High Line Park in New York

Introduction
In January 2003, the Friends of the High Line launched a proposal for the Design and Retrieving the High Line. An open society, an international competition of ideas, attract innovative proposals for the reuse of the High Line. The proposals do not necessarily have to be practical or realistic, participants were encouraged to be bold and create visions as unique and unexpected as the High Line itself.
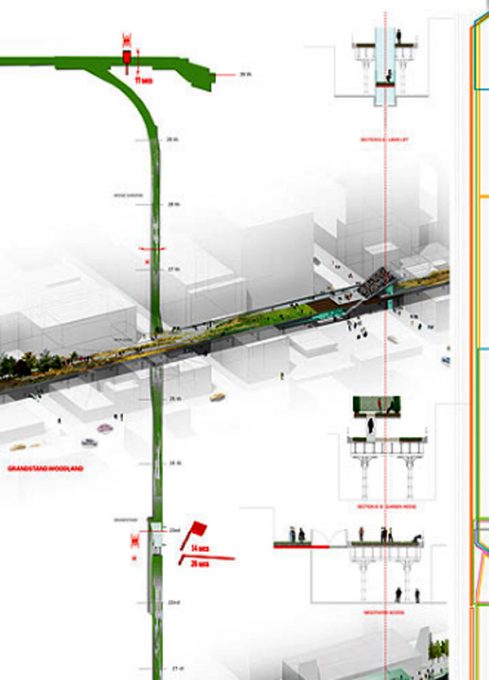
720 individuals and teams from 36 countries submitted proposals for the competition, of which there were four finalists. In October 2004, a Steering Committee comprising representatives of the City of New York and Friends of the High Line, the team selected James Corner of Field Operations (landscape architecture) and Diller Scofidio + Renfro (architecture) to begin the work, a park in height, 9 meters above ground level and with a total length of 2.33 kms.
History
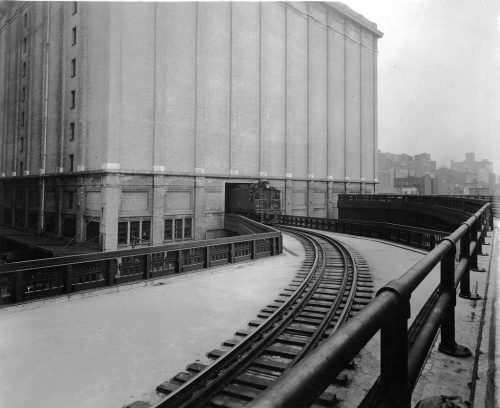
The High Line was built in 1930 to eliminate the dangers posed by the transport of goods in the streets of Manhattan. This railway line delivered milk, meat, raw materials and manufactured goods in the loading dock that had the stores and factories in the upper echelons. The last trains running in High Line did in 1980 and carried a cargo of frozen turkeys.
Location
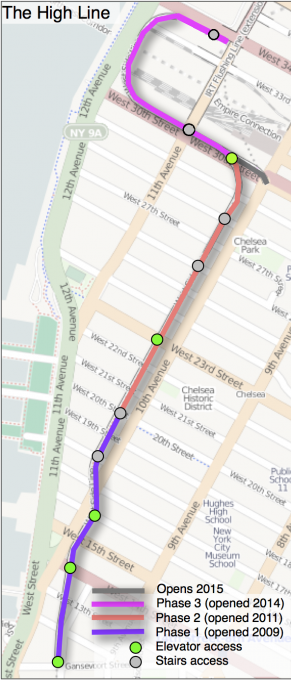
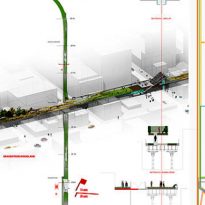
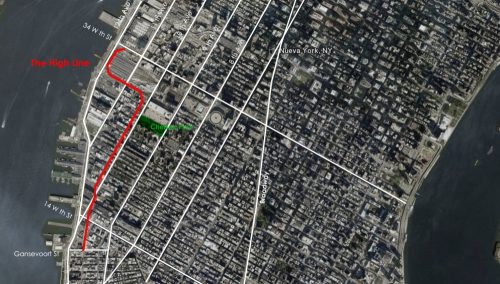
The High Line is located in the west of Manhattan. It runs from Gansevoort Street in the Meatpacking District to 34th Street, between Avenues 10 and 11. Section 1 which opened to the public on June 9 2009, runs from Gansevoort Street to 20th Street, Section 2 from 20th West St to 30th St is anauguró in 2011, the third phase, from West 30th to West 34th St St was opened in 2014. in 2015 is projected to open a small stretch of 30th Street with access to lifts in this sector.
Access: Access to the High Line can be performed in the following points:
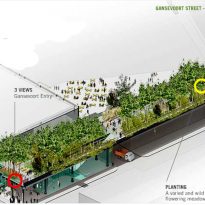
- Gansevoort Street
- 14th Street – with elevator
- 16th Street – with elevator
- 18th Street
- 20th Street
- 23th Street – with elevator
- West 26th St
- West 28th St
- West 30th St – with few meters each access by stairs and a lift
- West 34th St
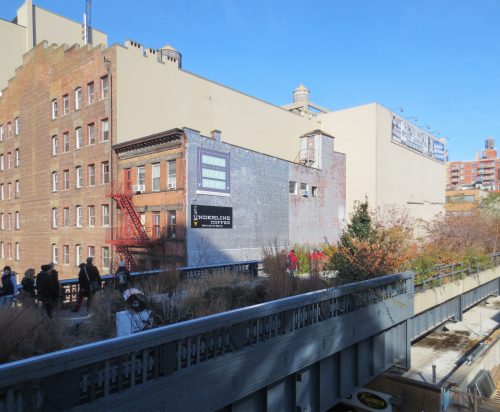
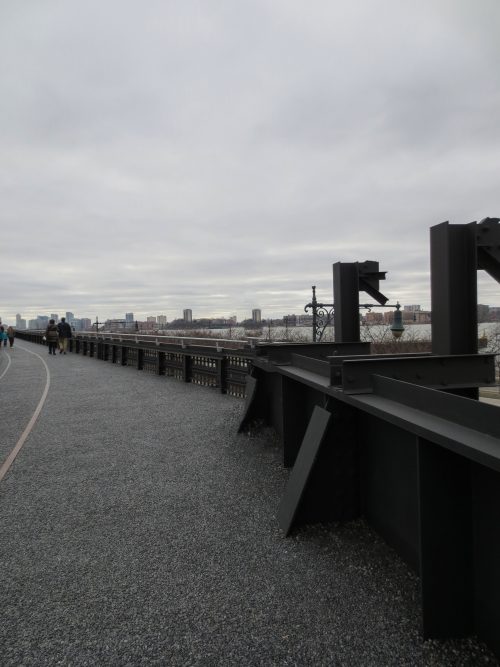
From the High Line Park you can see some of the best known sites in the Big Apple as the Statue of Liberty or the Empire State Building via overlooking the Hudson River and Manhattan’s financial district.
Concept

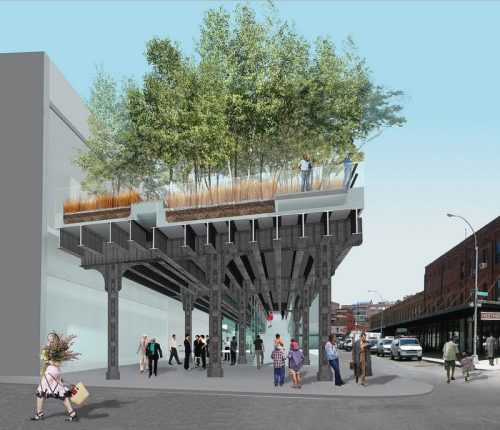
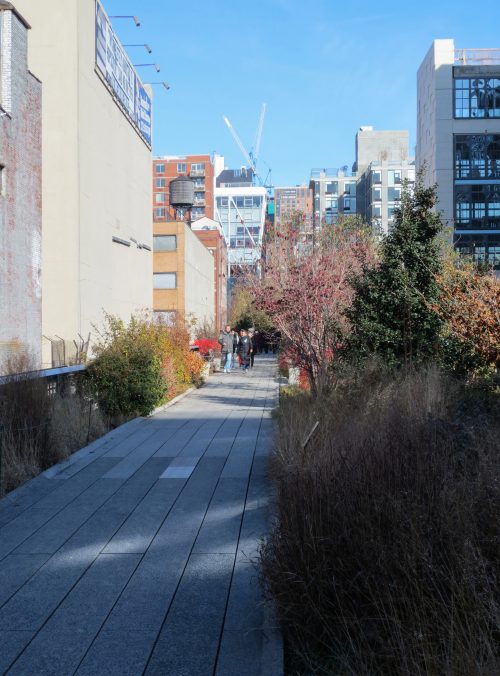
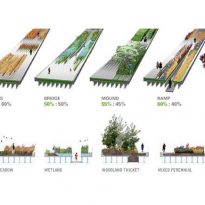
Inspired by the melancholic beauty and rebellious of the High Line, where nature has regained a vital piece of urban infrastructure, the computer reverts this commercial vehicle in a post-industrial instrument of leisure, life and growth. By changing the rules of engagement between plant life and pedestrians, the strategy of “agri-tecture combines organic and building materials in a mixture proportions amending and adapting to nature, culture, intimacy, and hyper -social.
In sharp contrast to the speed of Hudson River Park, this parallel linear experience is characterized by slowness, distraction and the other worldliness that preserves the strange character of the High Line. Providing flexibility and responsiveness to changing needs, opportunities and desires of the dynamic context, the proposal is destined to remain eternally unfinished, emerging growth and sustain change over time.
Construction

Reclaiming the High Line in New York has been conducted in different phases.
The first step was to clean and remove some elements of the old structures to clean up, strengthen and modernize the party was to be reused.
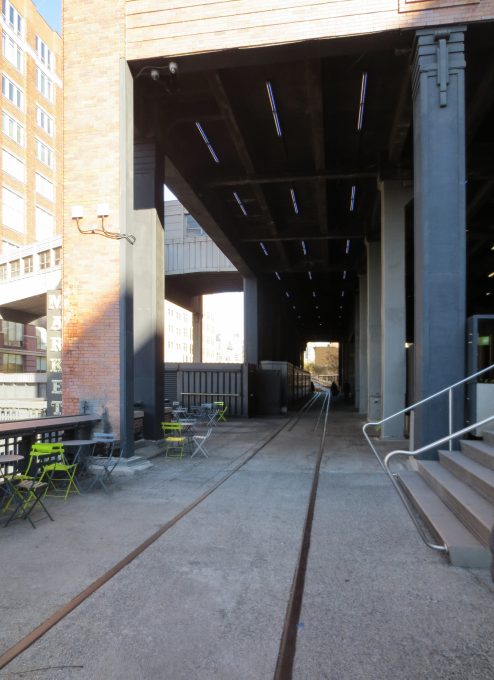
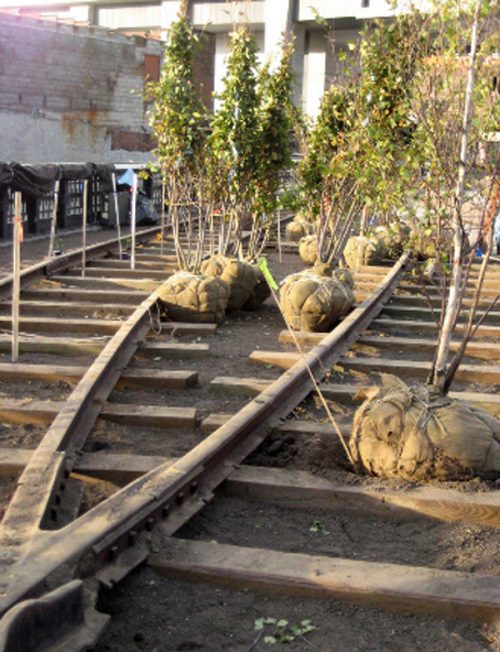
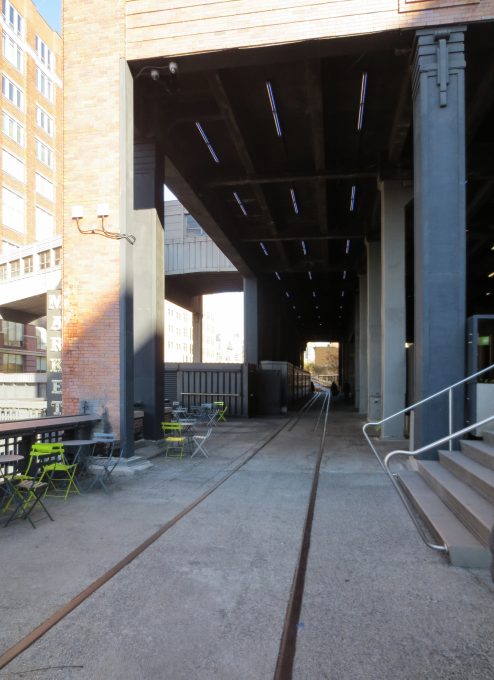
In many places the removed parts were restored and returned to their places of origin, for example the old railroad tracks, which were integrated in the formation of flower beds for planting.
The final phase in the transition of the High Line to a public park is the construction of the landscape of the park.
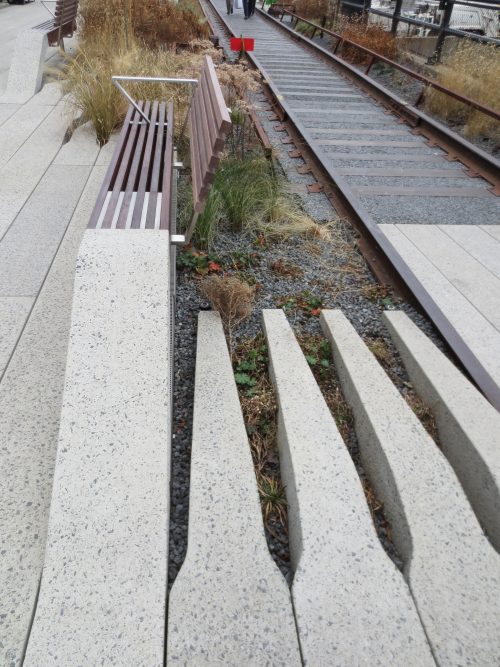
The walks in the park created from a conical flat plates and cement were placed above the waterproof layer of concrete, leaving spaces between them for electrical conduit and drainage.
Construction of stairs and elevators allow visitors to access from street level. It also has wheelchair access at access points where there is no elevator.
Spaces
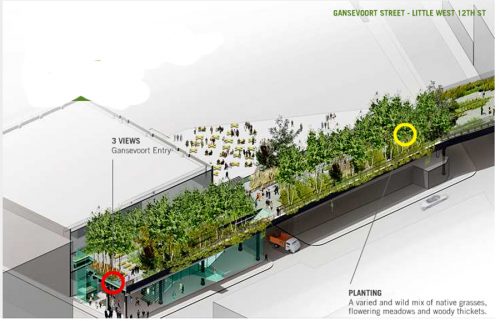
Conserving metallic structure and support rails, designing a green platform where open roads boardwalks, rest areas, restaurants, exhibition and small businesses. The play is based on recreating the ancient links and rail lines, with large flower gardens and little breaks more bounded.

The project was conducted in several phases:
- Phase 1 – The section runs from Gansevoort Street to 20th Street began in 2006 and was inaugurated in June 2009.
- Phase 2 – The High Line of Ganservoort Street to 30th was inaugurated in 2011.
- Phase 3 – The third and final phase was officially opened to the public on September 21, 2014 and reaches the 34th St. By 2015 it plans to open a short joint that connects the 10th Avenue to 30th Street.
Attractions
The biggest attraction along the nearly 2.50km of travel is to enjoy the outdoors and scenery recovered, with the Hudson River on its side, skyscrapers other and a green environment based on the vegetation that grew over time between tracks in disuse combined with built the place plantations. In some sections of the course were adapted to the placement of benches positioned to observe the landscape, relax or sunbathe on comfortable chairs. The park also offers cultural spaces for temporary shows, spaces that are projected to expand over time. In the summer of 2010 highlighted an installation by artist Stephen Vitiello composed whose tolling bells rang through many streets of New York. During construction of phase two works of art between 20th and 30th streets were installed: “Still Life with Landscape” Sarah Sze between 20-21 streets made of steel and wood, “Empathy Digital” Julianne Swartz, work audio messages used in bathrooms, elevators and water sources.
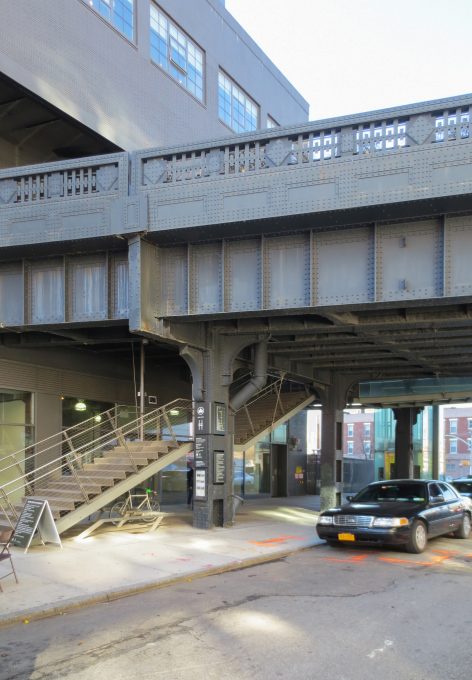
Structure

Reform
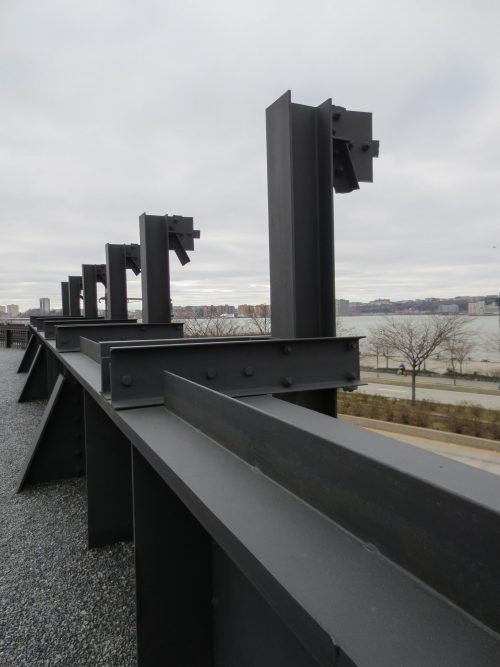
Before the new concrete structure could take shape, it was necessary to eliminate all elements of the former, since the steel rails, gravel, earth and debris and the first layer of old concrete. All that was needed to reach the steel structure of the High Line and make the necessary repairs.
Some of these repairs were waterproofing for the steel beams in concrete and drainage systems must be installed on the old structure.
- Stairs – In some places, the beams are removed to allow the stairs cut the structure of the High Line from the visitors center and meet face to face with the steel beams on their way to the park.
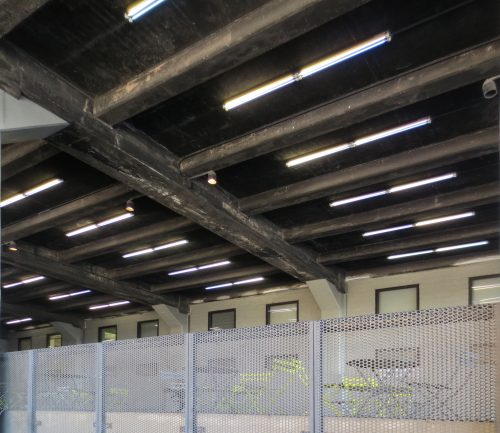
- Shielding for pigeons – This point has also been taken into account when making repairs installing metal strips that prevent pigeons alighting on the beams of the bottom of the structure.
Materials

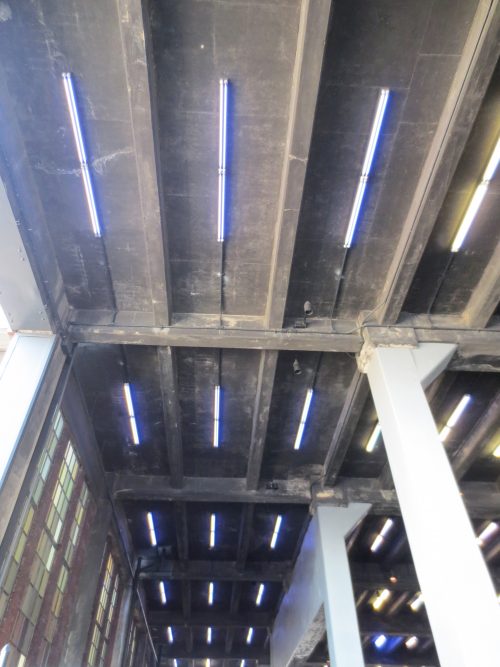
Lighting
LED elements integrated into the fabric of the High Line, illuminate the paths of the park at night. The lights are placed at ground level, creating safe to walk at the same time allowing walkers to enjoy the surrounding ambient light. These lights have also been placed in the bottom, between the beams, to gently illuminate the sidewalk. The lighting structures are aluminum and stainless steel.
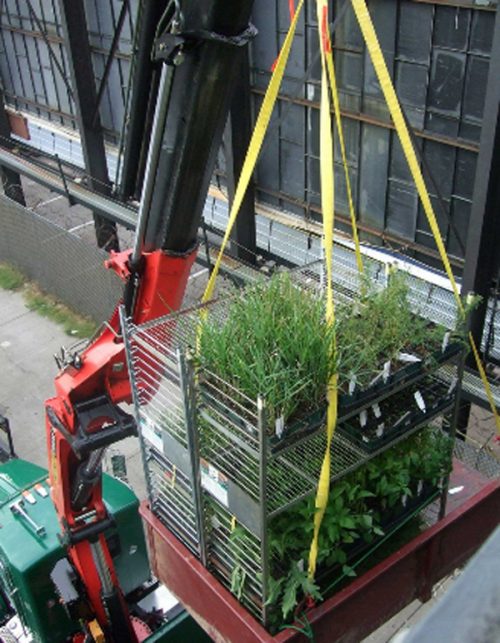
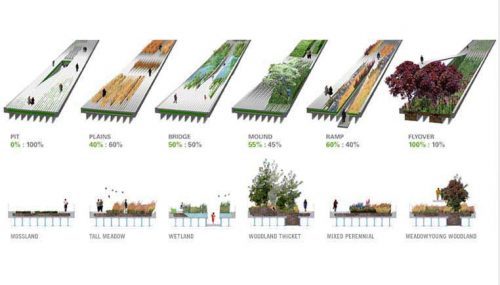
Plants
The land has been distributed in different planting areas. Plants have been chosen in this area nurseries and planted by gardeners teams of the High Line plans by landscape architects James Corner and Piet Oudolf. The vegetation ranges from different types of grass, shrubs, bulbs, perennial trees to tropical plants such as banana trees.
The pavements were resolved with precast concrete with wood of Ipe and aged steel planters like the side walls of the access stairs.
Restoration

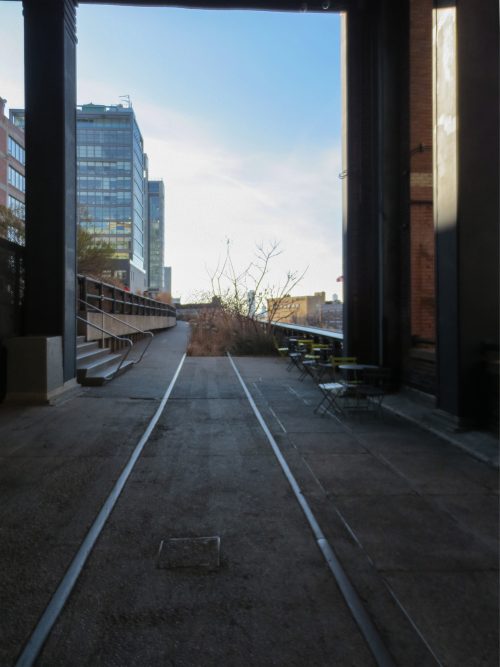
Railroad
During transfer, each section of the railway was marked and mapped its location to be stored for later to be returned to their place of origin and integrated together with various ornamental plantings.
Following the move, the steel elements of the structure of the High Line were treated with a sand blasting to remove lead from the original painting. This applies sandblasting containment with a shop, which moves along the structure, and clean an area of 7.50 m each time you apply. Once the steel has been treated, you spend 3 coats of paint. The top layer is closest to the original color of the High Line.
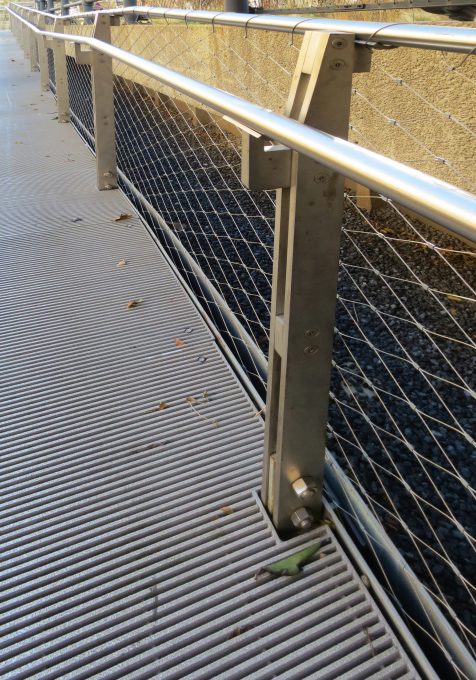
Ways and were reinstalled but also steel rails as rails were manufactured with steel cables and mesh mesh type black finish.
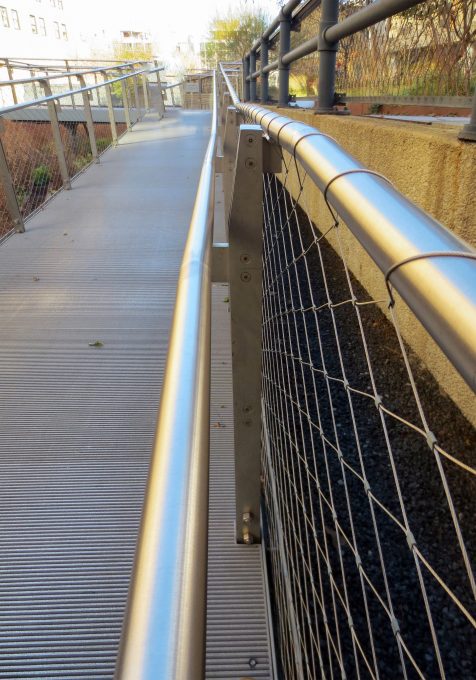
Railing
They also repaired the old Art Deco railings of the High Line. Steel is processed and the missing parts are made to restore the gates to their original design.
Videos