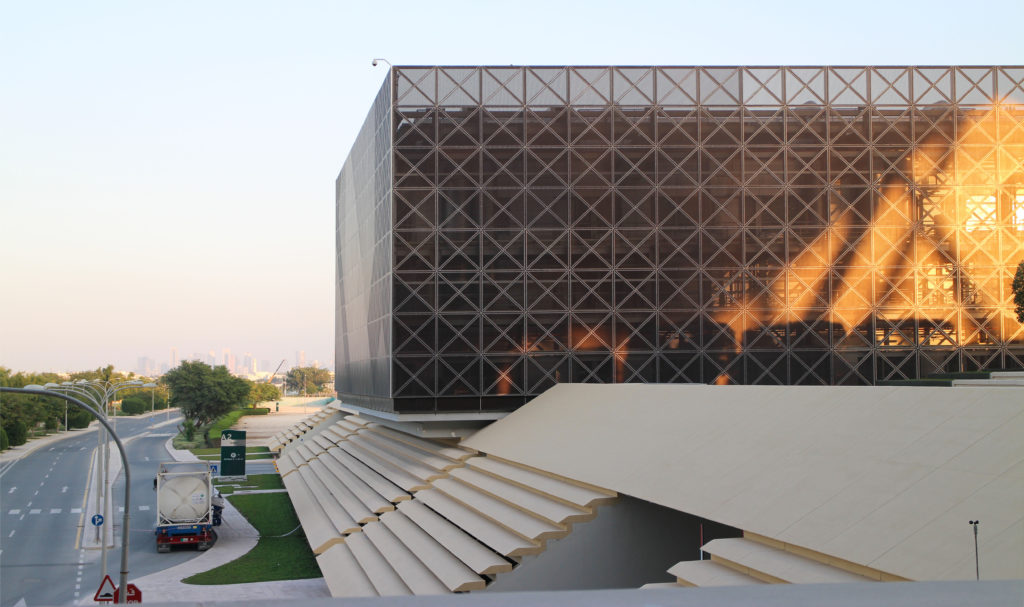
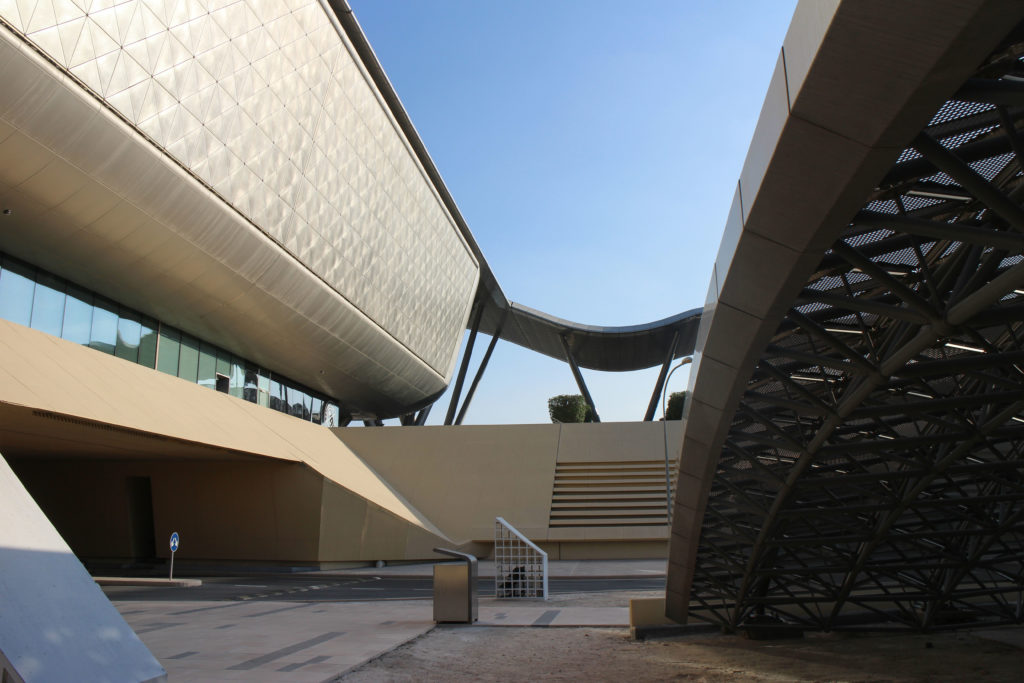
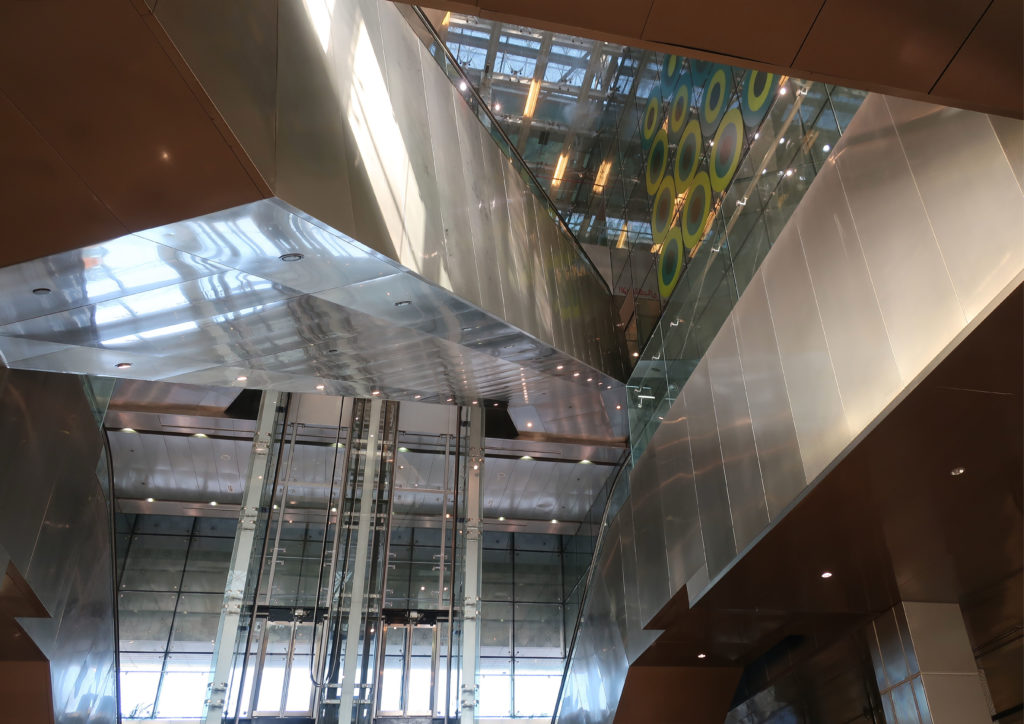
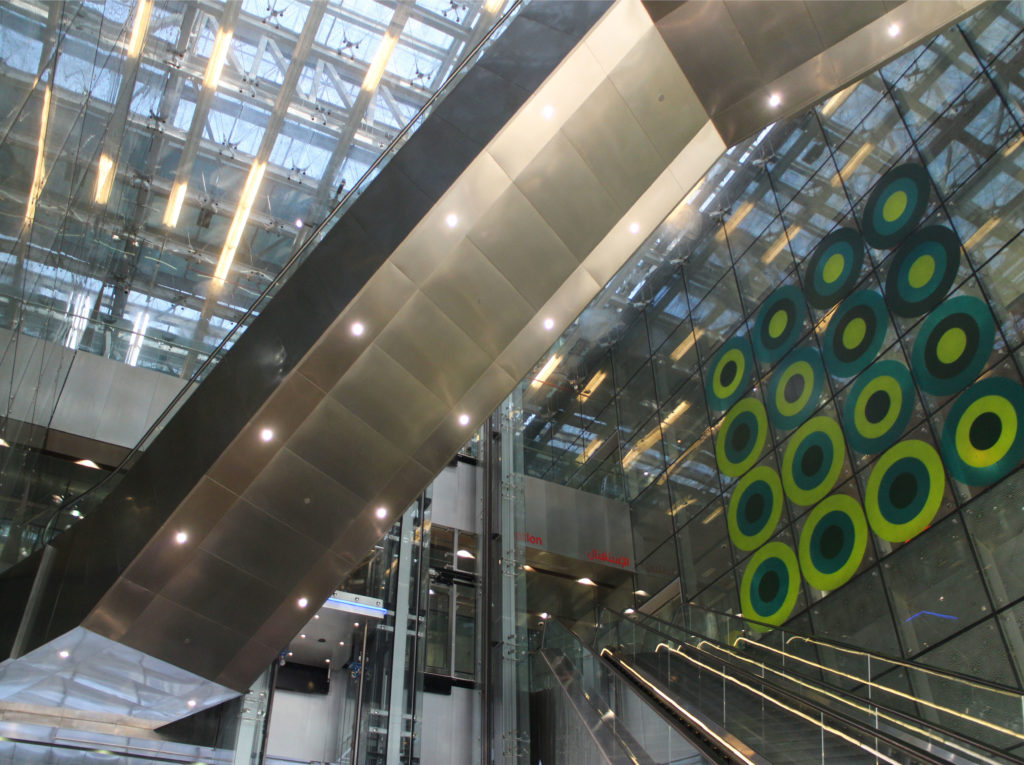
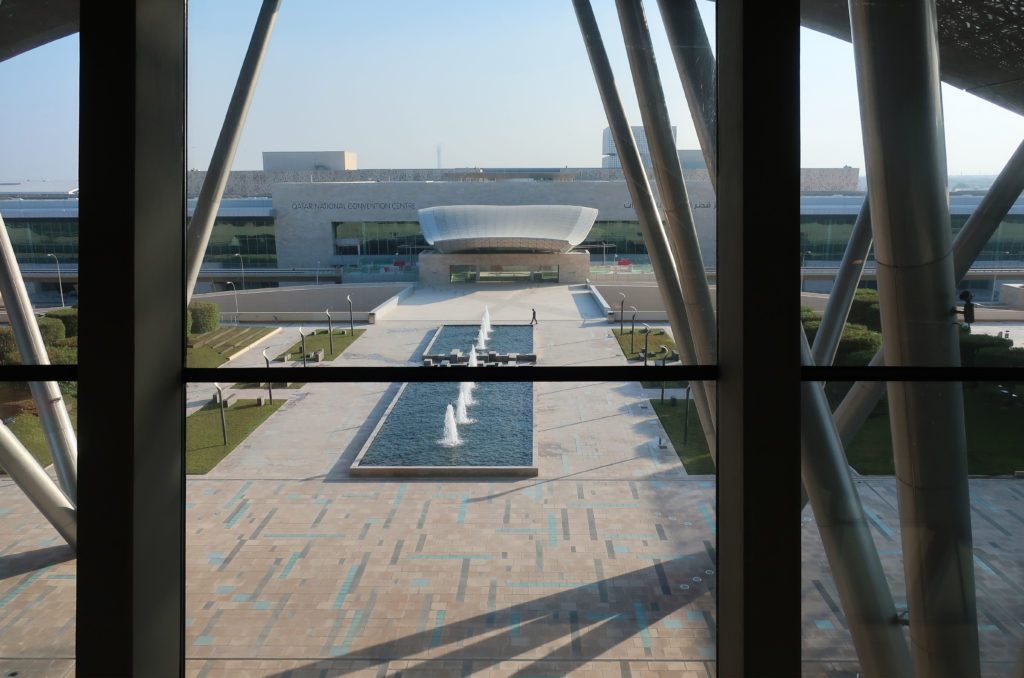
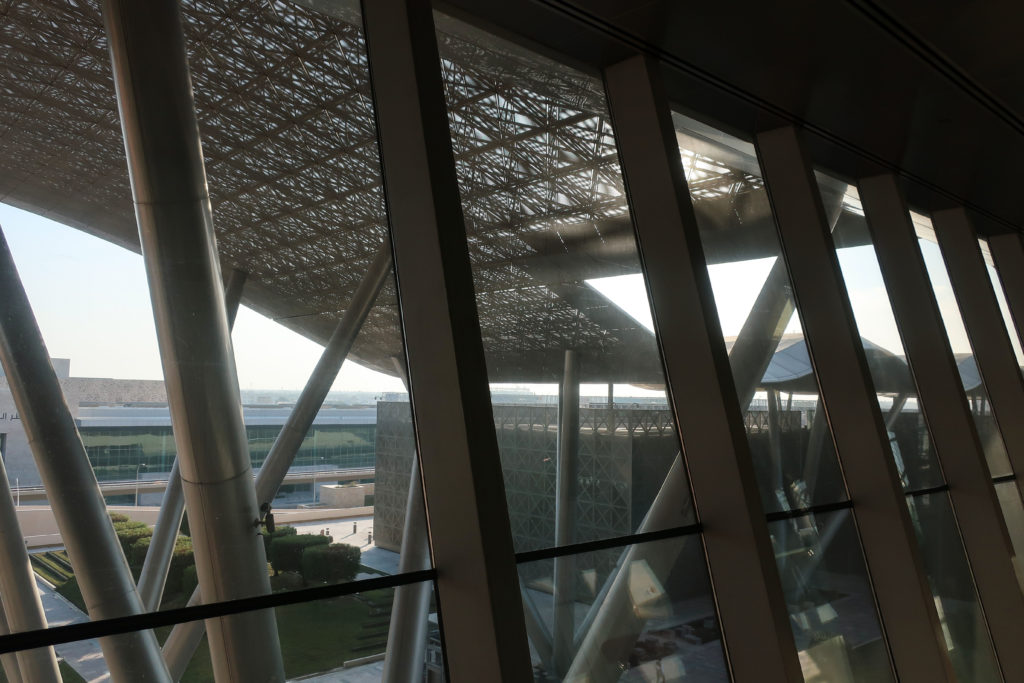
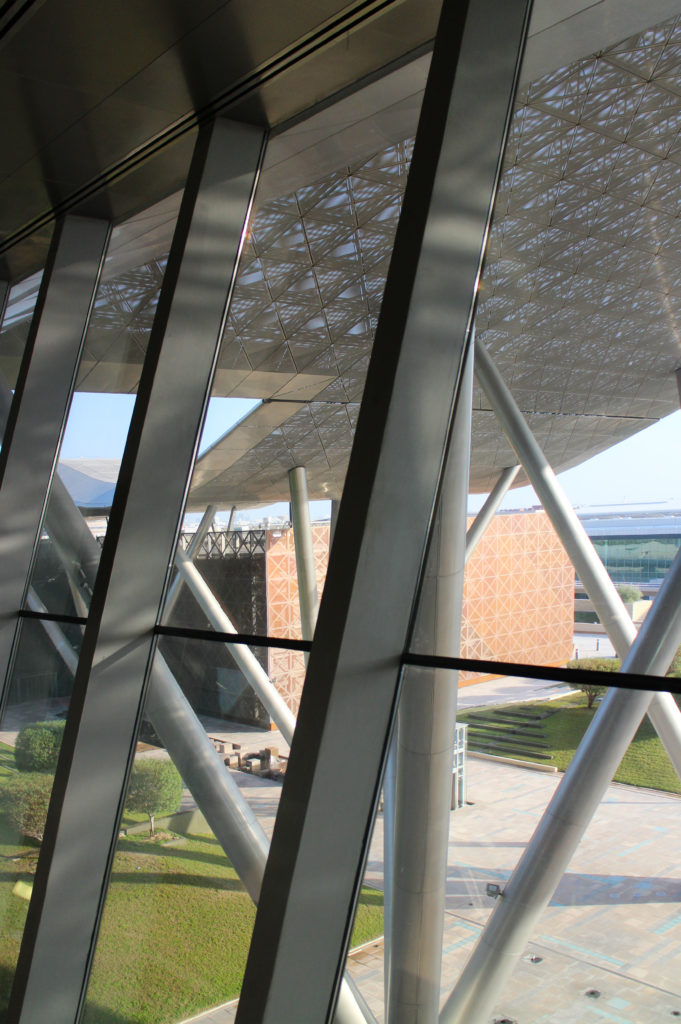
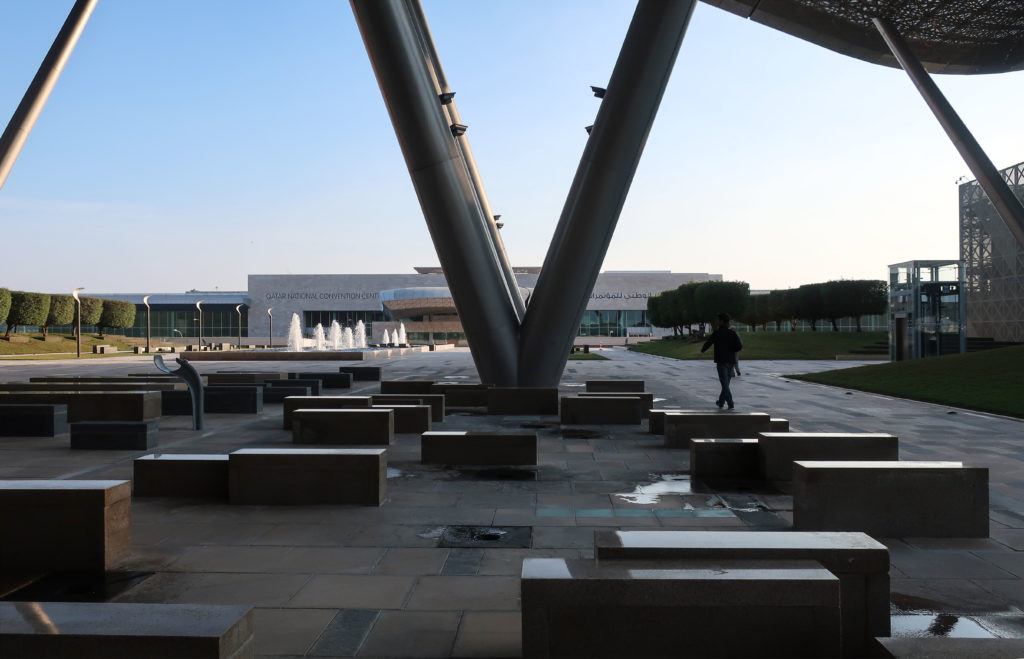
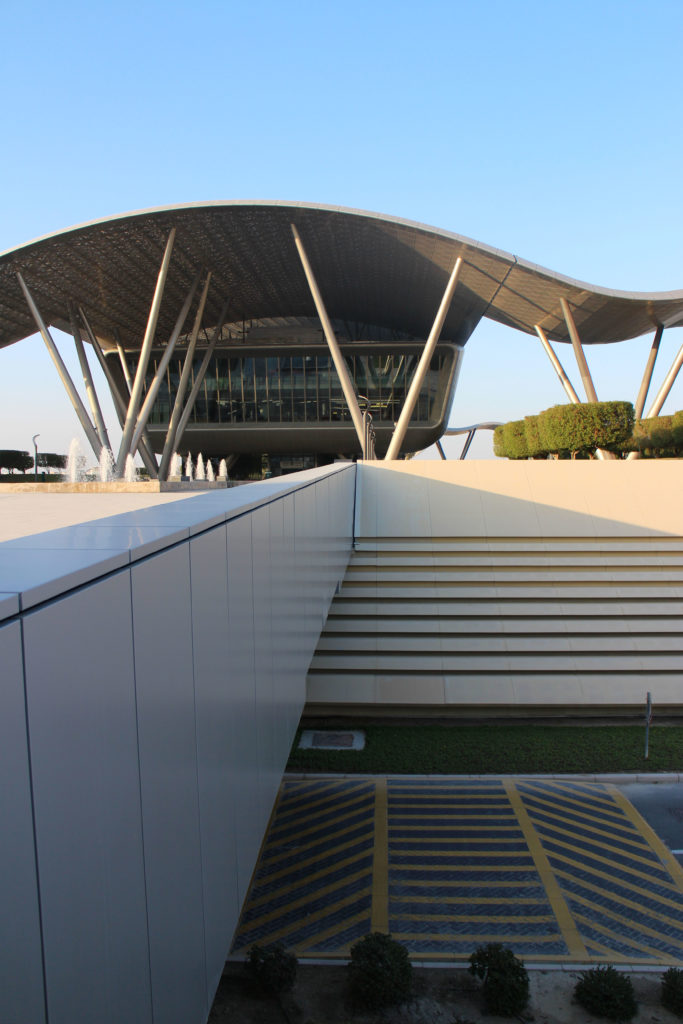
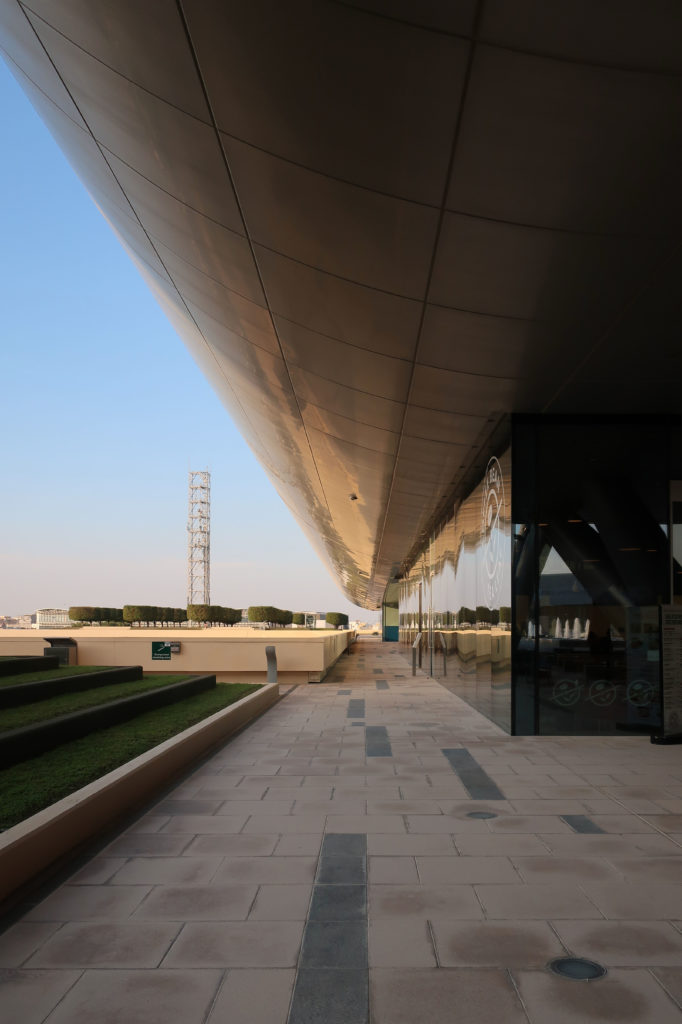
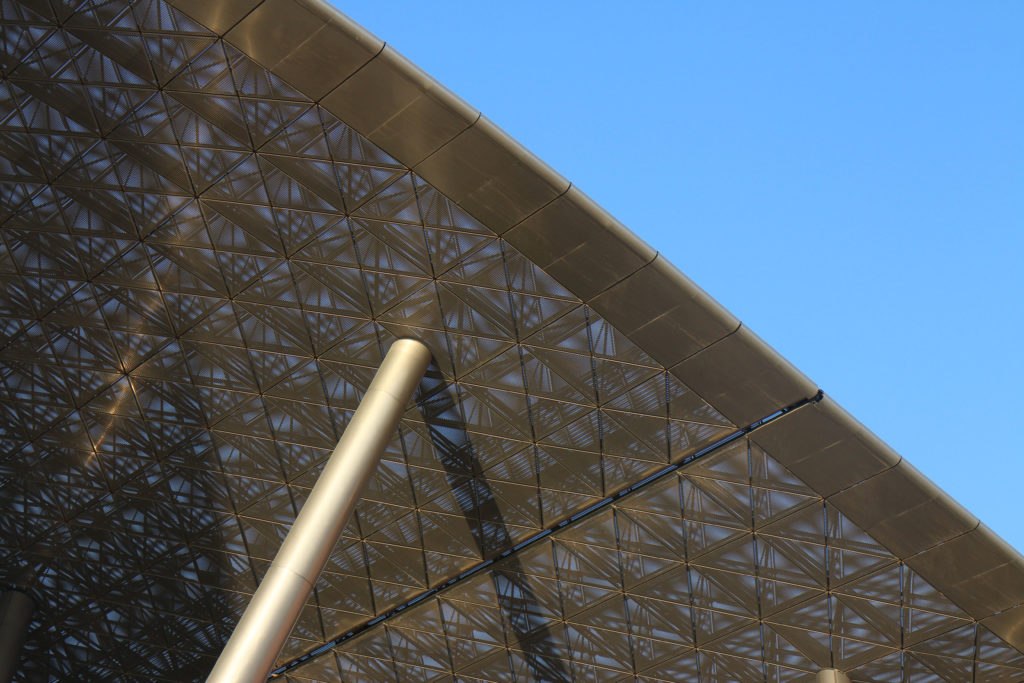
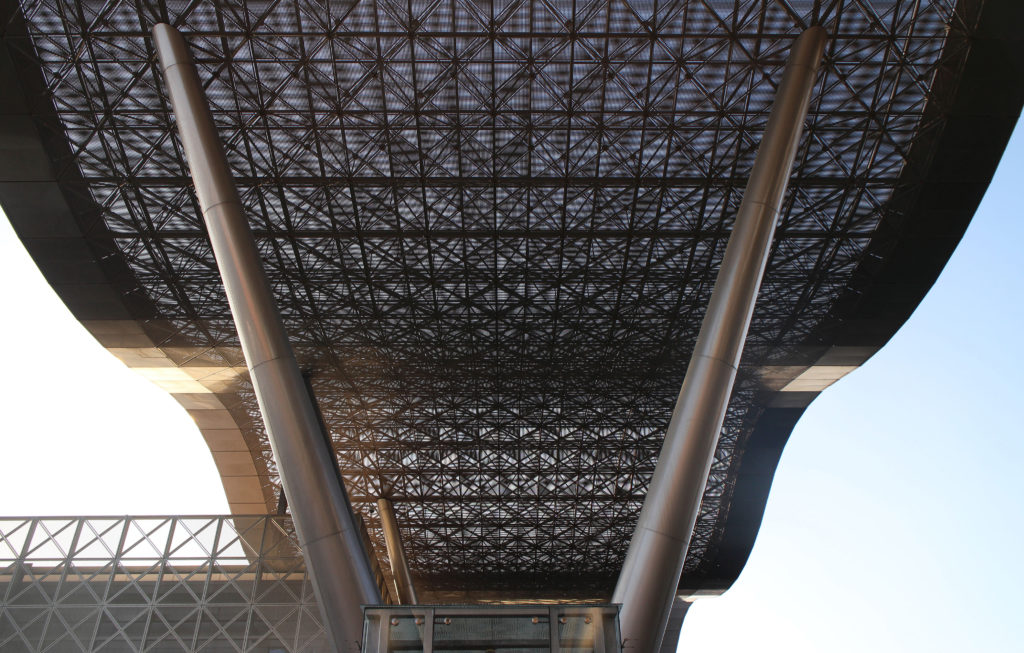
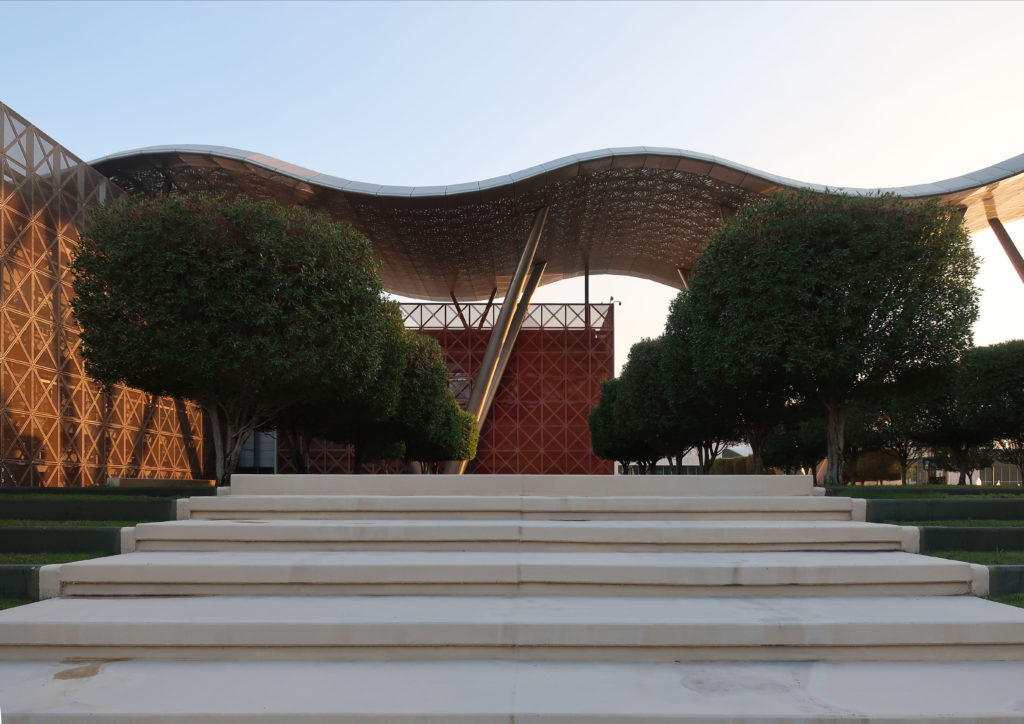
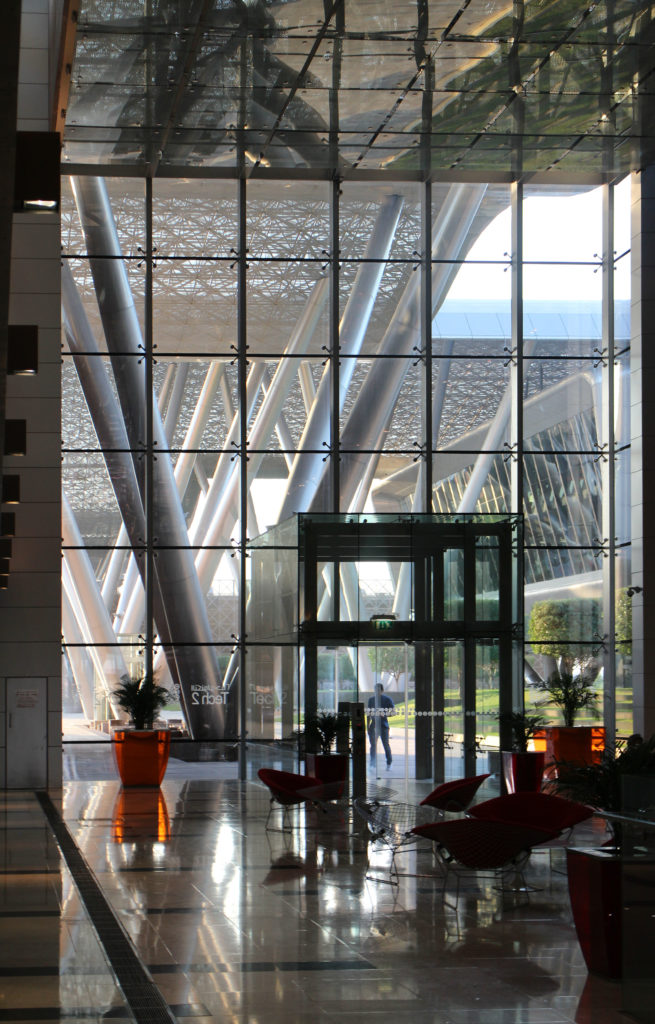
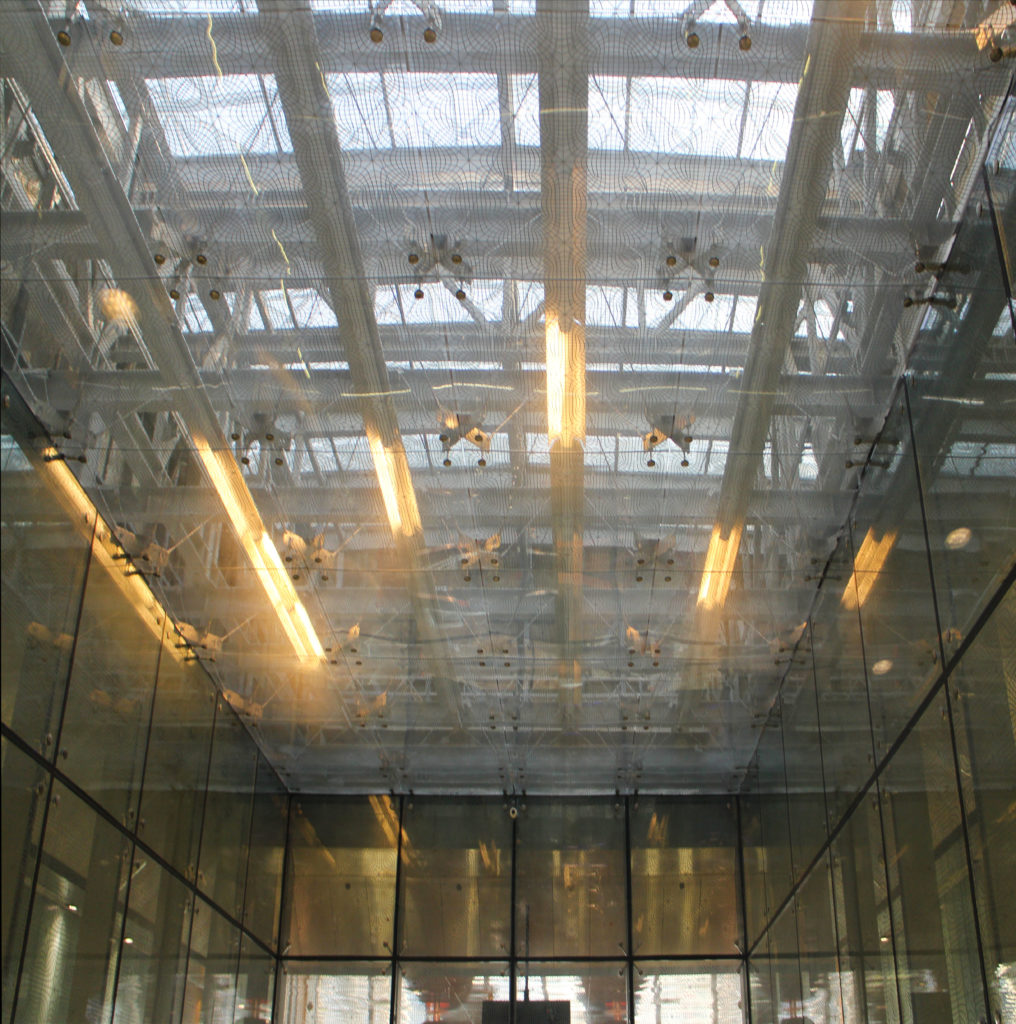
The distinctive wavy “veil” roof structure that covers the spine of QSTP circulation has a sculptural quality that contrasts sharply with the landscape’s horizontality. The multifunctional veil provides shade to outdoor areas and allows buildings to be connected physically and symbolically. The elevation of the veil over the Central Incubation Center accentuates the heart of the site and announces the main entrance through a 34-meter high atrium. The veil then extends east and west to the ITTC buildings and provides protection to the atrium and central courtyards, encouraging people to move freely between activity centers.
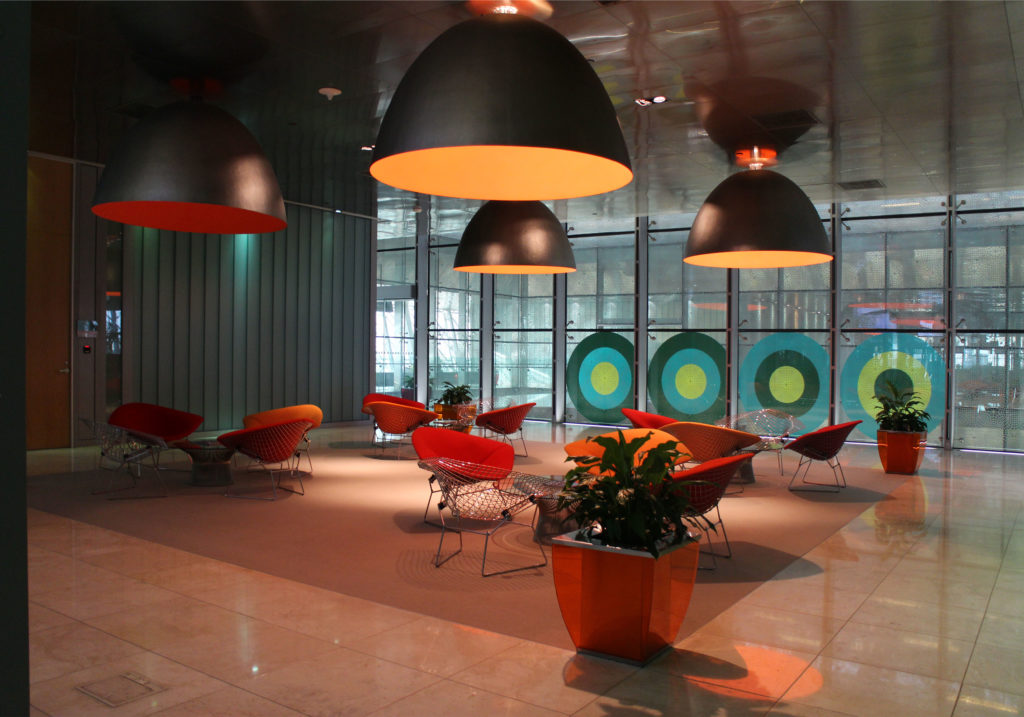
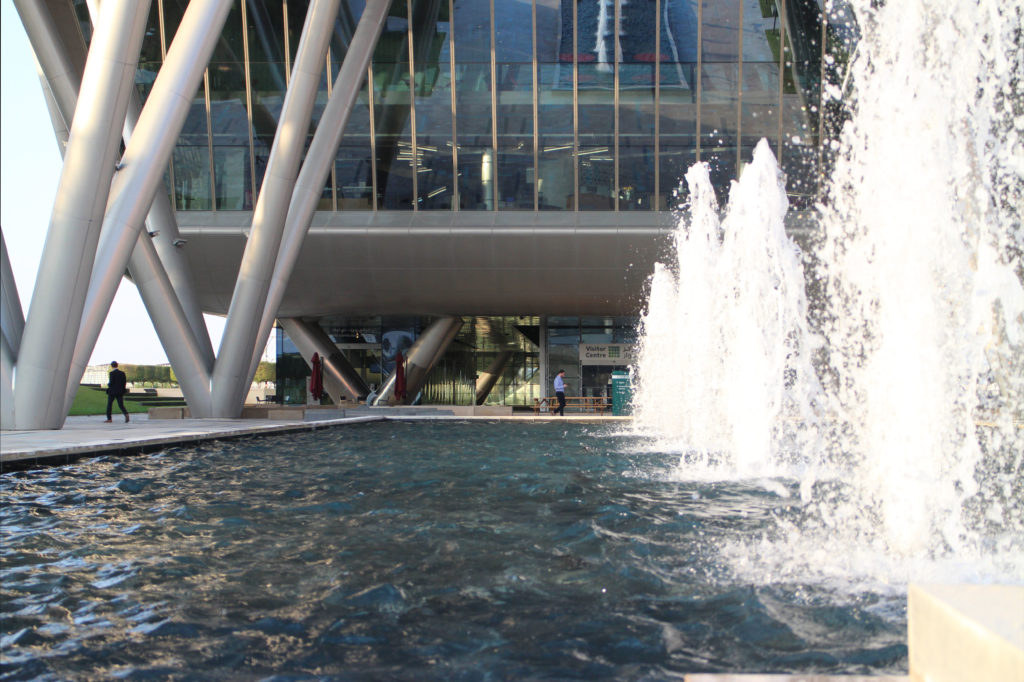
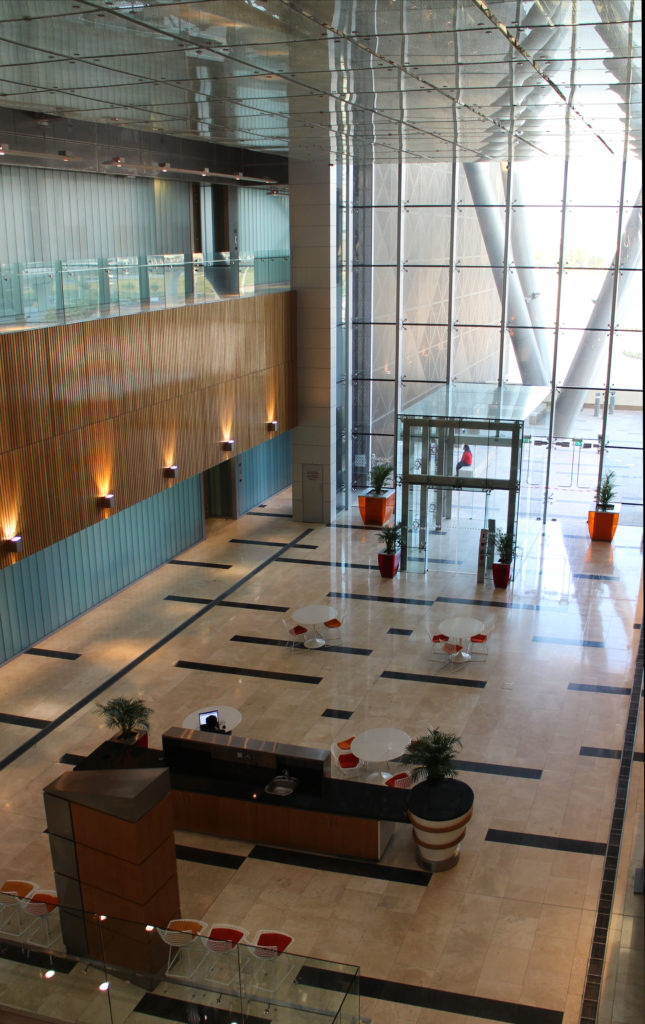
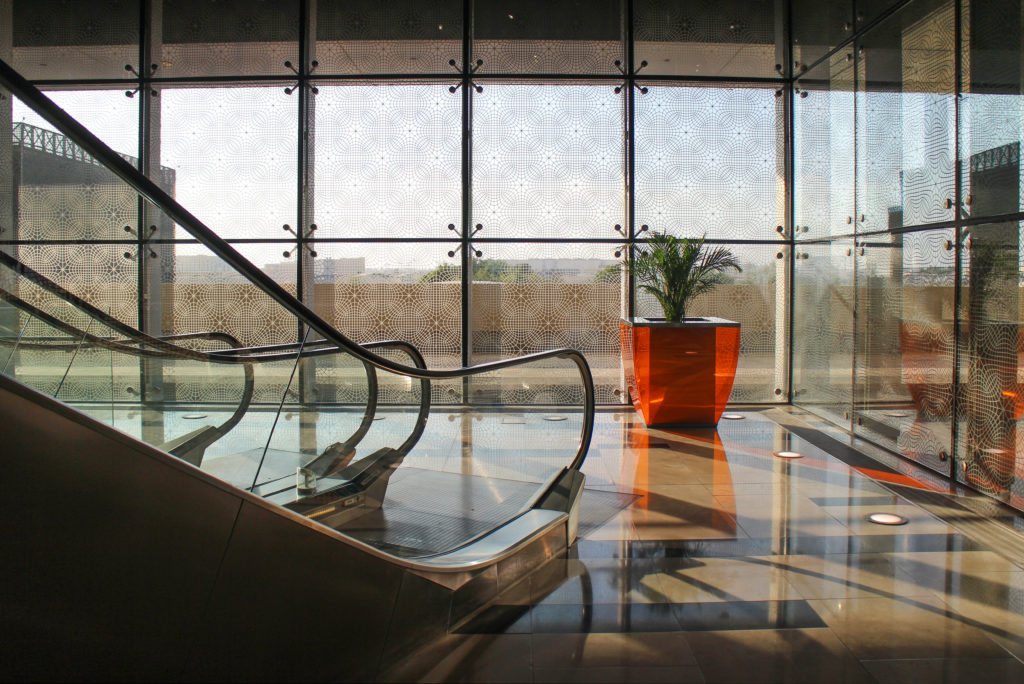
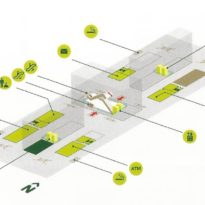
By elevating the downtown building, the entire spine under the podium is delivered to public areas and retail leases that include banking, travel stores, restaurant, prayer rooms and other amenities. Opposite the main entrance opens a public square with a water fountain and landscaped sides.
Atrium
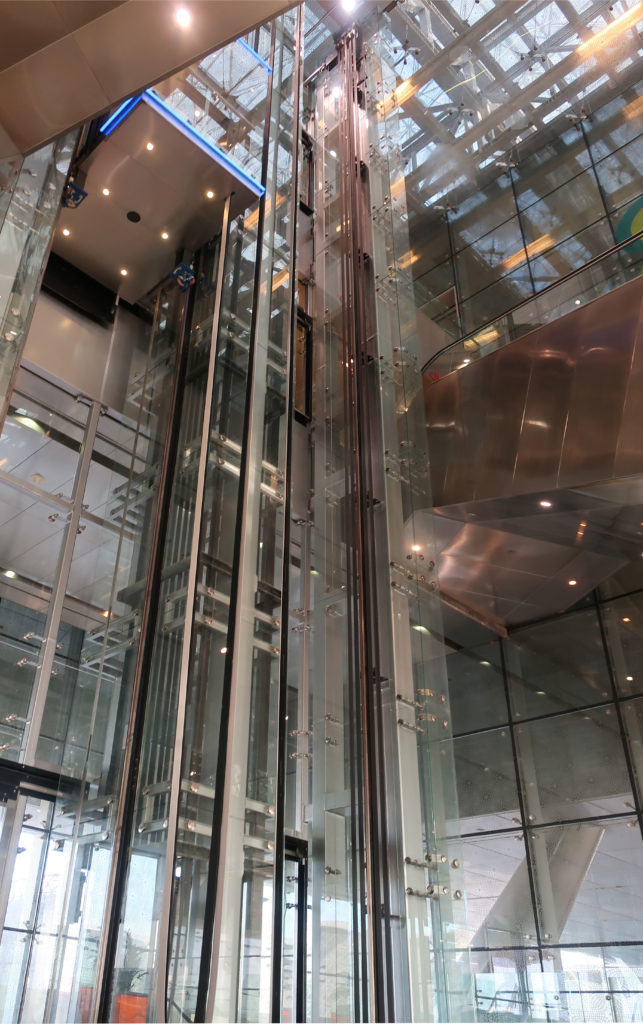
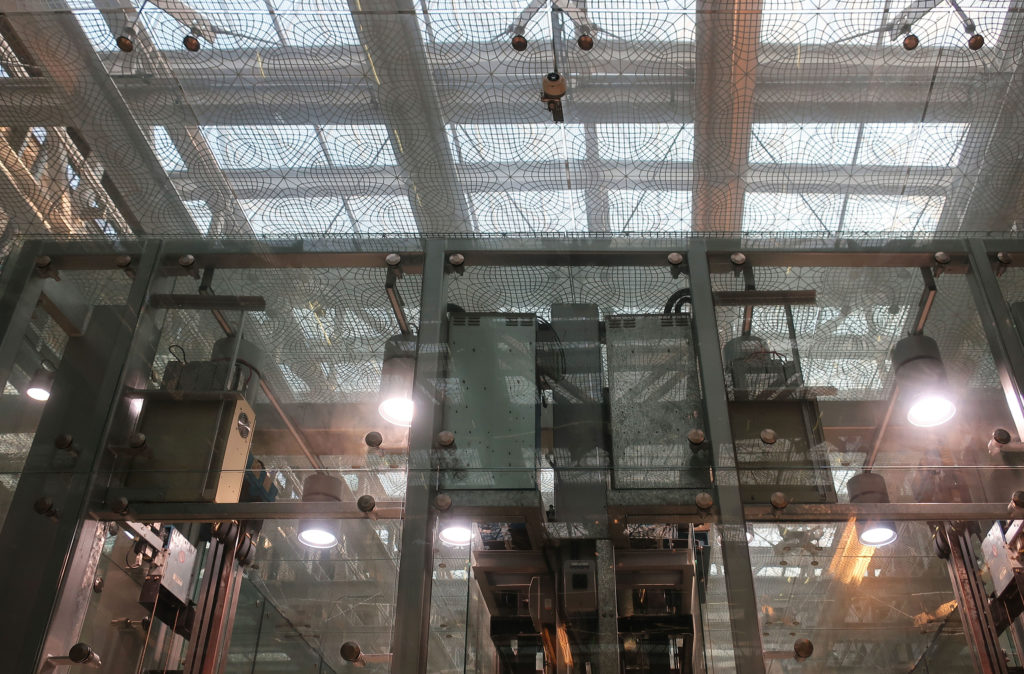
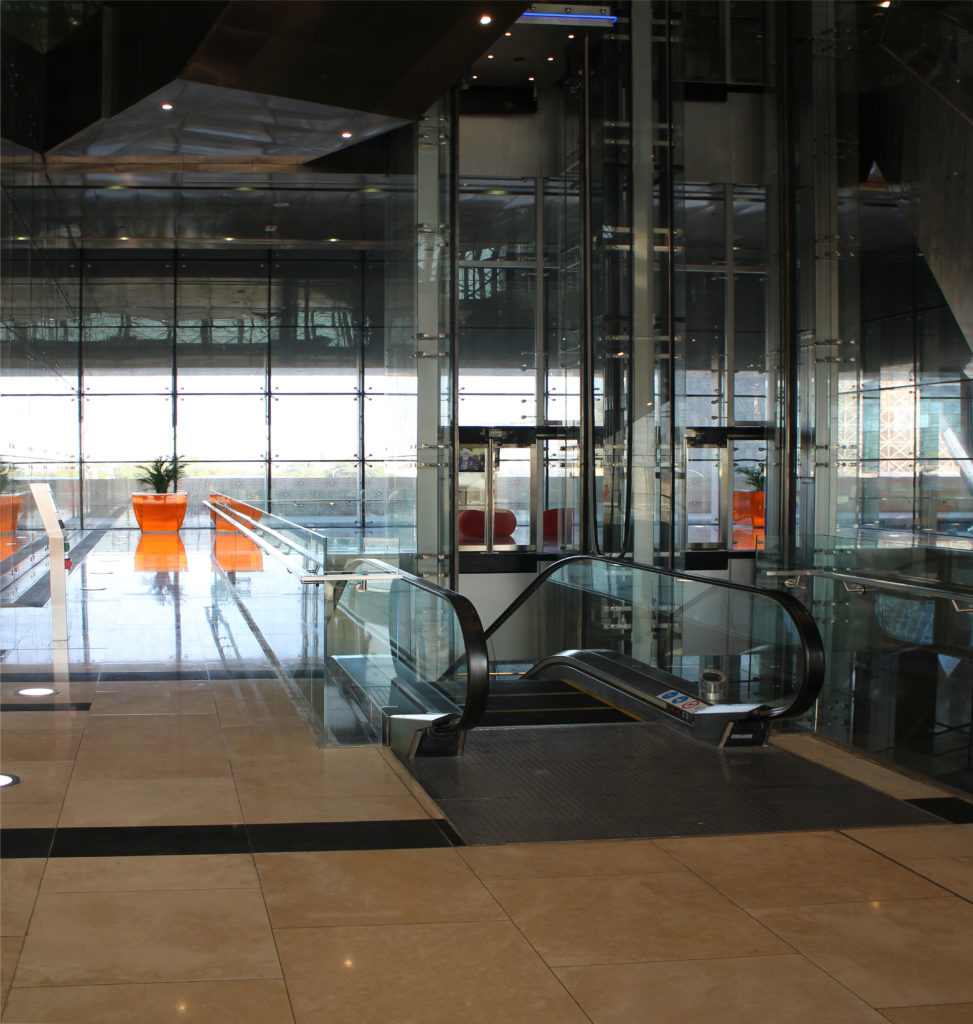
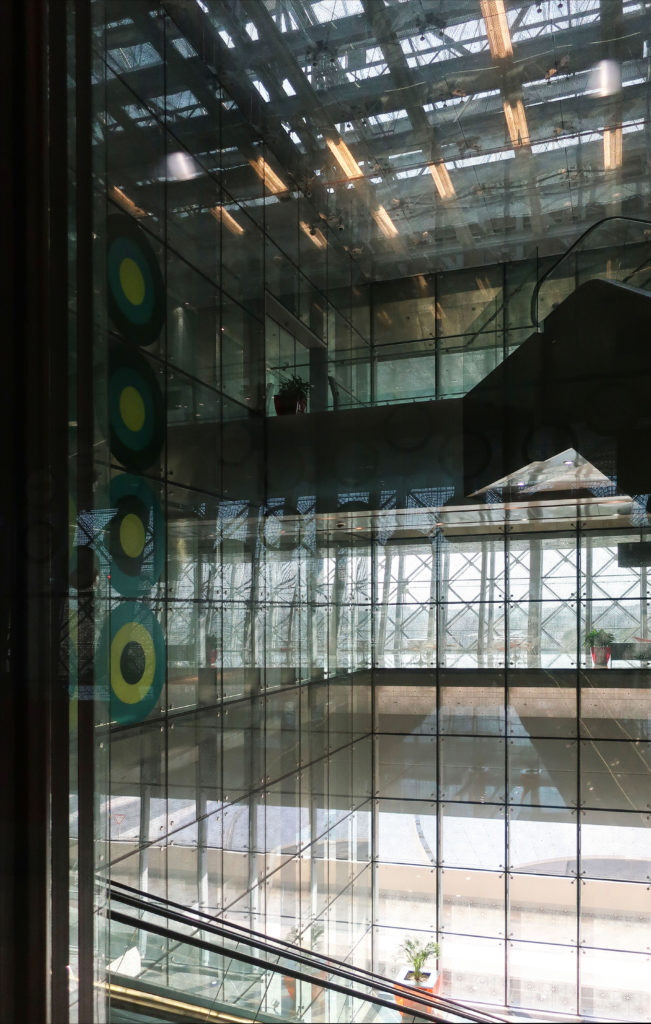
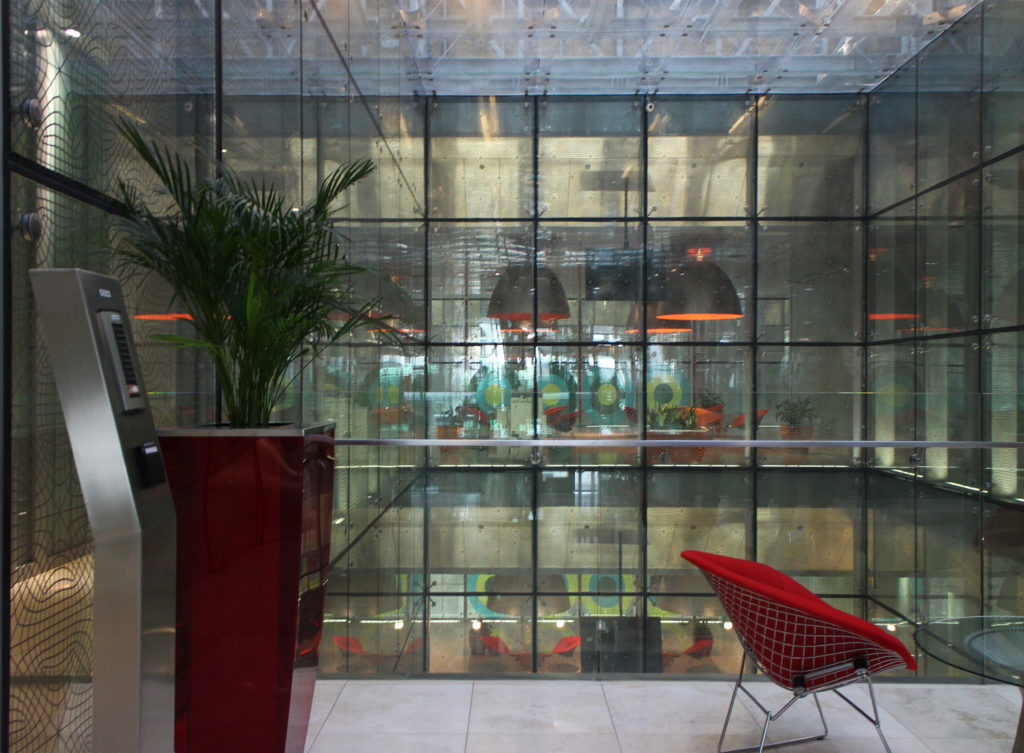
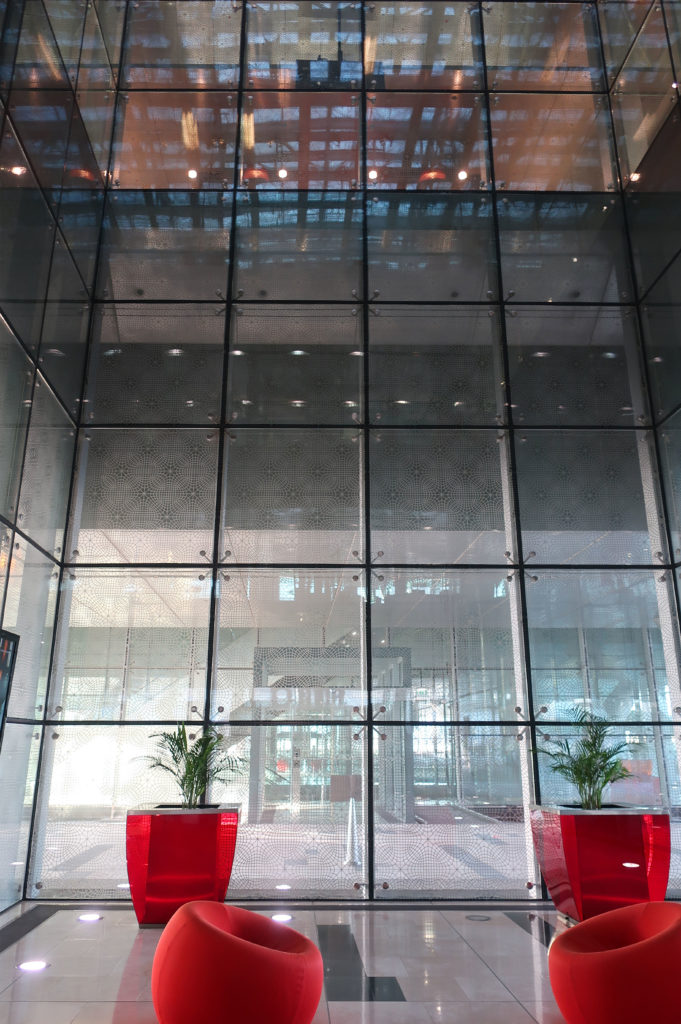
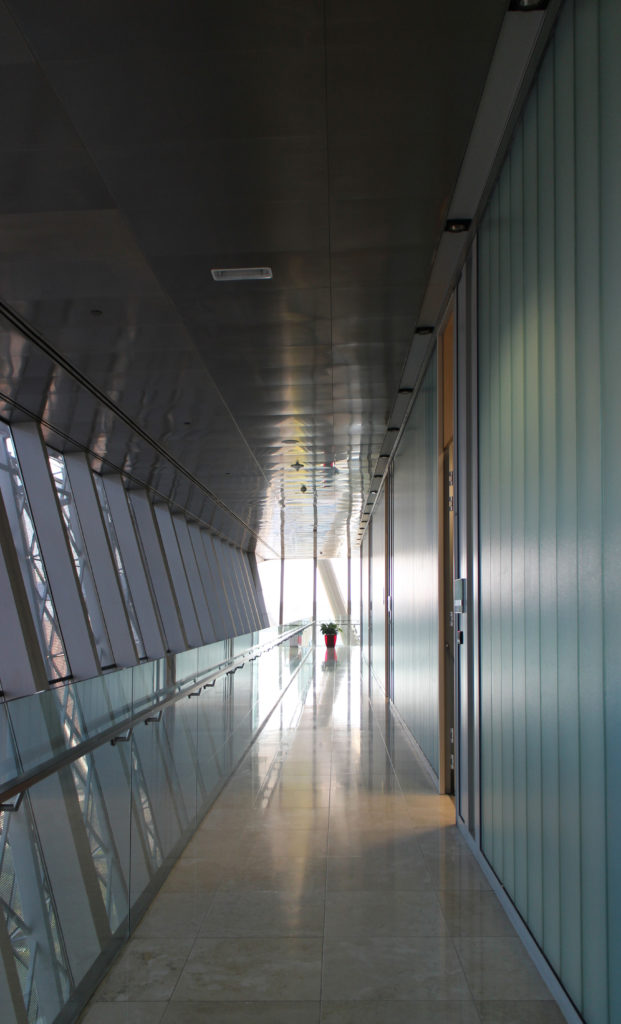
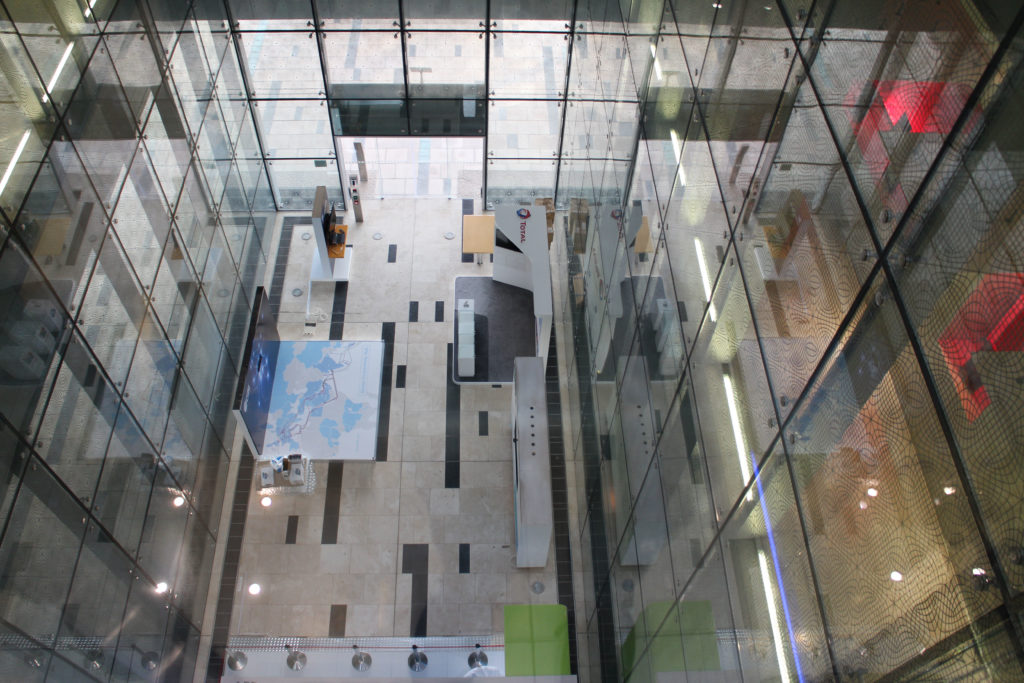
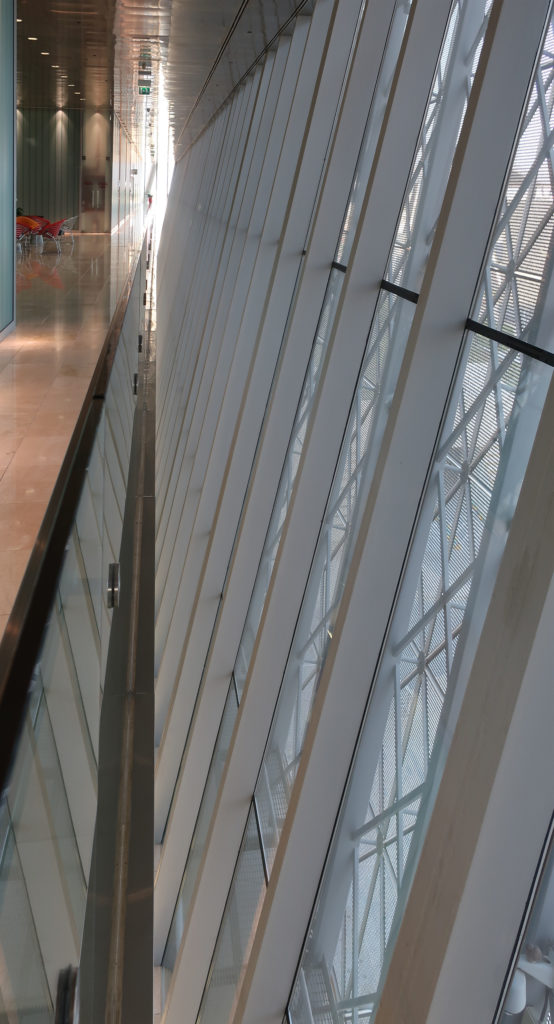
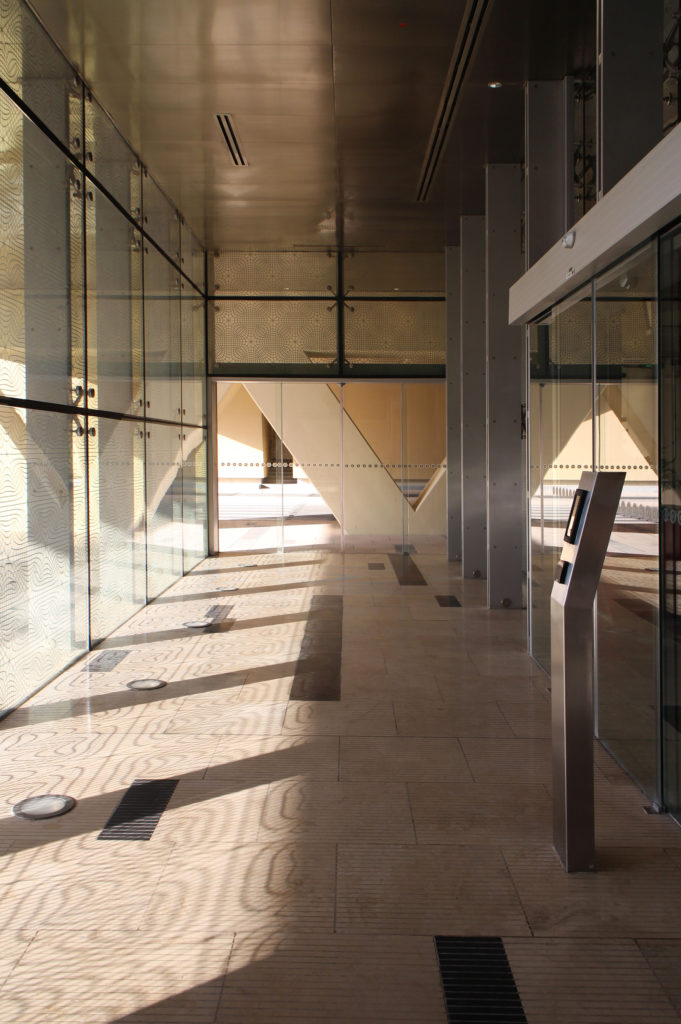
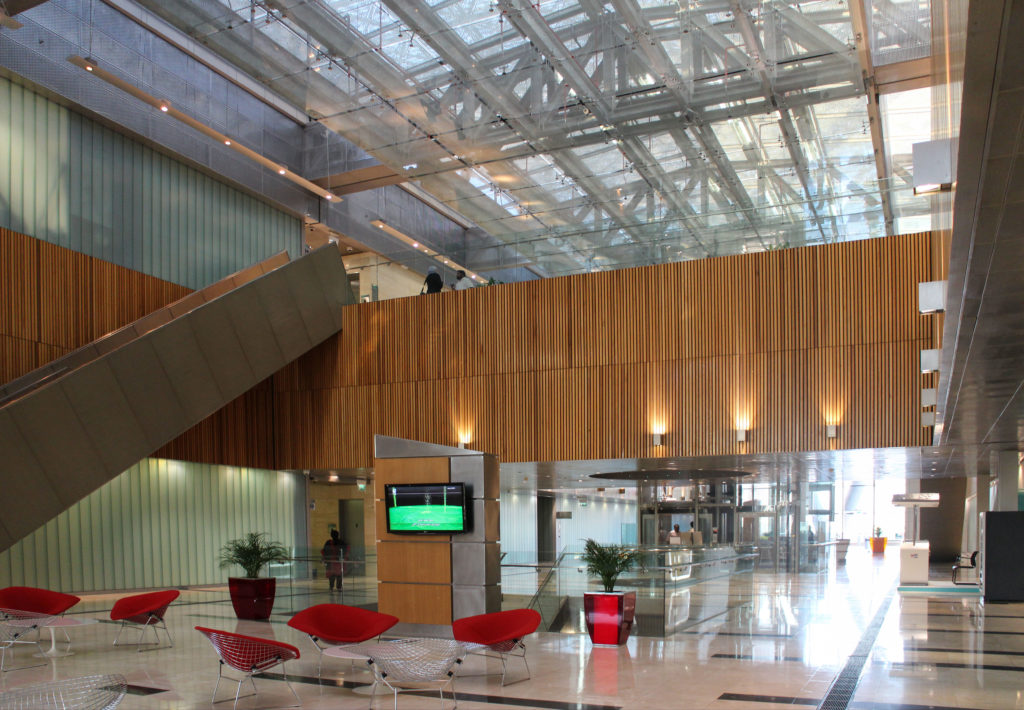
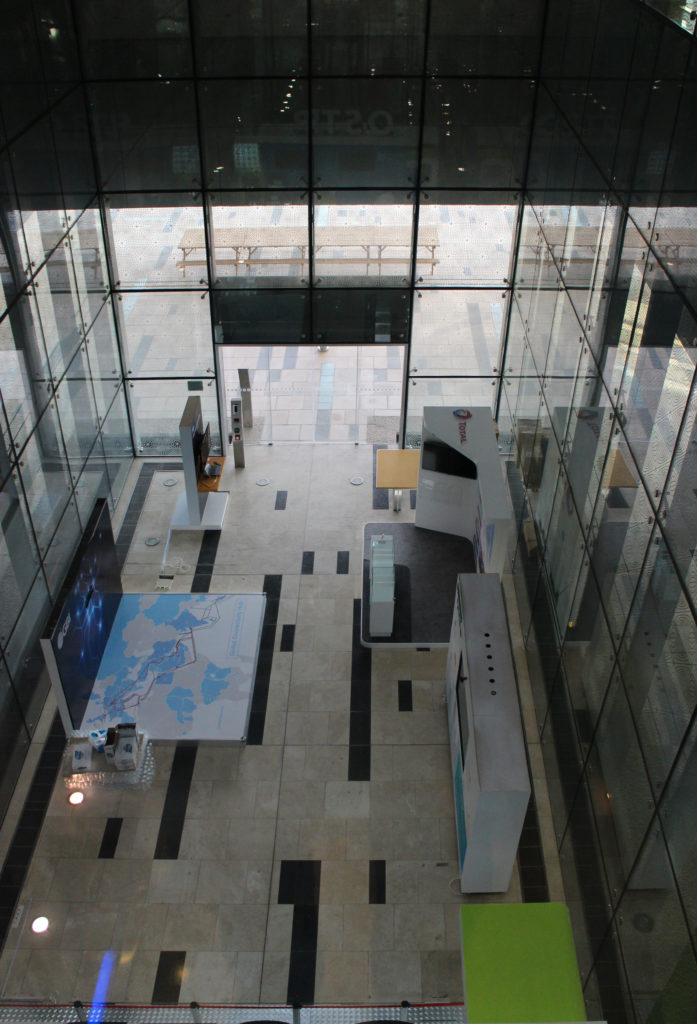
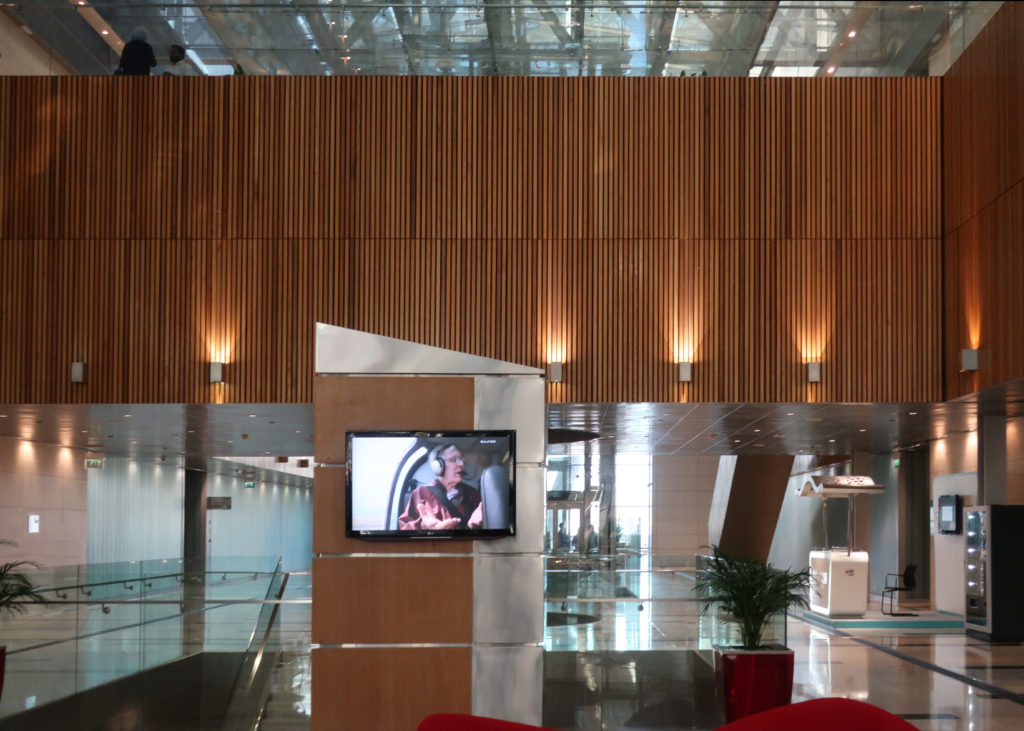
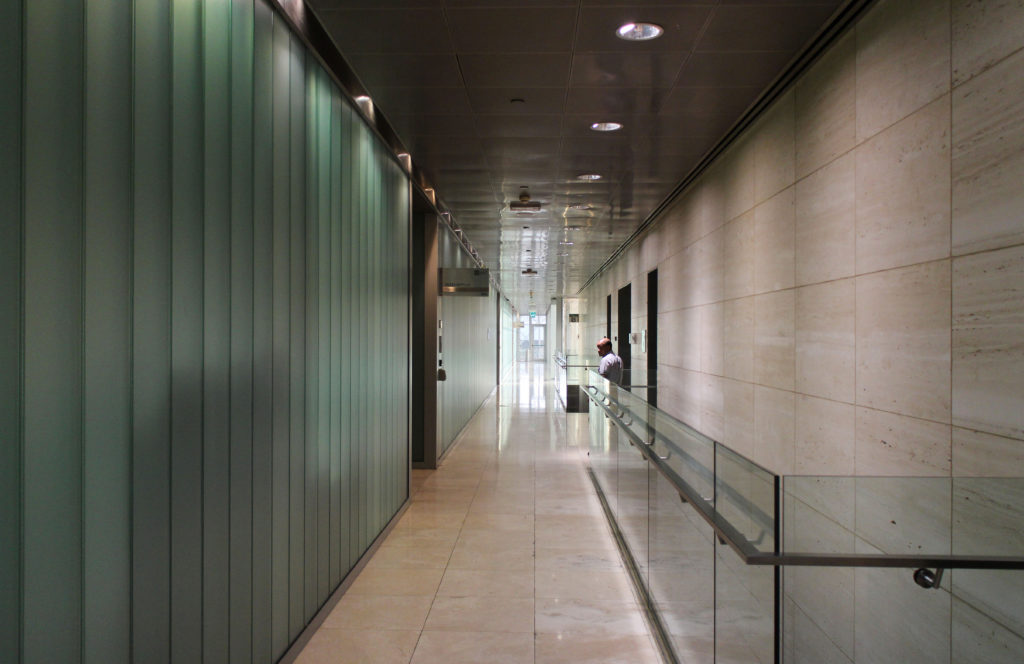
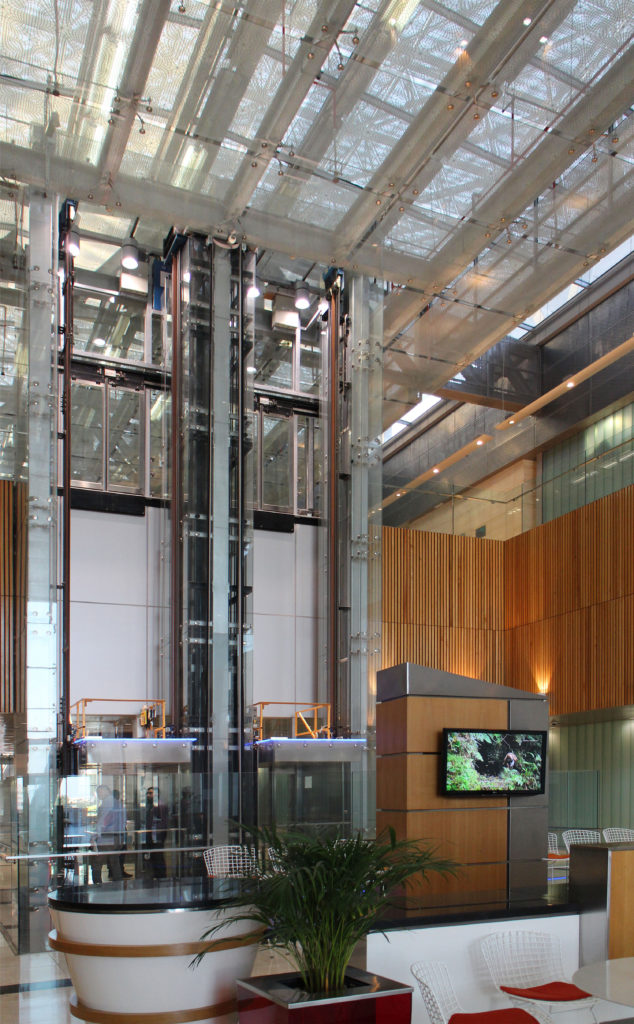
The central area of the roof, where the veil rises, highlights the main entrance, through a 34m high atrium. The impressive atrium receives the visitor with a display of elegance and combination of materials, steel, glass, marble and wood combine to create an environment that meets the expectations sought. Stairs and elevators lead to the upper floors that balcony towards the atrium.
“… This works in harmony with the architecture. The external walls offer a feeling of privacy and humility, while the interior is rich and colorful… ”says Seeling, another of the architects in charge of interior design.
Incubation Center
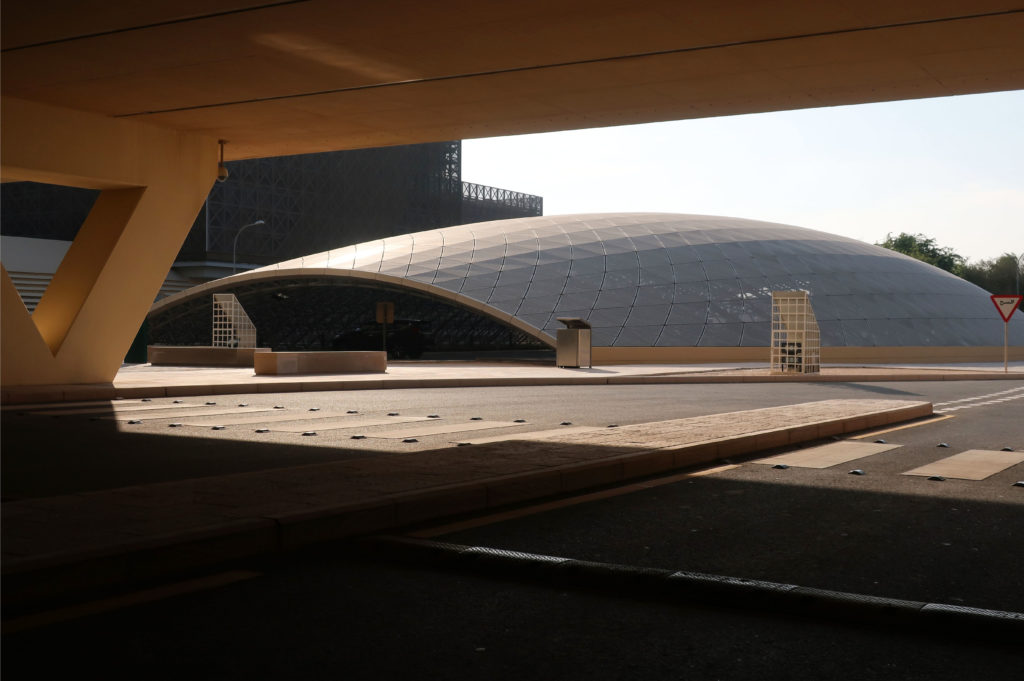
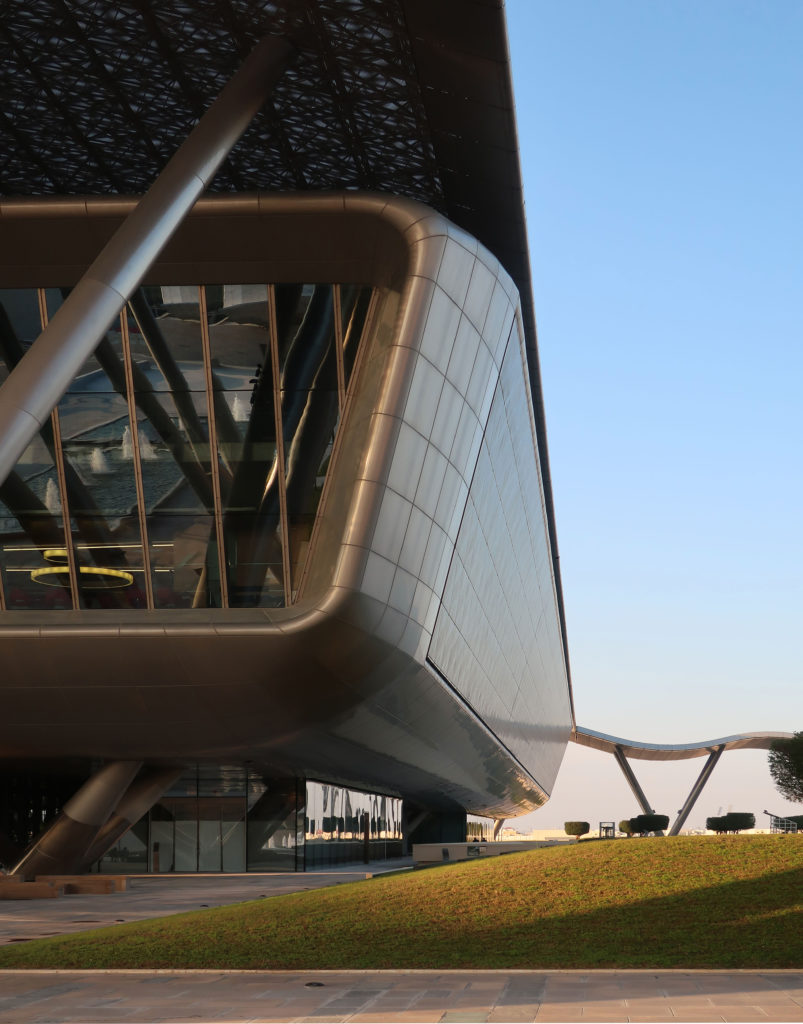
Taking advantage of its strategic location, the iconic Incubation Center is the core of QSTP. Located in the center of the building, on an elevated podium, it has an aeronautical quality and seems to defy gravity, like a floating UFO, which gives it a subliminal presence in the landscape. The installation offers a flexible space that can be expanded and exchanged as needed.
The laboratories have double volume spaces and high load capacity available in large areas. The groups that work in the building have the central atriums as informal meeting spaces.
The Technology Park shares through an overpass the access to the new metro station with the Qatar National Convention Center, also serving as a connecting loop between the two buildings.
Transfer, Innovation and Technology Center
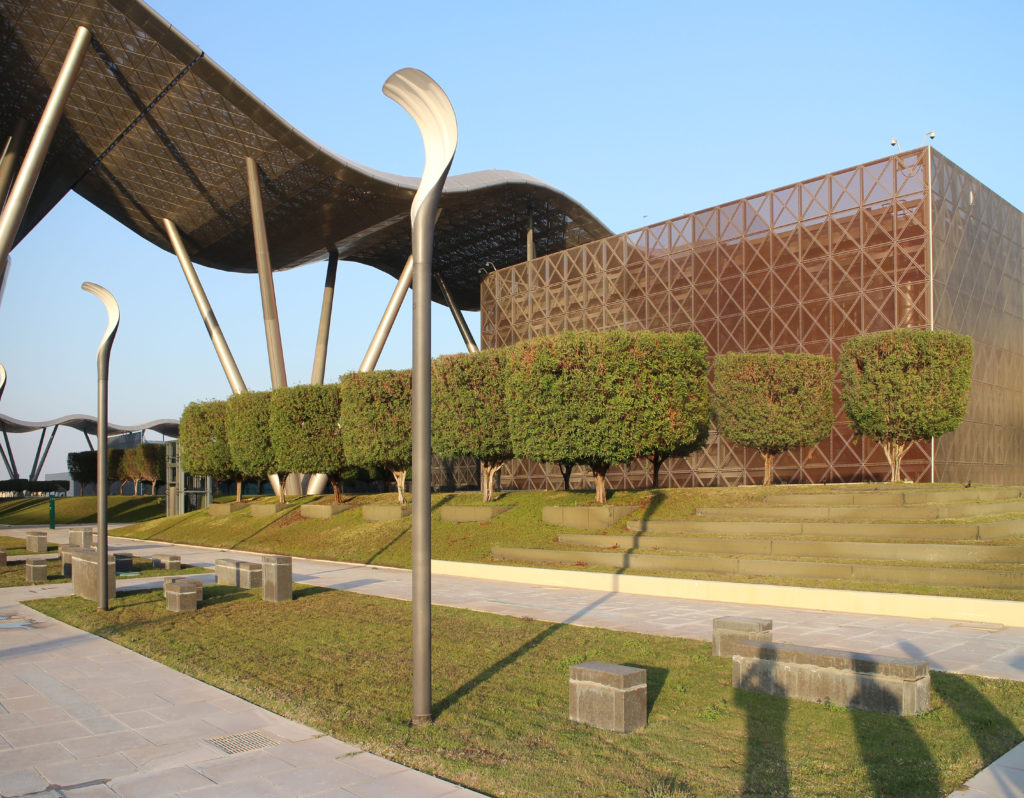
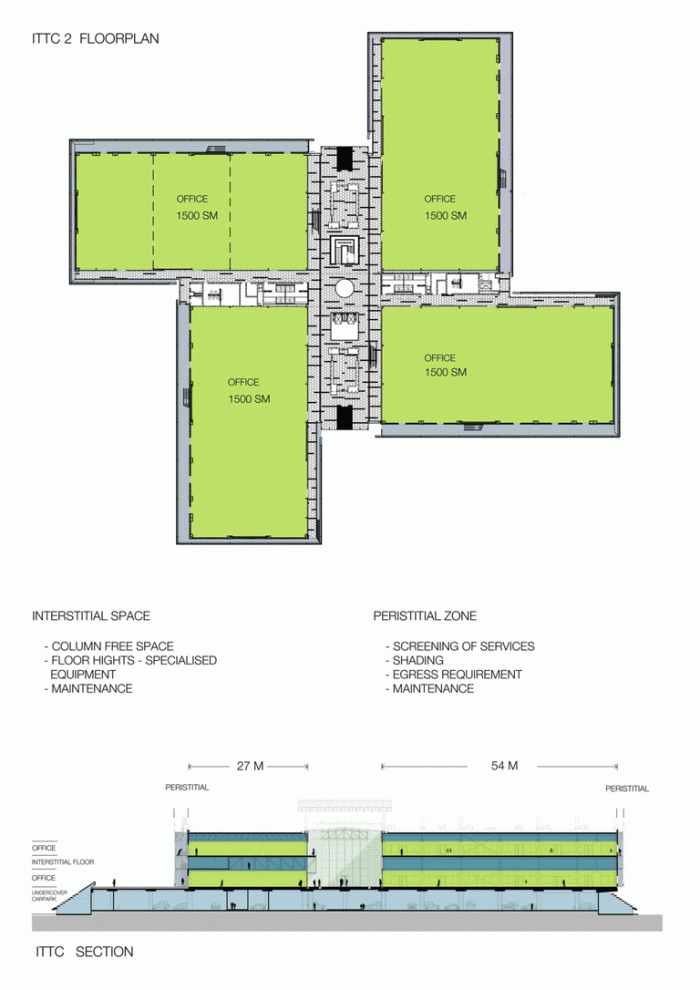
The Incubation Center is flanked by groups of ITTC laboratory buildings (Transfer, Innovation and Technology Center) that are coated with patterned steel screens to create striking geometric shapes while protecting and facilitating high-level research.
The client requested flexible spaces that could be developed, expanded and exchanged according to the user’s needs. Responding to this request, the Woods Bagot team incorporated interstitial floors, with easily incorporated spaces, with flexible open plates, allowing services to the upper and lower floors and placing the mechanical services in external locations around the perimeter of the building.
The ITTC buildings work in the same way as the Incubation Center, they are tough and austere externally, but then offer rich, light-filled spaces for meetings in the inner courts. Inside the building, activity centers form the heart of creative communities, with places where tenants can interact, exchange ideas and share knowledge. From an architectural perspective the buildings that group the new possible companies look and function a bit like an Islamic pattern that can be repeated and modified.
Structure
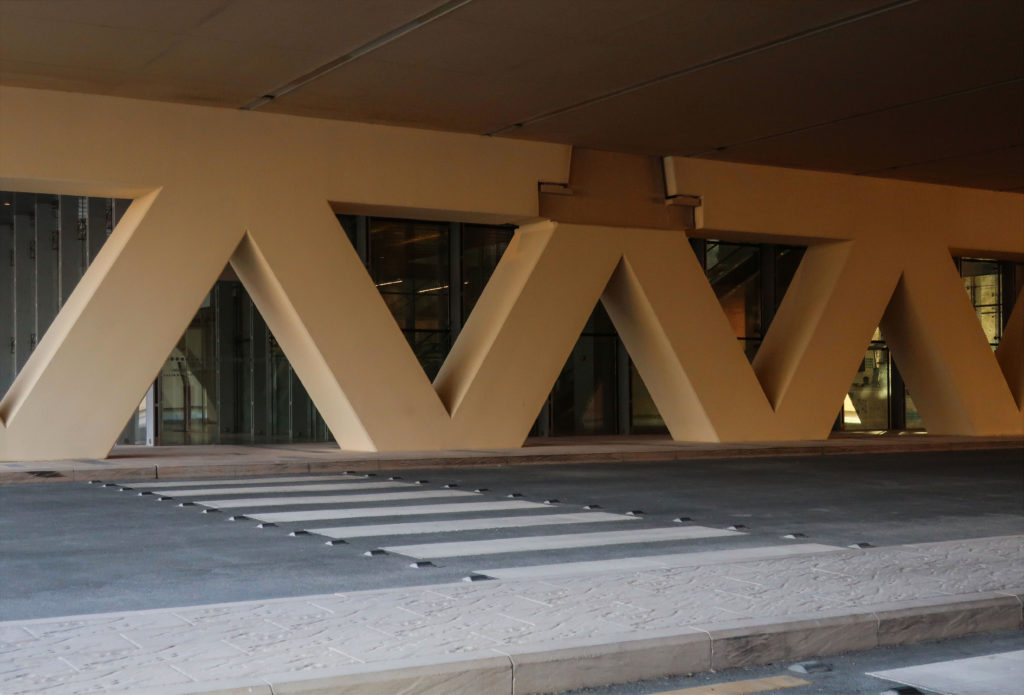
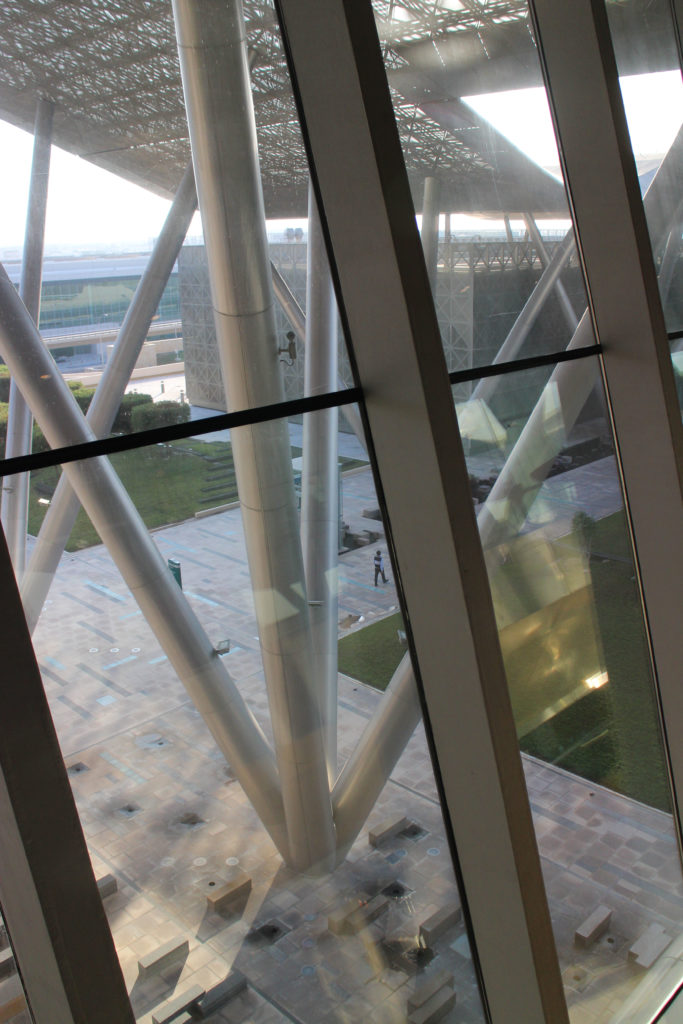
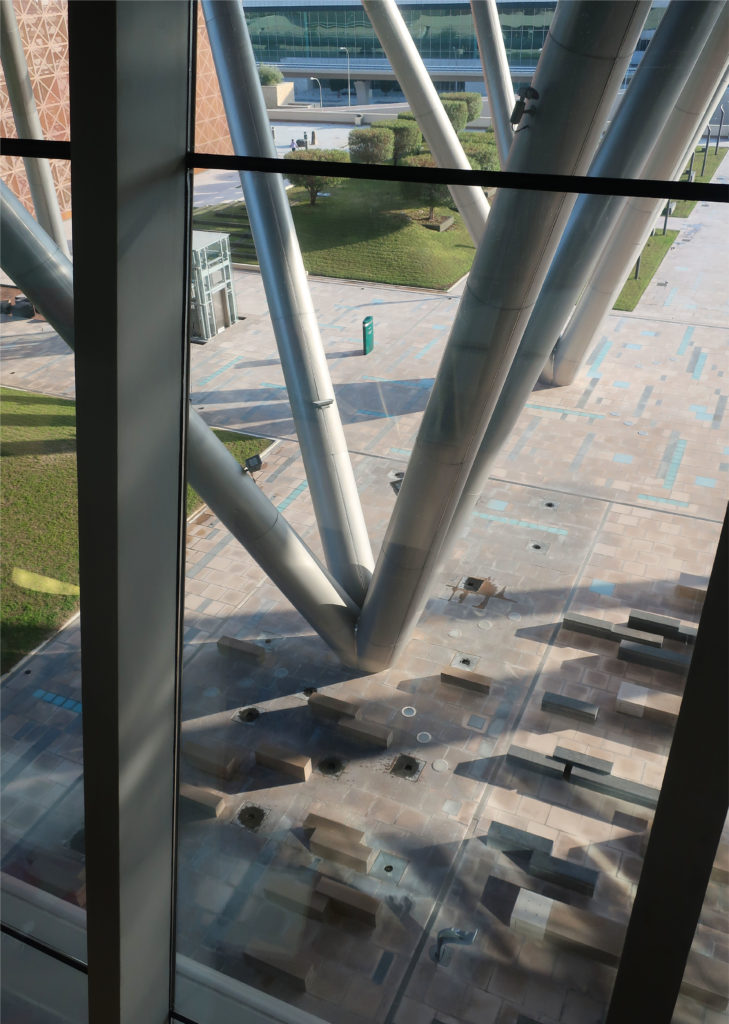
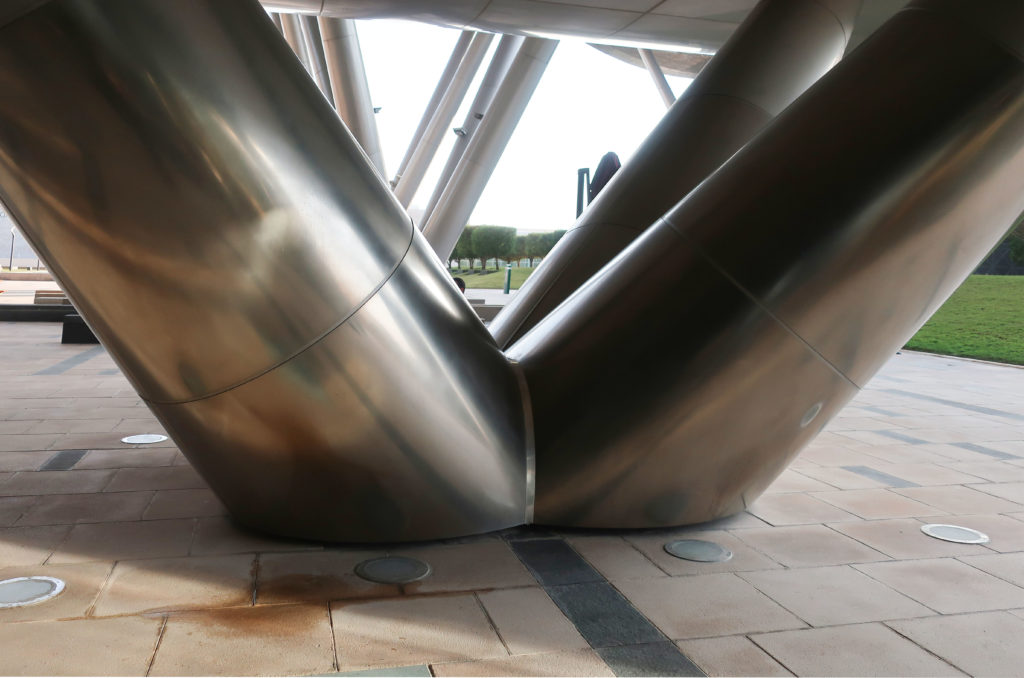
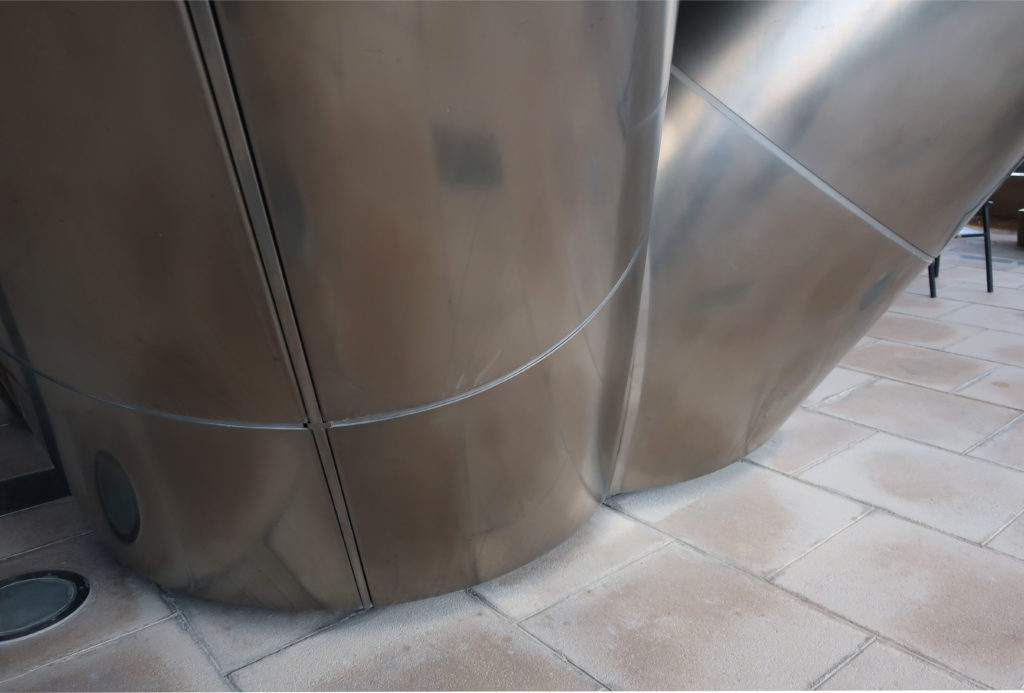
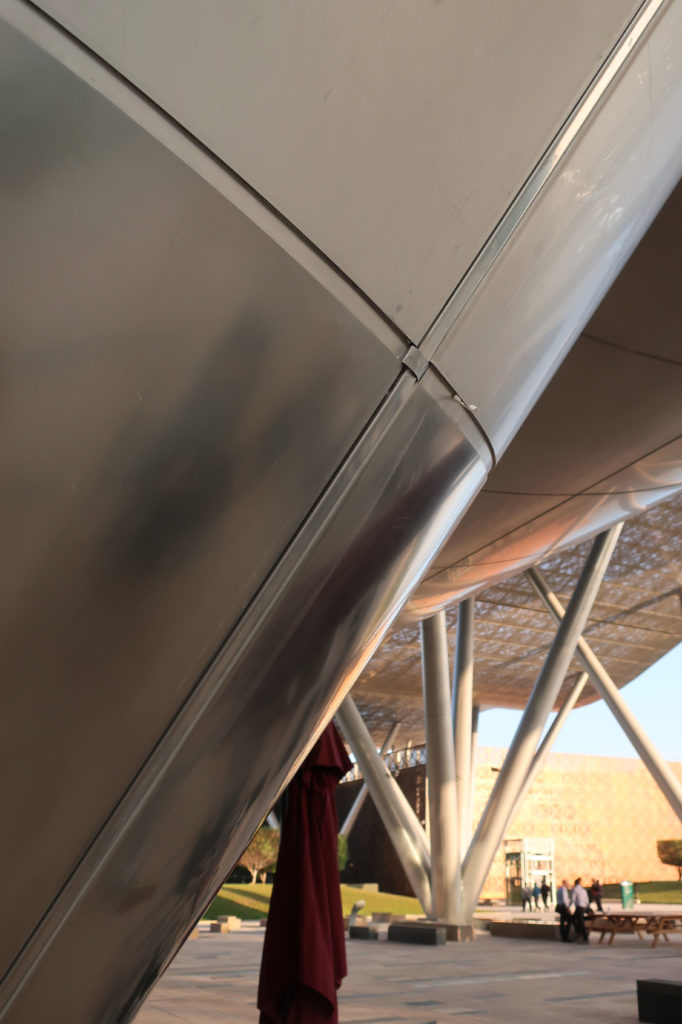
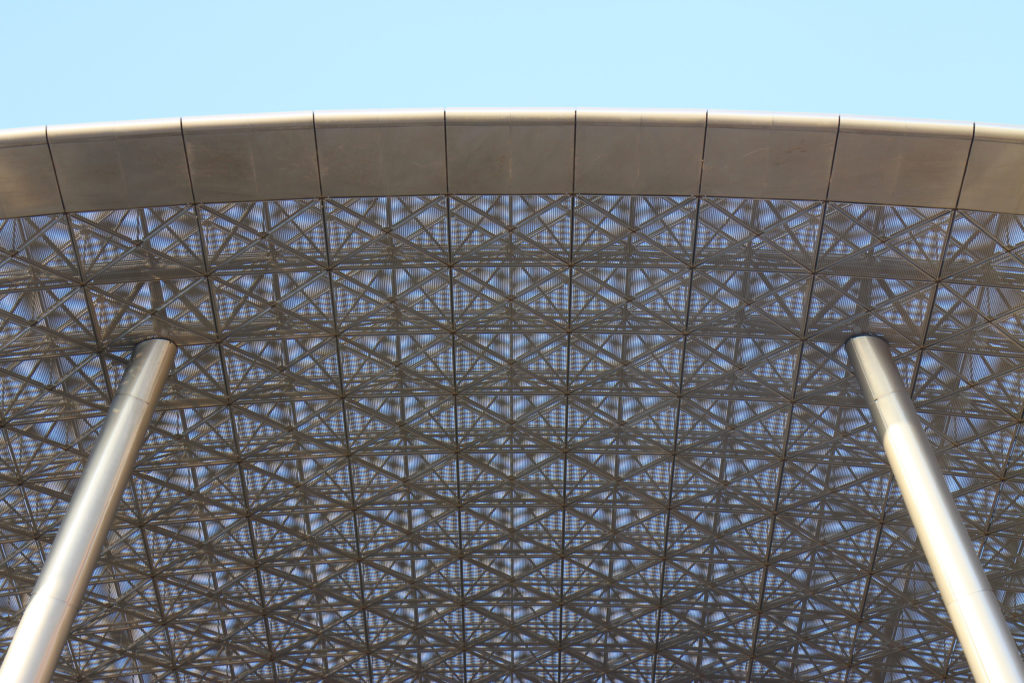
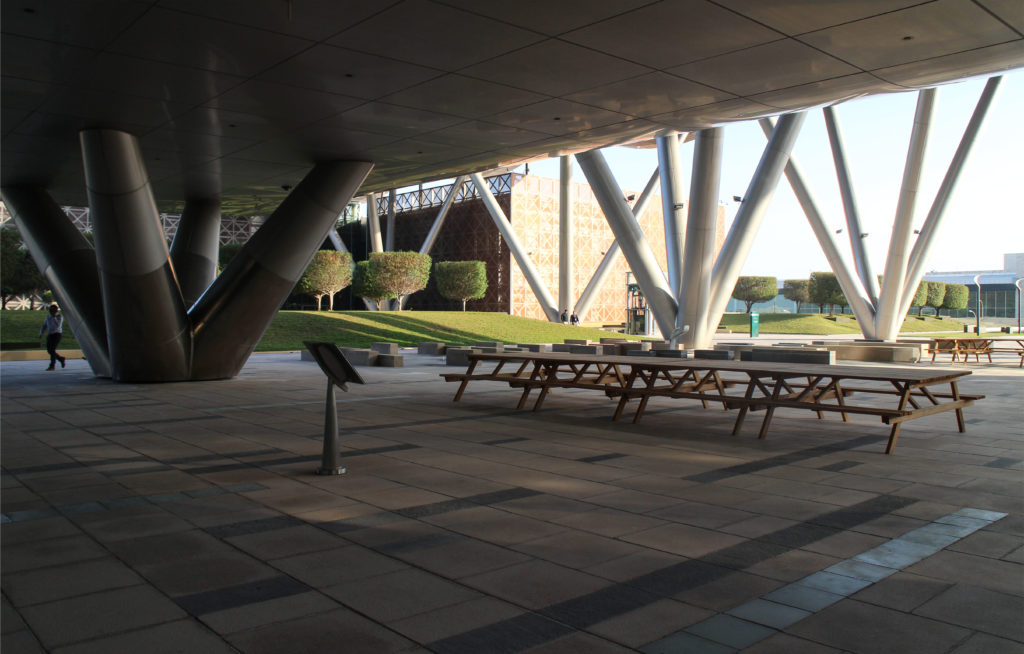
The multifunctional “veil” that covers the building in addition to serving as a bond between the buildings acts as a housing that reduces heat gain and total energy consumption. This veil is created with two layers of perforated and modeled stainless steel that seen from near creates a sensation of movement and from a distance contrasts with the horizontal landscape. These layers cover a tubular frame that responds to a pattern and that rests in all its width on beams of 4 inclined tubular steel columns that go from greater to smaller diameter. In front of the main entrance, this set of columns is doubled in response to the wider width of the roof. Towards the sides continue with 4 columns each. These columns were specifically chosen to be a metaphor for the local tree of Qatar that, historically, witnessed the narration and schooling under its branches. The raised main body of the floor also relies on groups of 4 columns, this time lower and more robust.
The solution of achieving flexible and wider spaces by placing mechanical services outside of office or laboratory spaces was a point of reference in the architecture of the place and made unnecessary the load columns within the workspace. By providing a 27m floor plate without columns and flexibility for maintenance and overhaul along the outer perimeter, the buildings remain fully adaptable and safe. In addition to sun protection, the exterior façade hides maintenance equipment, such as gas cylinders, exhaust ducts, high pressure air hoses and everything that laboratories or maintenance personnel may need.
Materials
All the facades of the building incorporate a zone of external wall of glass and metal of double skin that helps to the control of the gain of heat and reflects the light again in the interior spaces what reduces the load of artificial lighting necessary in the building. High performance double glazed window systems were also used to reduce the amount of heat load.
The unique wavy “veil” type roof structure uses perforated aluminum that runs along the front end of the structure provides protection from the sun.
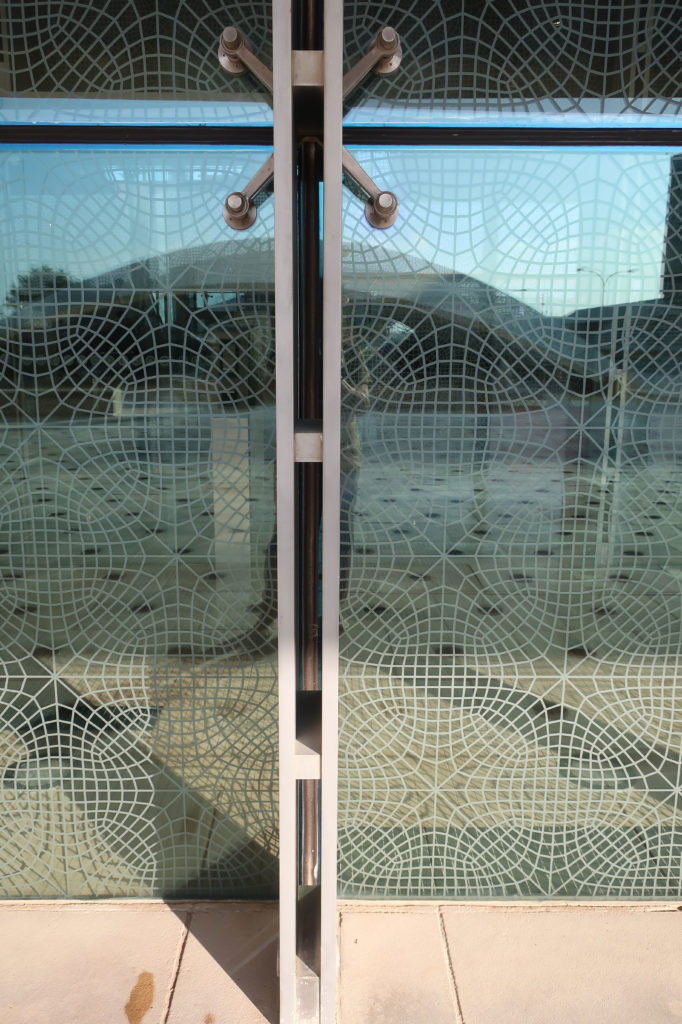
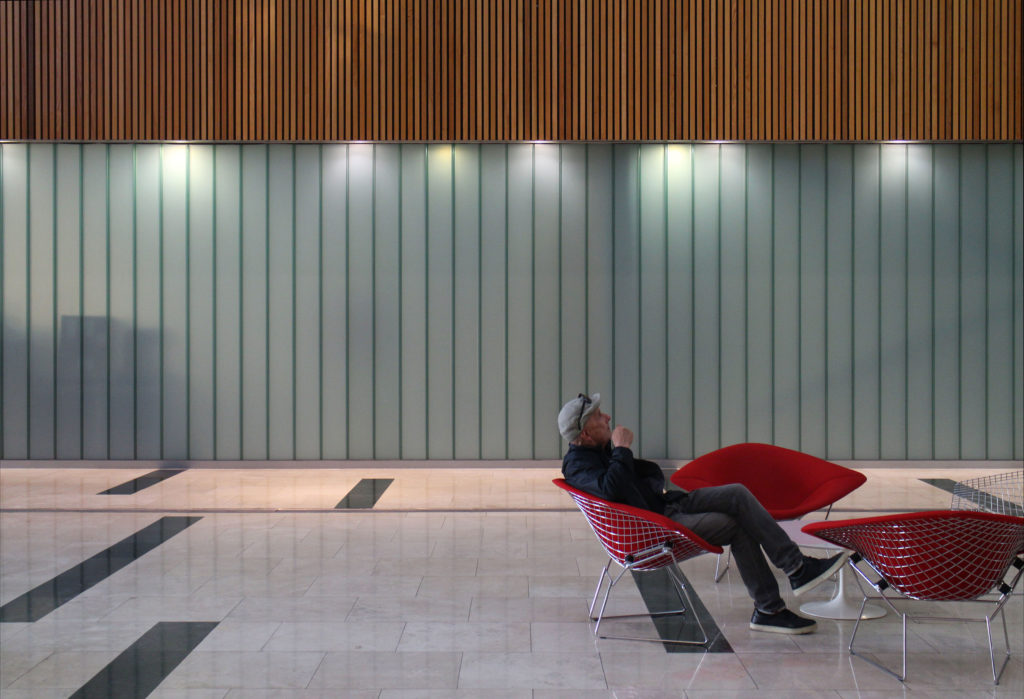
Inside, different types of crystals have been combined, transparent, some carved with Islamic motifs such as the large squares of the atrium roof, others translucent such as rectangular bands that are combined with wooden slats at the main entrance.
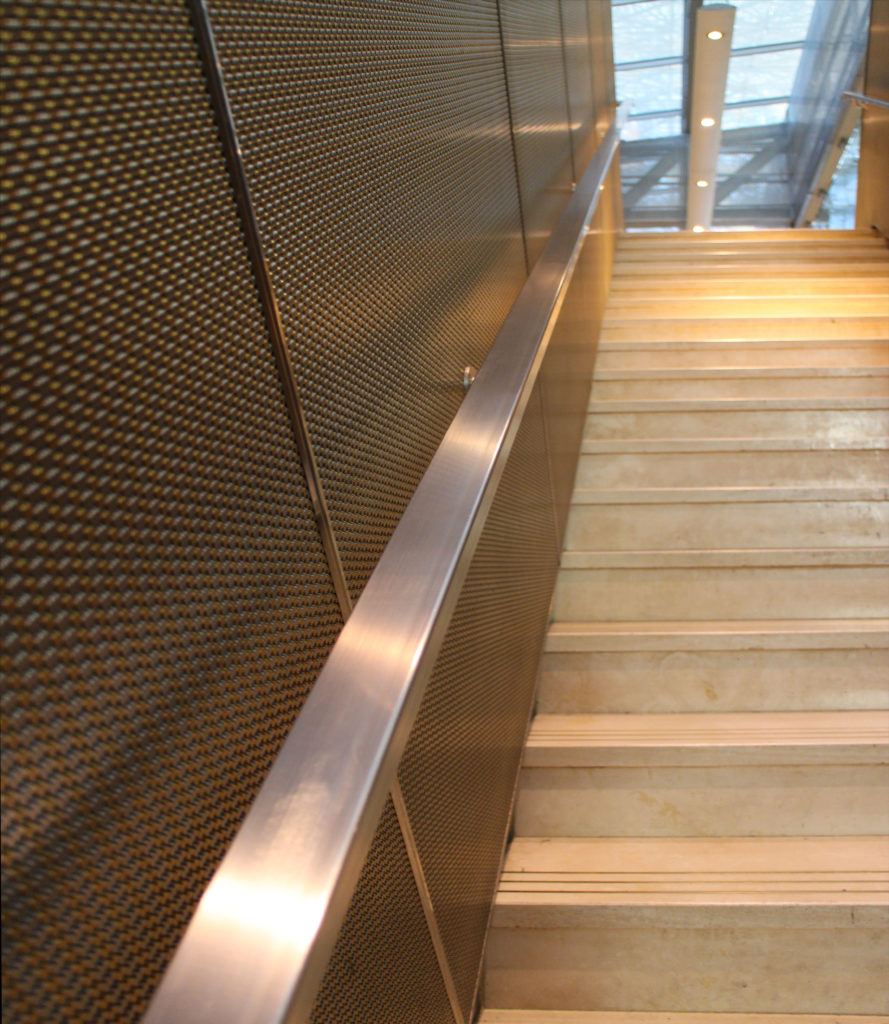
Different combinations of marbles are used in the floors, as in the stairs that are often flanked by railings made of steel mesh.
ITTC laboratories are coated with hard steel curtains to offer privacy and protection to high-level research inside, however, they were built to the most modern specifications and include components that ensure organic expansion.
Video