Saturnino Institute Unzué

Introduction
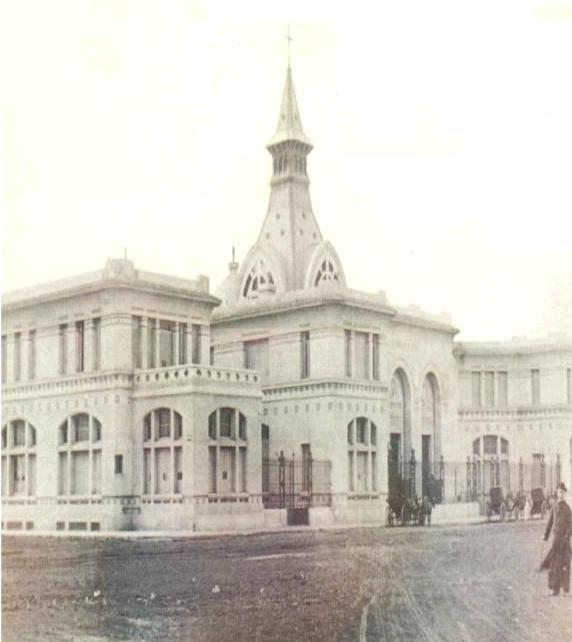
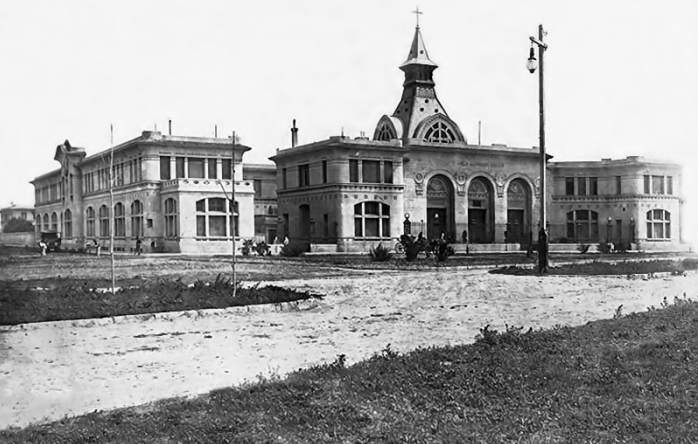
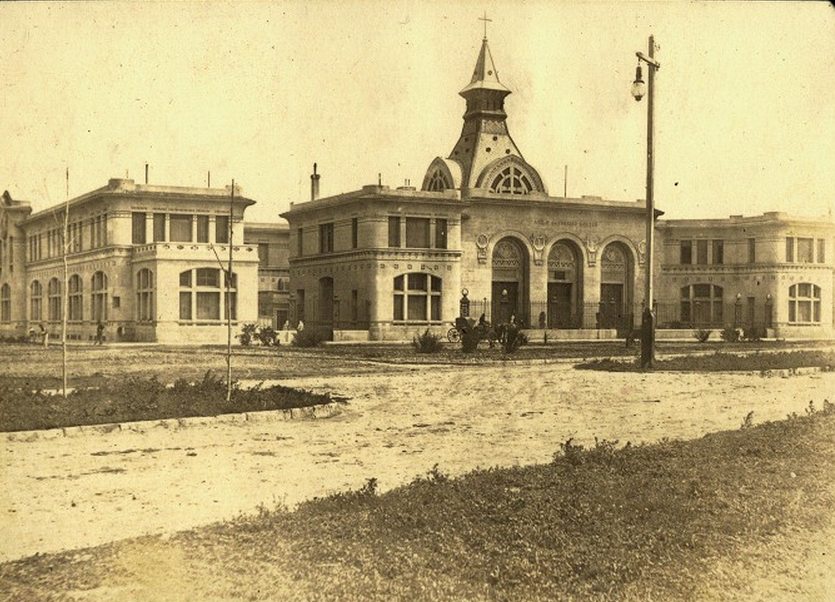
Started in 1910, on the initiative of the Unzué sisters, was inaugurated on March 5, 1912. In later years the Asylum Unzué was donated to the Charitable Society by sisters Maria de los Remedios Unzué de Alvear and Concepcion Unzué de Anchorena.
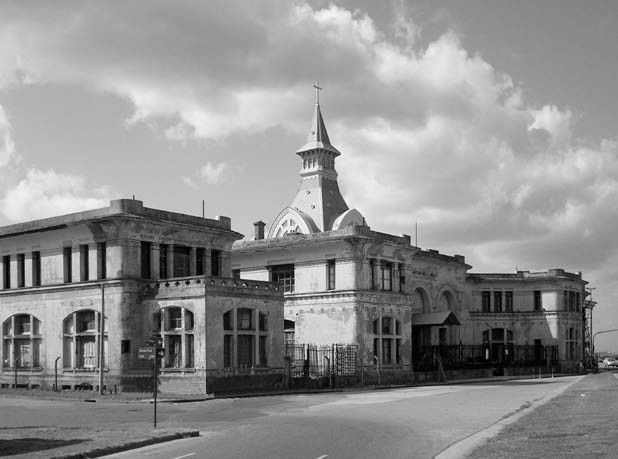
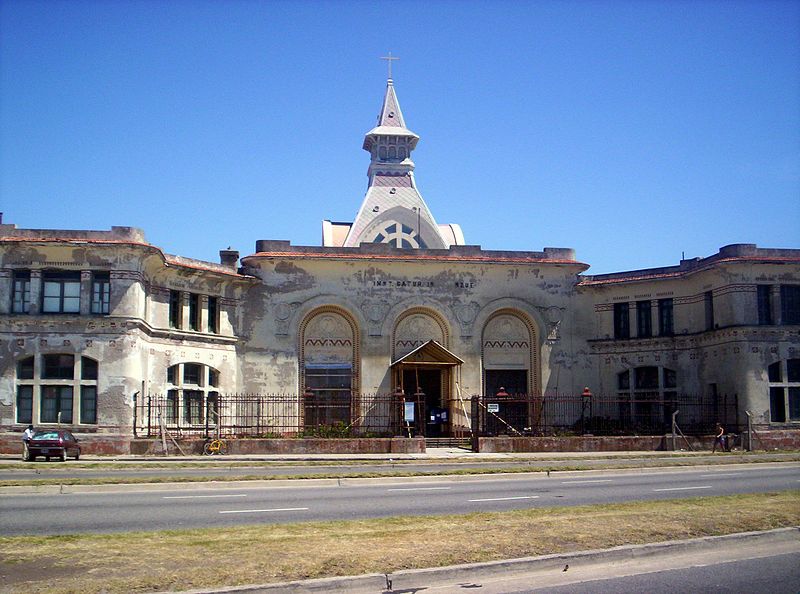
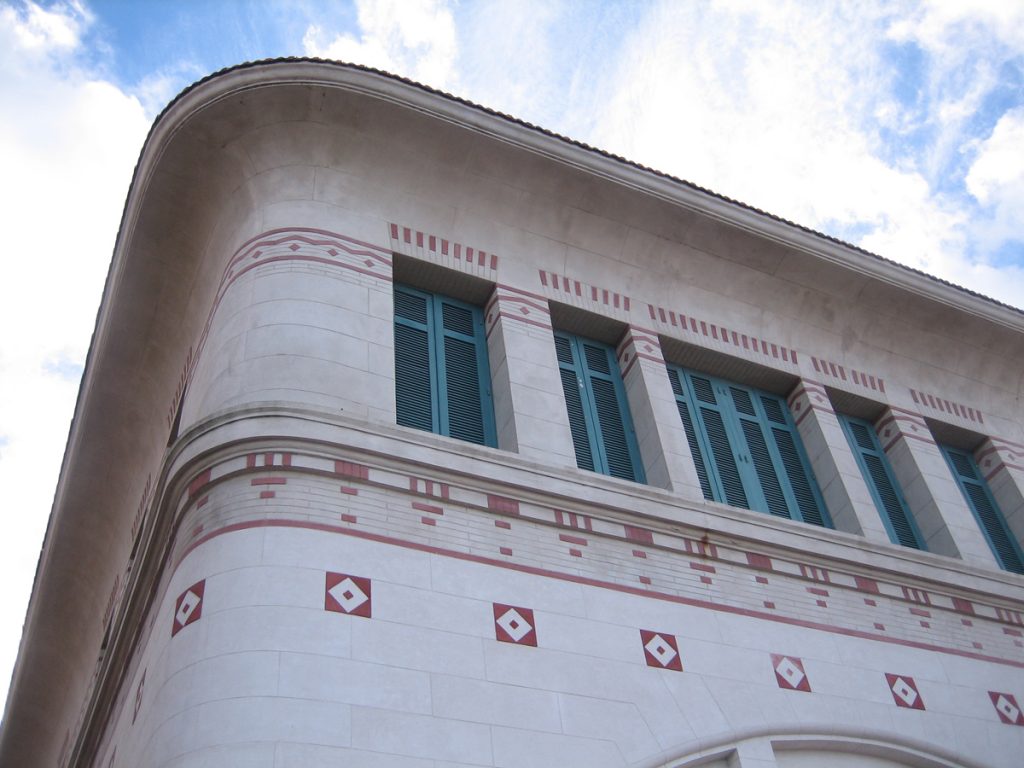
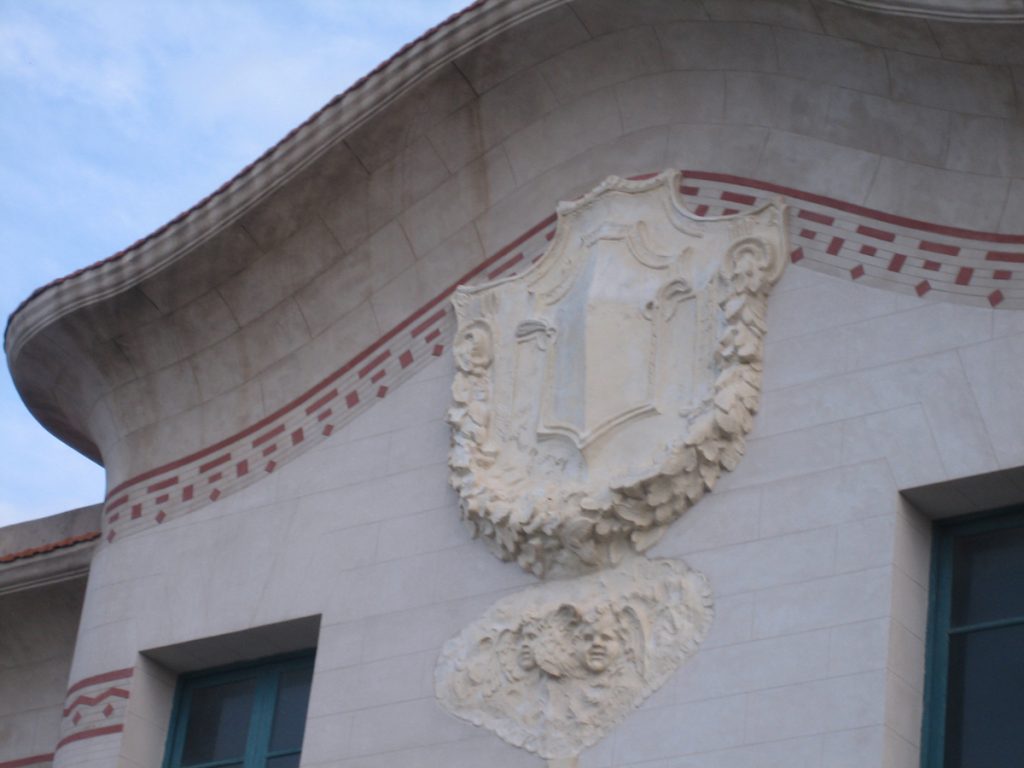
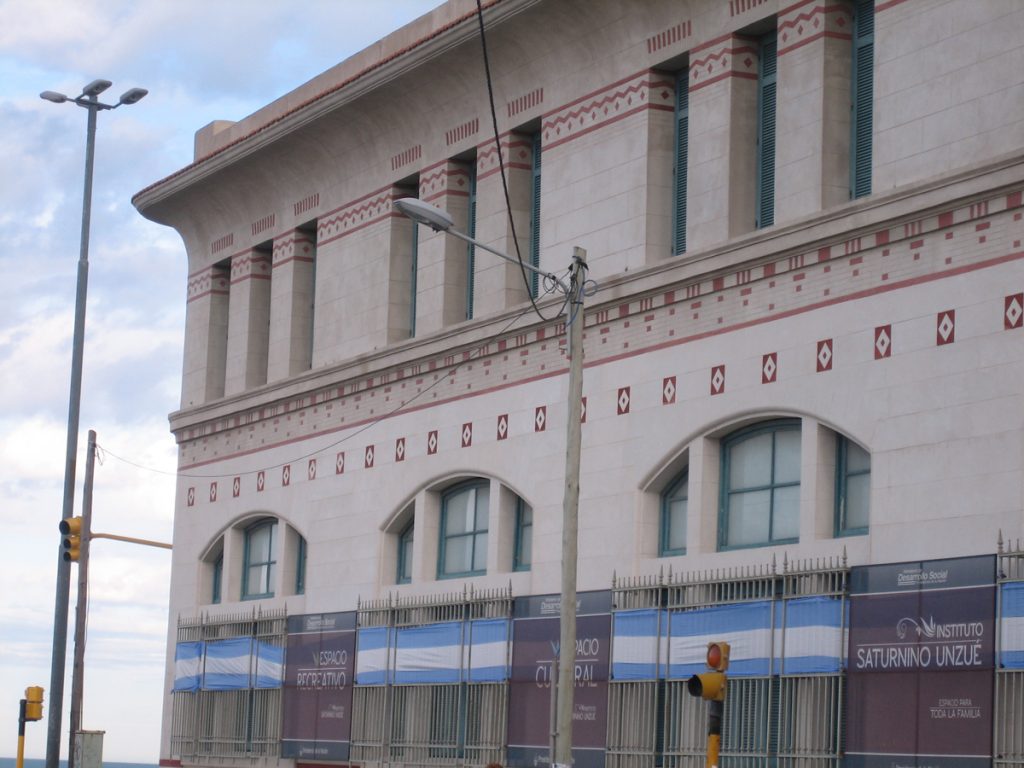
Architecturally, it is a building of pavilions, eclectic style influenced by modern avant-garde of the early twentieth century, especially the Viennese Secession contemporary, artistic and architectural movement within the academic.
In 1989 he was named a National Historic Landmark
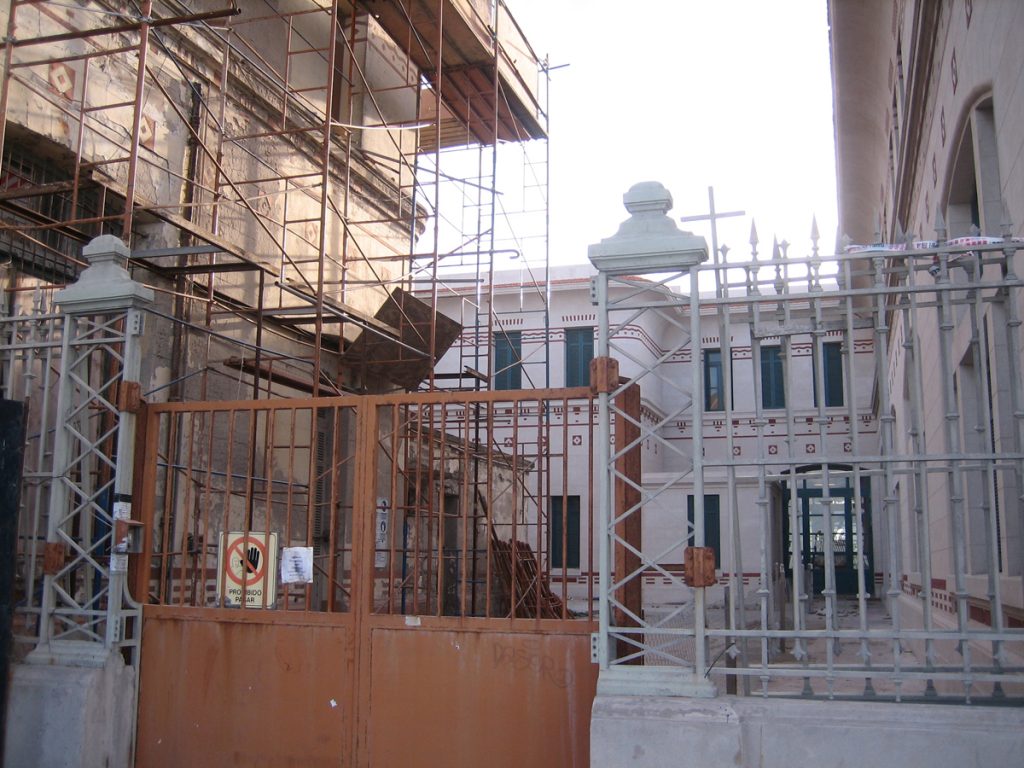
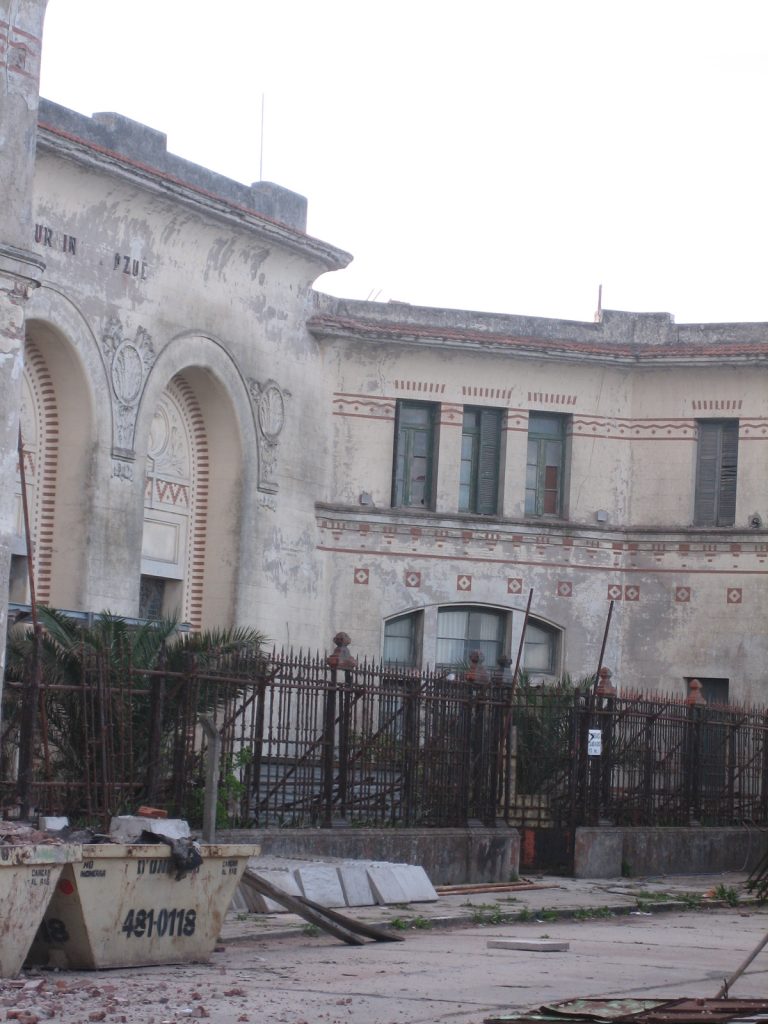
After almost 100 years since the start of the construction of this building, it became apparent deterioration in external masonry, railings, windows and ceilings. For these reasons, restoration work began in order to recover the social and cultural role of the institution.
Location
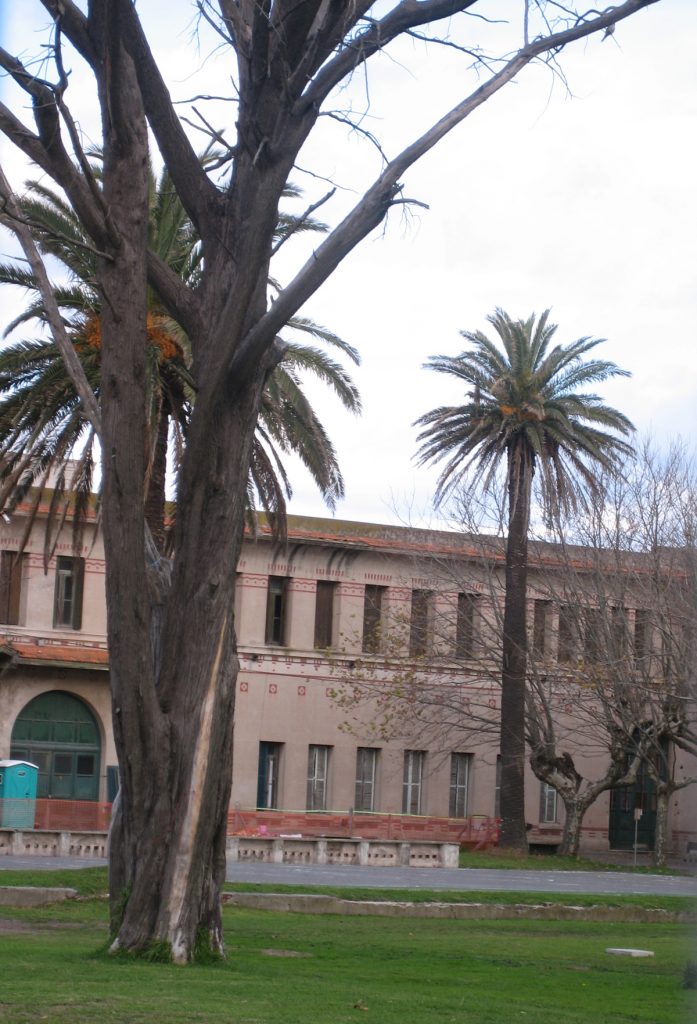
The asylum, which can be distinguished from the coast for its modernist architecture, Romanesque-Byzantine style, 2 acres bounded by the streets Jujuy, XX September, Santa Cruz and Río Negro, in the city of Mar del Plata province of Buenos Aires, Argentina. The building was built in the middle west, “328 farm” property field Unzué sisters.
Concept
All the planning, from the top to the base of the columns is inspired by accurate and rigorous science of sacred numbers, in this case the number 8, which is often repeated in the plan of the temple and in the details of the decoration, abounding cryptographic details of deep sense.
The building was designed to provide shelter for orphans in the province, providing schooling, general knowledge of home economics, sewing or other crafts designed, basically, to the orientation of women towards family life.
Plant
The main body of the building is symmetrical, developed into a H-shaped floor with the entrance to the chapel for the facade that faces the sea, protected and flanked by the two legs of the H, the building appears as a complement to the structure main side pavilions enclosed on two floors and the bedrooms were located, work rooms, classrooms, meeting room, kitchen and area closure. The service complemented wings on the streets Santa Cruz and twentieth of September.
In 1990 he began a long restoration process.
Spaces
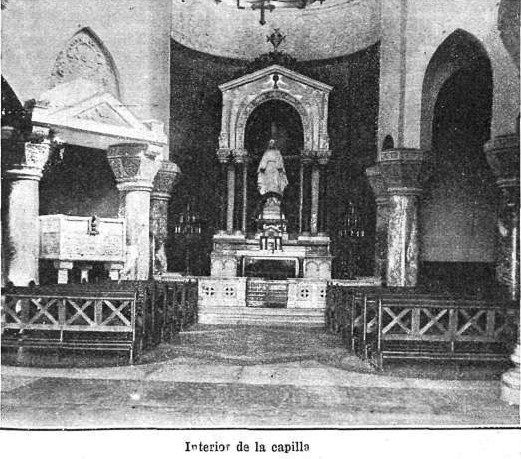
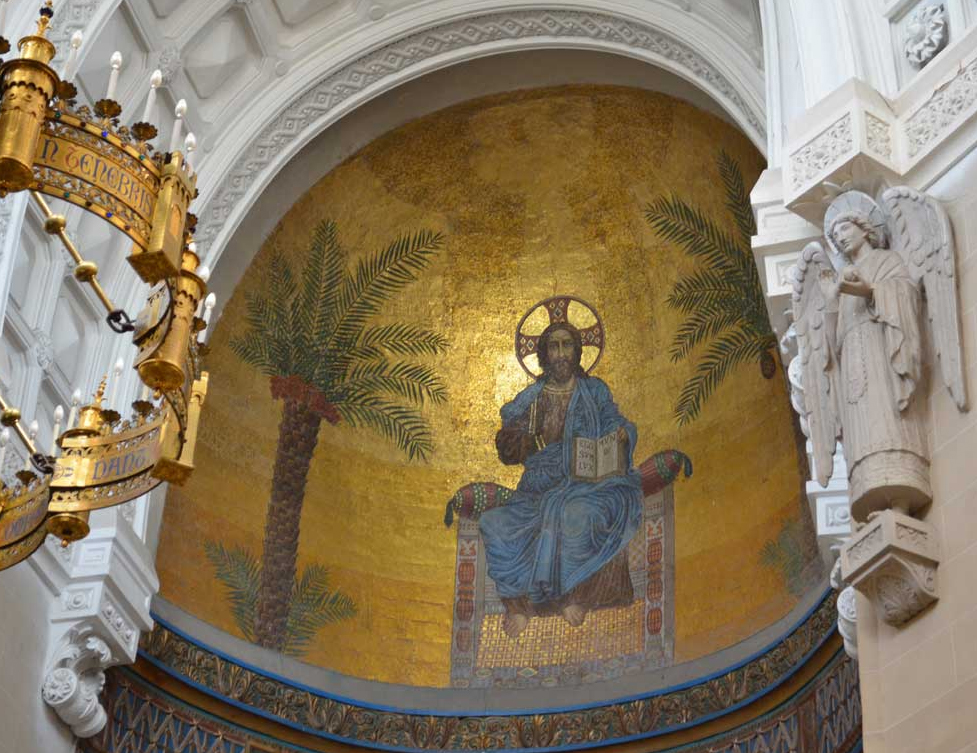
The austere exterior of the building contrasts with the luxury interior, especially the chapel and oratory, in which Italian ornaments abound. The Pantocrator is magnificent replica that enriches Hagia Sophia on Istanbul, Turkey.
The other part of the whole, the building dedicated to asylum is more austere style.
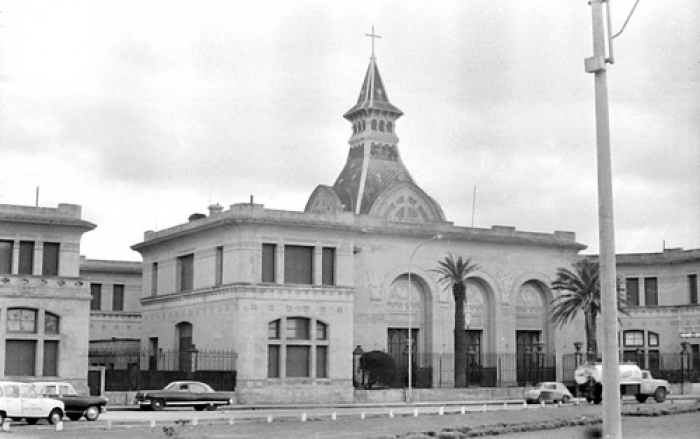
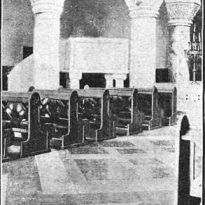
Chapel of the Immaculate Conception
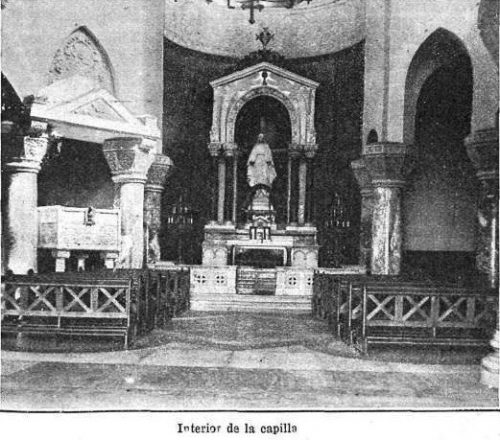

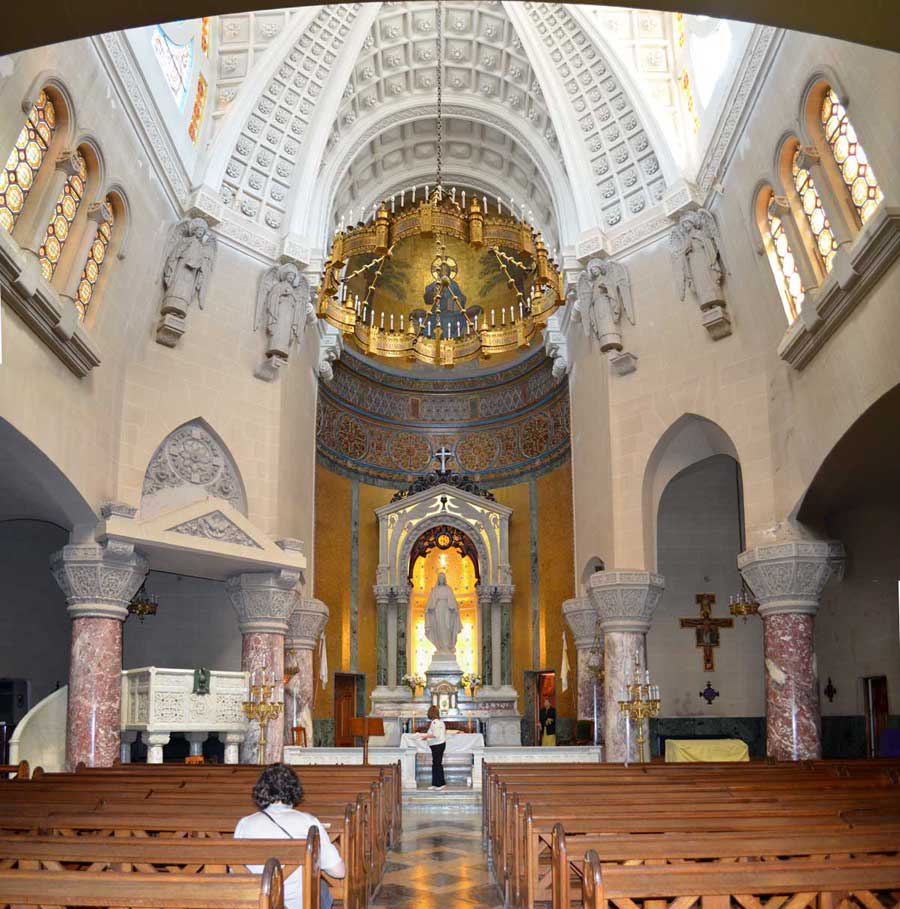
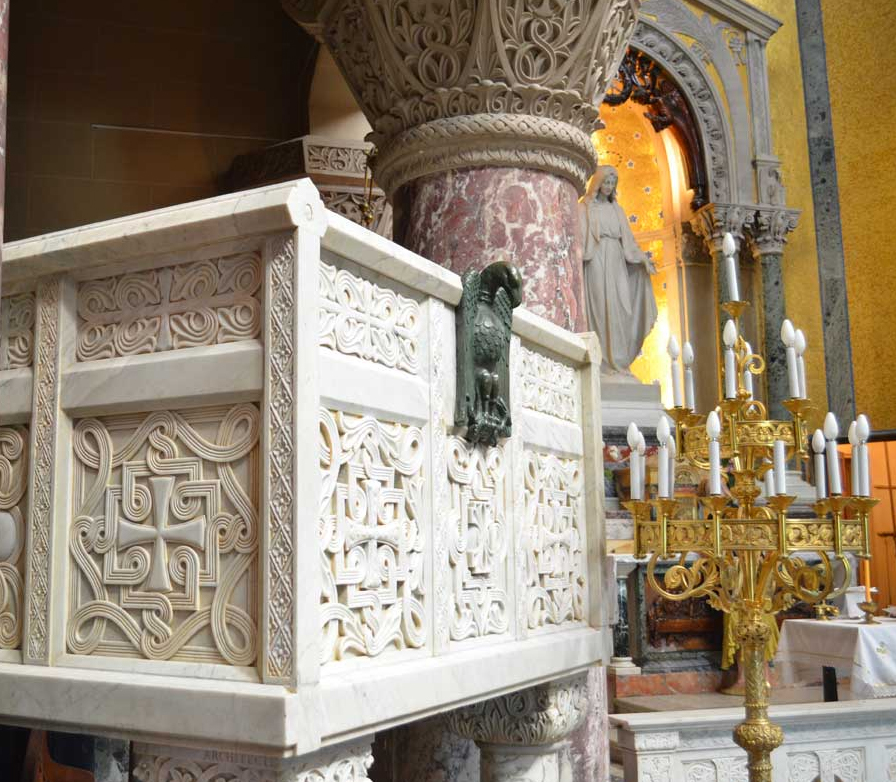
The Chapel of the Immaculate Conception, designed by French architect Louis Feure-Dujarric, is neo-Byzantine style, highlighting the altar, the pulpit, the statue of the Virgin, an image of a Byzantine Christ and the communion rail.
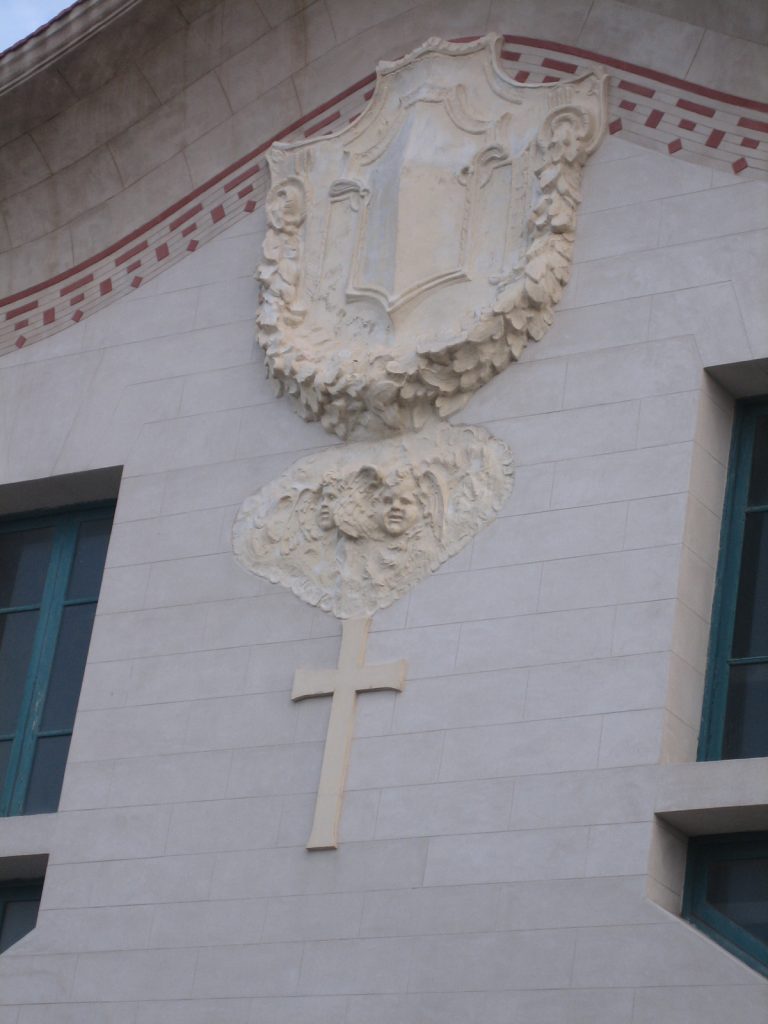
In the central door richly carved entrance to the chapel stands a Latin cross flanked by stylized acanthus foliage and crowned eight Mystic Rose petals on background of small squares arranged in a cross. The two wings were adorned with leaves geometric designs.
Everything inside has been ordered with mystical intentions to use contemplative souls with delicate symbolism expressed with figures of foliage, animals and highly spiritual images that facilitate the stages of communication with God.
Eight angels, with their attributes, attached to the wall, haloed, with wings open and bare feet, holding the ribs resting on imposts placed on their heads.
The equilateral cross in a circle is repeated on the floor of the ship, in the singular correspondence given by the covered ambulatory that surrounds circulated externally on your floor while you develop a geometric theory of deep symbolism.
- Oratory
The Oratory of the Institute was conducted by Curzio Unzué Capobnetti-Esegui in Rome and later transferred to the city parts of Mar del Plata. It is an example of neo-Byzantine architecture, with a notable liturgical symbolism. Built with materials, keep a balanced proportions and high religious symbolism from the exterior to the theorem proposed marbles and mosaics inside the church, like the old cathedrals.
- Pantocrator

The apse itself, has 3 registers beautifully decorated with geometric interlocking and interlacing. The upper register is chaired by the Pantocrator Sedative, the image of God as a priest forever man while painful for the Christ image of the Byzantines.
- Pulpit
Square projection, the pulpit is located under the ciborium, in intercolumnio of 2 of the 4 columns supporting it. These small polychrome marble columns topped with capitals of white marble with intricate latticework offer like the ciborium, a beautiful symbolic order.
The Carrara marble front draft, presented in 2 registers, 4 equilateral crosses surrounded by tracery. In the center of the upper register, a bronze eagle alludes to the Word. A marble staircase, at left, shows the high knowledge of Byzantine art that had Louis Faure Dujarric and expertise of its executors.
- Batteries for holy water
This oratorio lacks baptistery, but has two batteries for the holy water which have two issues rarely used in Christian art: the turtle, symbol of strength and creative power of faith and the duration of the Church, for their long longevity and symbolic colors: red or red, blue and white.
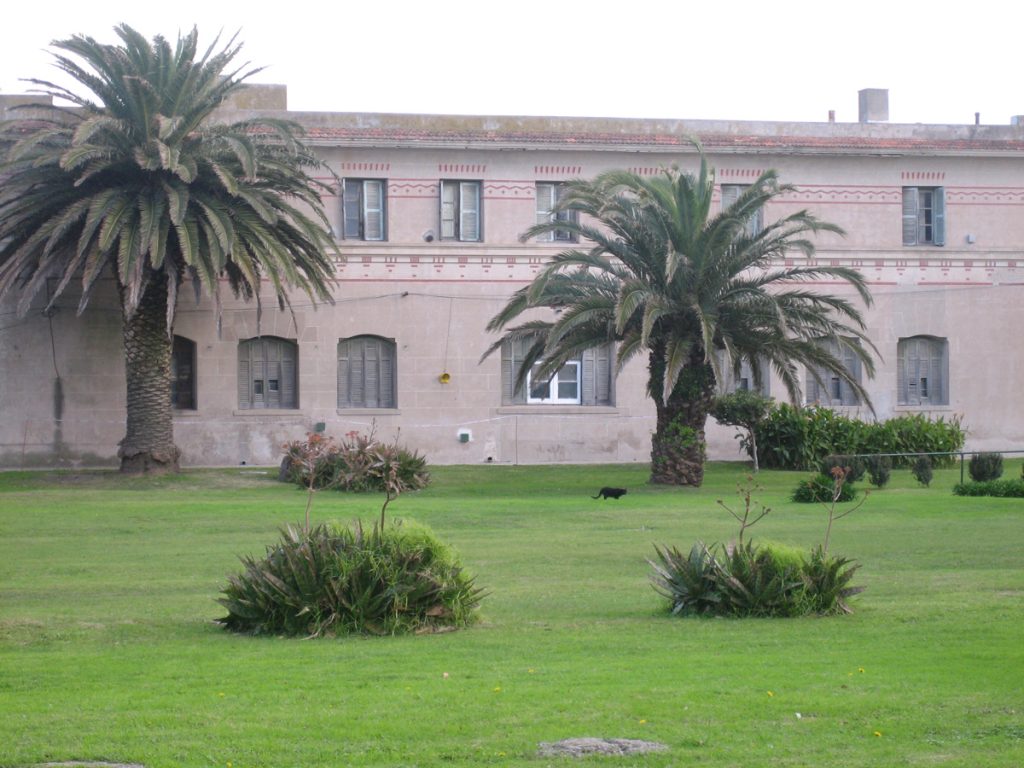
Park
Behind the building with H shaped plan, between Calle Santa Cruz and Rio Black on the sides and closing September XX plot, we designed a large garden that had, at the time, with a small train moving on a laying tracks, used for recreation of the inmates. In the garden center was placed on artistic font and rear facade of the main building, overlooking the garden, a clock reproduction of Westminster Abbey, London, England.
Structure

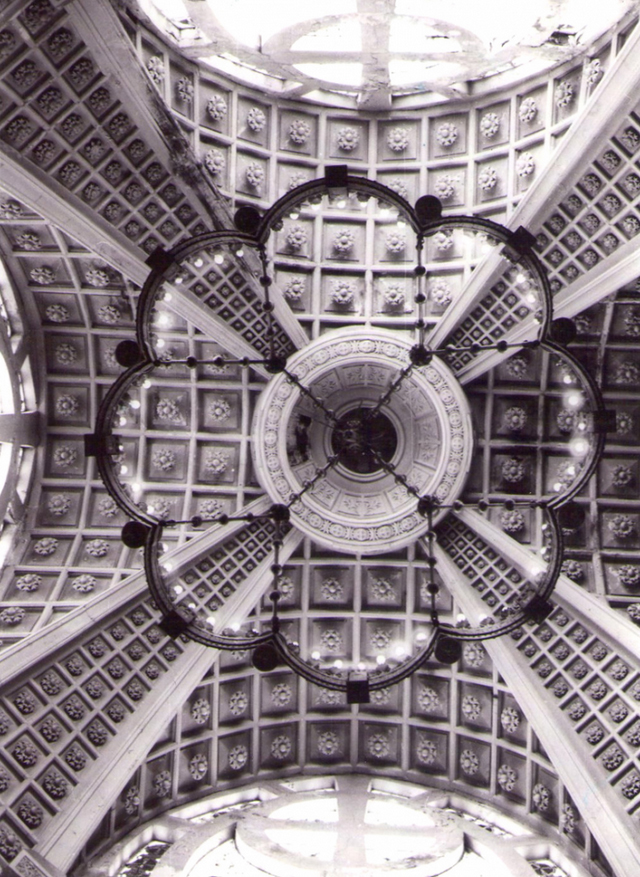
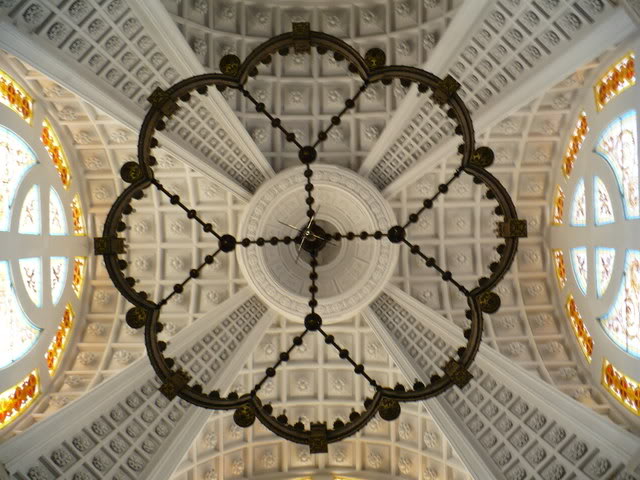
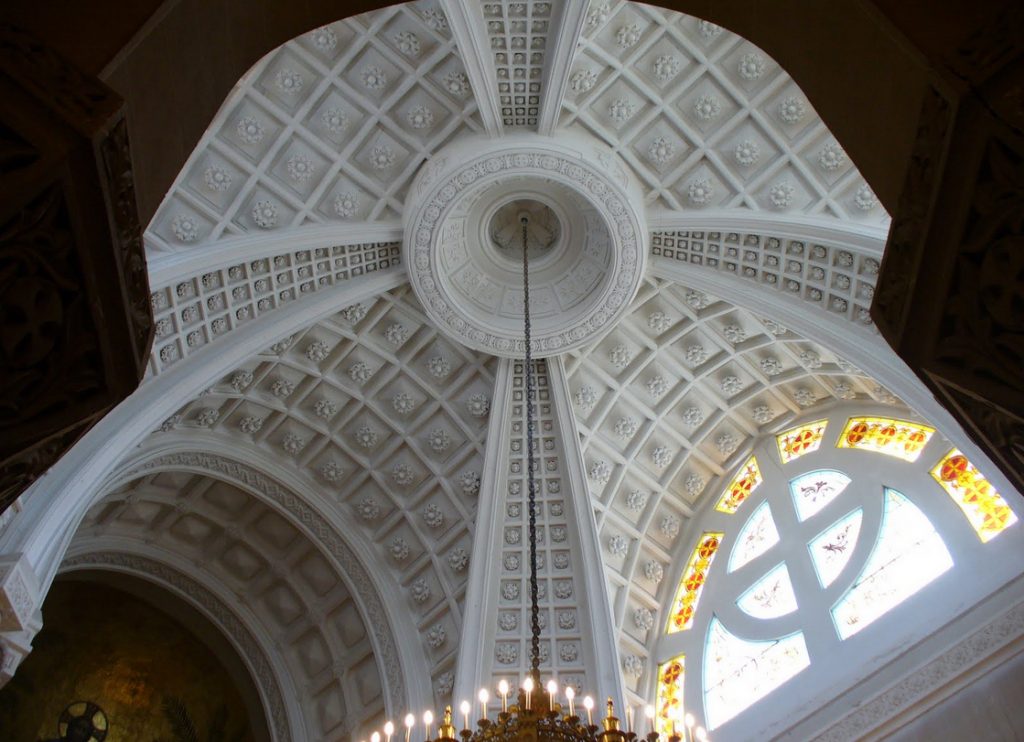
The vault of the chapel has four double nerves only a decorative function, as it is supported by eight columns of mighty shaft also contributes to the Oratory visual balance. Intertwined draw acanthus leaf number 8 topped by an equilateral cross in a circle on each of the capitals resistant banners.
The beginning of the ribs and the vault is indicated by a frieze ornamented with geometric and vegetal elements that are topped with rosettes representing Rosa Mystica on the soffit of the vault and the openings of the ribs.
Its dome is about ten meters in diameter three pyramid-shaped arches, a small barrel vault and a bell tower with spire or needle
Materials
Among the requirements Unzué sisters asked the architect for the building of the institute was the use of noble materials.
All carved woodwork and interior decoration with polychrome marbles were made in workshops in France and Italy. The entrance to the chapel is of Slovenian oak. The confessionals and wooden benches were specially made by local carpenters
In the construction of the chapel was used 18 different types of marble Abyssinia and Proconeso Carrara. The pulpit was honored in 1910 with the First International Sacred Art Prize, awarded to Seville, Spain, before moving to Argentina.
The chapel was endowed with a striking bronze candelabrum eight segments arranged in four registers that hangs from the center of the dome, and numerous ornaments made especially by Italian architect Capponetti Esegui Curzio, in the city of Rome, with its own characteristics unique pieces of arts-inspired ornamentation broncístico Byzantine Carolingian. The apse walls are completely covered with gold background tiles.
The brass fittings and decorated with carved foliage and geometric designs are unique pieces of fine jewelry specially made for Asylum oratory also has an organ built in 1905 by the firm Aristides Cavaillé-Coll and harmonium of French origin dating from 1890-1900, built by Alexandre et Fils, Paris.
The fourteen Stations of the Cross are cloisonne enamel.
Video