Barcelona Biomedical Research Park

Introduction
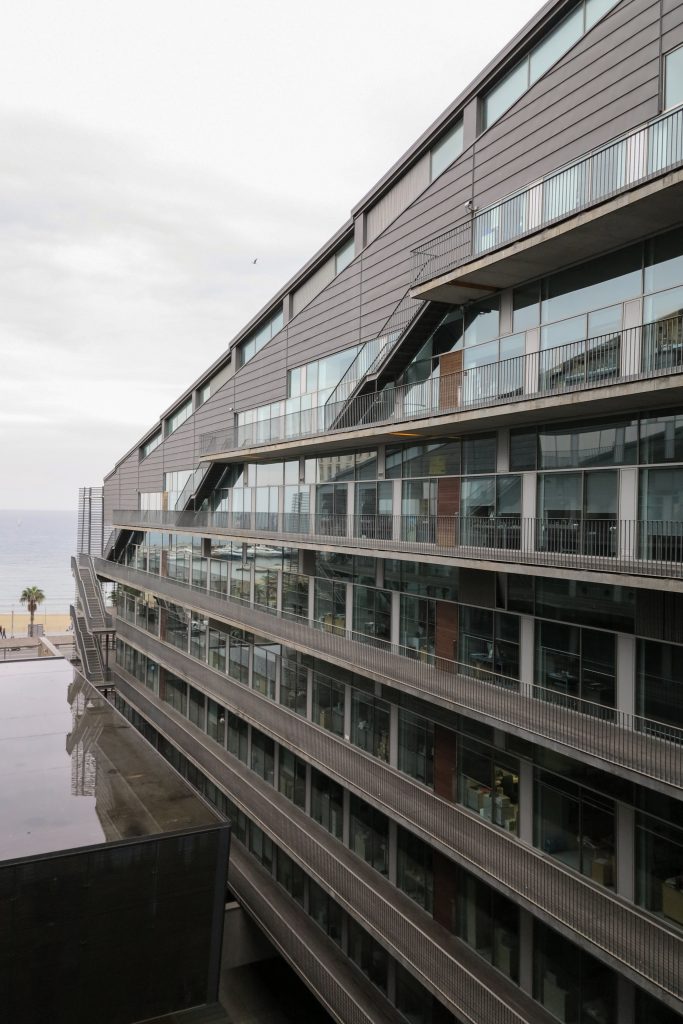
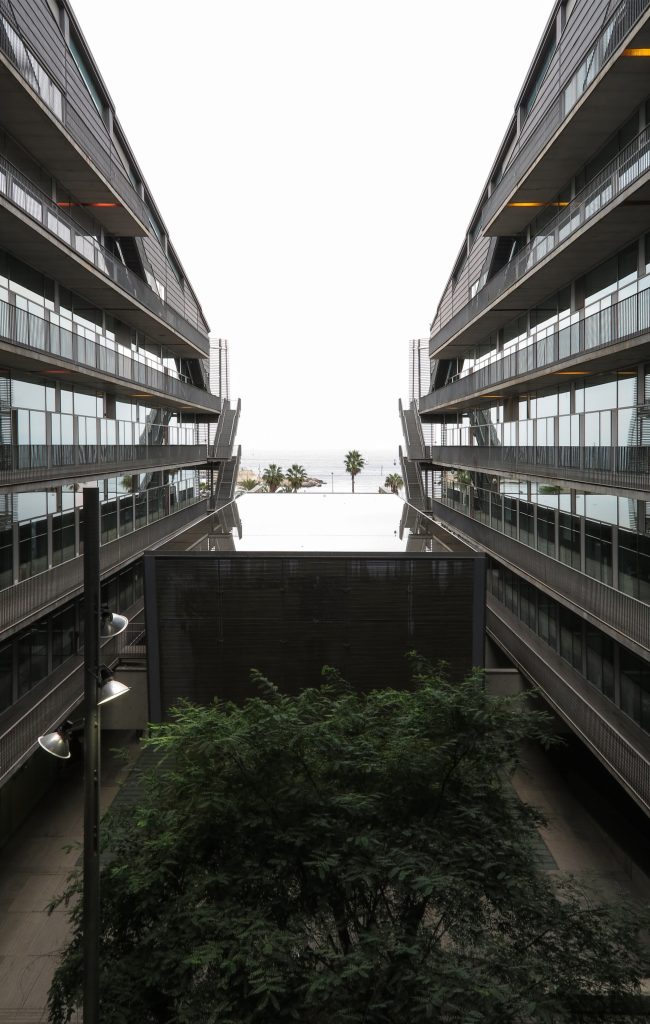
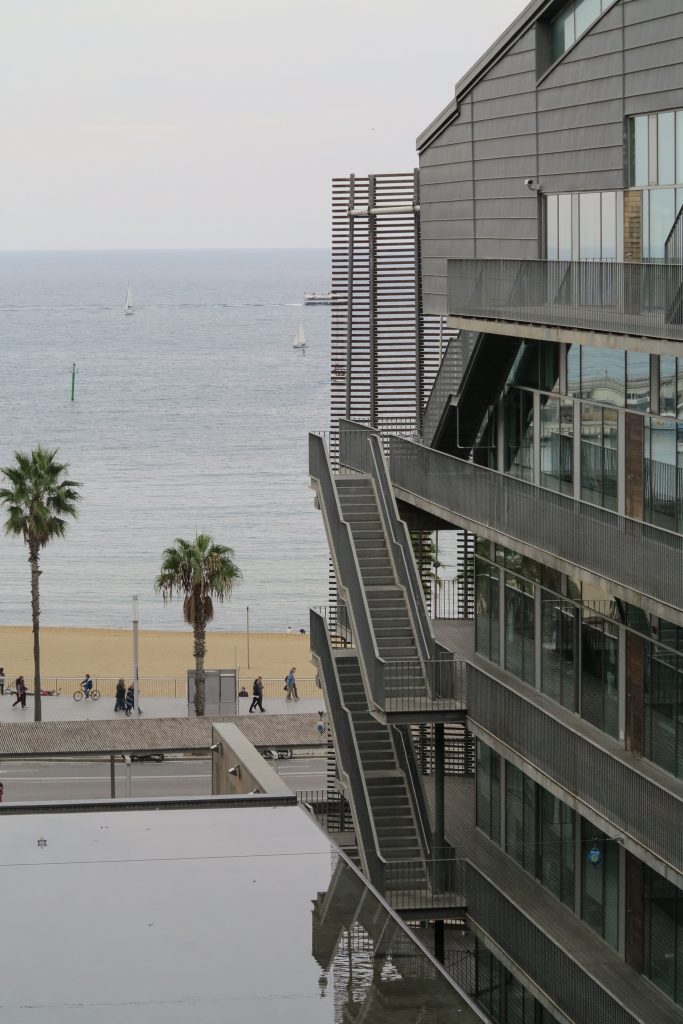
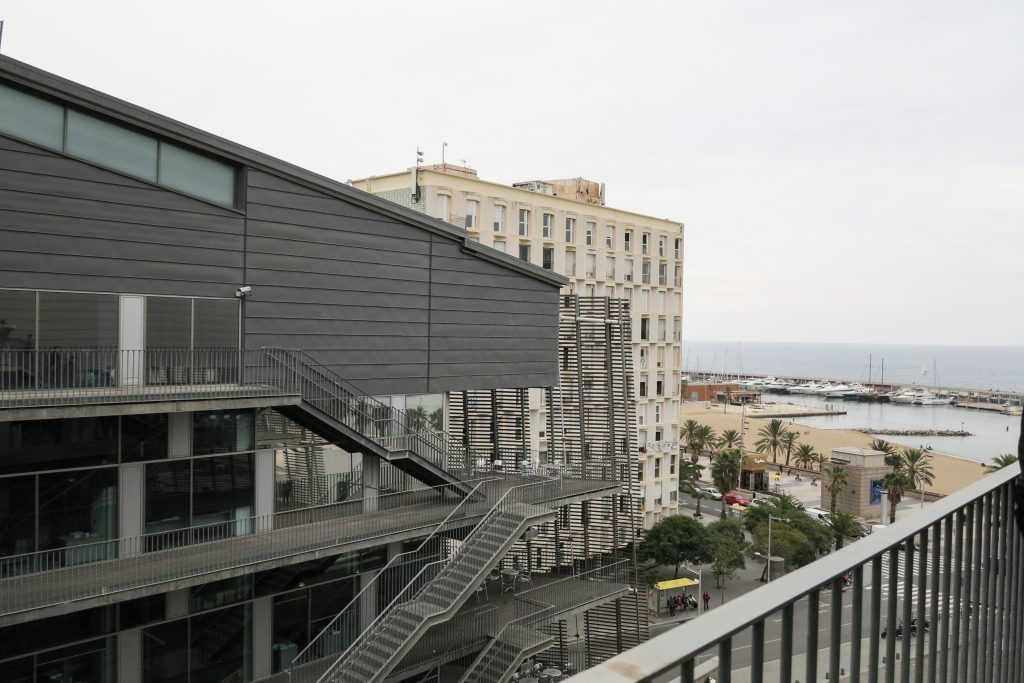
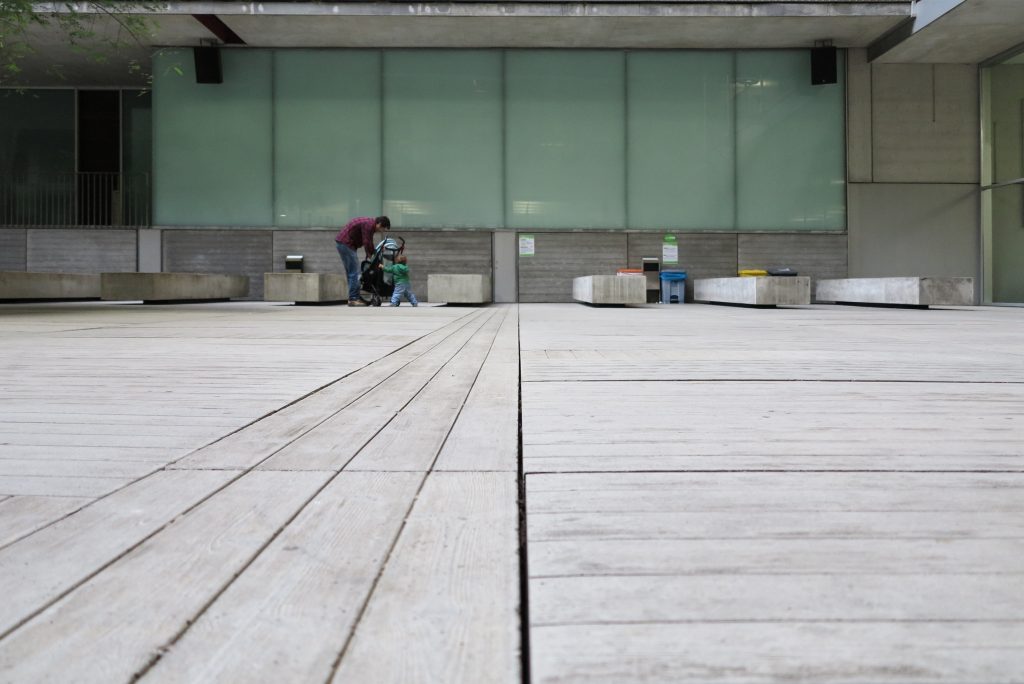
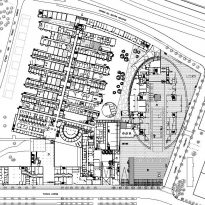
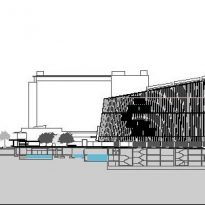
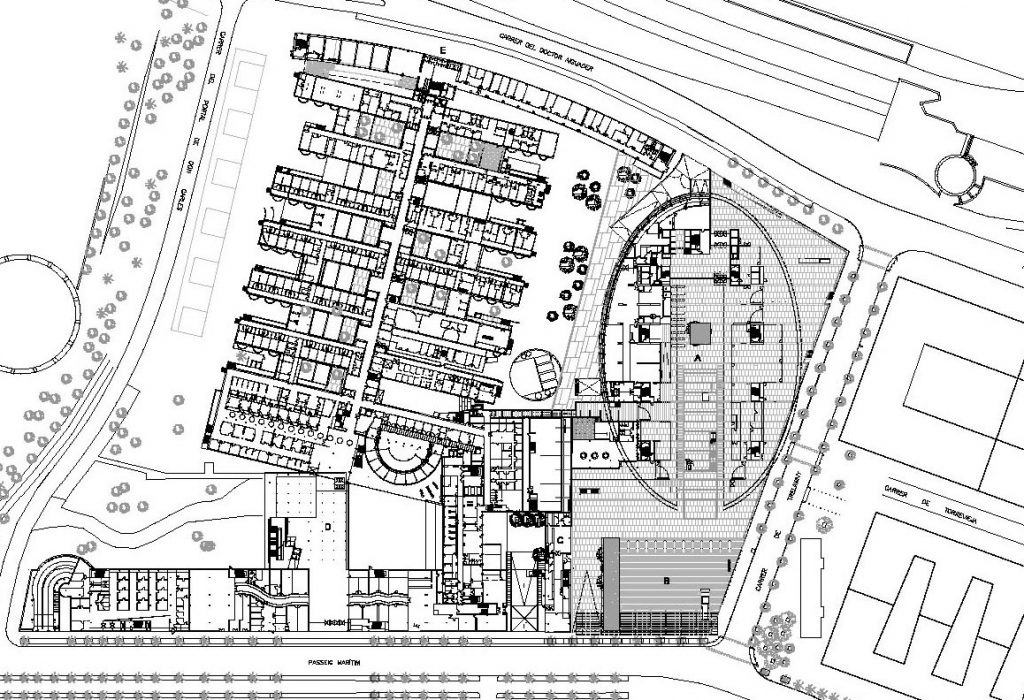
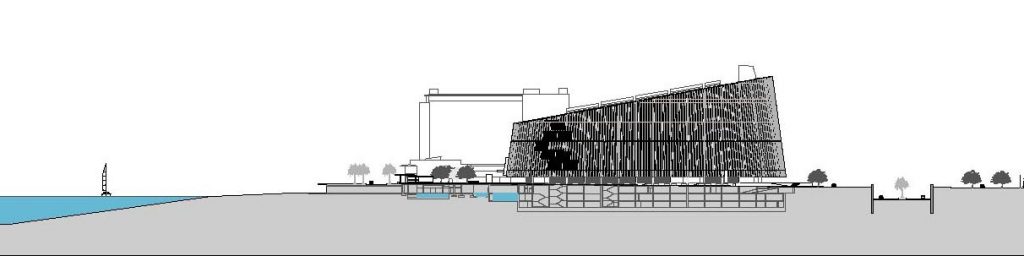
The Barcelona Biomedical Research Park is a building with a high density of occupancy due to the relatively small size of the trapezoidal lot on which it stands, 7.916m2 in which an area of approximately 55,491 sqm, 20,000 corresponding to the basement was built and the rest distributed in 9 floors above ground. To avoid possible overcrowding architects resort to a project with a smooth geometry, a lightweight building, open sea and sky overlooking the coastal belt of Barcelona on the other side.
To avoid competing with the environment, buildings of different heights and nearby skyscrapers of the Olympic Village, the building of the Research Center seeks dialogue and integration, a clear and sharp image that hides the large volume built inside and seen from outside lose its scale and becomes a particular and specific item.
Location
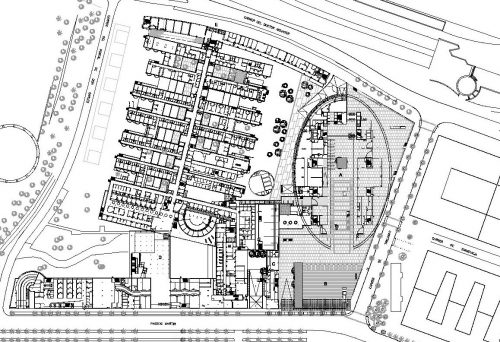
The Biomedical Research Centre is built on a plot located oceanfront, Carrer del Doctor Aiguader 88, surrounded on the east and west by several buildings equipment, offices and housing, near the center is the Hospital del Mar, and South Park Ciutadella, in Barcelona, Catalunya, Spain.
The site is characterized by its longitudinal geometry sea-mountain, its geometric irregularity and volumetric pressure of different perimeter buildings, the hospital tower with 11 floors and the hospital itself which together with a previous sports obstruct the view of the promenade in that angle, a block of flats 8 floors, and in the distance, but within the visual field of the solar skyscrapers Olympic Village.
Concept
The location of the land on which the Research Center was formerly an area of industrial buildings, with large gas installations La Catalana and gas meters is built. These large structures formally define the range of these land between the beach and the train. Linking these images of large industrial elements with the new building has allowed the architects responsible reflect on urban visual memory. The project proposes a symbolic image of “large industrial object”, which links large industrial buildings of the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries with the “new industry” research XXI century.
The intention was that the appearance of the new building meet any of the characteristics of those industrial elements that marked an era in the city, in the neighborhood, to somehow take root in context, looking for a sense of its location and at the same time, a response to existing, confusing and irregular environment.

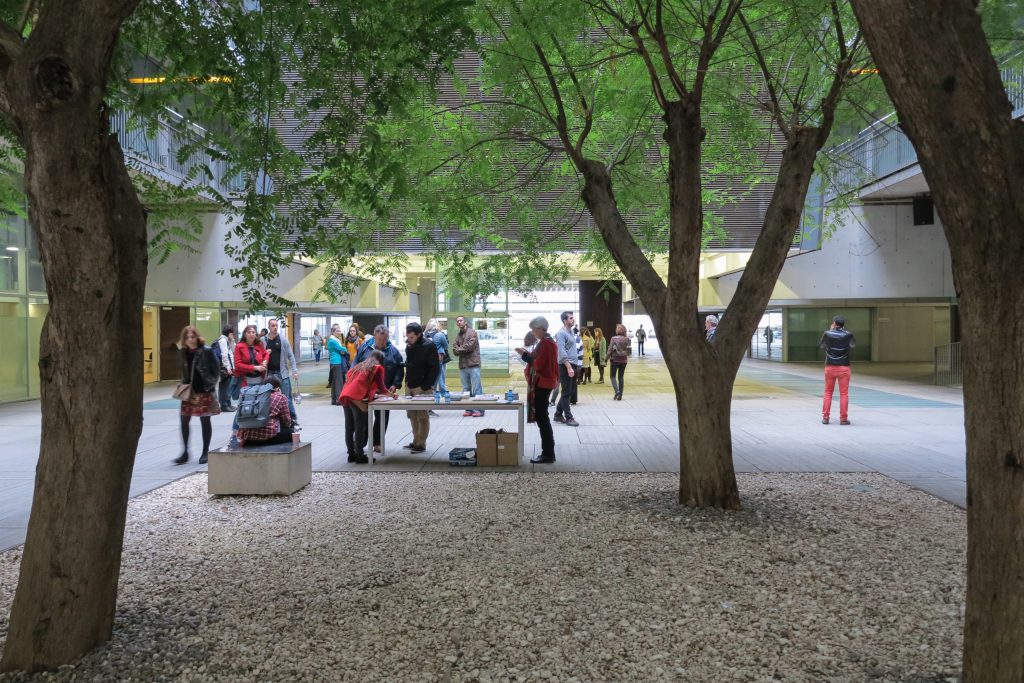
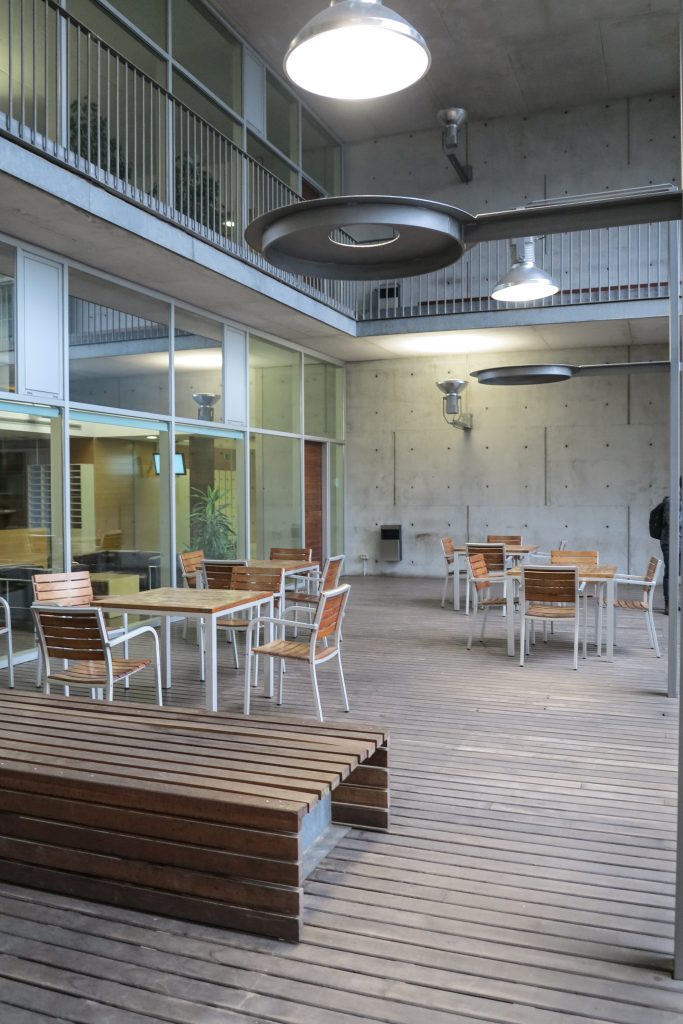
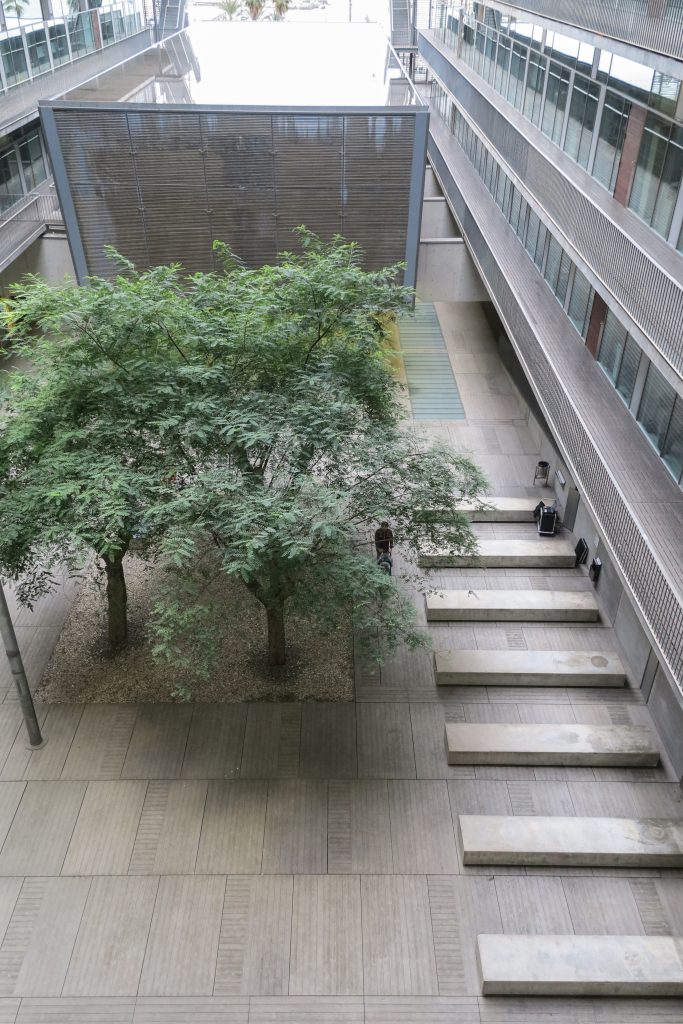
Another factor considered by those responsible for the project was to achieve an atmosphere of “domesticity”, meaning it certain degree of comfort for people who spend many hours in their facilities and those who come to it for various reasons. The courtyard-cloister of various heights located in the center of gravity of the building helps to achieve that environment and is equivalent to the “campus” glue of the first universities. The structure is supported by the different elements used in its construction, its textures, durability, hygiene and quality to strengthen a friendly atmosphere.
Another of the images that have contributed content to the project has been the Salk Institute for Biological Studies of La Jolla, of Louis Kahn, the architects visited on several occasions. In addition to sharing its opening to the sea, the influences of the California Institute are subtle and varied, more explicit, as the appearance within the cloister park a sheet of water on the roof of the auditorium and its fusion with the Mediterranean, inspired by the water channel of the central courtyard of the Salk laboratories in this case are lost in the Pacific.
Spaces
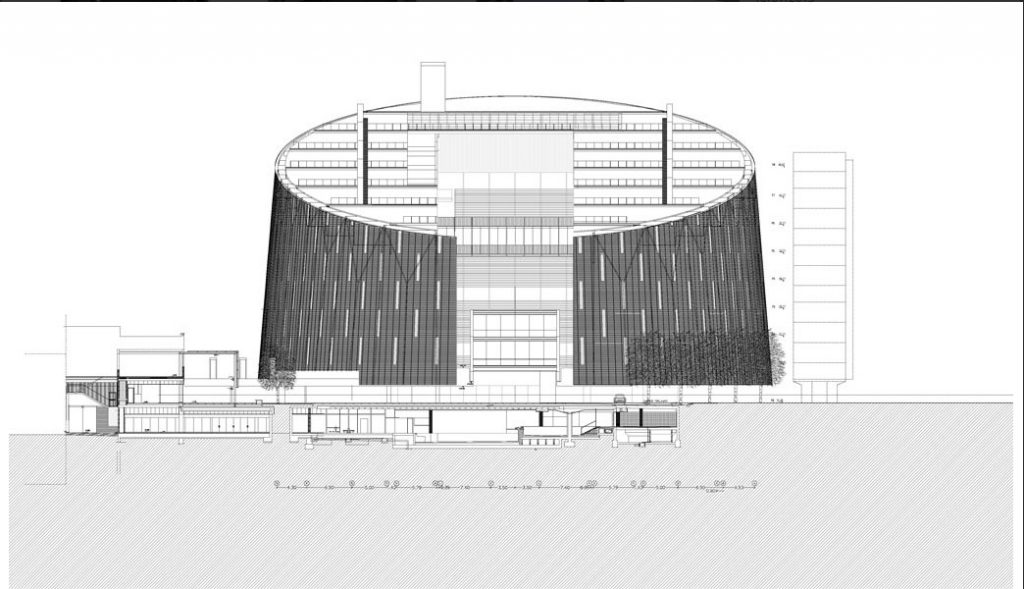
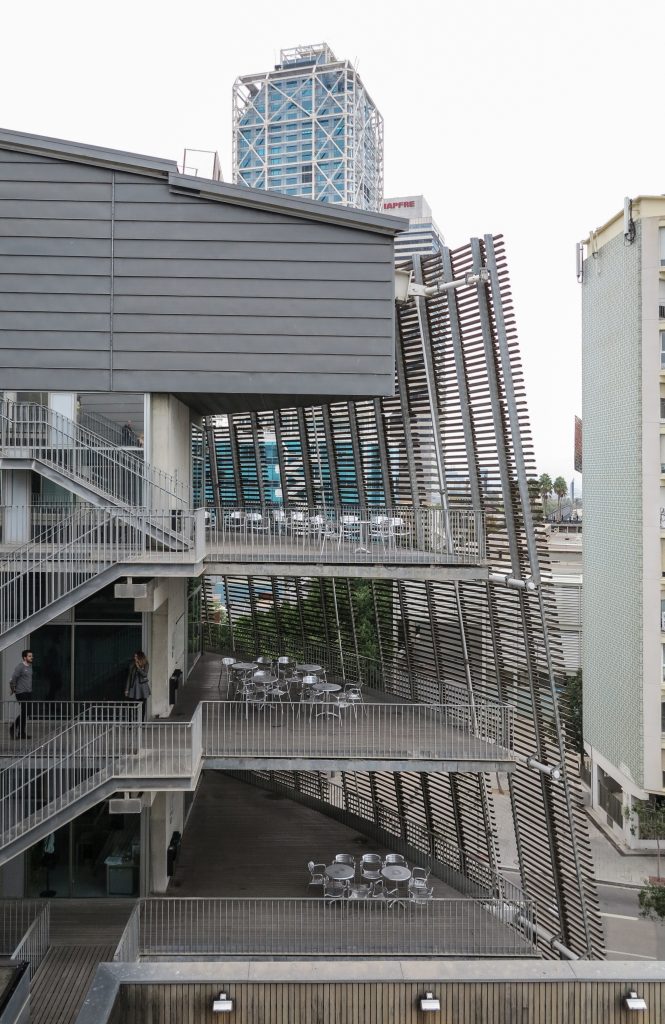
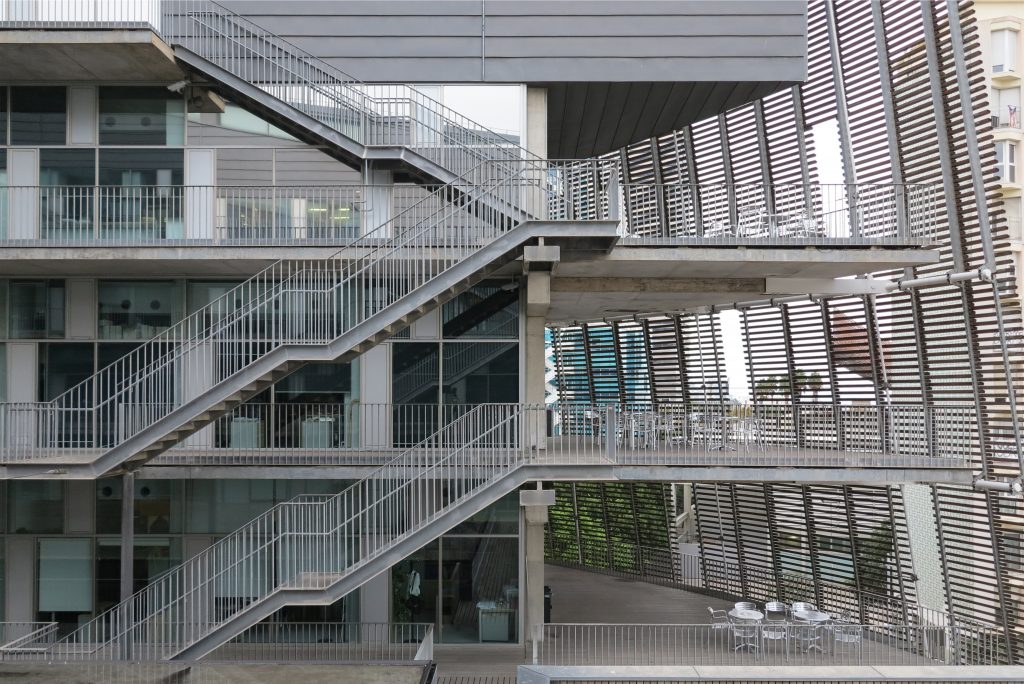
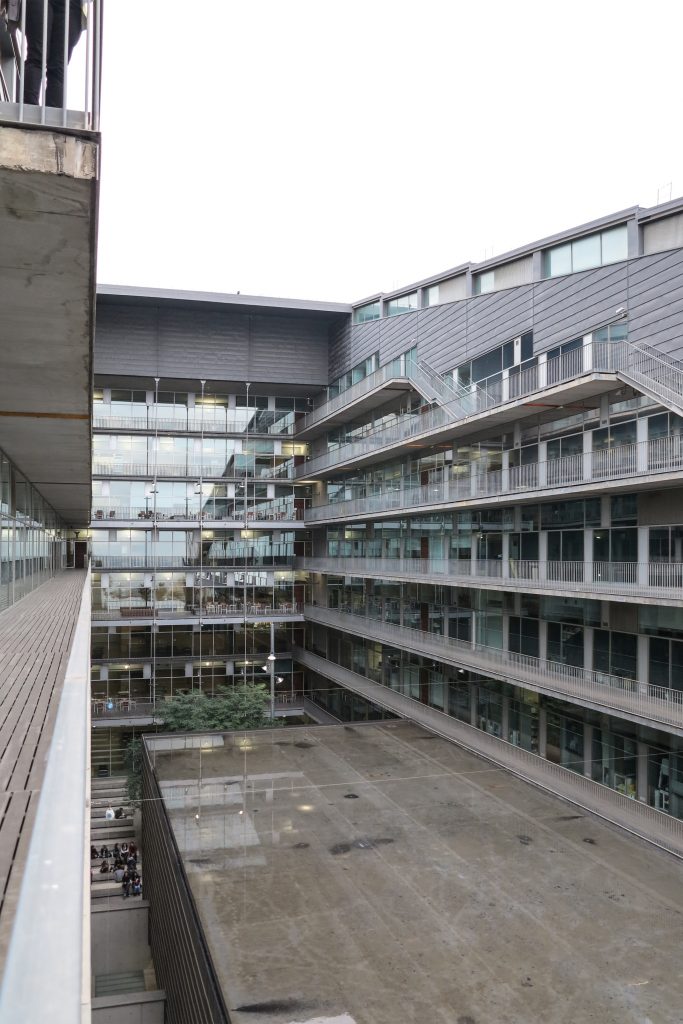
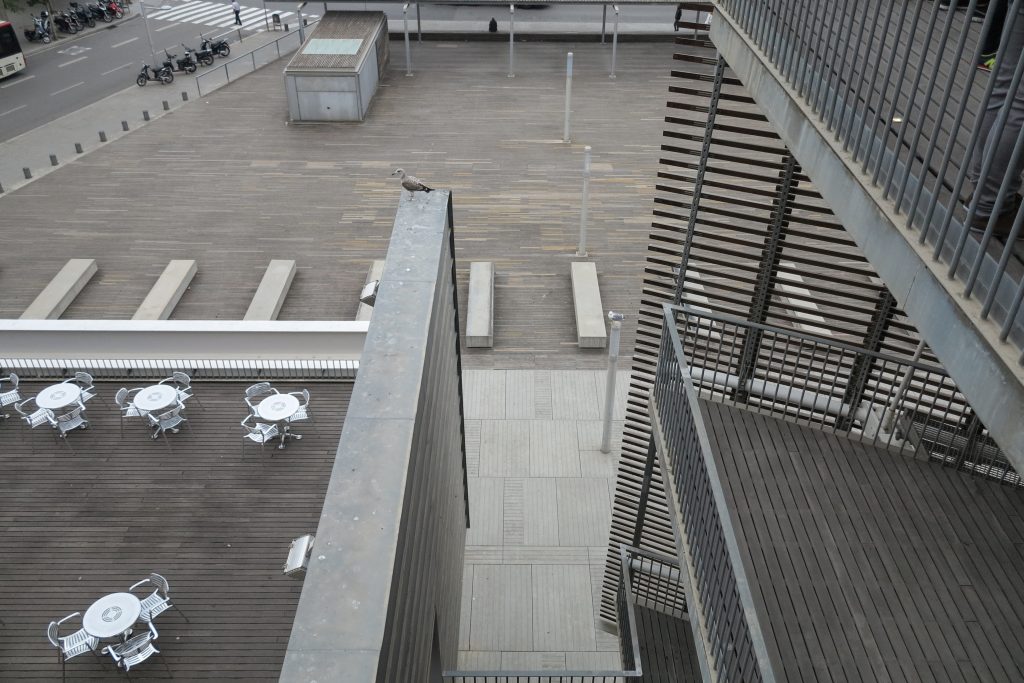
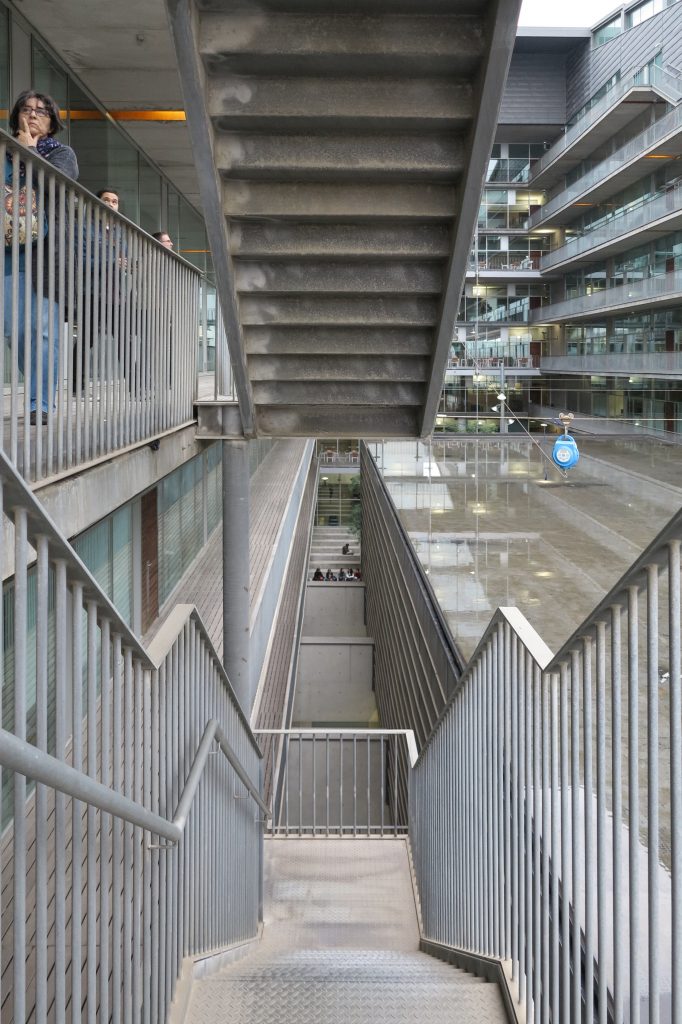
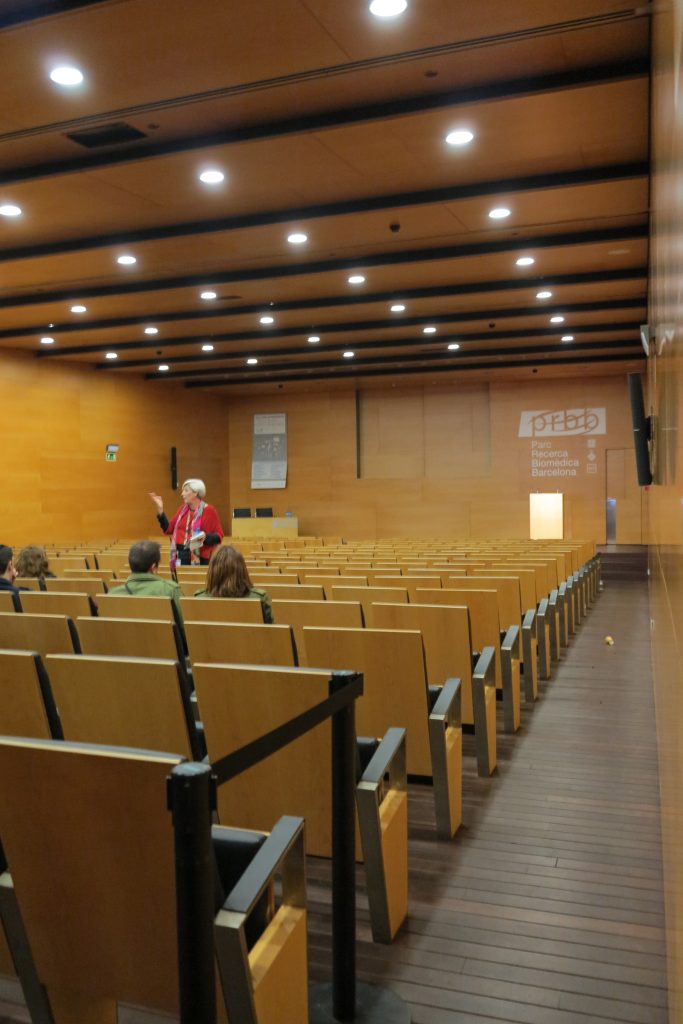
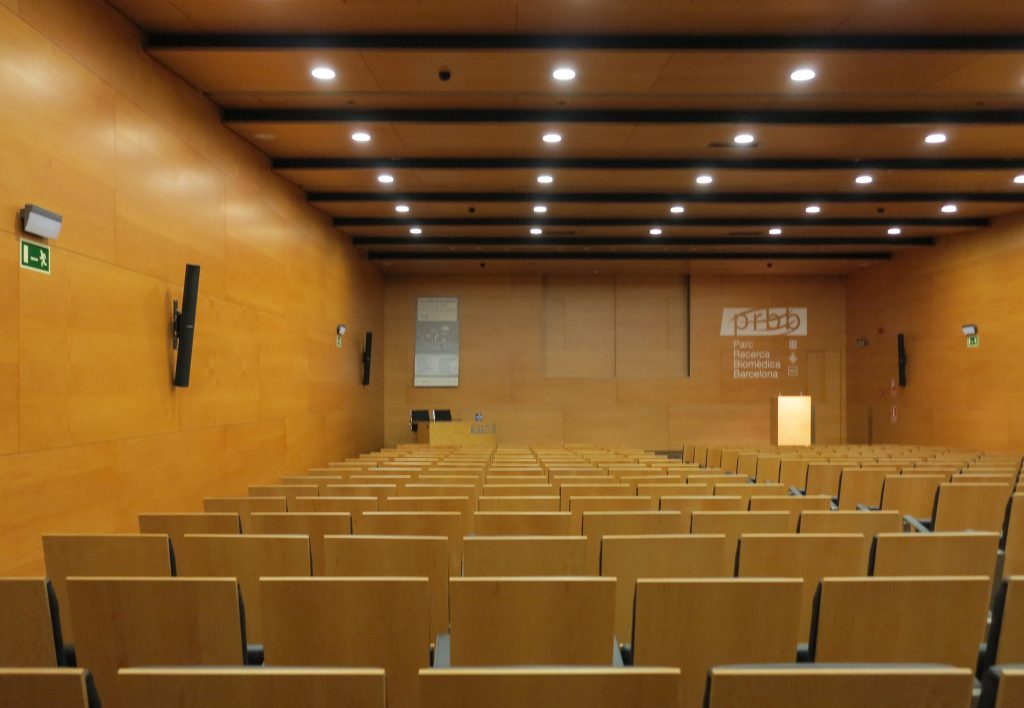
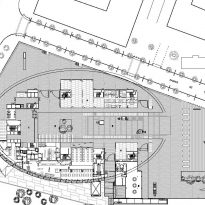
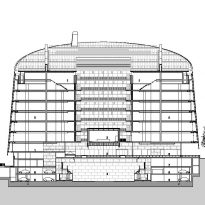
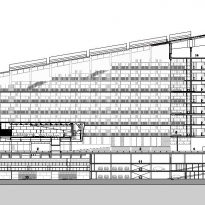
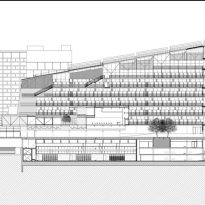
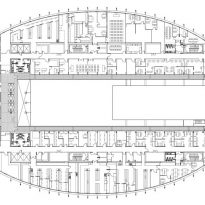
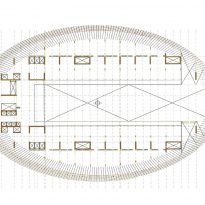
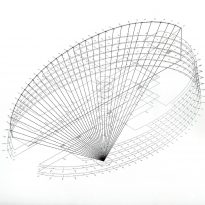
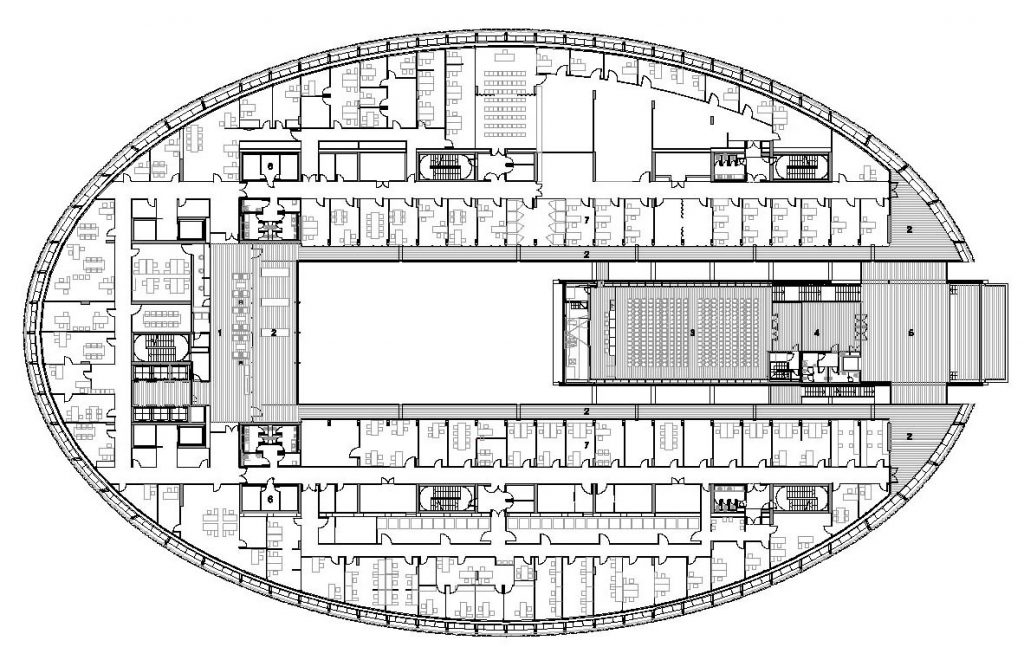
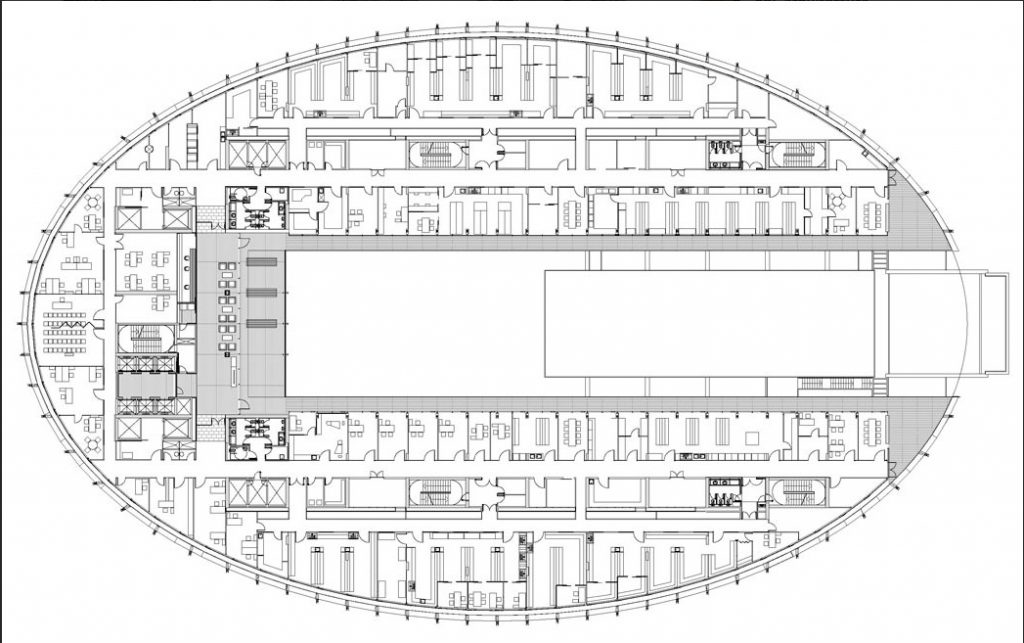
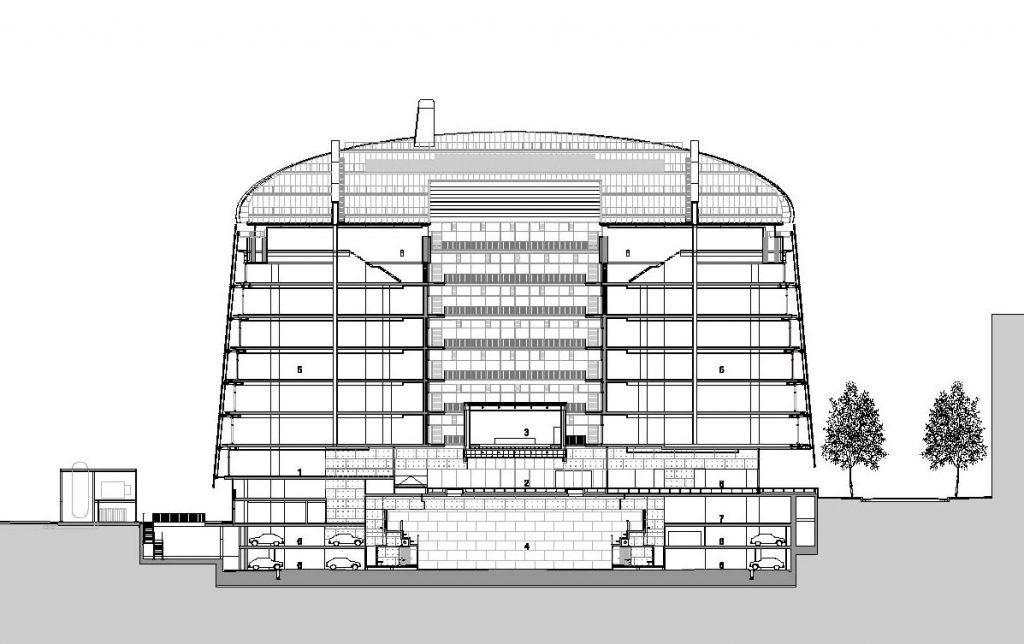
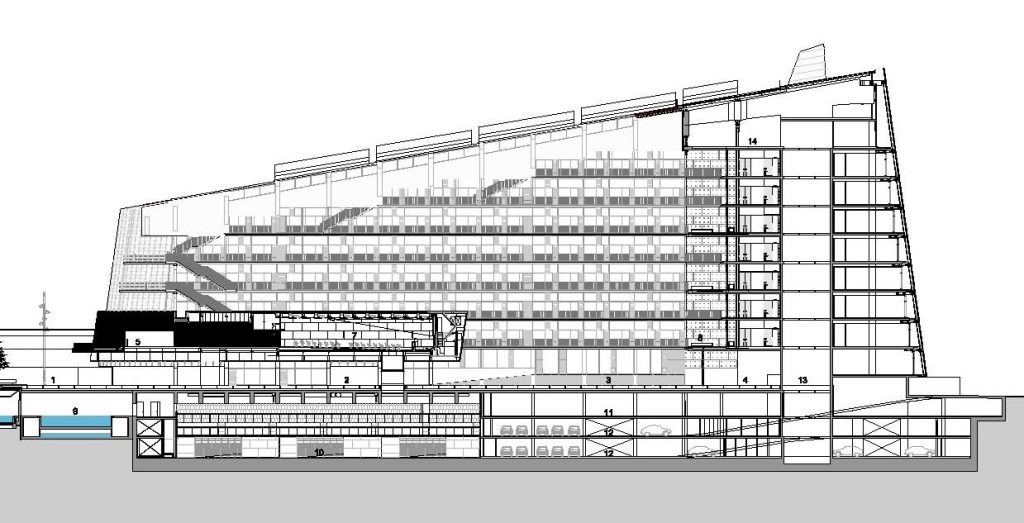
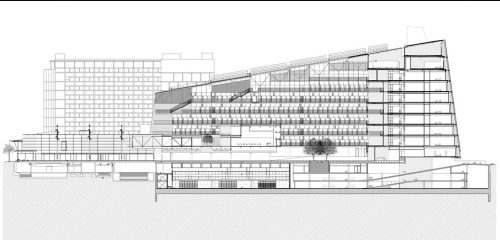
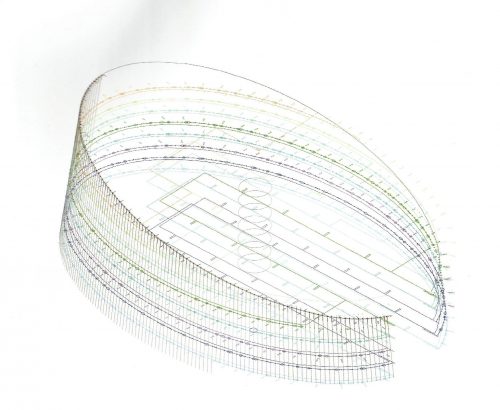
The building consists of three sectors or strata basically generated by the vacuum that public space on the ground floor left between the underground floors and hanging plants elliptical. Defined 4 floors above ground in the area facing the sea and 9 in the area of the coastal belt, all they organized in a U-shape around the central courtyard. As you gain height and because of its elliptical frustoconical surface are losing plants.
Stratum A
This layer below the bound O consists of three levels, two underground and one semi-subterranean, is the major structural connections with the environment and the basis on which rest the upper levels.
Talassotherapy Center: with irregular spaces that only seek to consolidate site geometry, the facility houses a thalassotherapy center, located under the Public Square giving access to the Biomedical Center and connected to the beach by a tunnel that passes under the promenade. The center offers swimming pools and aquatic facilities.

Sports Center : the sports center occupies three underground levels and functions as a single unit with the thalassotherapy center. Its facilities receive natural light through large skylights and connection to the center is established through a large window in the entrance area between the two spaces.
The facilities have 3 basketball courts and two side bleachers for 300 people, with their toilets and changing rooms. Electrical and energy facilities of sports are independent Research Park.
Dock: a ramp for cars gives access to the basement where the focal point of providing all facility is located. This ramp is shared with the nearby Hospital del Mar. In the spring loading and unloading the goods to be deposited in Annexes stores and provides access to level -1 it is received.
Level -1: at this level are a cyclotron facilities belonging to the Institute for Advanced Technology (IAT) and used for diagnostics and pharmaceutical and clinical research. This cyclotron is the engine of the facilities, is confined in a concrete bunker.
It also has a radio room pharmacy directly related to the Hospital del Mar, a CT scanner and vivarium where guinea pigs are available for numerous investigations, on the north side connected with the Hospital del Mar.
Level -2 and -3: in the last two underground levels of power and water supply facilities are located. Around the space occupied by the sports center it offers a large parking lot, shared with the hospital, with 350 seats.
Stratum B

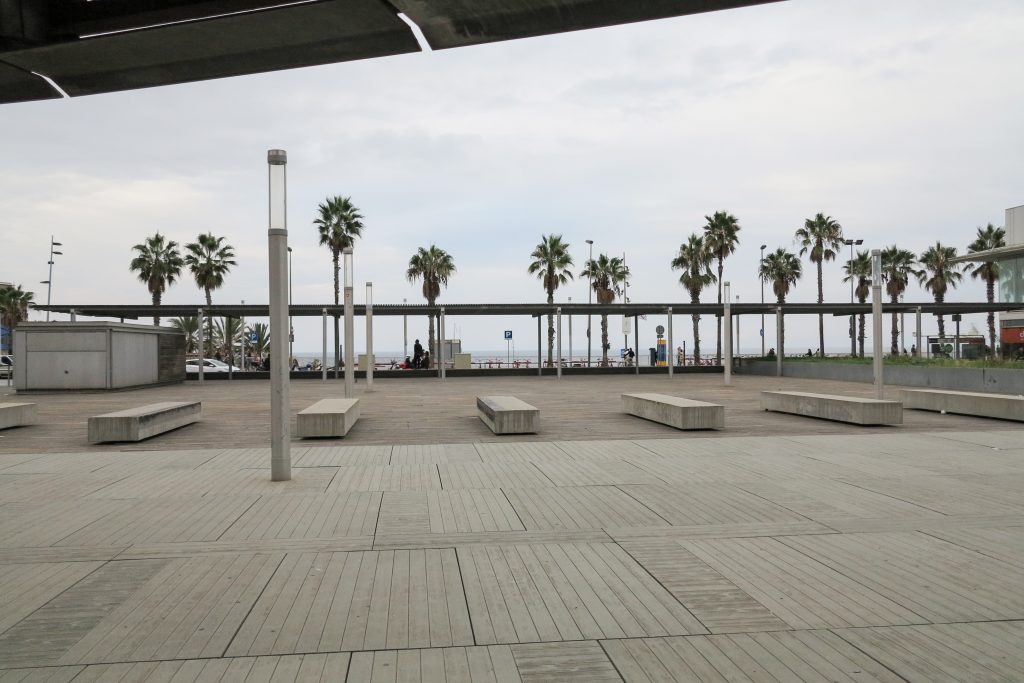
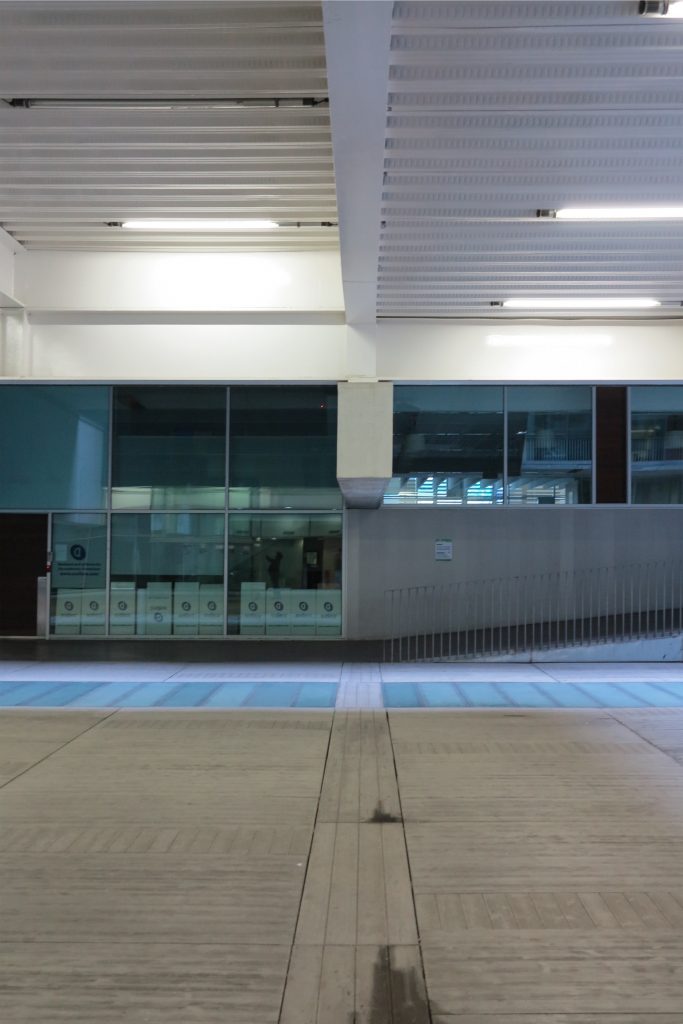
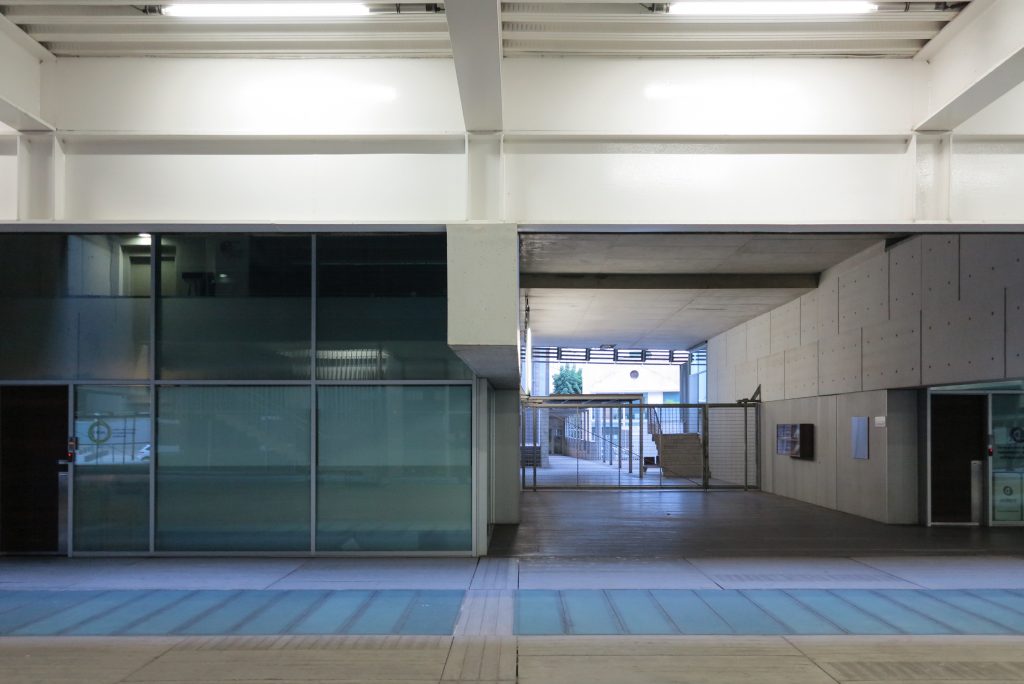
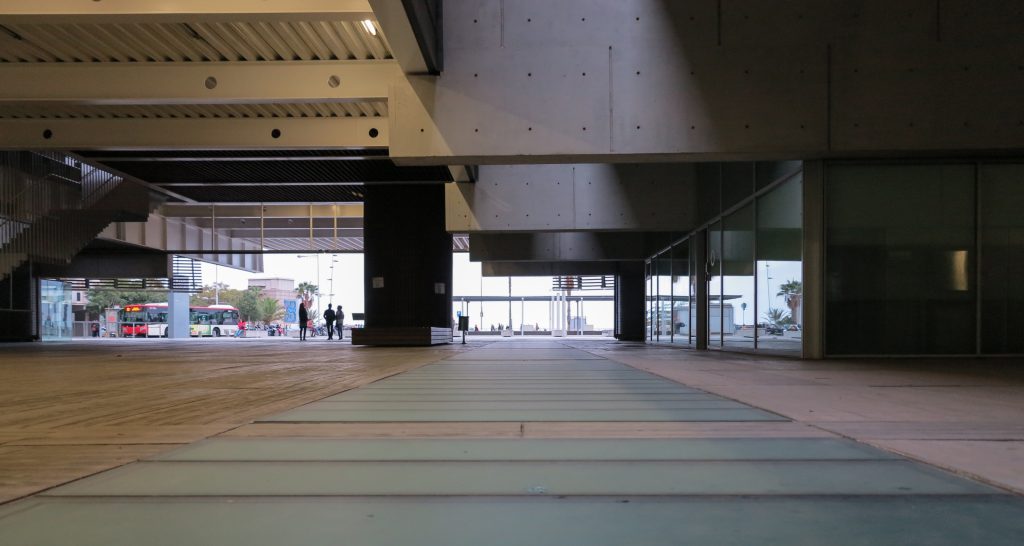
The layer B is the large horizontal platform located at level 0 ranging from the promenade to the coastal belt. This great urban space connects all the spaces and surrounding streets, serving both support for the rest of the building, and gathering all access to the facilities, including the Hospital de Mar.
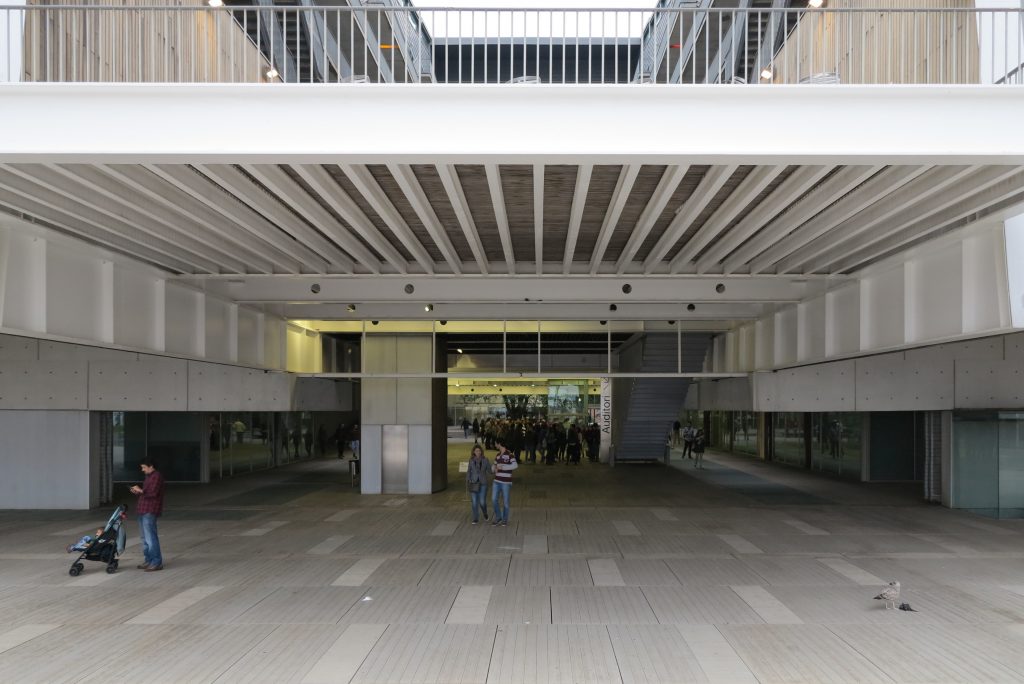
Touching the Paseo Marítim and near the sea a large square pool that holds large lobby to the building, characterized by a large parallel pergola walk and the buildings surrounding it, in which rivers different activities, external consultations performed unfolds hospital, access to the fitness center, a bar, a restaurant, newsstand or commercial premises.
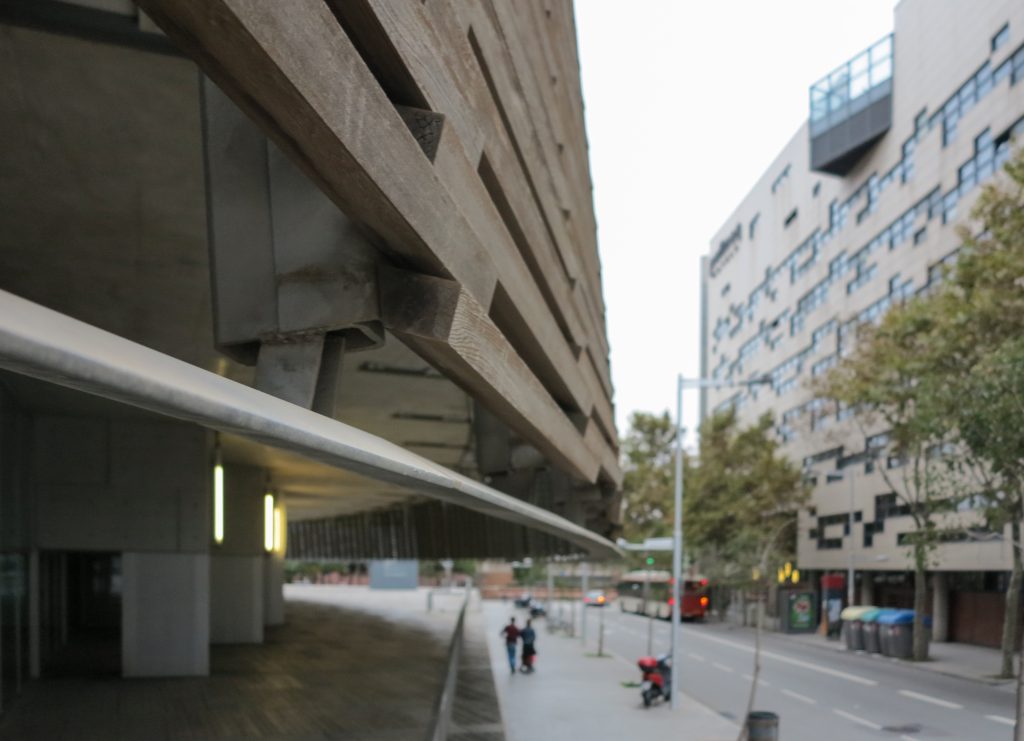
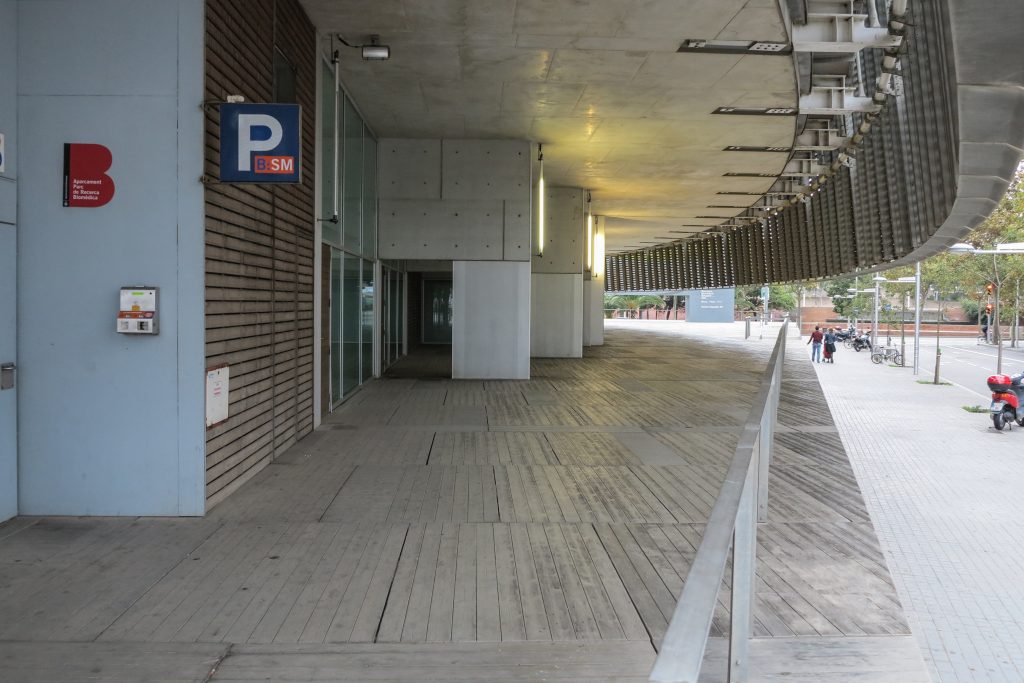
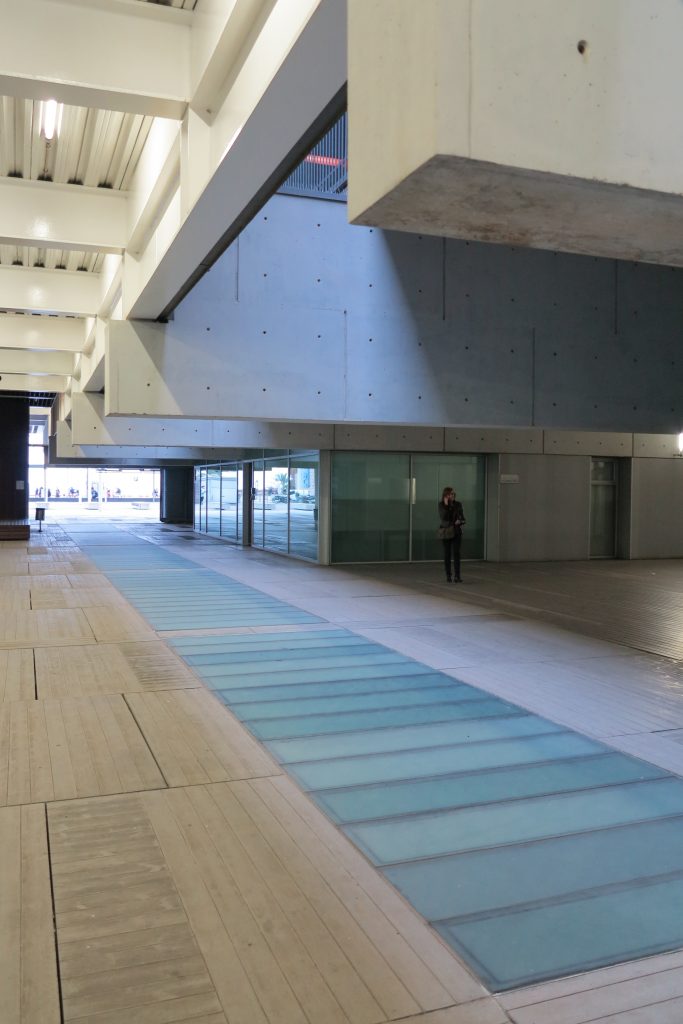
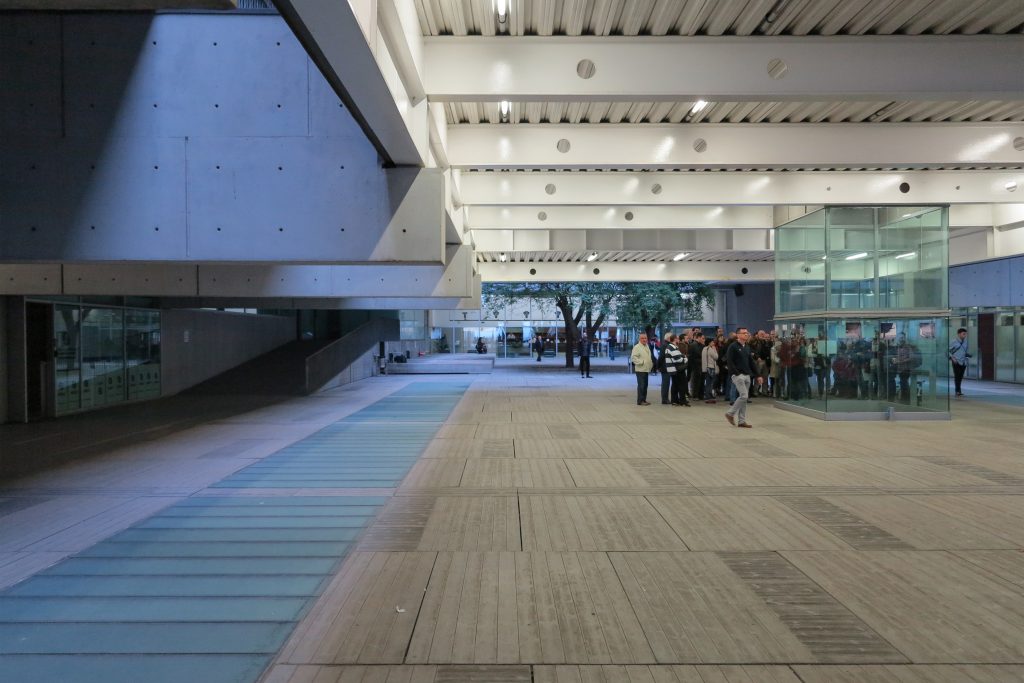
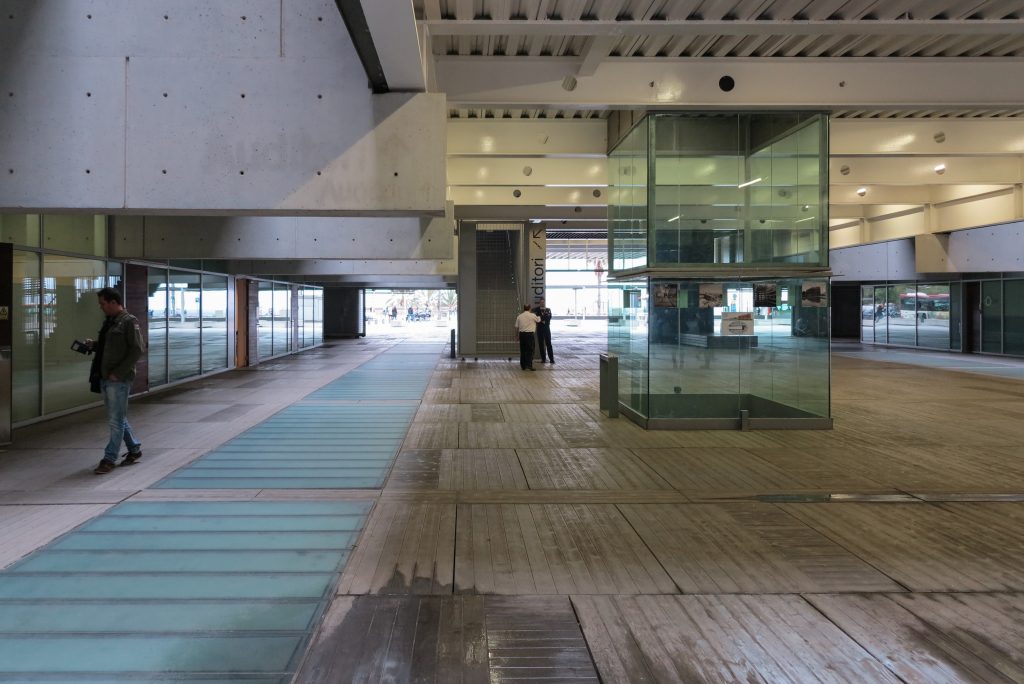
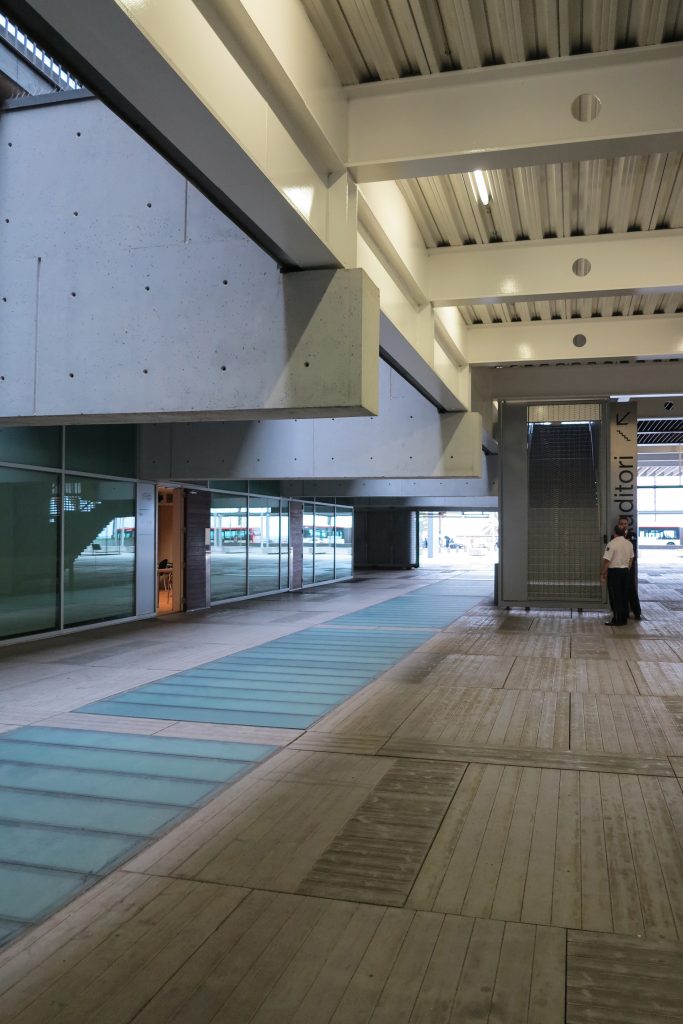
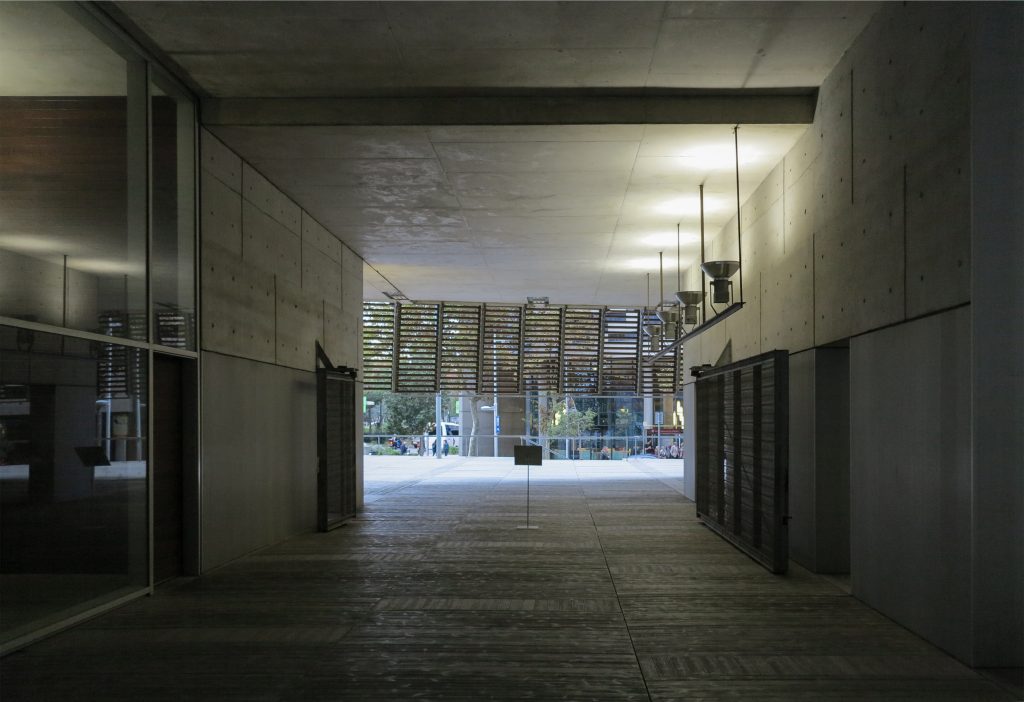
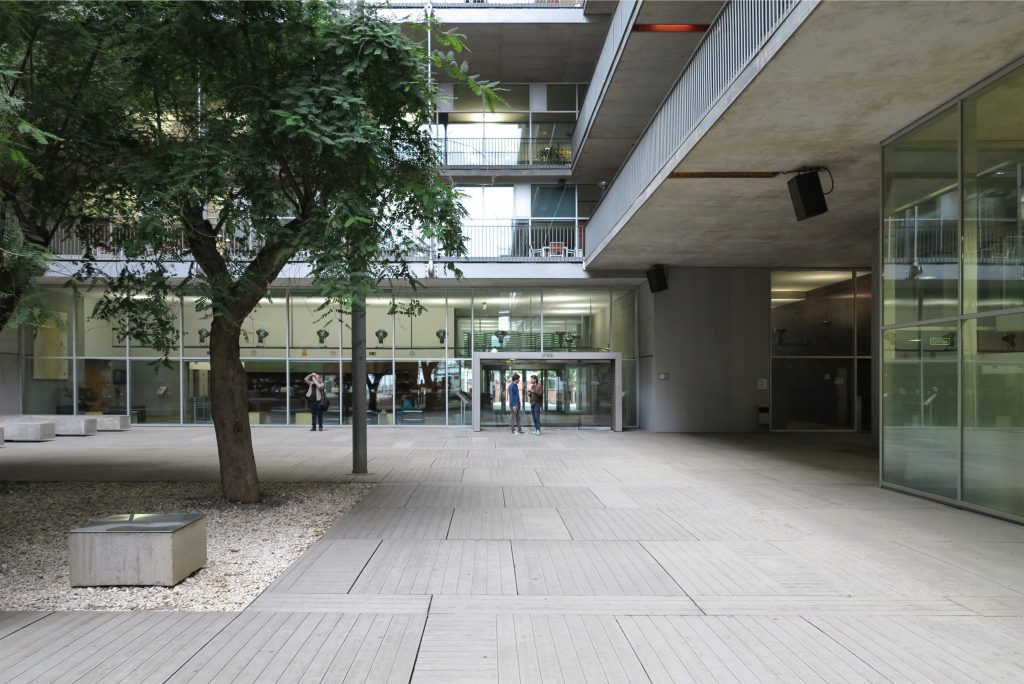
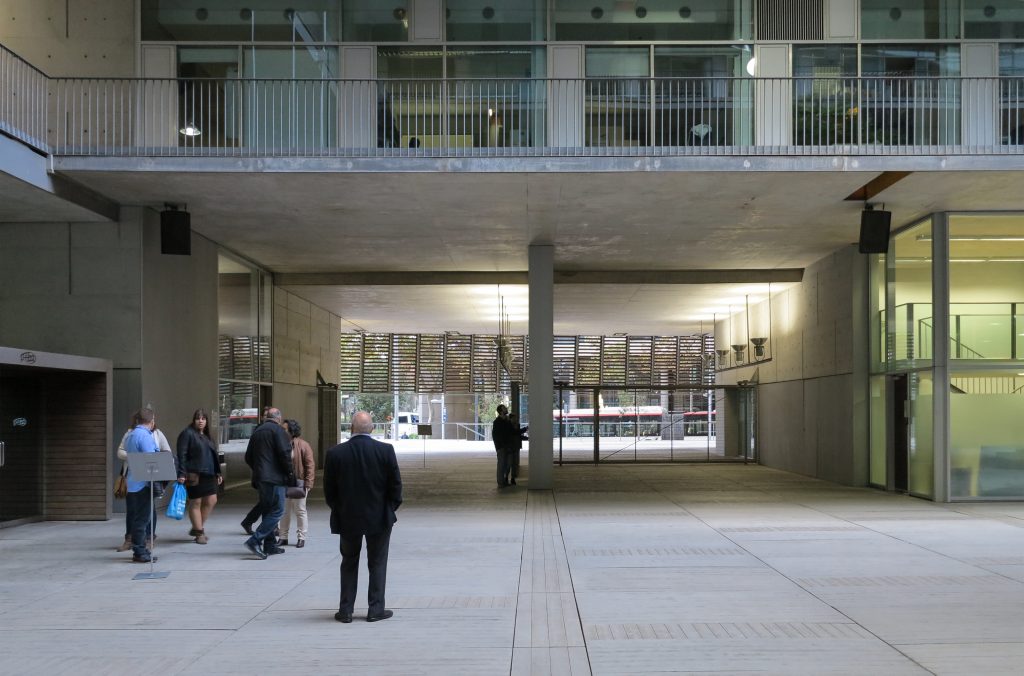
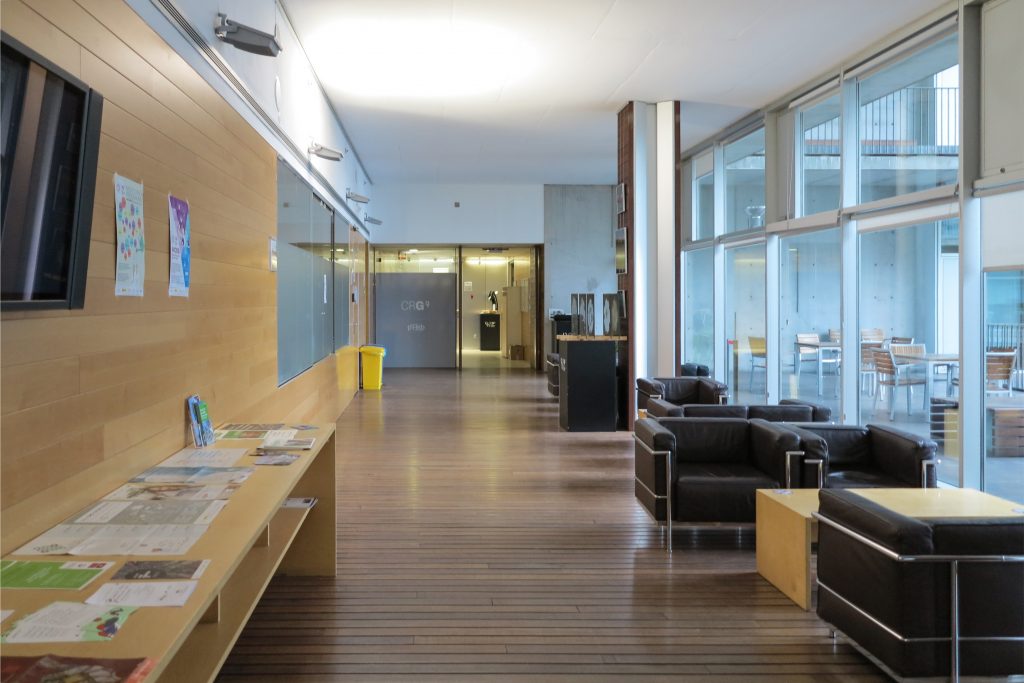
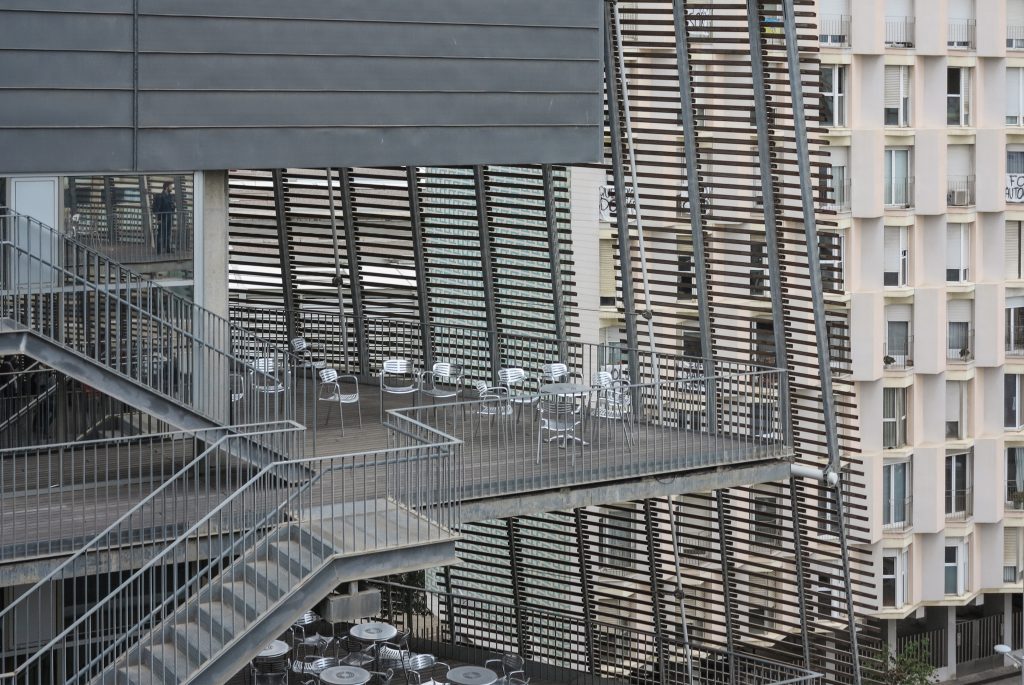
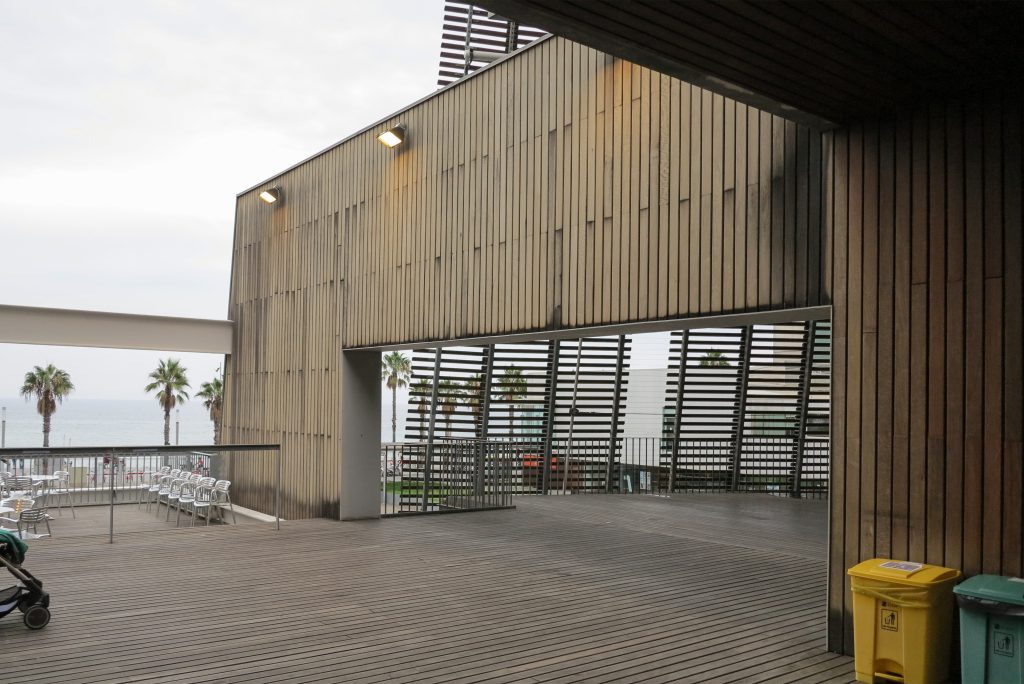
Since this plant is made one of the main entrances to the Research Center under the space defined by the outer foyer of the auditorium, built with a floor of wooden slats that function as a kind of canopy that extends inward under the forged the auditorium. On the sides of the entrance courtyard premises they are arranged. Then the cloister courtyard is the central space of the building and gives access to the main hall, the latter can also be accessed from the coastal belt and from the side, down the street Trelawiny appears. Closing this courtyard on the west side and raised 1.50m above ground, there is a restaurant for researchers.
Stratum C

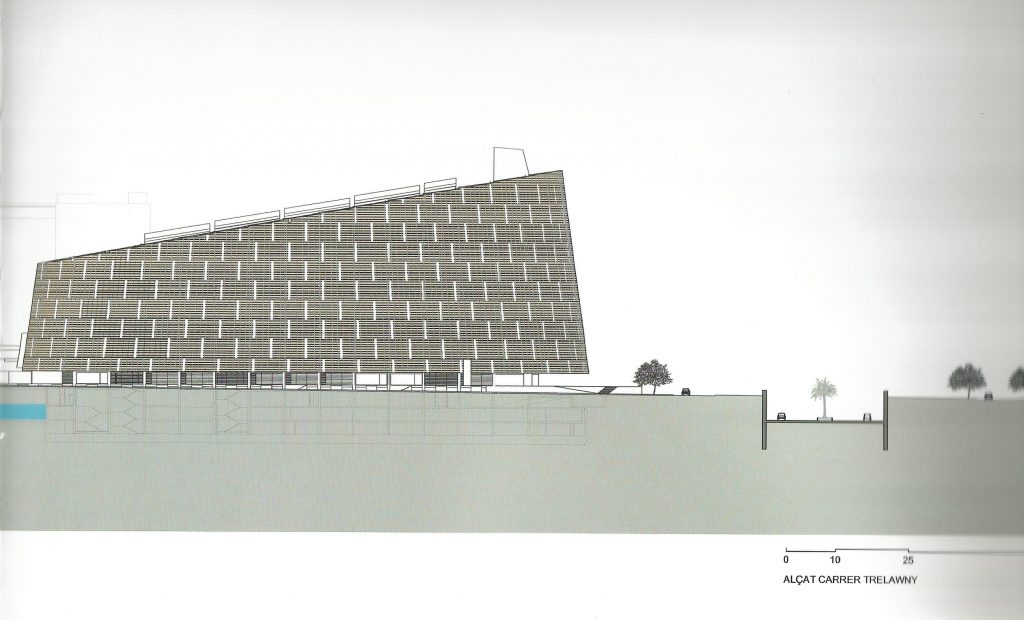
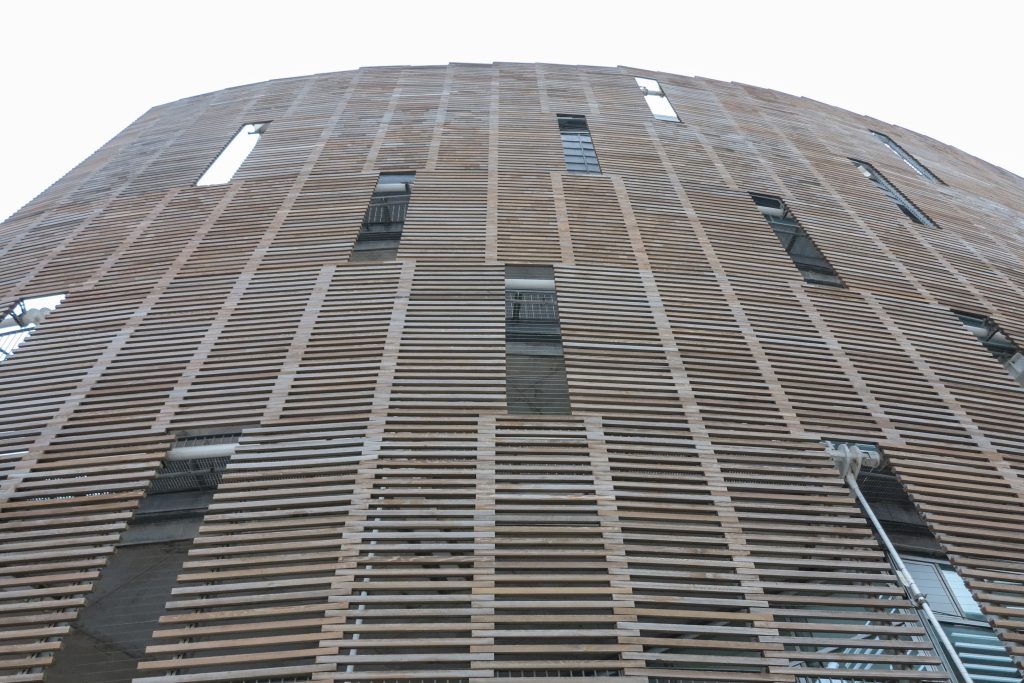
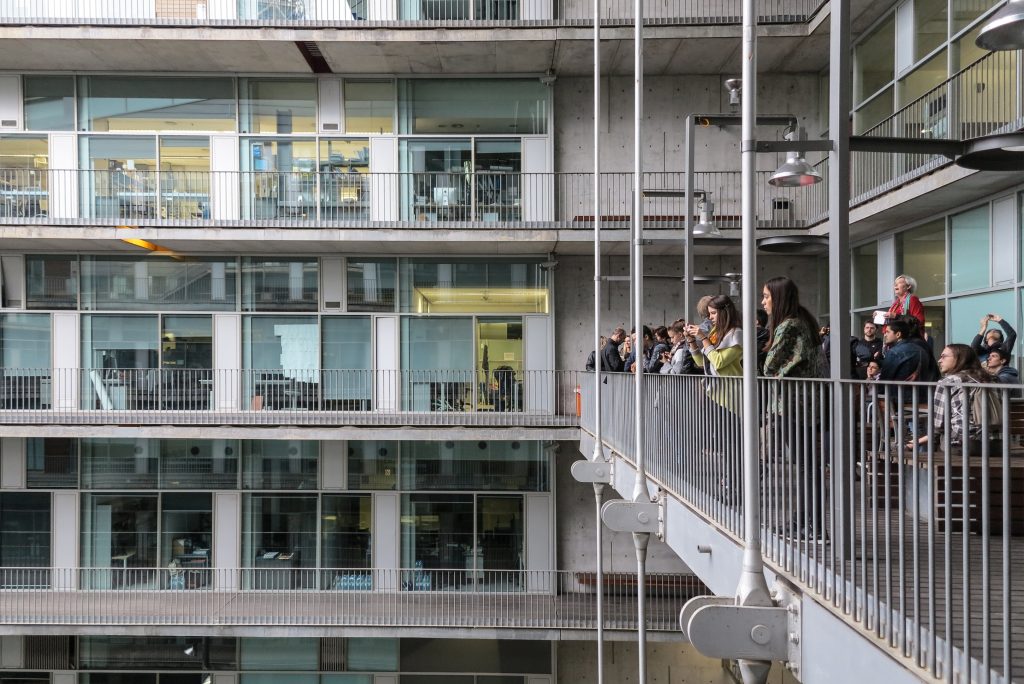
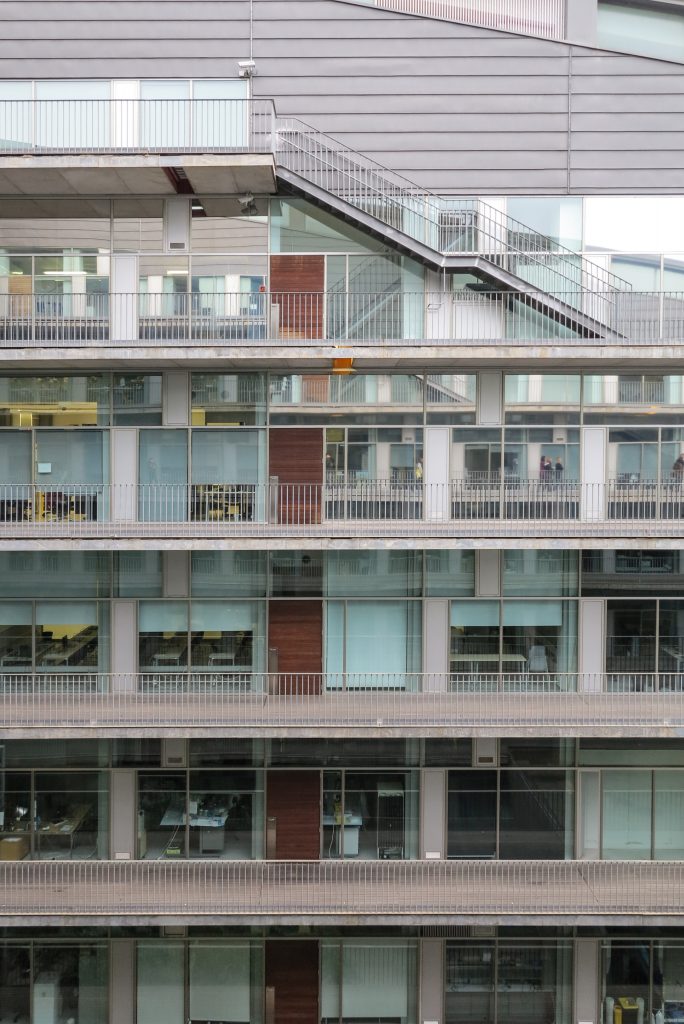
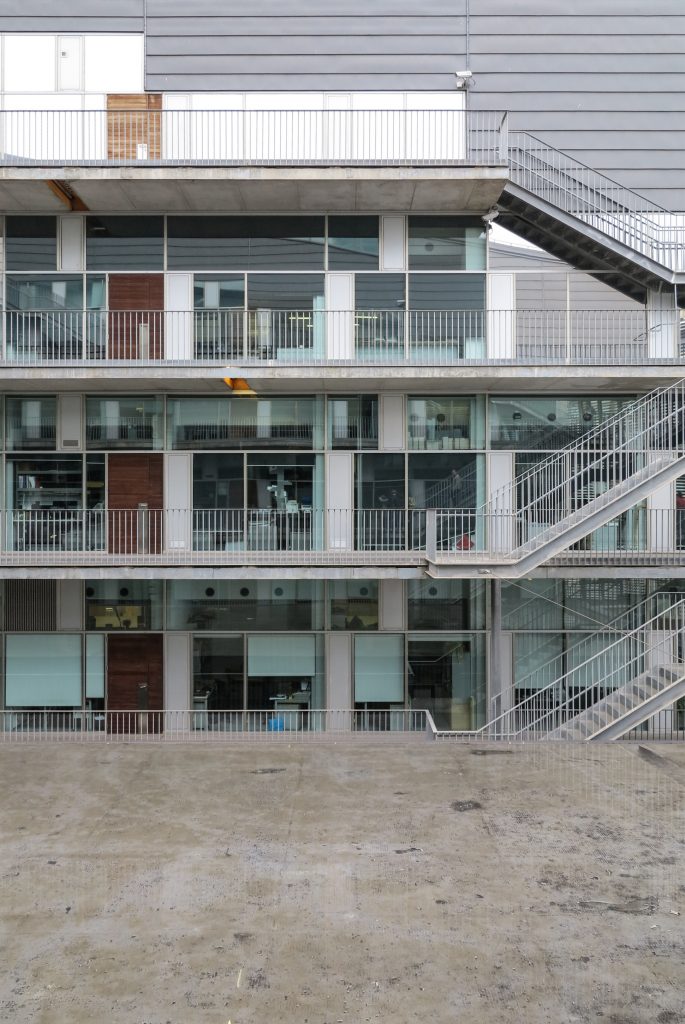
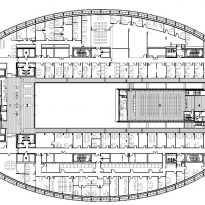
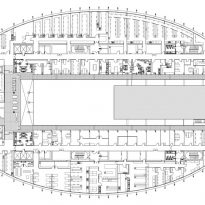
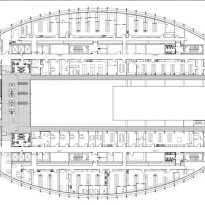
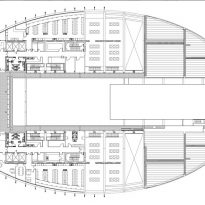
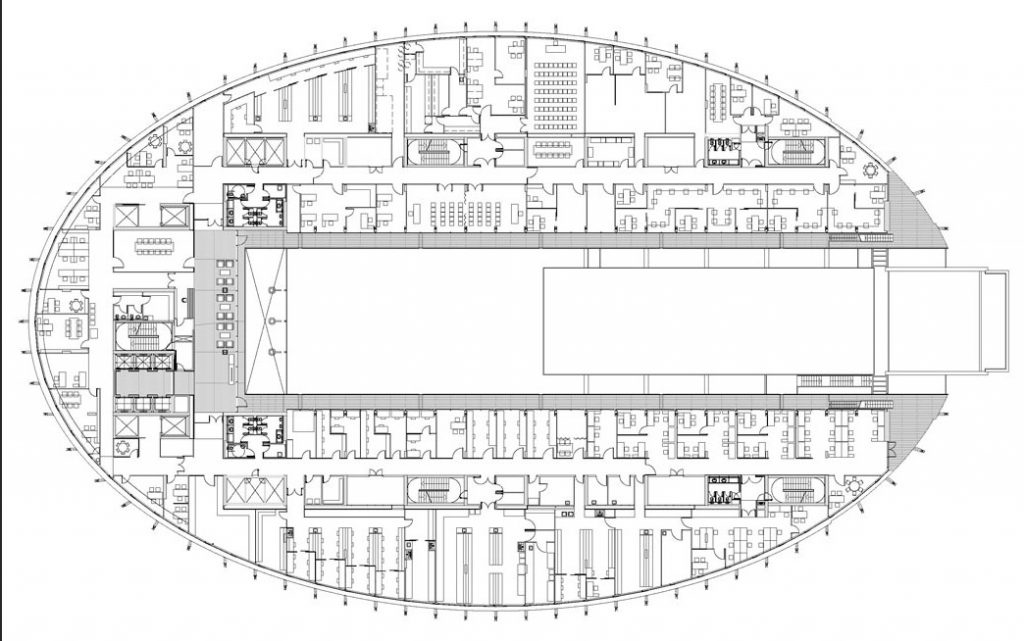
This layer corresponds to the most visible and recognizable building Biomedical Research Center part. A frustoconical building with glass facade and suspended wood on the ground floor. Volumetrically this trunk elliptical cone is cut by an inclined plane defined by the cover and in which research laboratories and offices are located. This trunk is hollowed in the middle, along the north-south axis, to get the largest area of facade in relation to the compact volume, only partly occupied, up to the first floor, a volume that moves slightly towards the square and that houses the hall. Access to each floor are made through a large hall located on the south side of the courtyard that extends outward by large terraces overlooking the sea.
On the top floor you can only take advantage of a small area of the ellipse, the north quadrant, which has been designed to facilities for hot and cold air conditioning in the building and technical services water. The sloping roof of zinc terminates the development of the building and it vents laboratories, car parks and the flues of the boilers were located.
Structure
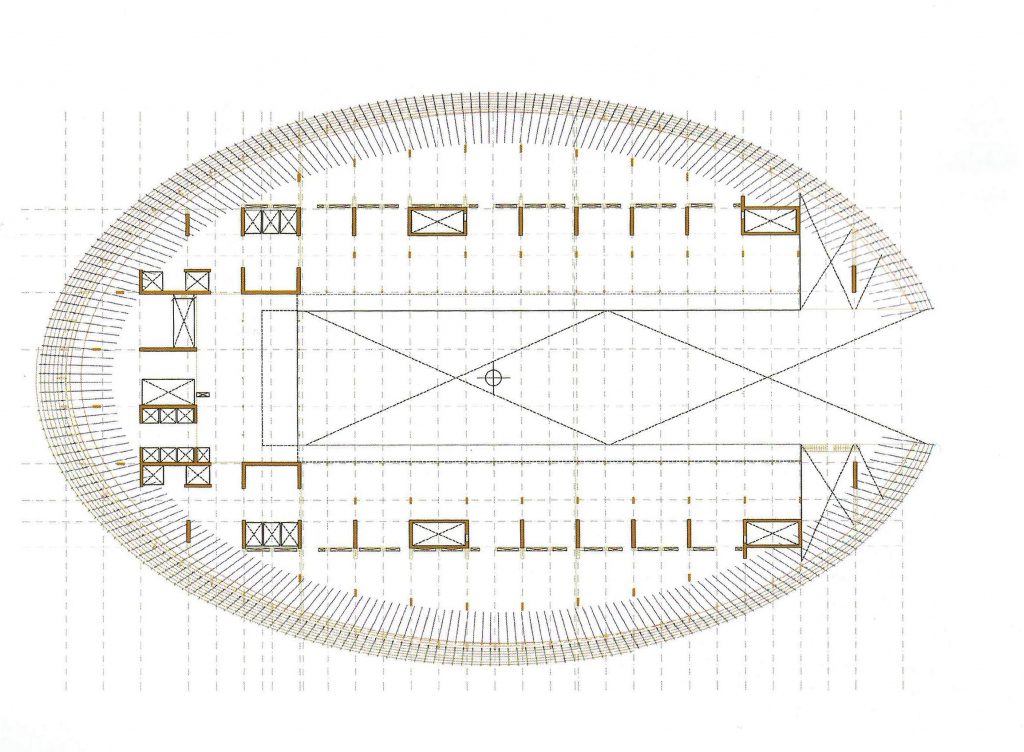
After studies and taking into account three factors essential conditions for the choice of structural system to choose:
- Architectural Will release supports the ground floor, to thereby obtain as transparent as possible surface for public use.
- Geometries in different areas basements array of supports in orthogonal grid and body of the building above ground formed by concentric elliptical plants.
- Placing A sports court in the basement.
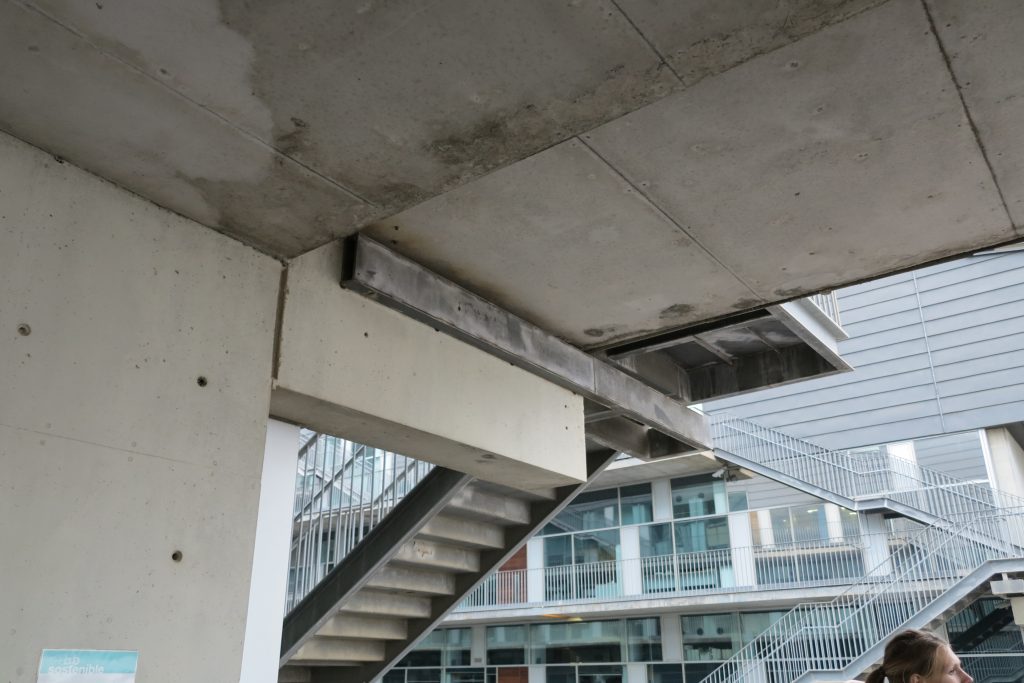
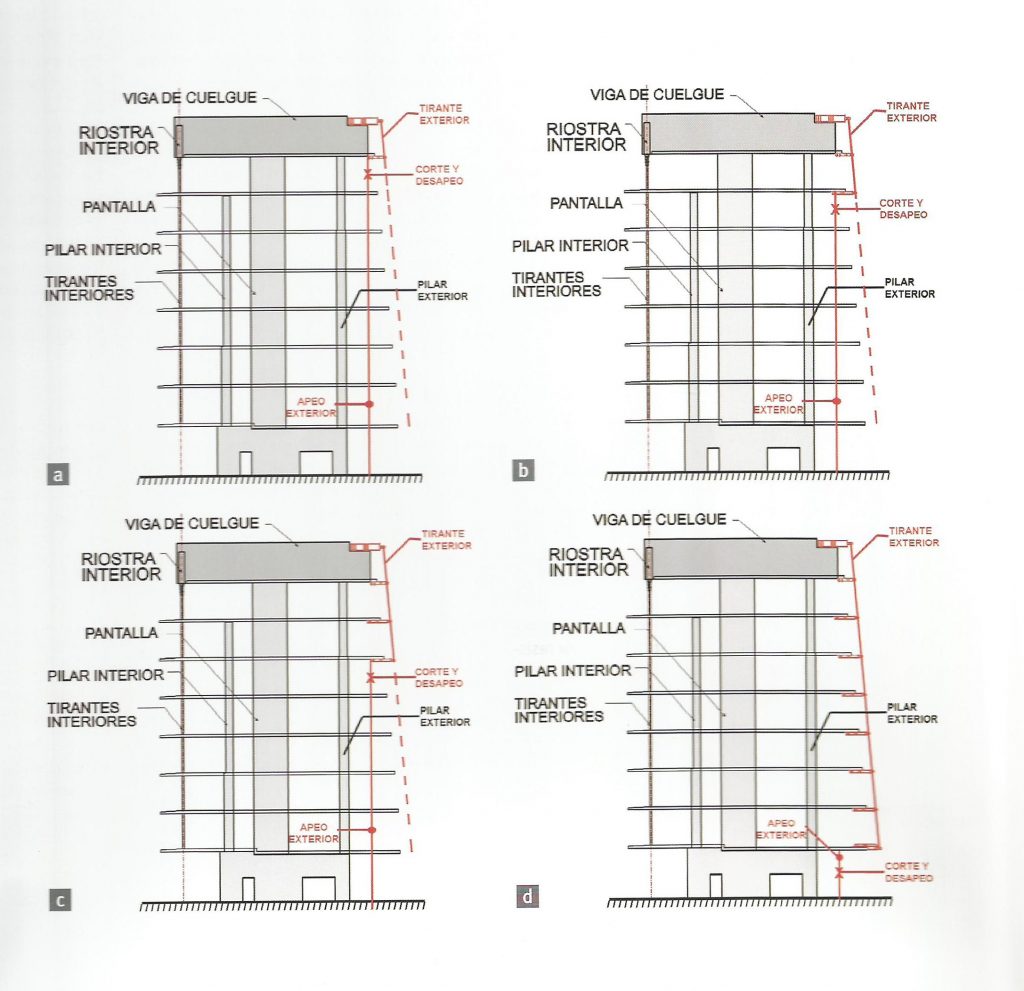
the project team opted for a system of hanging slabs supported by beams arranged under cover around the perimeter of the building and coinciding with the areas of facilities, offices double height and facades of the large inner courtyard.
To compensate loads hang, both external and internal, of different levels a rigid central core that matches circulation areas and whose reinforced concrete walls combined with the beams cover prestressed concrete was built HP-40 form a elevation shaped structural T.

Foundation
In the area of the basement the building occupies almost the entire solar presenting an almost constant level of 3 meters below the water table. At this level the subsoil has a granular consistency of sedimentary contribution from the sea with sand medium grain and low in limos that allows you to withstand the loads of the building. With these features we chose to build a continuous reinforced concrete slab of about 8.100m2 and 180cm thick reply to the thrust hydrostatic underpressure and distribute the pressure on the ground uniformly introducing matching piles with the areas of greatest load. These were designed by screen panels 60cm thick and 9m deep that follow the path of the main walls.
Containment perimeter
In order to make the foundation slab dry and below the water table it was necessary to raise a perimeter containment through screen panels 60cm thick 6m sunk below the slab and a drainage system to lower the water table within the perimeter. Previously a trench depth of 7.6m was dug and once finished a gravel layer 20 cm spread then proceeding to placing a system of drainage pipes connected to pumping wells.
Decks
The floors of the 3 underground floors have solid slabs of 30cm thick, except for the areas of loading docks or heavy traffic where the thickness varies between 32-35cm. In the 9 floors raised above ground level the slab thickness is 28cm.
The symmetrical building above ground with respect to the major axis of the ellipse is not in the perpendicular direction by presenting a cut by a plane inclined 10.5º that generates an increasing height from the sea side, with 4 floors above ground, to the opposed to 9 floors. All of them create a large central courtyard 17.6x86m.
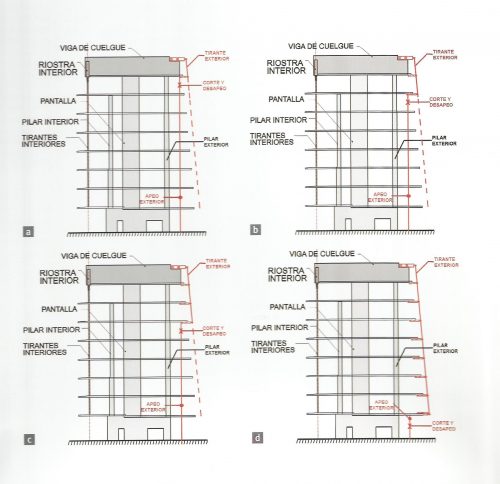

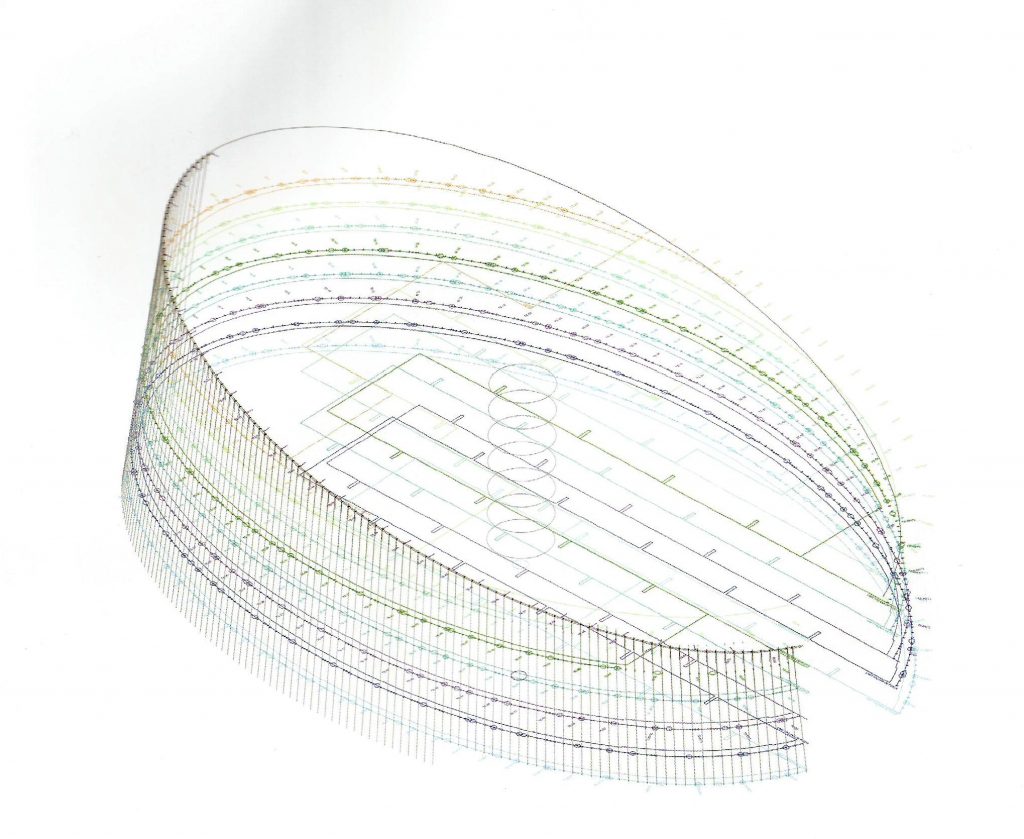
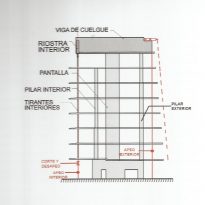
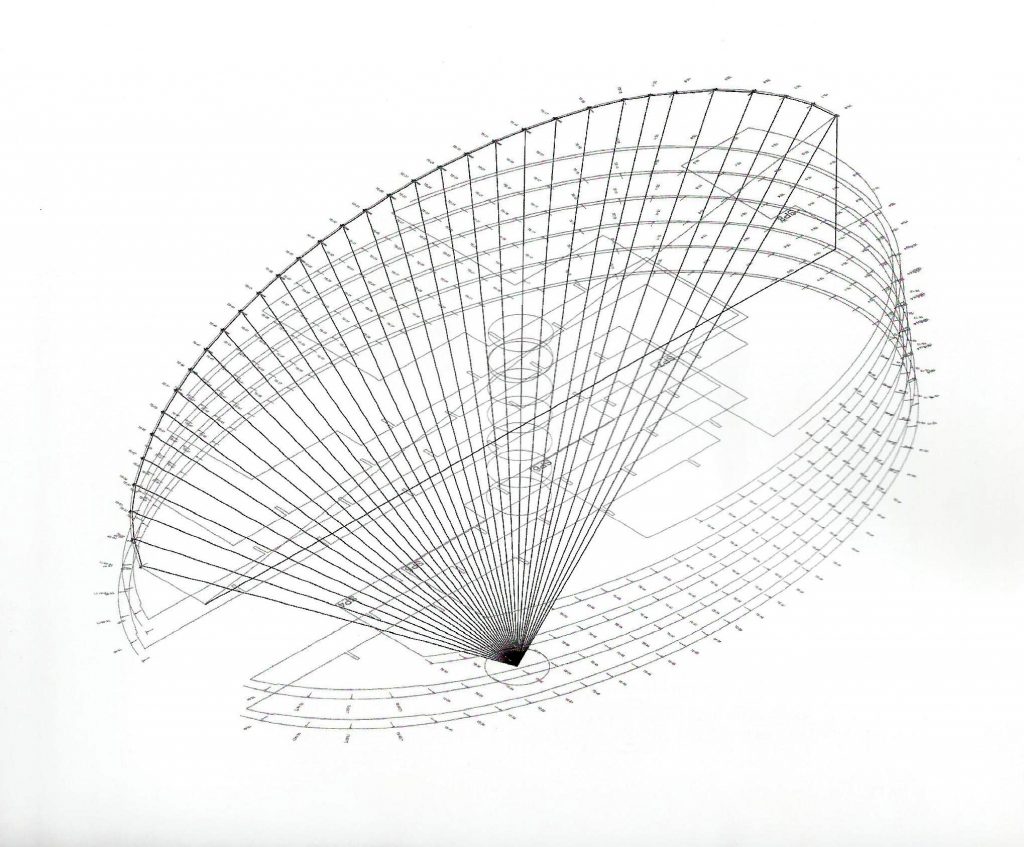
The outer structure of the building hanging out with 69 suspenders with varying inclinations between 4.8 ° and 8 articulated placed every 3.6m plant to plant and attached to the upper structure hanging by a hinge to the upper lugs.
The forged inner structure is divided into two sectors. In the first hangs from the inside to the cantilevered pillar 19 by inner straps on each side, at a distance of 3.6m also.
Constructive details
Flexibility
For a building dedicated to science and research it is essential to the possibility of changes since their use is complex and must be adapted to some progress in constant progress. In this case that adaptability is made possible by the use of flexible structures from a spatial and mechanically.
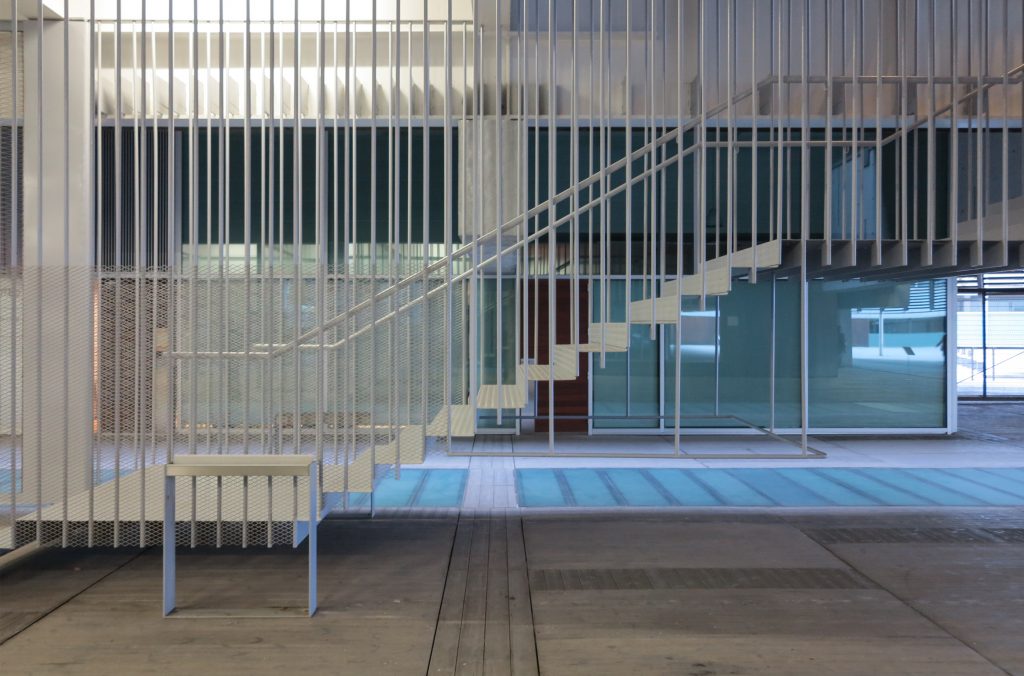
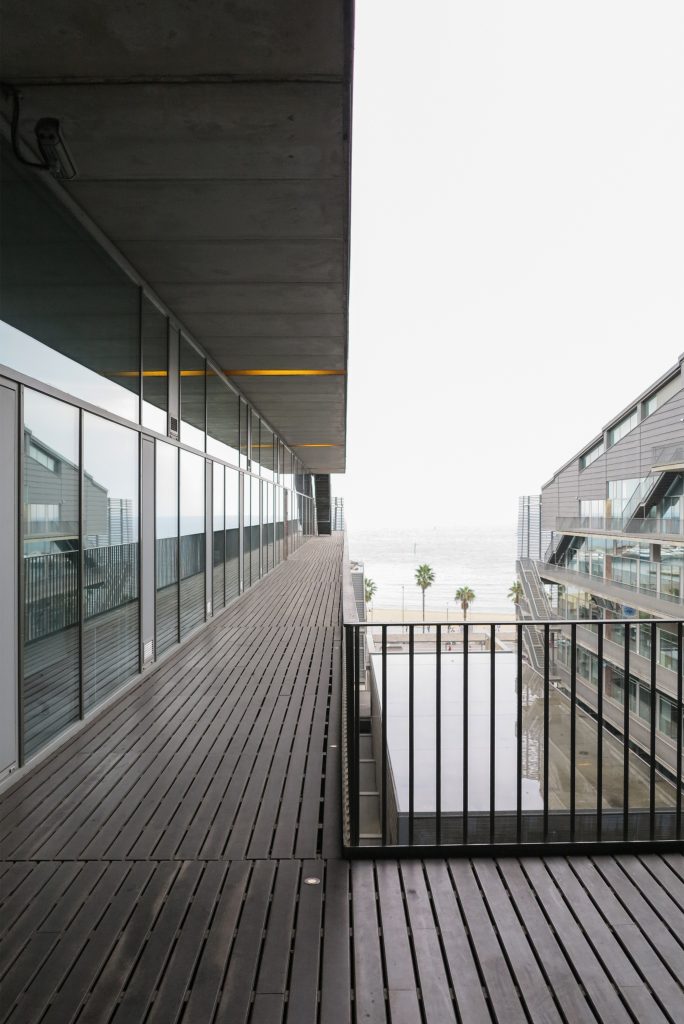
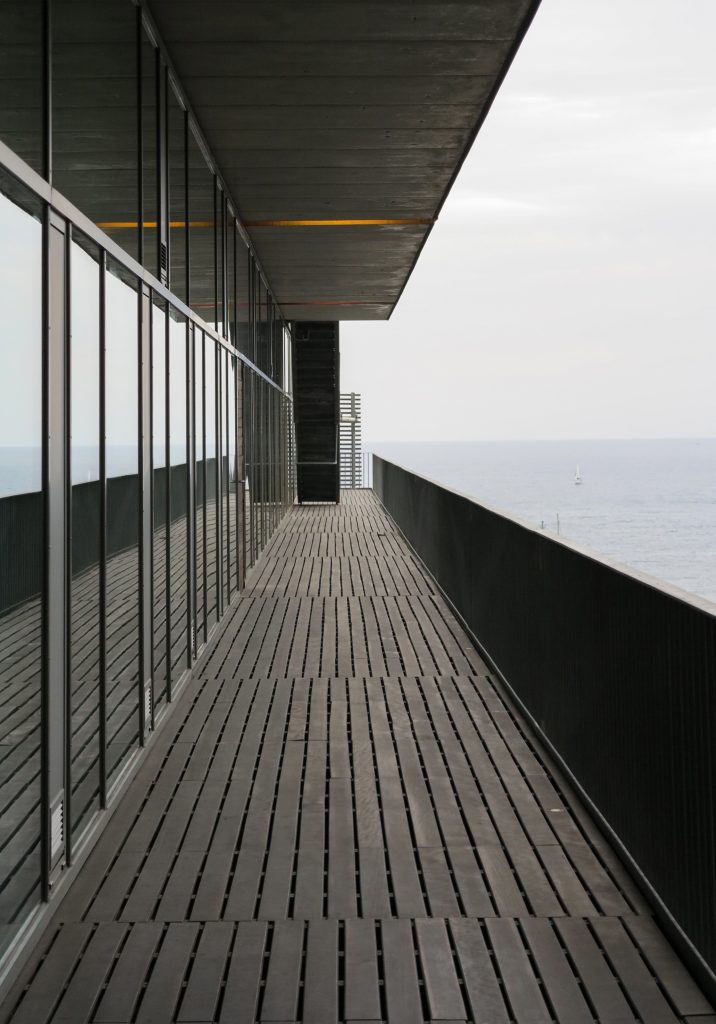
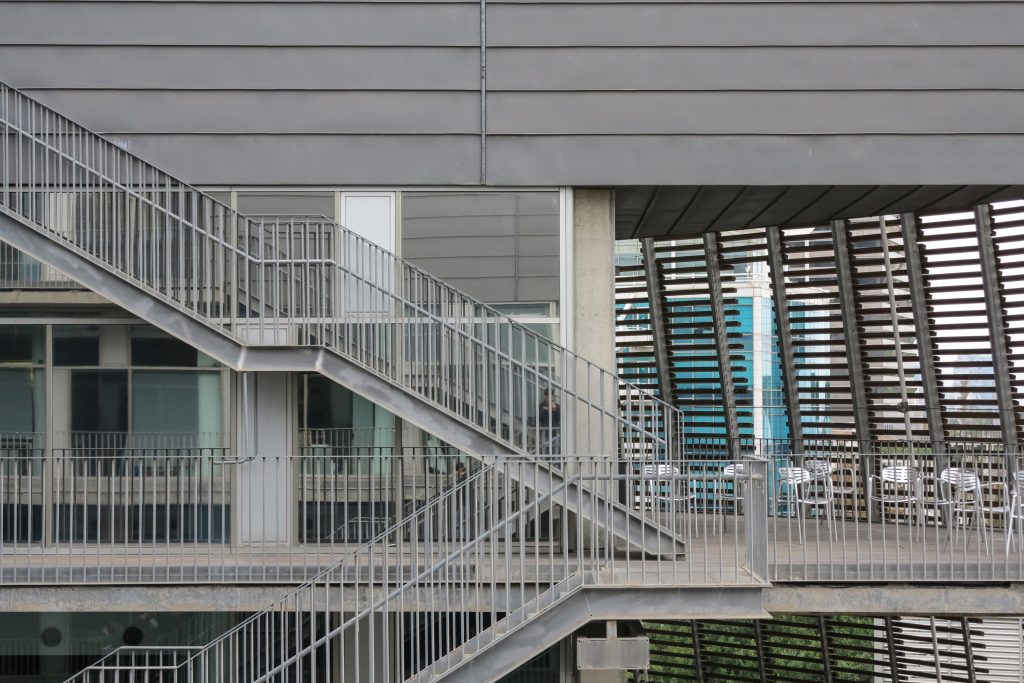
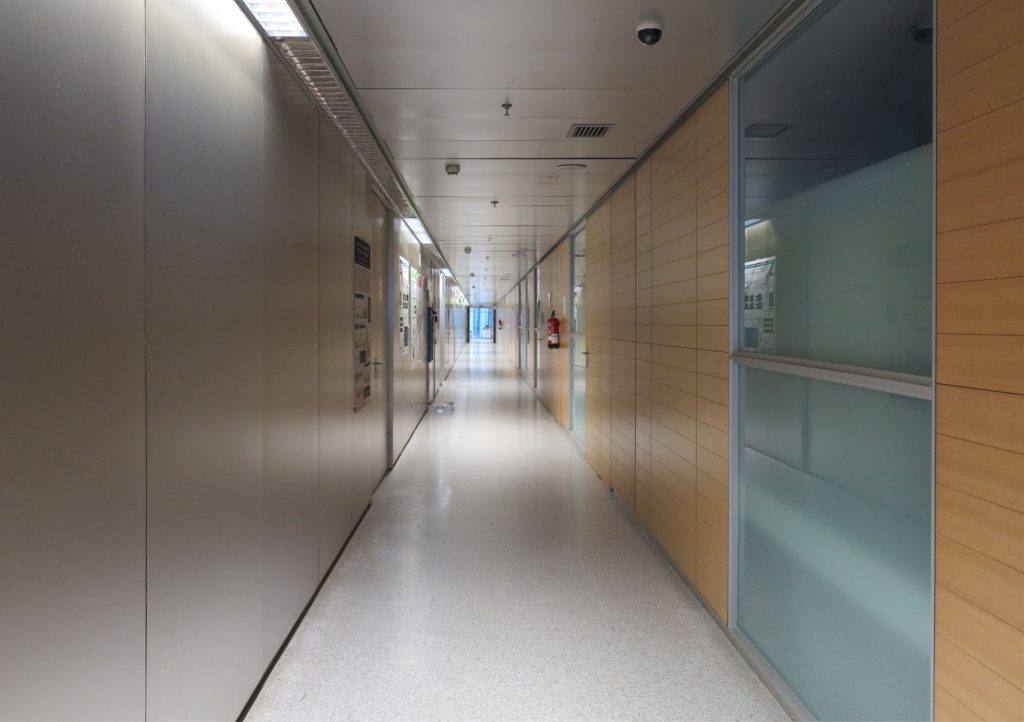
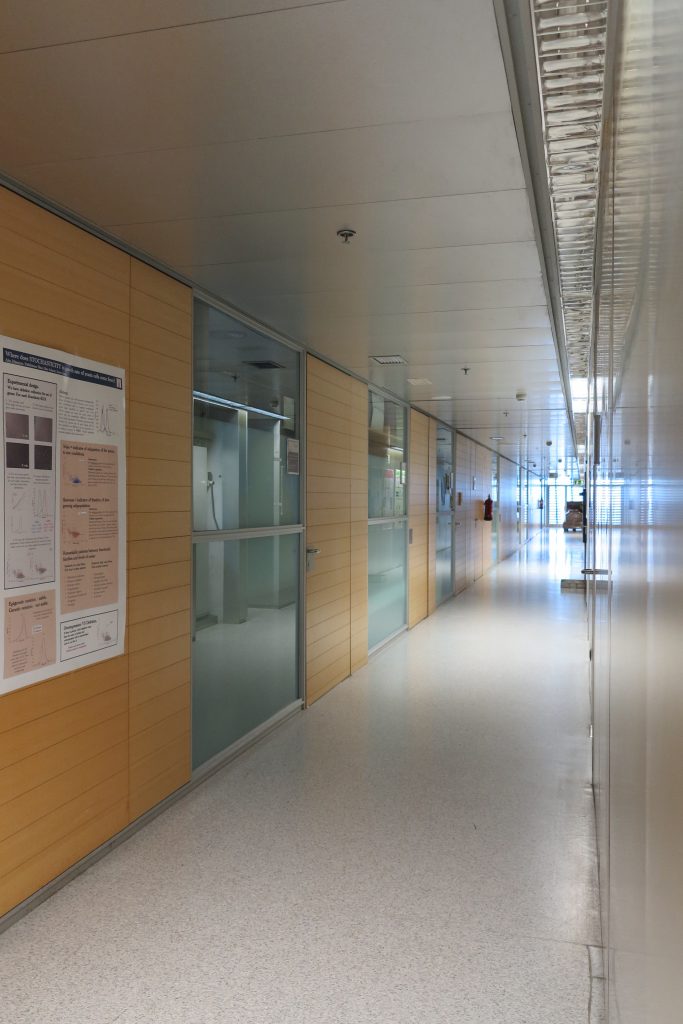
The Biomedical Park has raised quantitatively well spaces, regular and patterned geometries, well distributed facilities and a double skin facade. The match access, lifts, wells, facilities and stairs to the geometry of the supporting structure allows certain homogenisation in plants and a willingness to change, like the aisles U-shaped, both the outside courtyard and inside the building that provide great variability of movement.
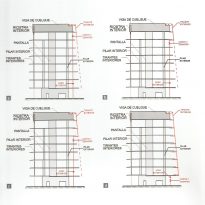
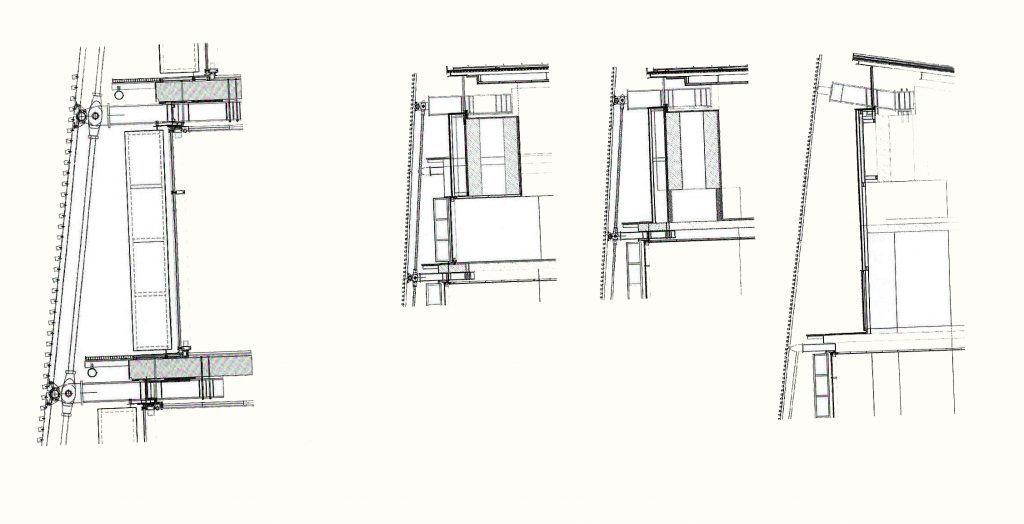
Double skin facade

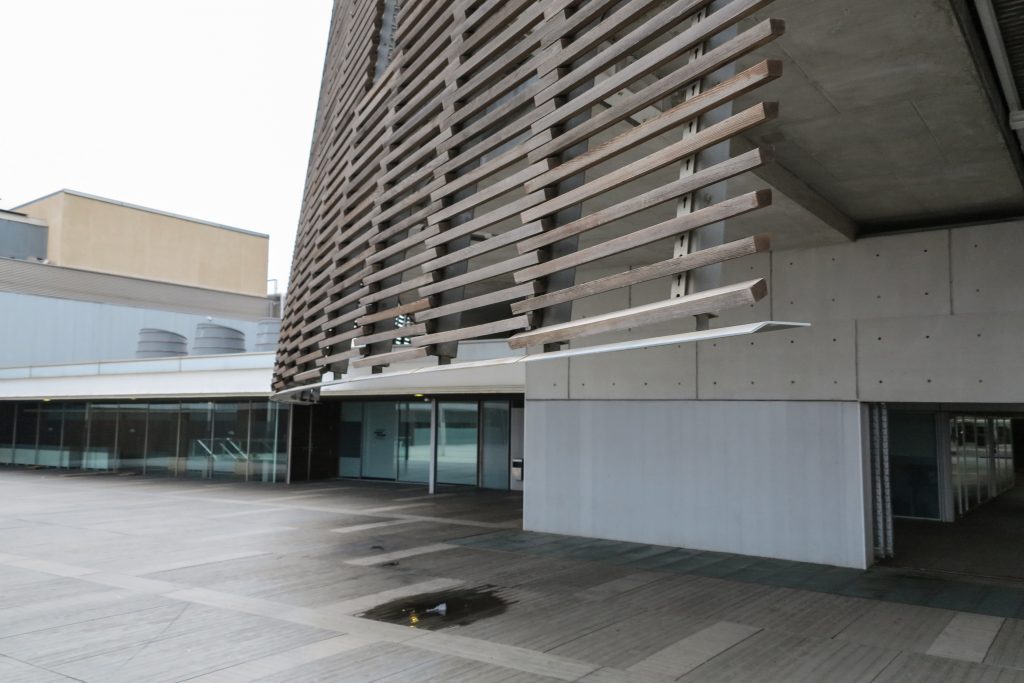
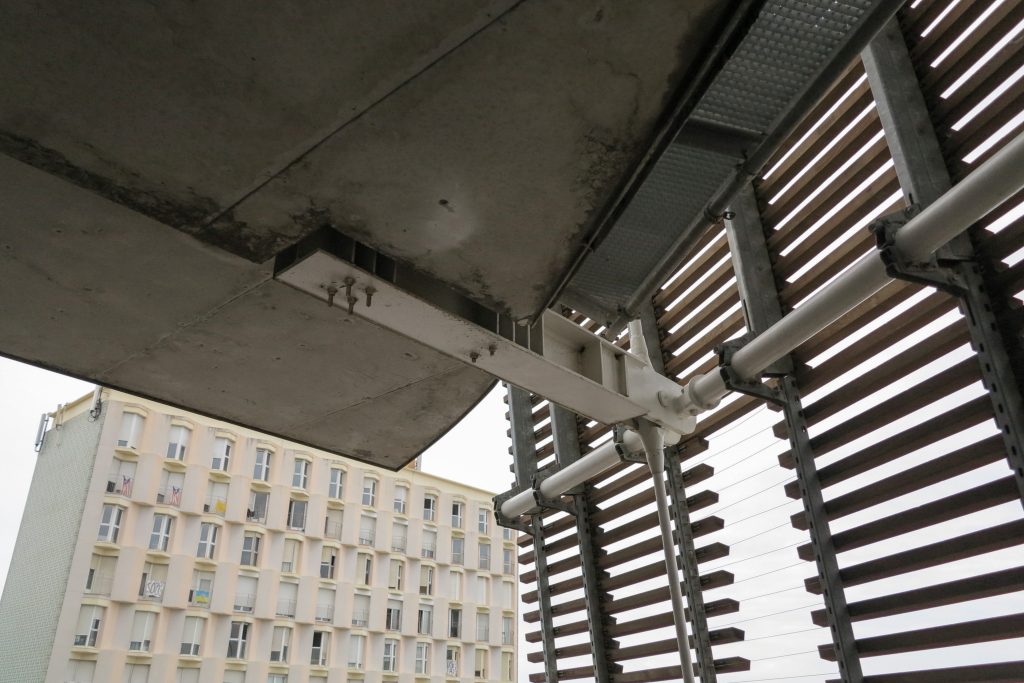
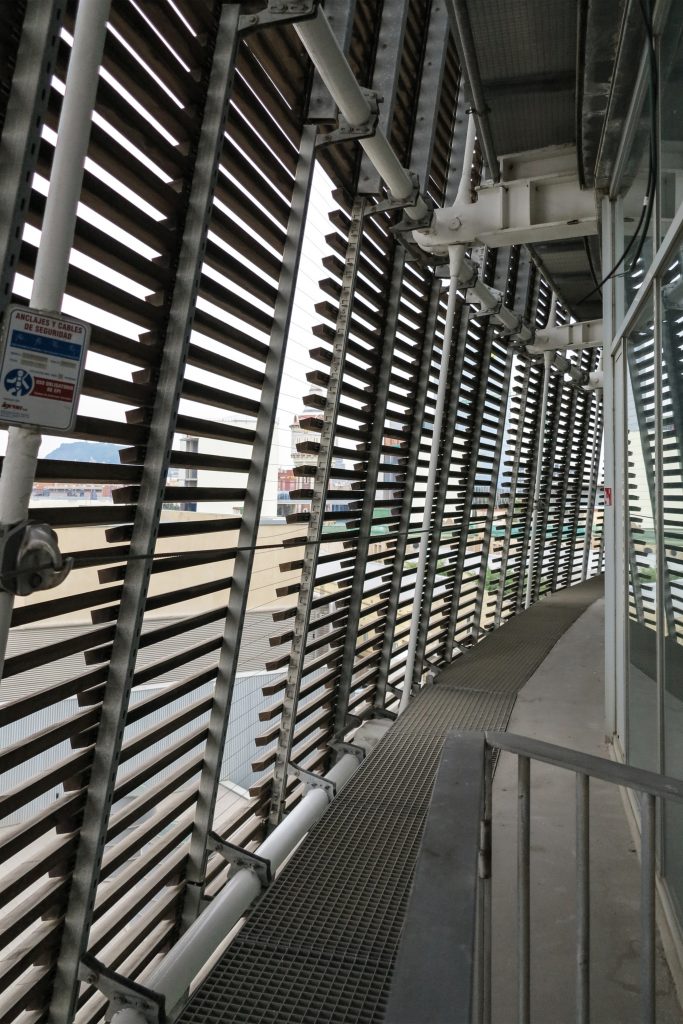
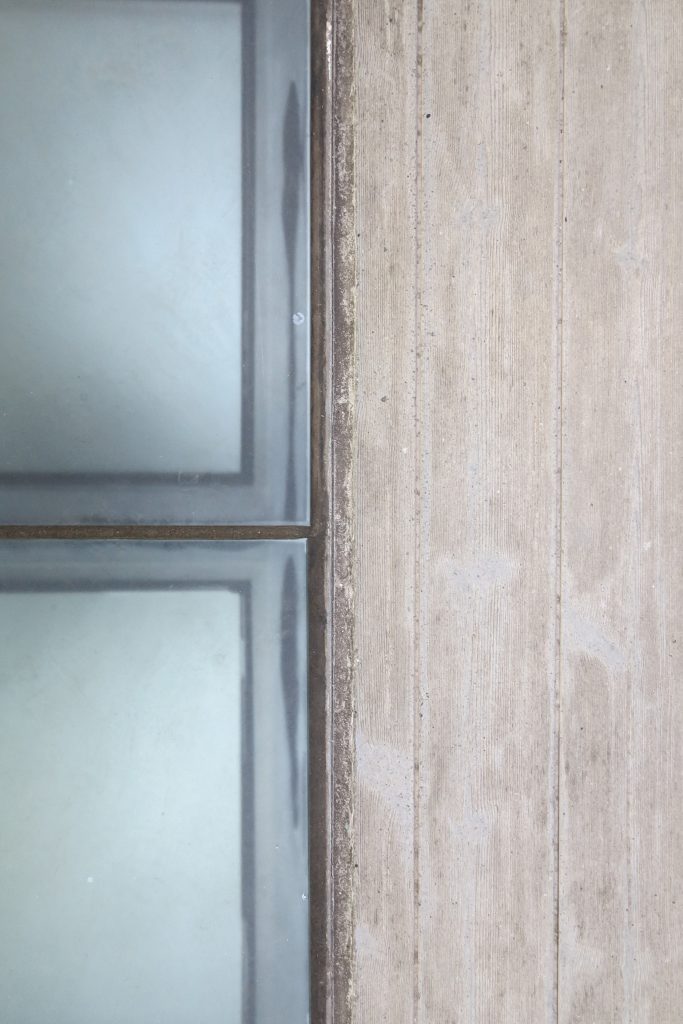
The double skin façade chosen for the building Biomedical Research Park plays several important roles in the development of the project. Among them is responsible for the geometric resolution of the entire building to be a continuous casing surrounding the structure, configuration enables high light utilization inside while protection against direct solar radiation and finally is the permanent face and Center representative to the outside, allowing inside all necessary changes over time are performed.
The resolution of a double skin and the materials used allow each of the layers fulfill a clear role: regular and transparent inner layer provides sealing, light and natural ventilation, also ease some possible variations of the program. The outer layer of wooden slats, protected from the sun and is the main responsible for the material aspect of the building.
Materials
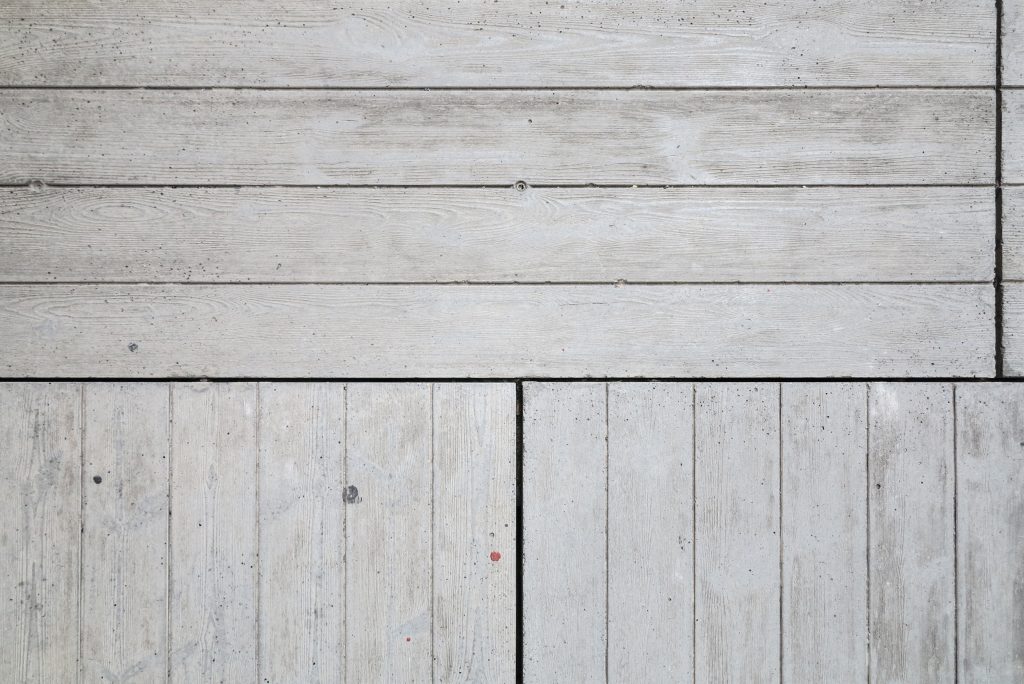
The large horizontal platform that defines the public space of the building at level 0 is treated with a floating floor made of large pieces of concrete that give a uniform appearance, except for the large entrance plaza where due to overload ceiling thalassotherapy center pavement laminations of wood is placed.

The cover of the hall of the first floor is solved with a sheet of water that creates a special microclimate appreciable from the balconies of the upper floors.
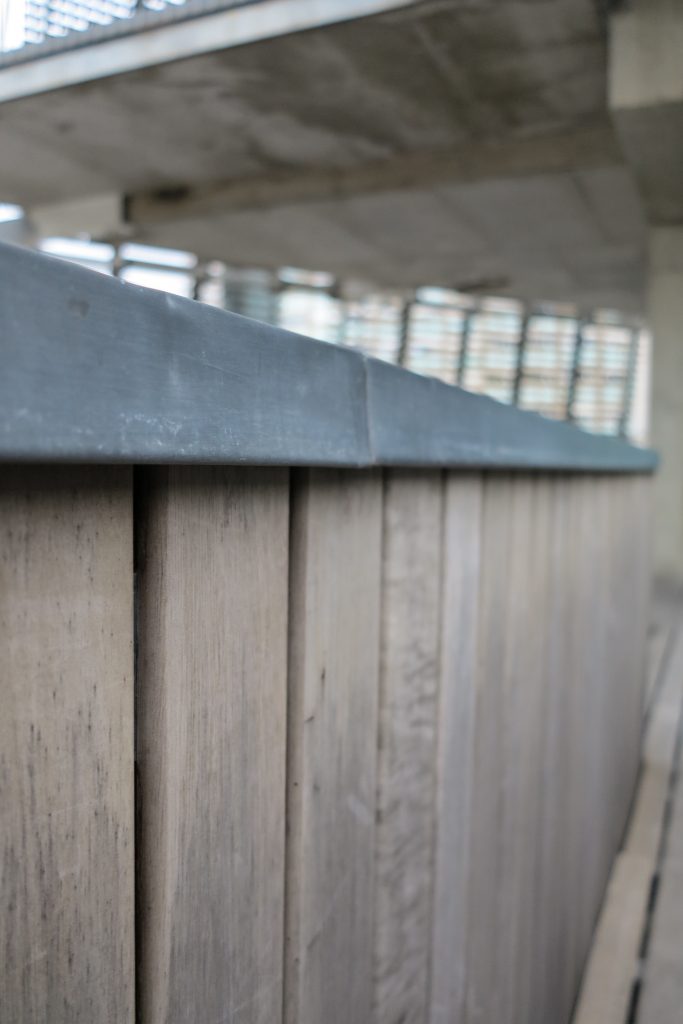
The roof of the building was carried out in zinc and besides being used for the outputs of vents has a surface with solar collectors that help in the production of hot water, this function is favored by the slope of the entire building.
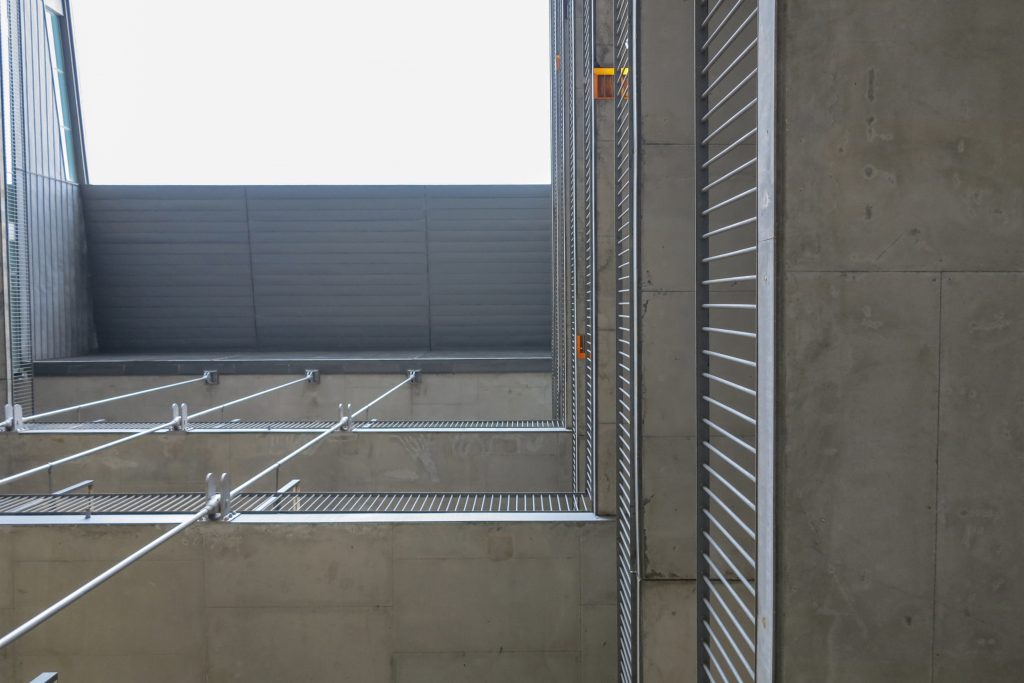
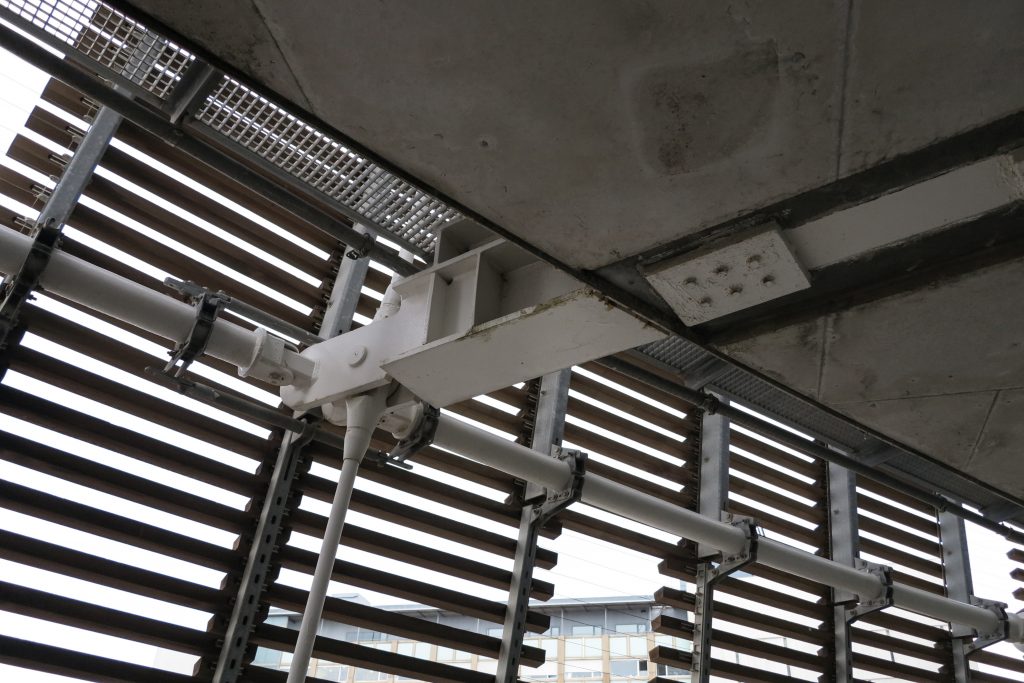
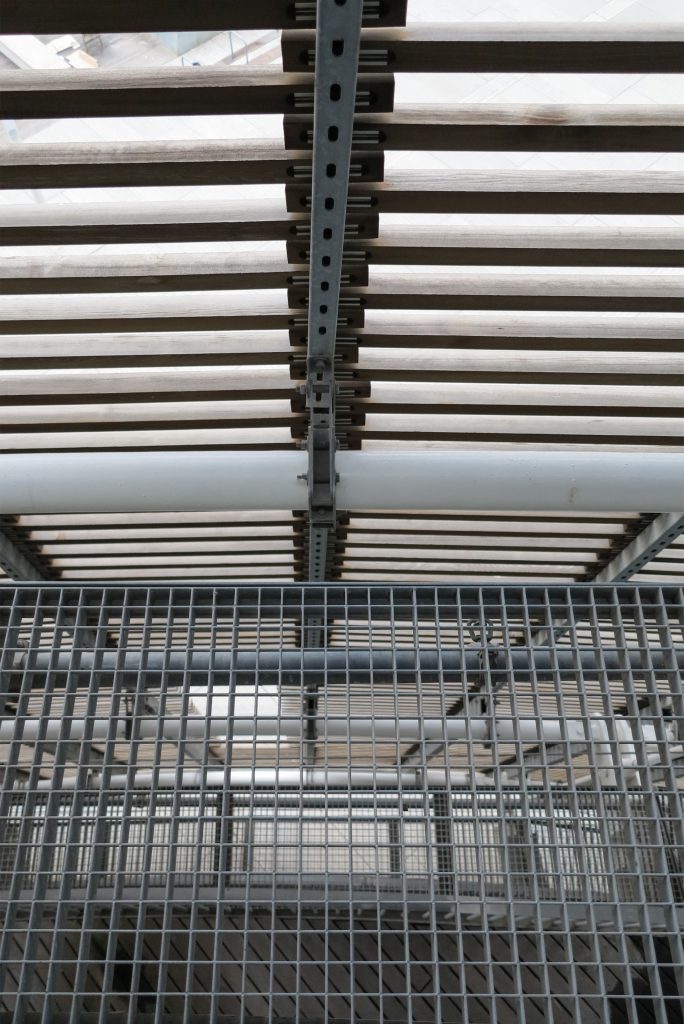
Among the space created by the double skin facades access maintenance walkways alloy galvanized steel, fire prevention system are located by sensors and water curtain covering the entire surface of the wood if necessary and the layers necessary for prevent the invasion of birds without interfering with the supporting structure.
Double skin facade
Inner skin
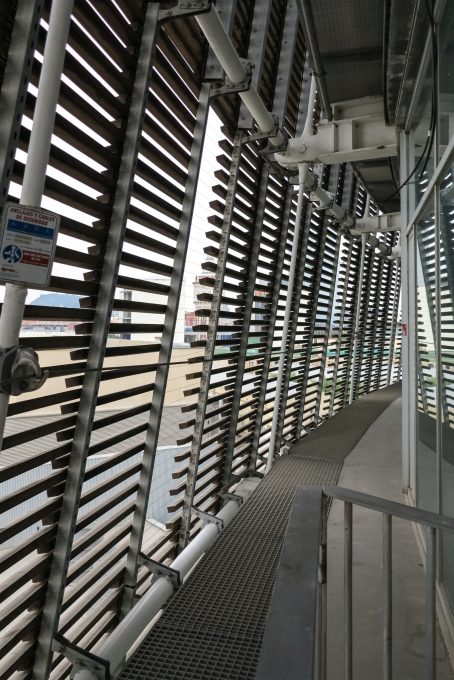

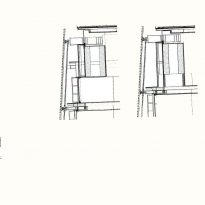
The inner skin is between floors. An aluminum curtain wall supports the glass and camera equipped with closure. Crystals between two different heights and a system of aluminum shutters are for ventilation intercalates. The size of the glass panels of each floor varies due to the elliptical shape of the same. The structure of the inner skin, which is totally independent of external support structure continues crystal to the seventh floor, where it becomes steel sheets in the 8th and 9th, ending with the crowning of zinc on the cover.
Outer skin
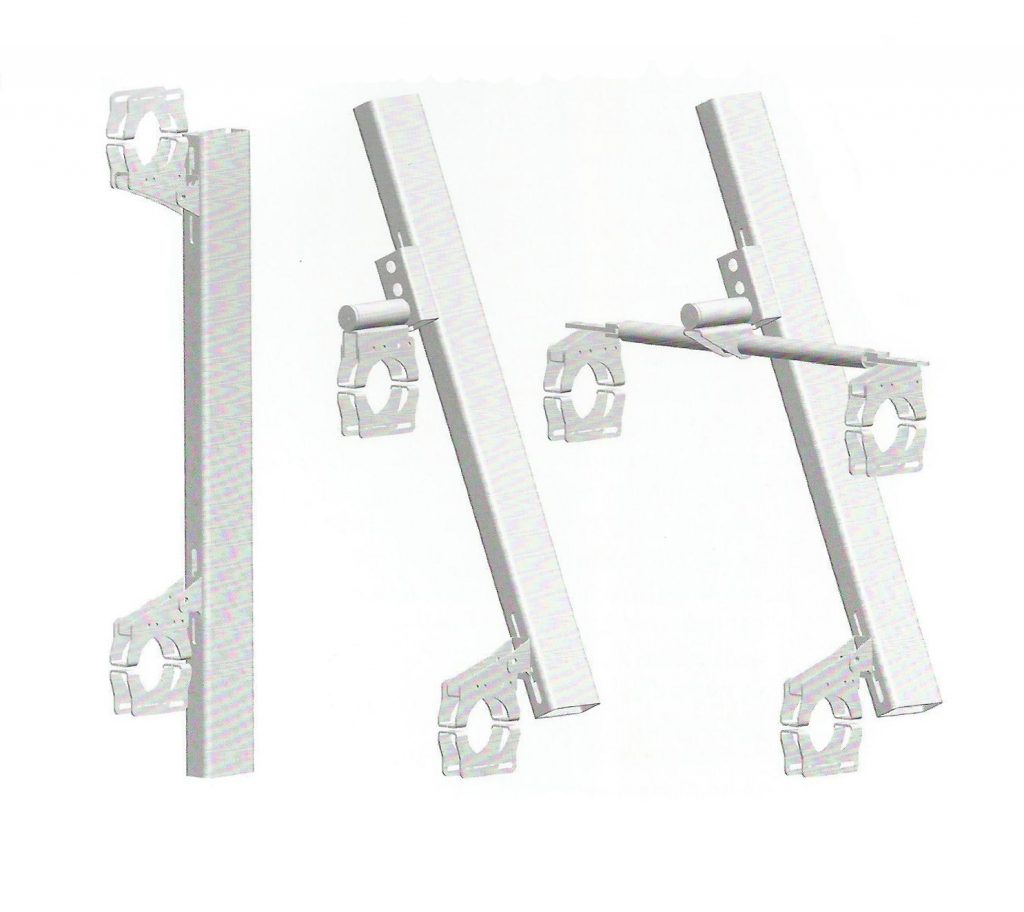
The outer skin of the facade is made up of 237 lines of vertical posts anchored to the perimeter ring of steel tube of each plant. According to the light to be saving these amounts are different measures 80×80 or 160x80cm. This secondary structure is formed with axes of rotation, articulated joints, overlaps and tolerances, all in galvanized steel without using welds. On the uprights and over 44,000 elements wooden slats pink cedar, in each level are all the same size and decrease as you go up 1cm plant were deployed. Your settings were performed using an anchoring system with a guide and a clipping mechanism.
Features wood facade:

- Trade Name: Red Cedar.
- Origin: North American West Coast.
- Color: reddish brown uniform.
- Smell / taste: aromatic, bitter, like cedar.
- Growth rings: are easily distinguished. The dark bands mark the summers.
- Fungi: Durable.
- Termites and other: sensitive.
- Humidity: rot-proof. Excellent weatherability.
- Condition: no maintenance, fungicide-insecticide, unless it is in natural terrain.
- Conservation aspect: lasures or preferably applied by spray oils.
- Screwed: delicate.
Suspension Structure

From the ground 1 to 3 slats are metal outer suspension structure with solid, circular section of 56mm in diameter that varies as the building rises from 3 through 5 64mm and 76mm from 5. The yield strength of the steel is 460 N / mm2 and are placed every 3.6m.
The inner braces are metal profiles HEM300, HEM200 and HEM120 connected to concrete floors by metal spreaders. Throughout the structure longitudinal post-tensioned concrete girders and variable geometry they were used.
Video