Roman Coliseum

Introduction
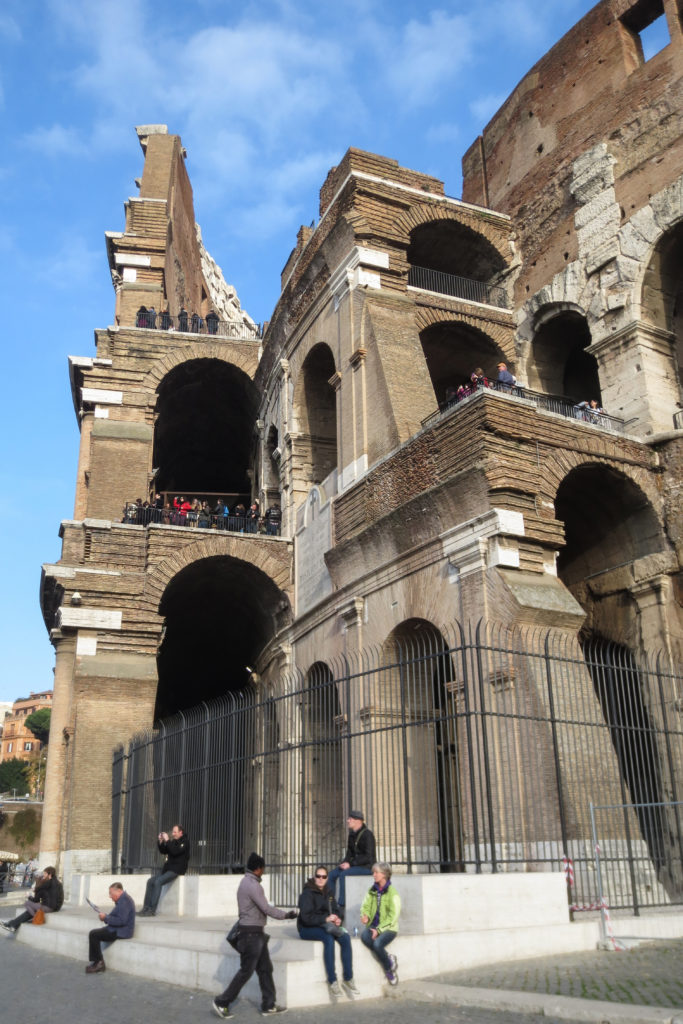
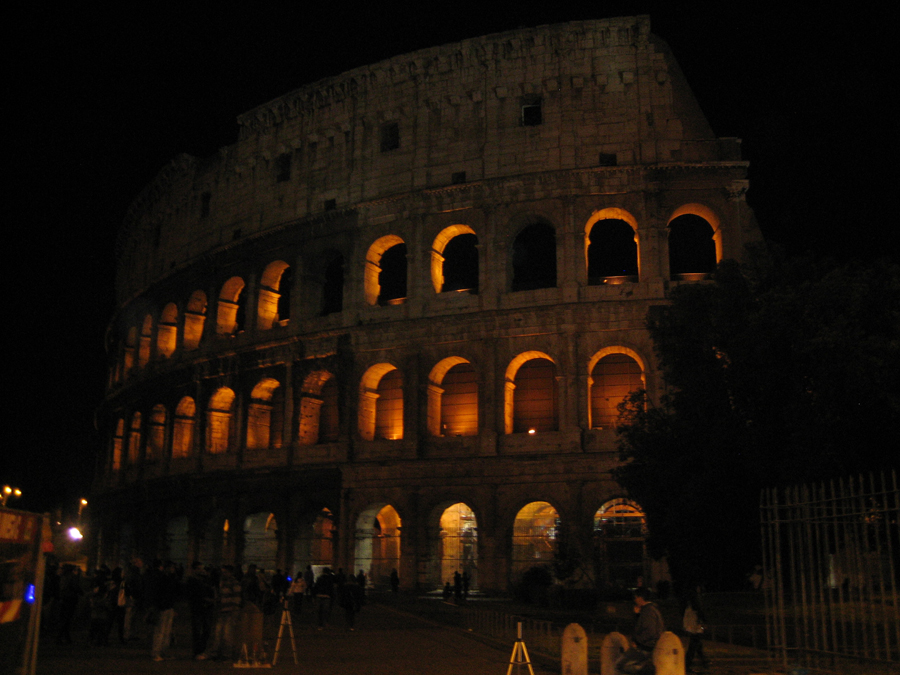
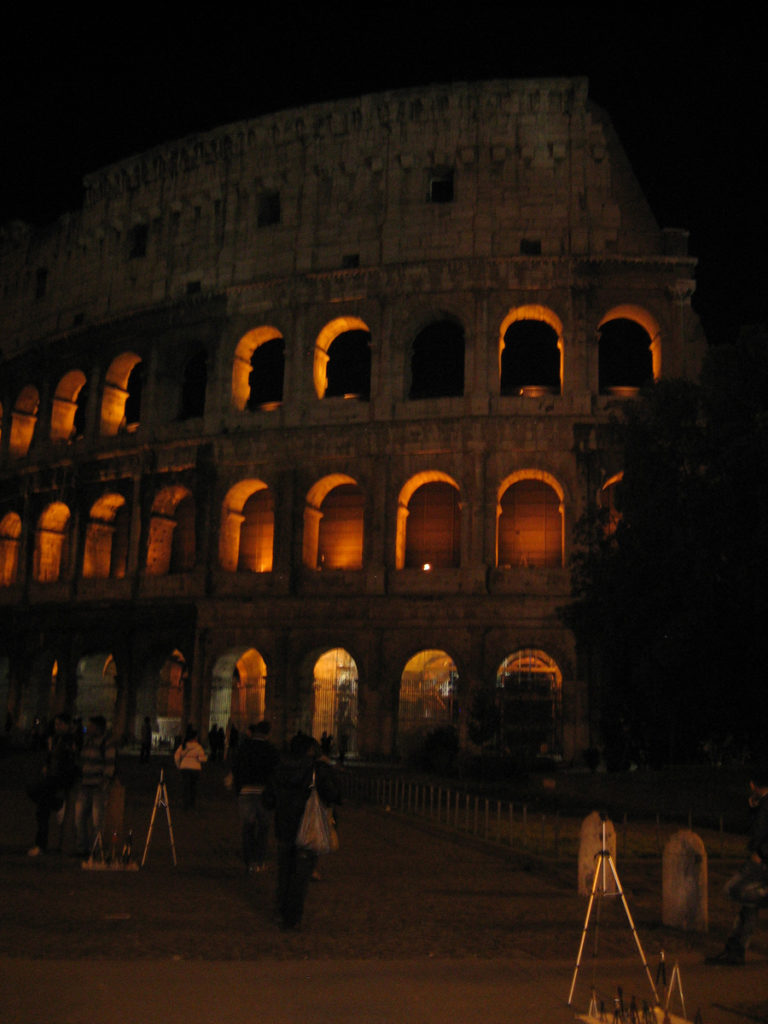
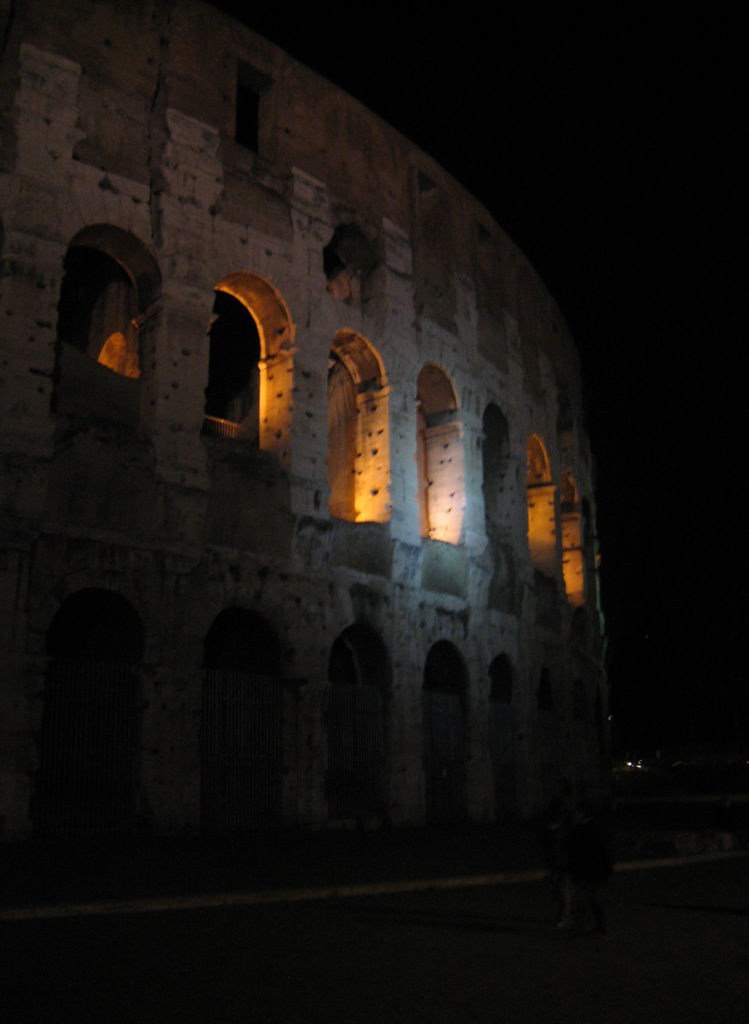
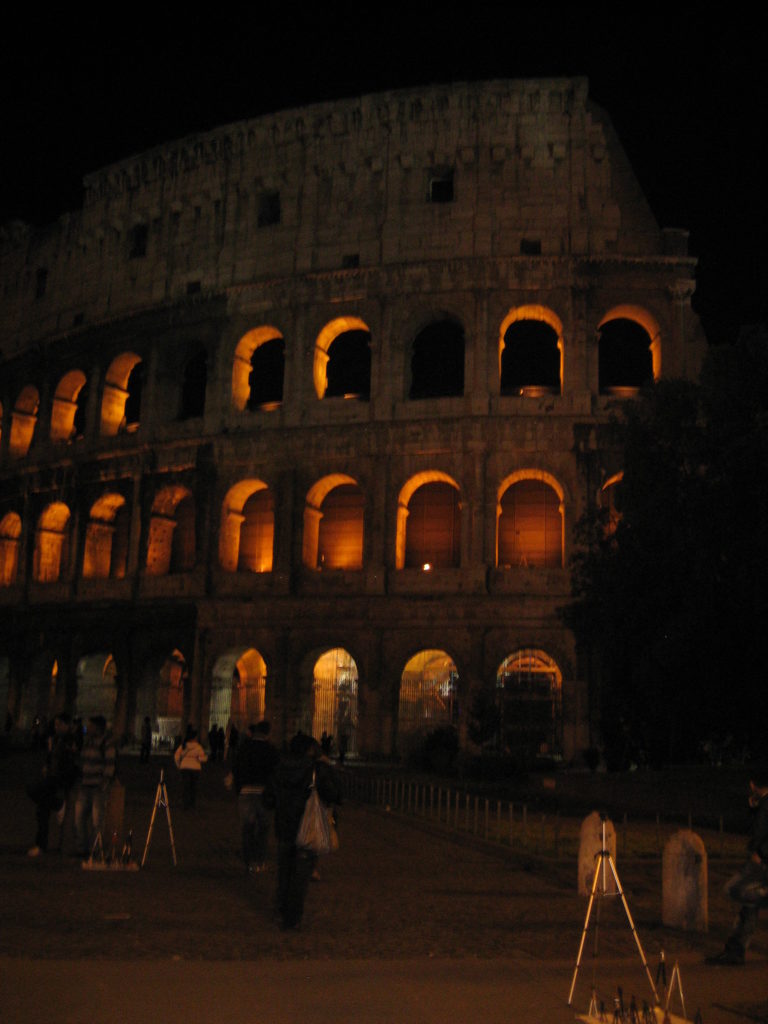
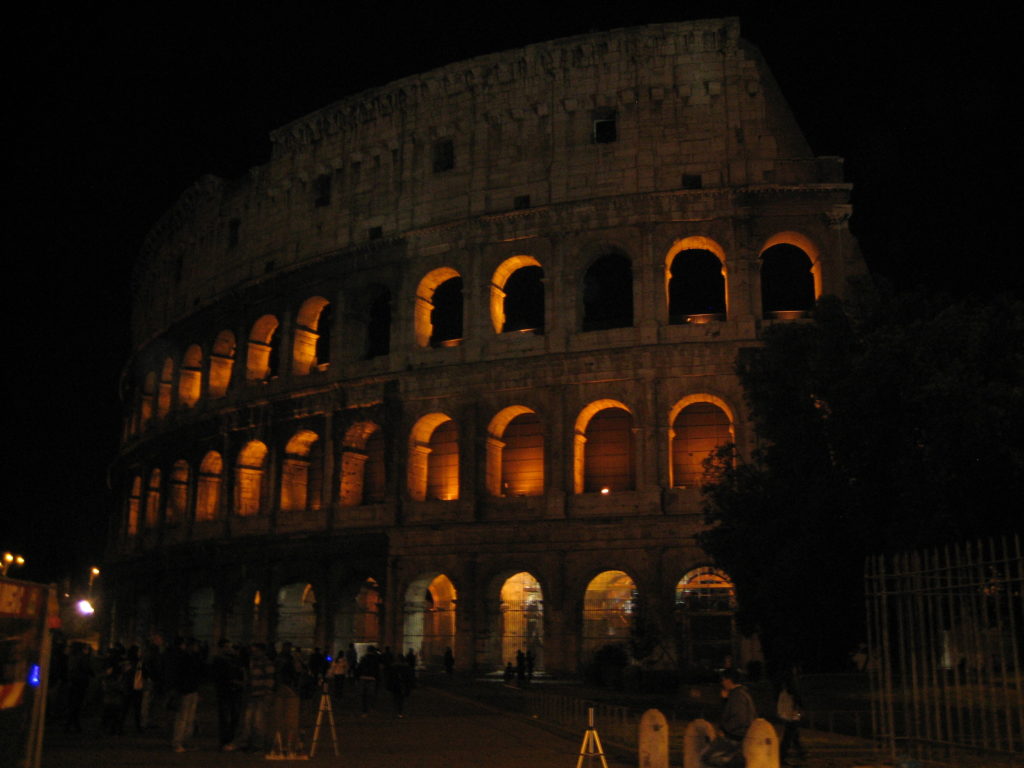
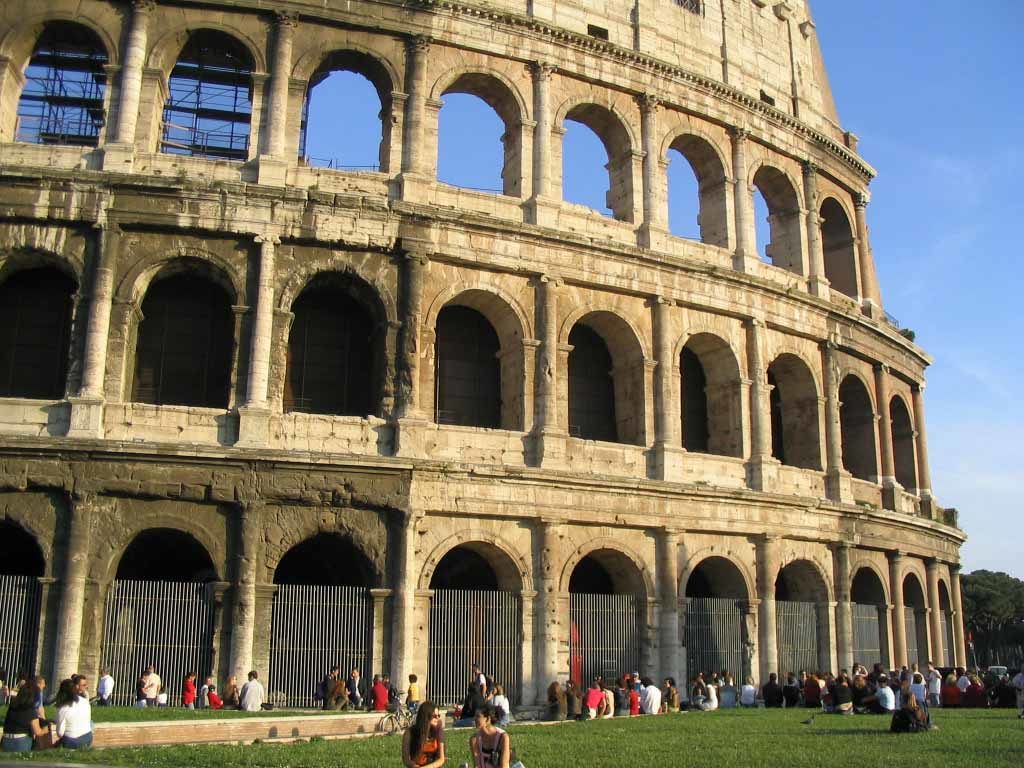
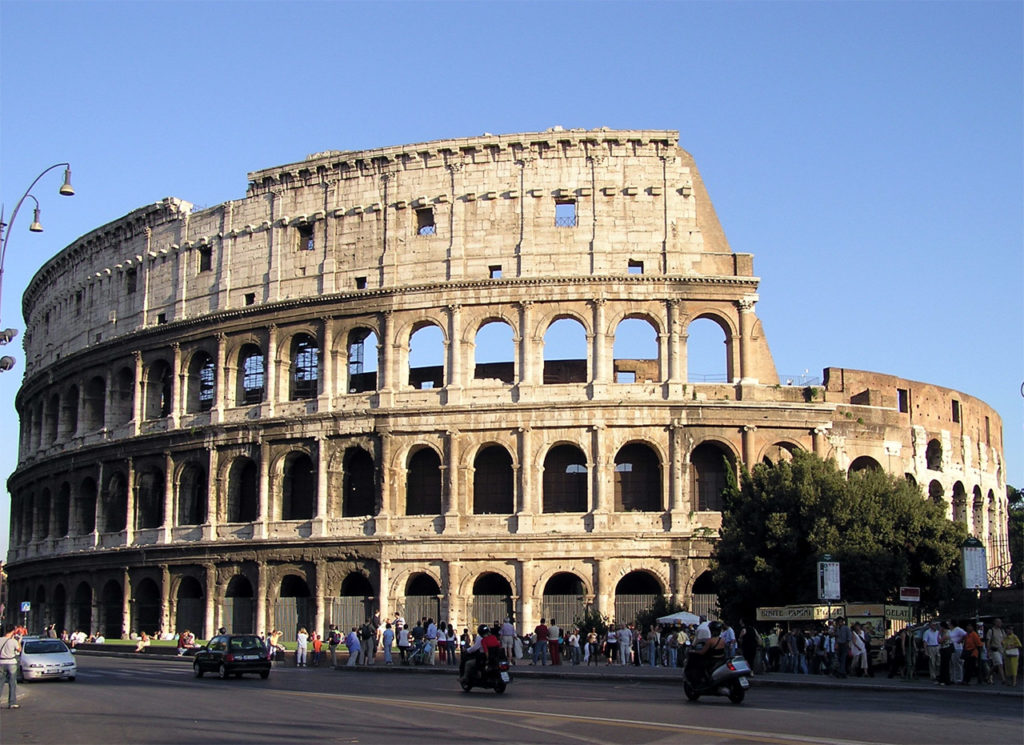
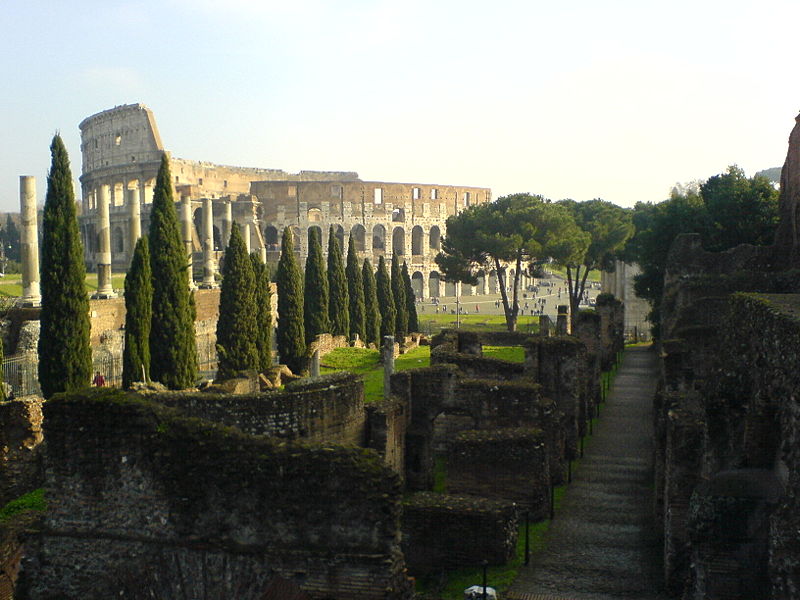
The Coliseum (Colosseum in Latin), originally called the Flavian Amphitheater (Amphitheatrum Flavium) is a large building in the center of Rome, capital of Italy. In ancient times had a capacity for 50,000 spectators, with eighty rows of bleachers. Those close to the arena were the Emperor and the Senate, and as they stood were lower strata of society. Took place at the Coliseum gladiator fights and public.
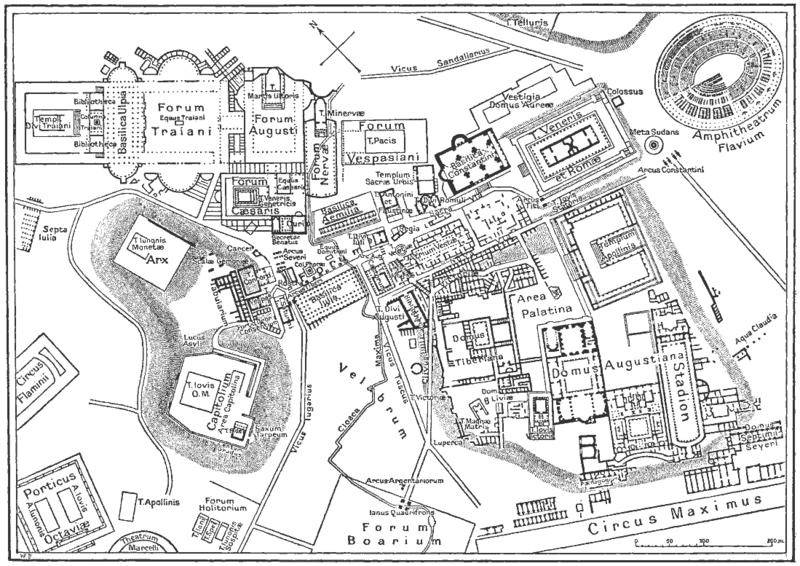
It was built just east of the ancient Roman Forum where erjia is the Domus Aurea, the residence of the Emperor Nero. Work began in 70 A.D. and 72 AD, under mandate of the Emperor Vespasian. The amphitheater, which was the largest ever built in the Roman Empire, was completed in 80 AD by the Emperor Titus, and was modified during the reign of Domitian.
The identity of the architect of the building, as in general most of the Roman works: the public buildings were erected for the greater glory of the emperors. Throughout the years we have discussed the names of Rabirio, Severo, Gaudencio or Apollodorus of Damascus, although it is known that the latter came to Rome in the year 105.
The Colosseum was used for nearly 500 years, held in the gladiator fights and many other public events taking place here, as naumaquias, hunting animals, executions, re-creations of famous battles and dramas based on classical mythology.
The building was being used for these purposes in the High Middle Ages. Later, he was re-used as a refuge, factory, home of a religious order, strength, quarry and a Christian shrine.
Location
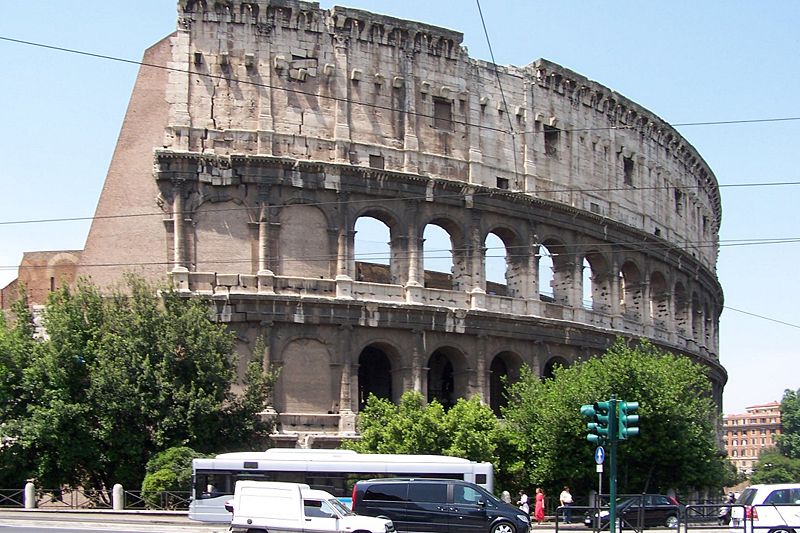
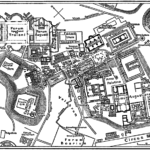
At present, the Coliseum in Rome is situated in the Piazza del Colosseo slightly east of the Roman Forum.
In the years of construction the site chosen for the project were Desrrollo marshy land between the hills and Caelian Esquilino erg where formerly the Domus Aurea, the residence of the Emperor Nero.
Description
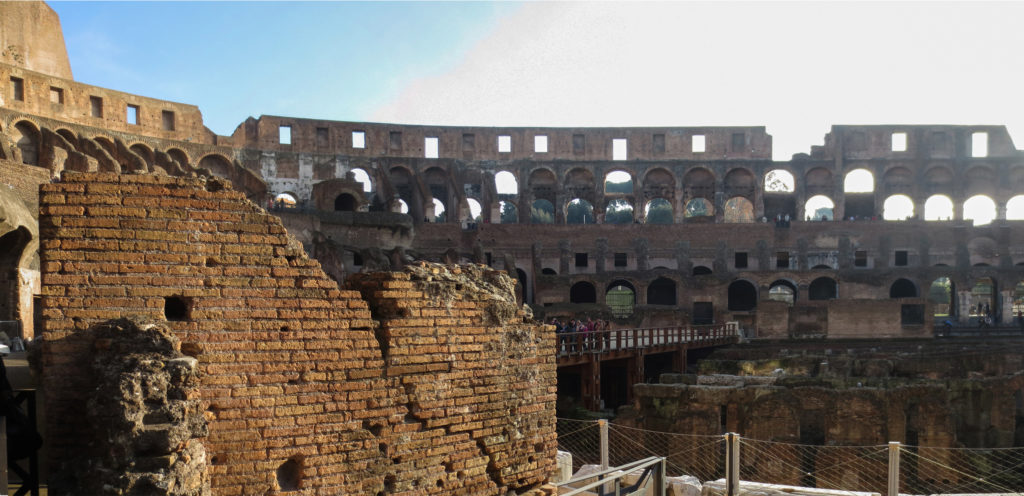
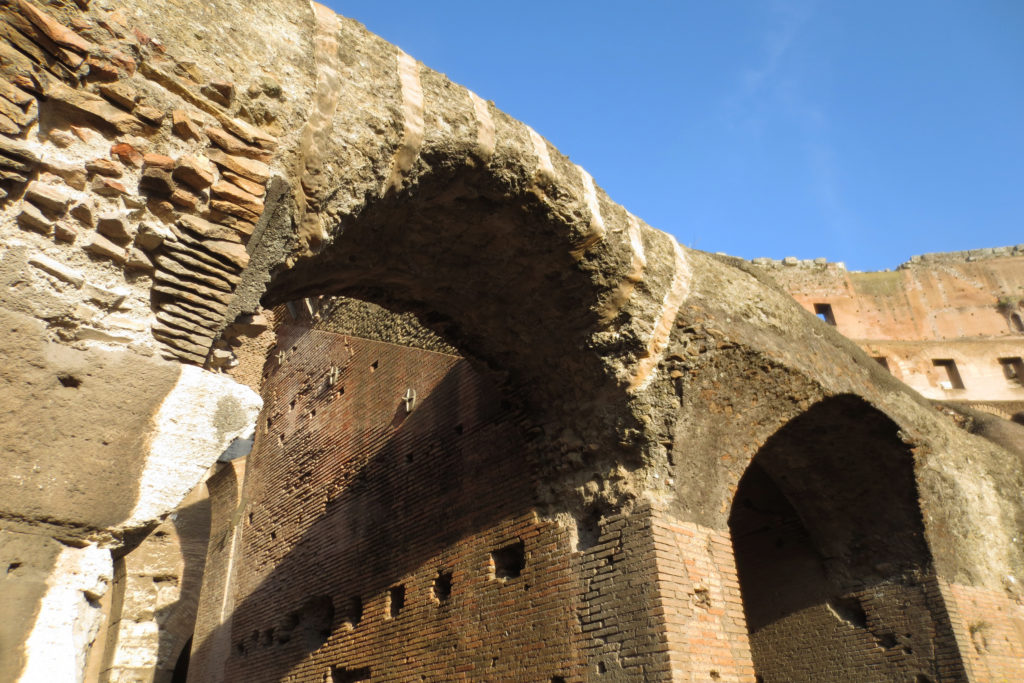
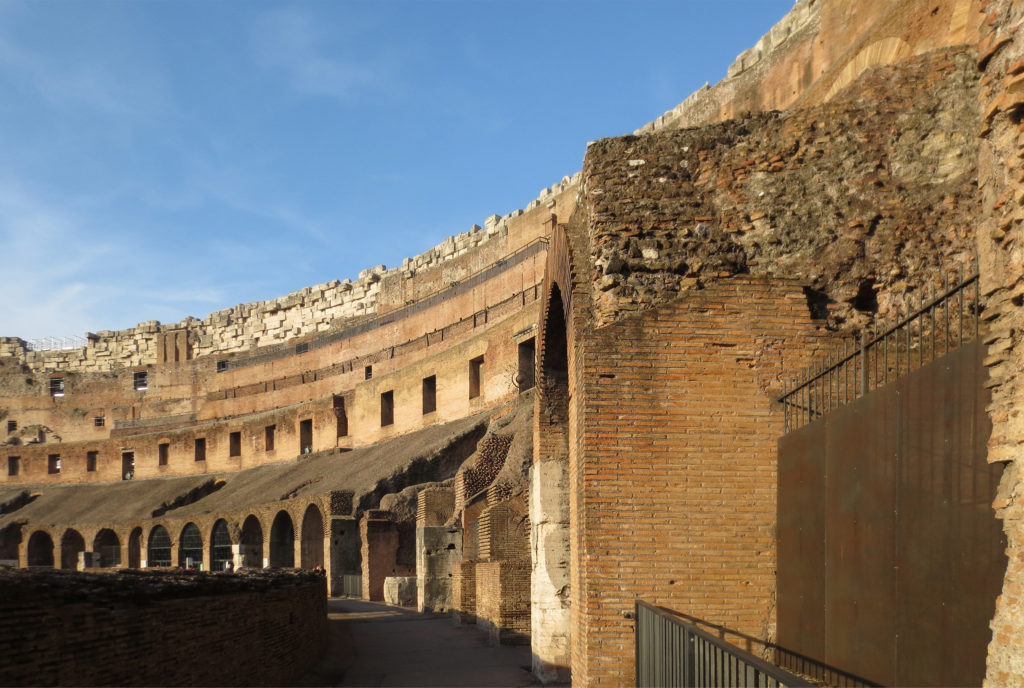
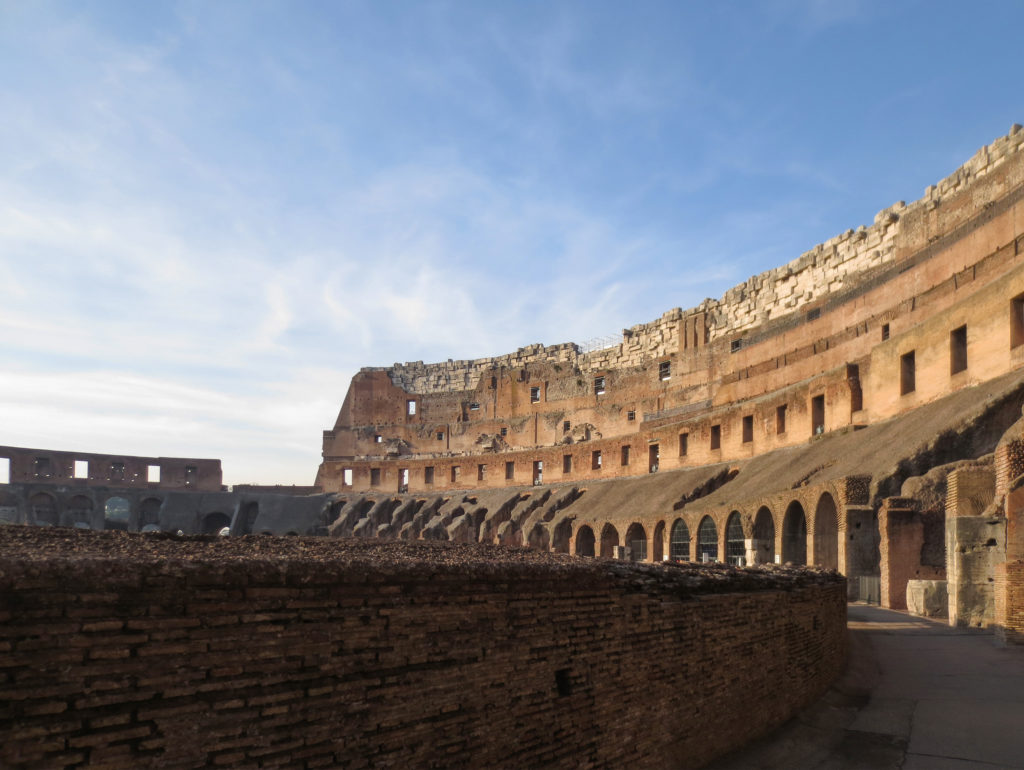
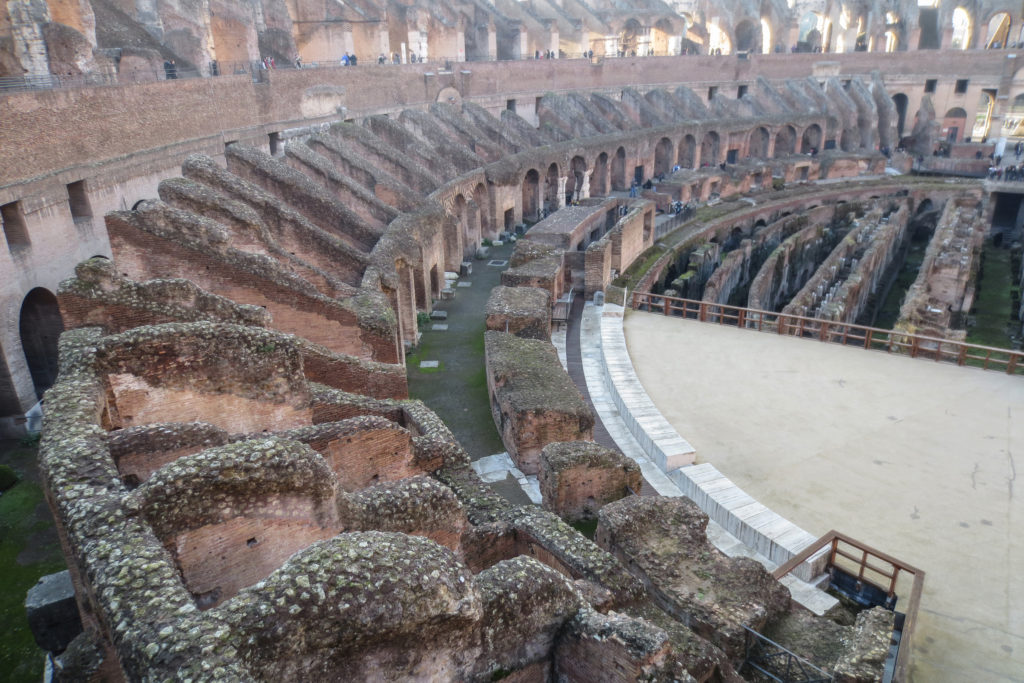
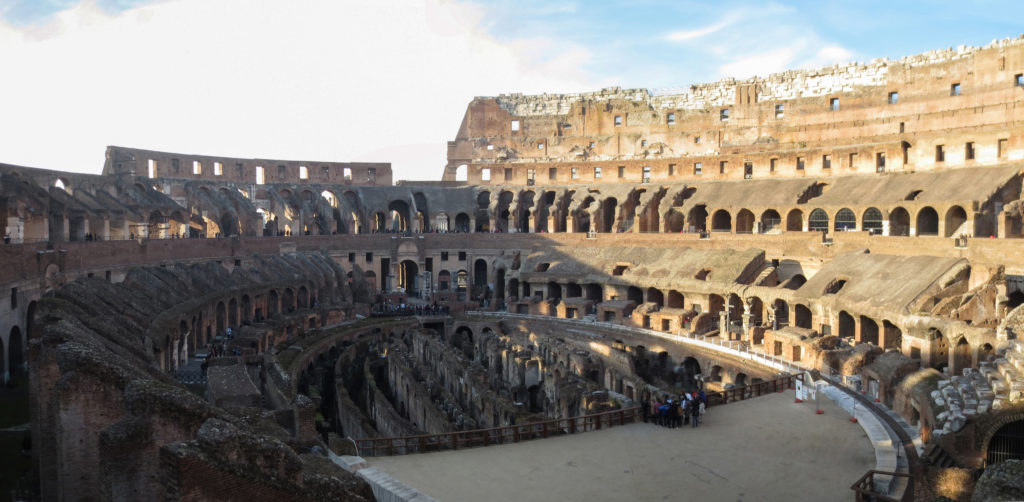
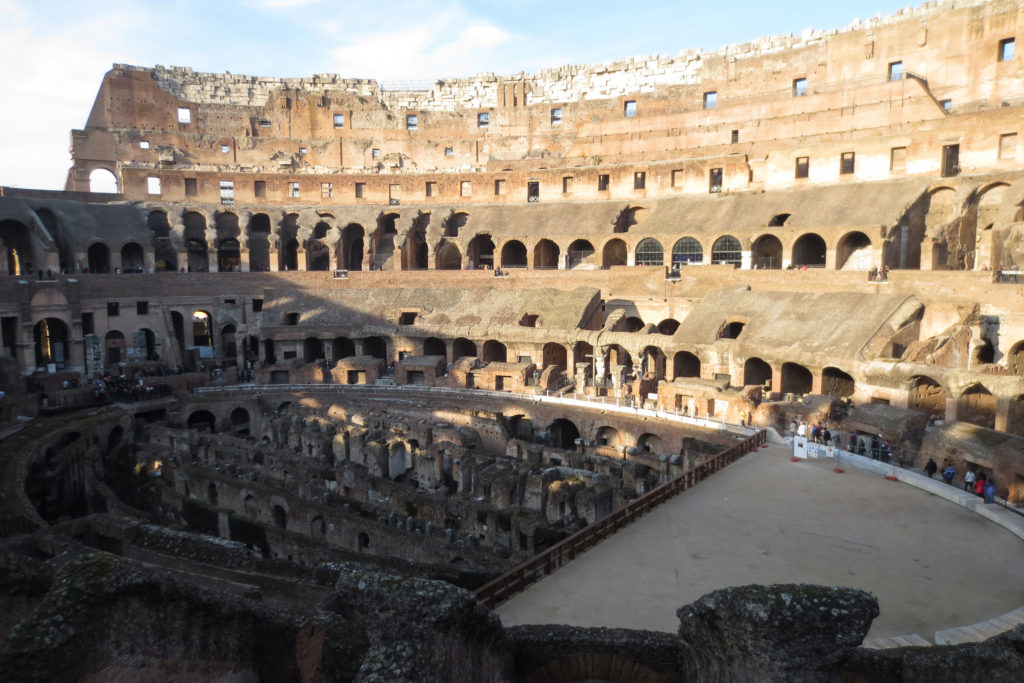
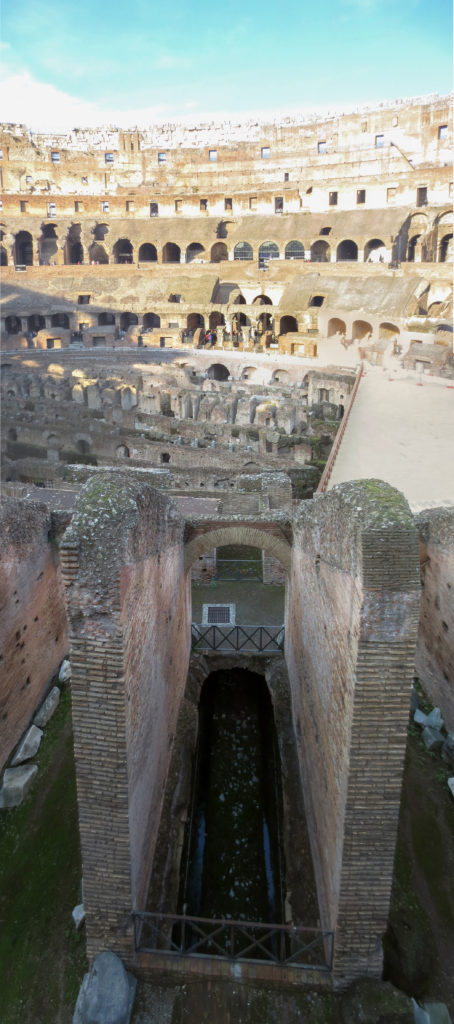
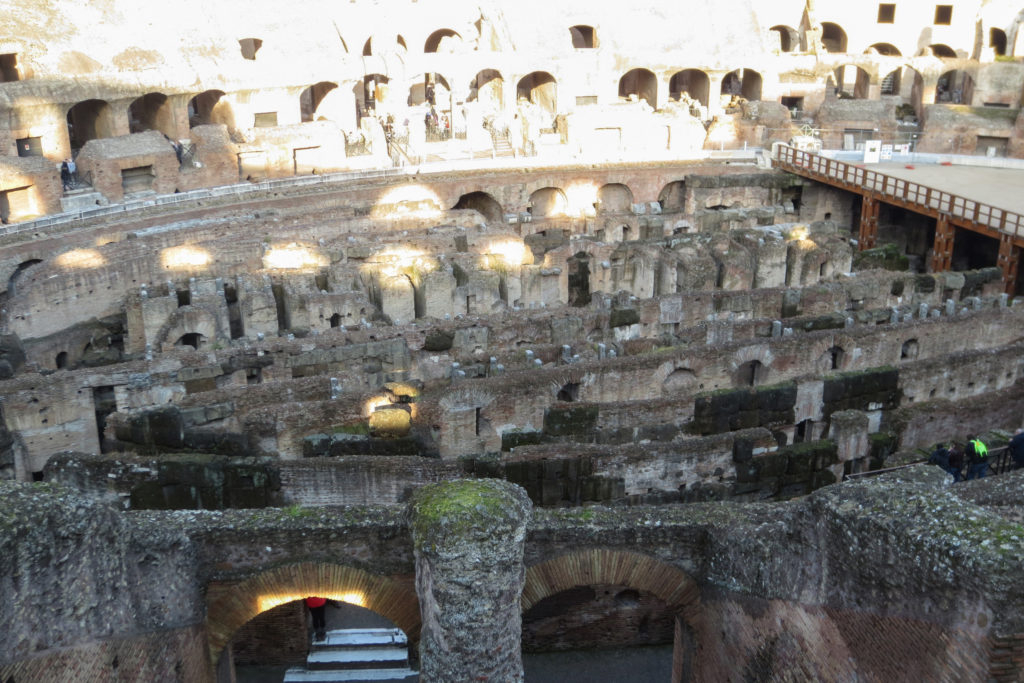
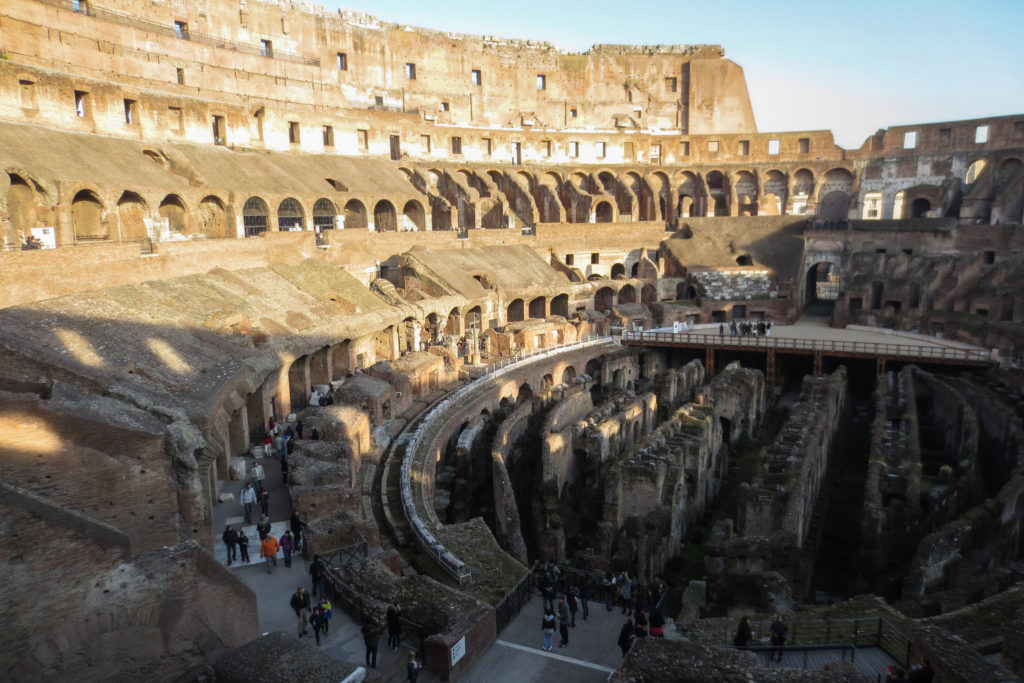
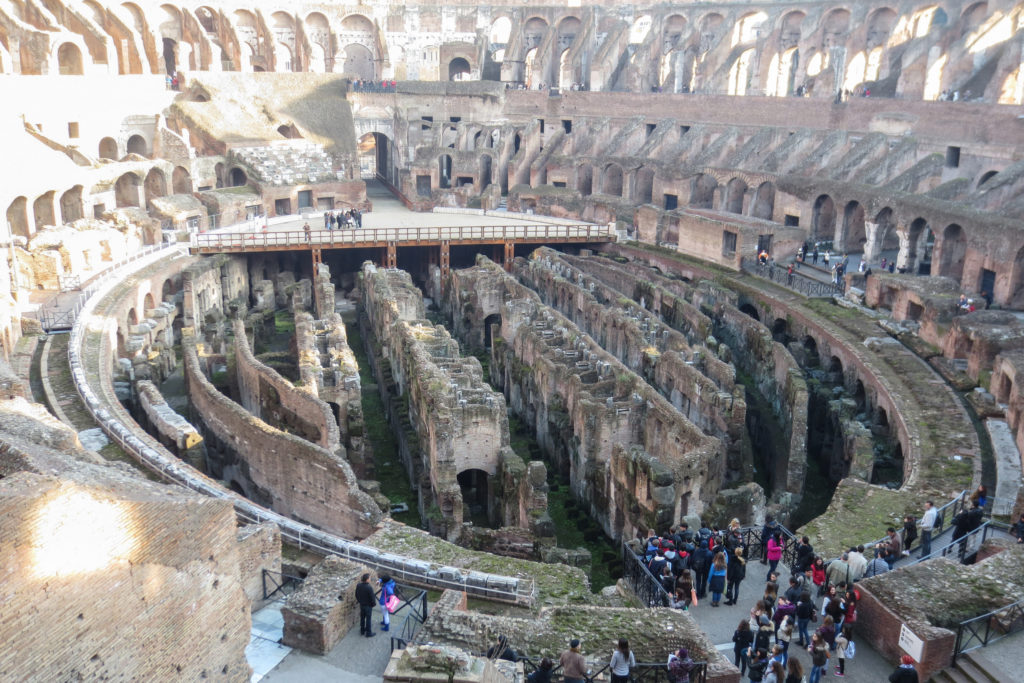
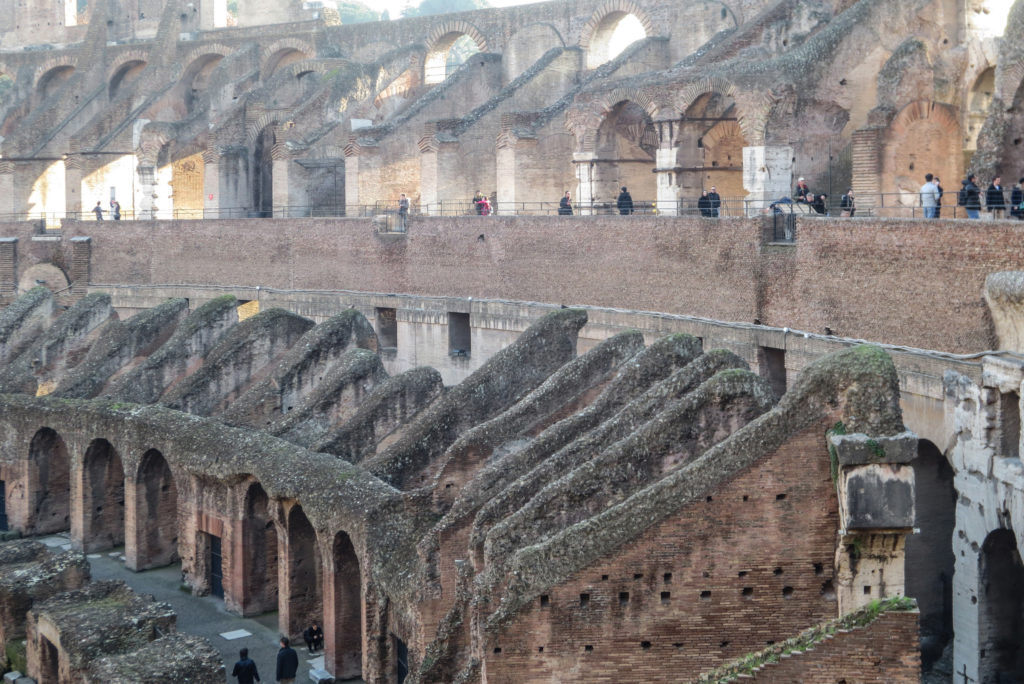
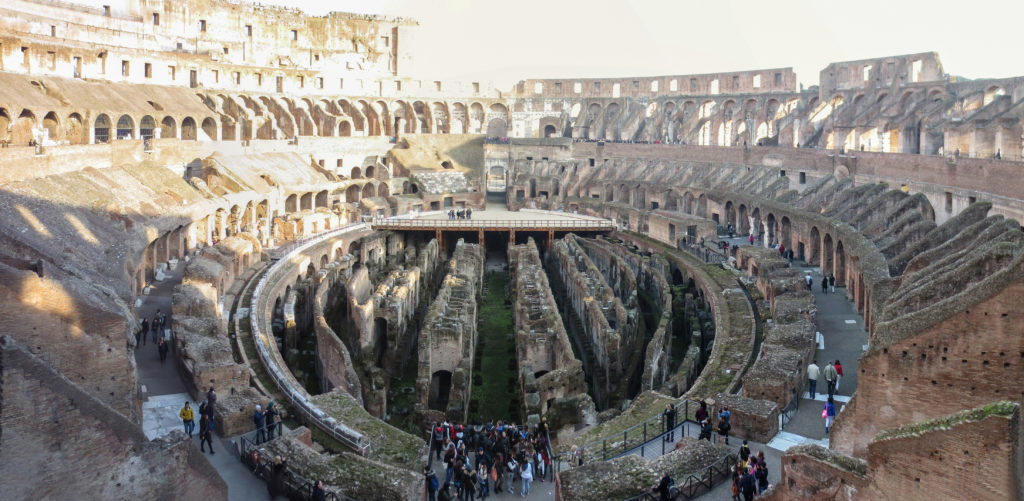
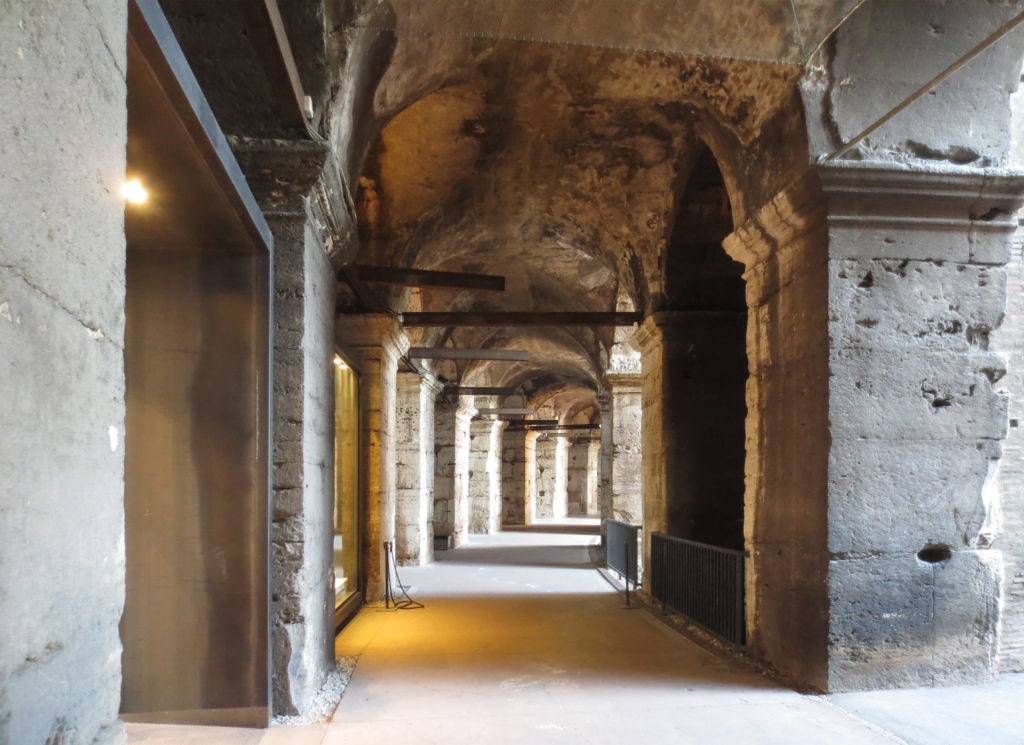
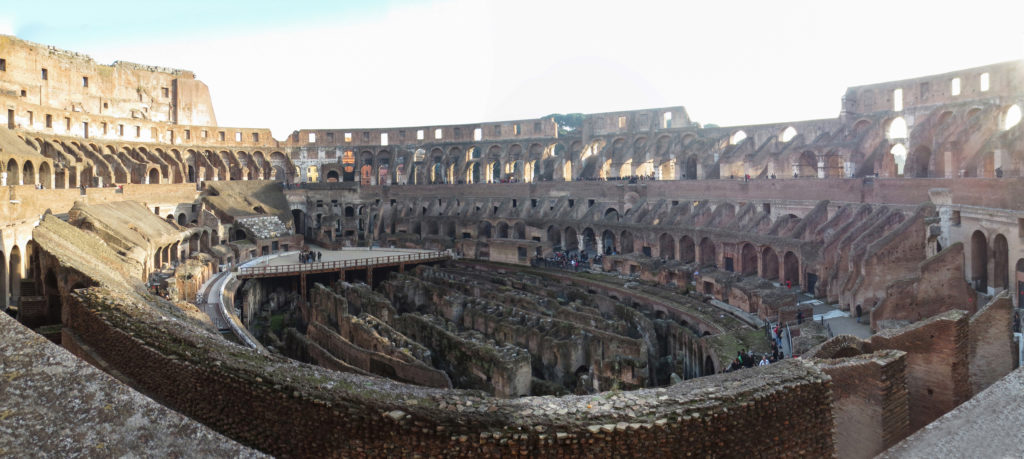
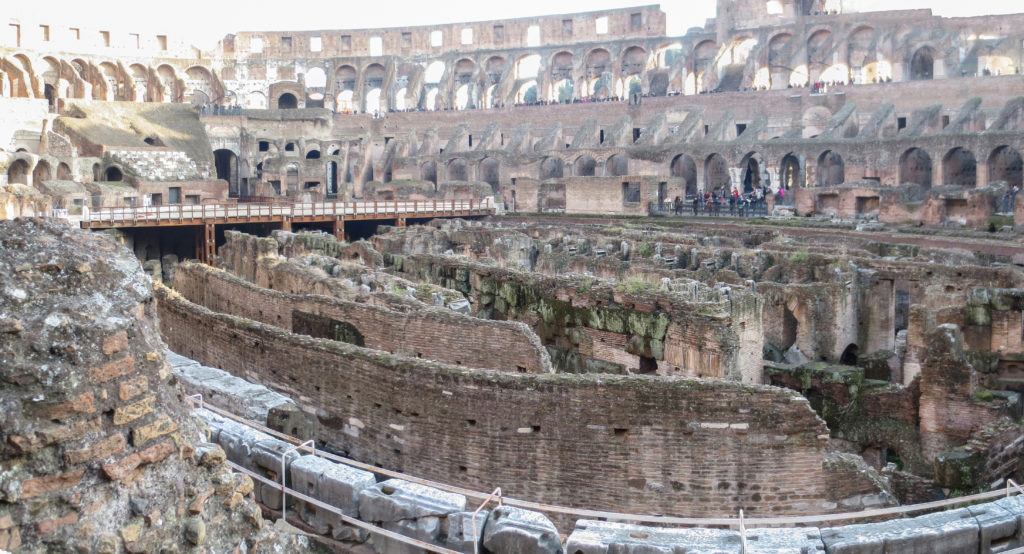
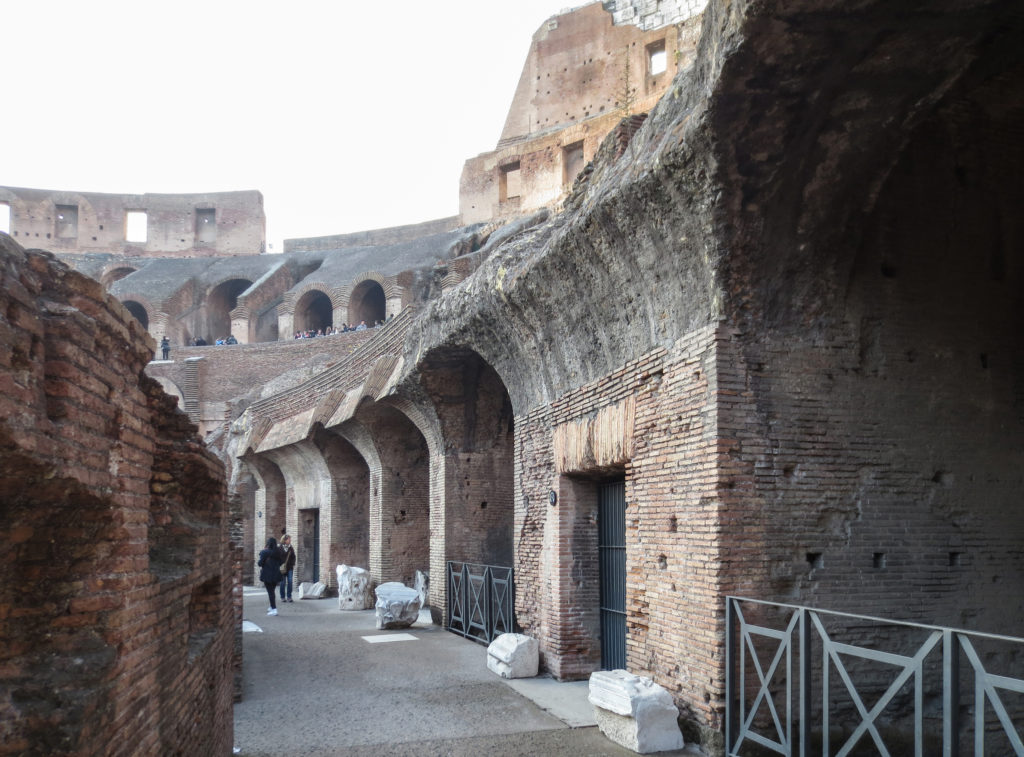
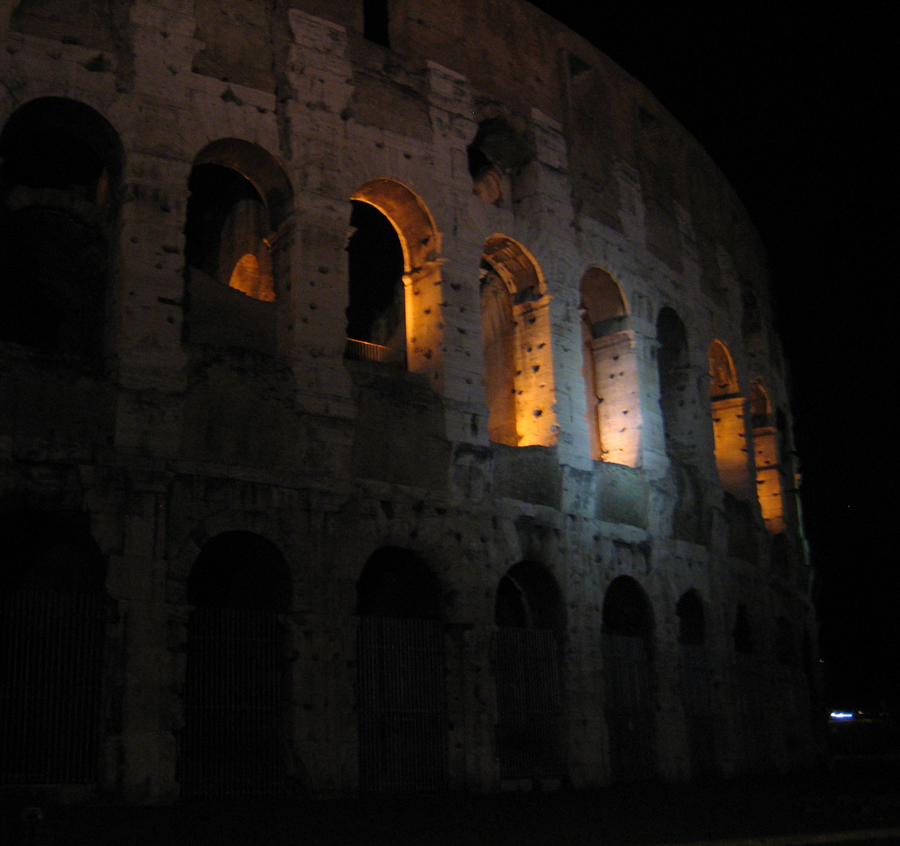
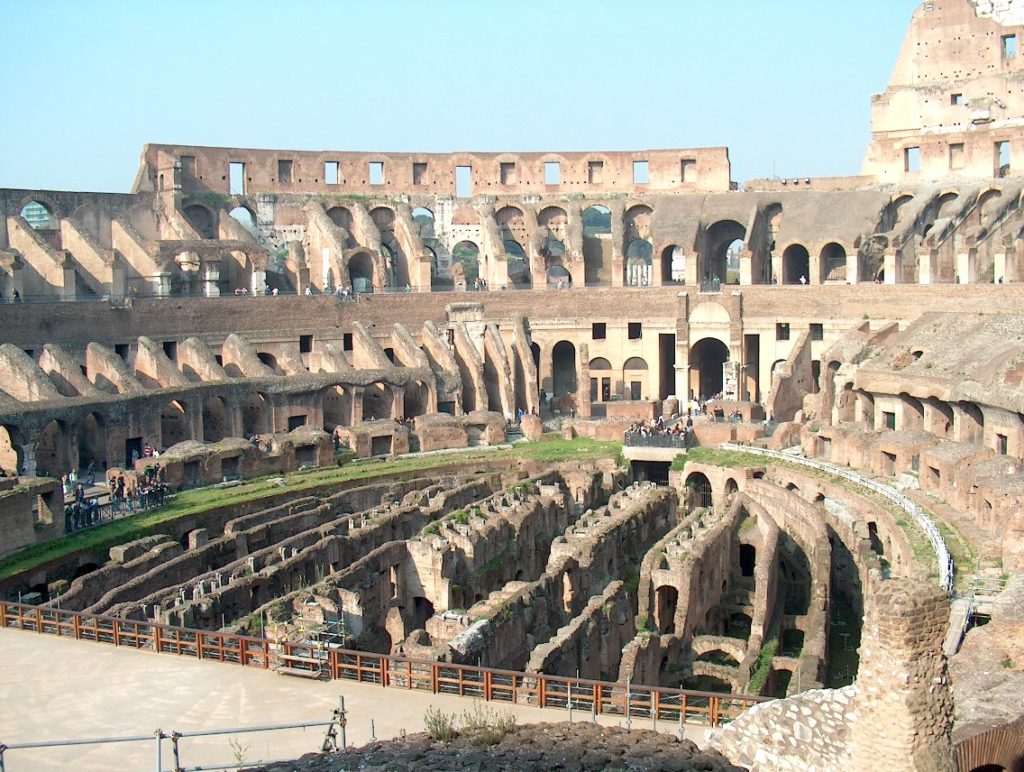
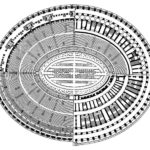
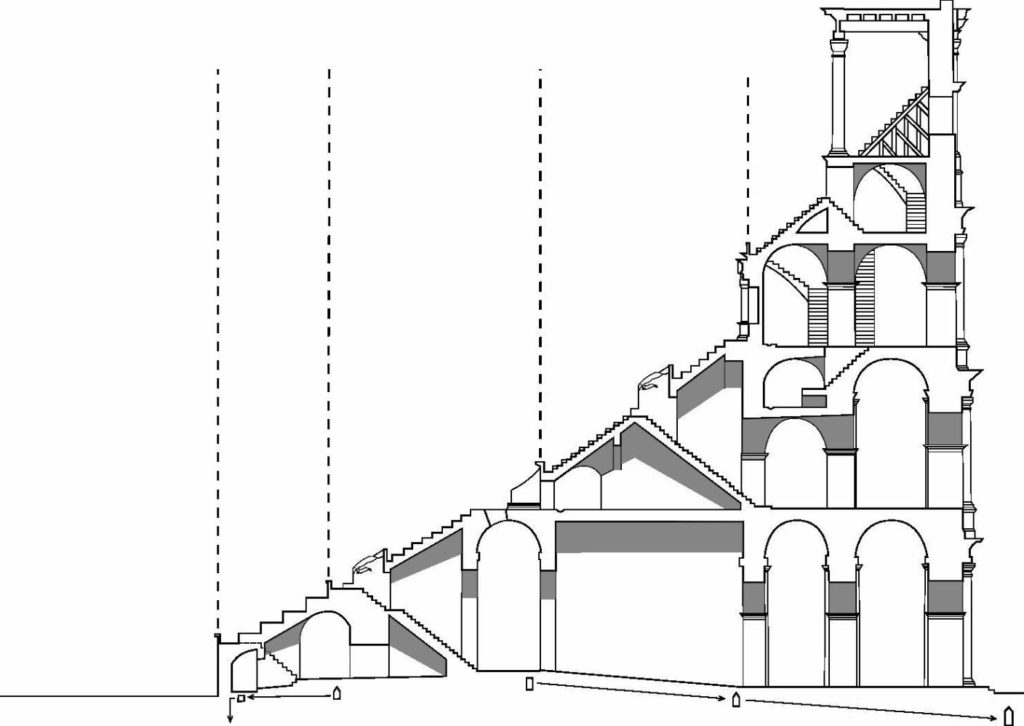
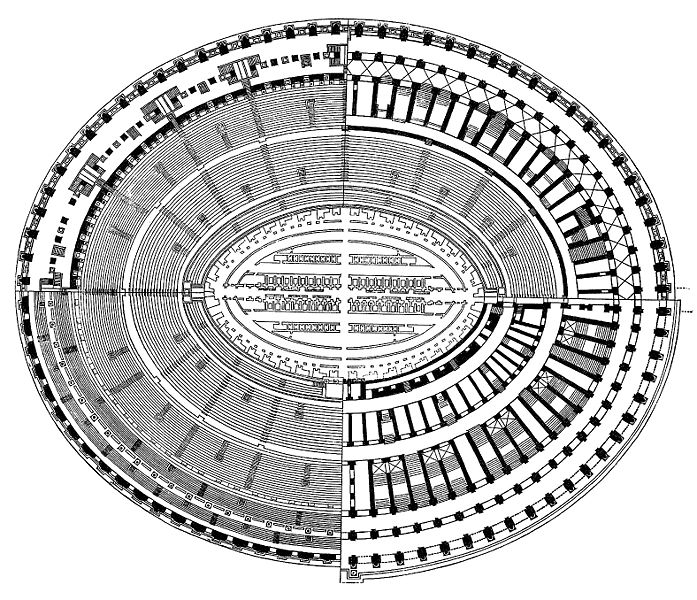
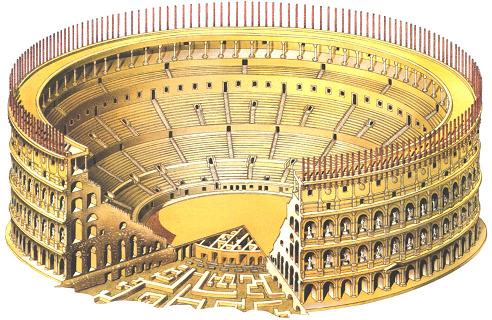
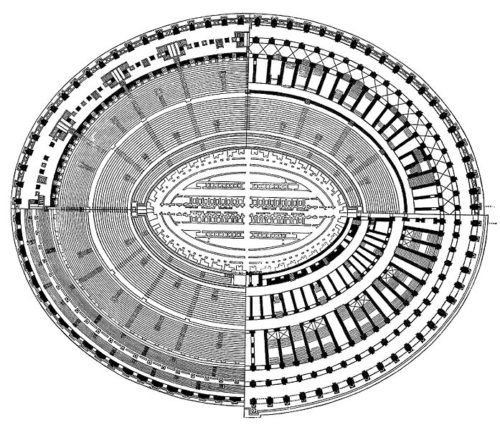
The Flavian Amphitheater is a huge oval building 189 meters long by 156 wide and 48 meters high with a perimeter of 524 meters elliptical.
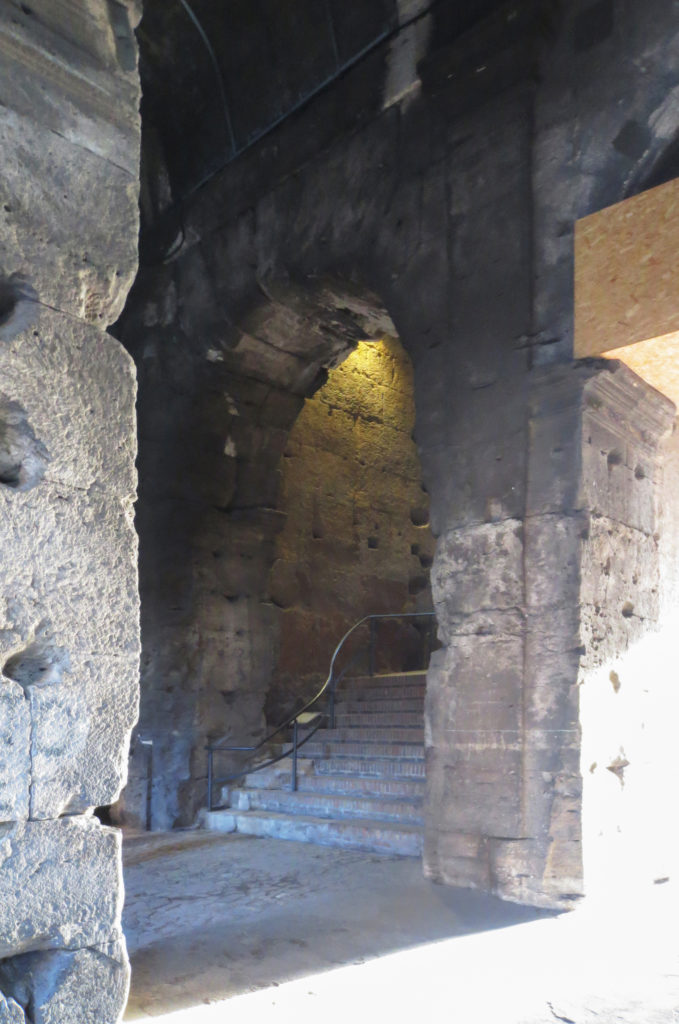
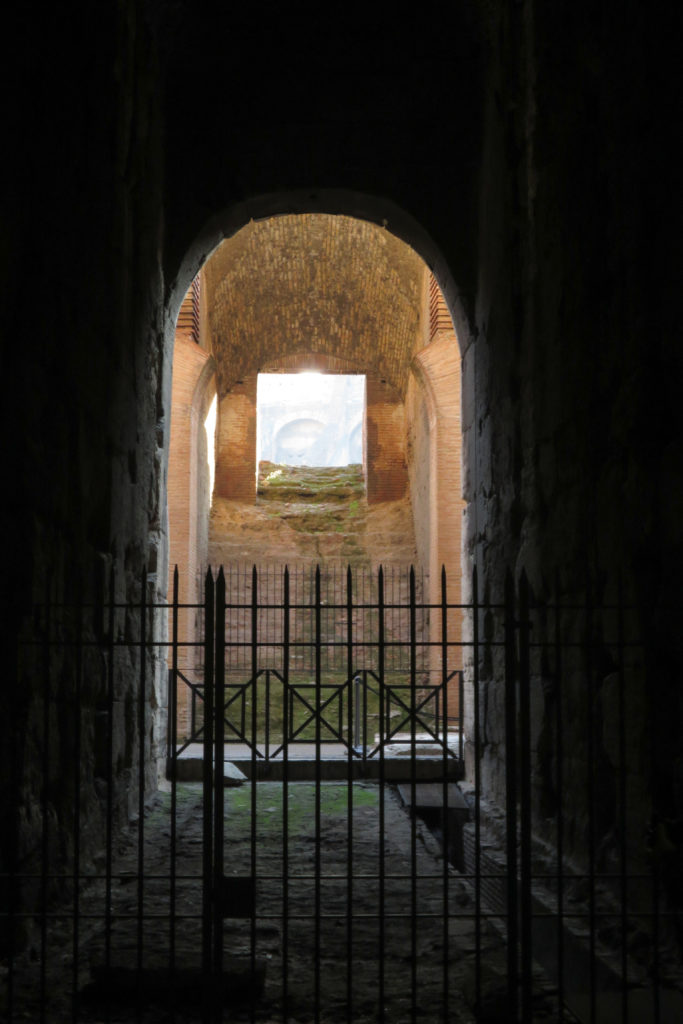
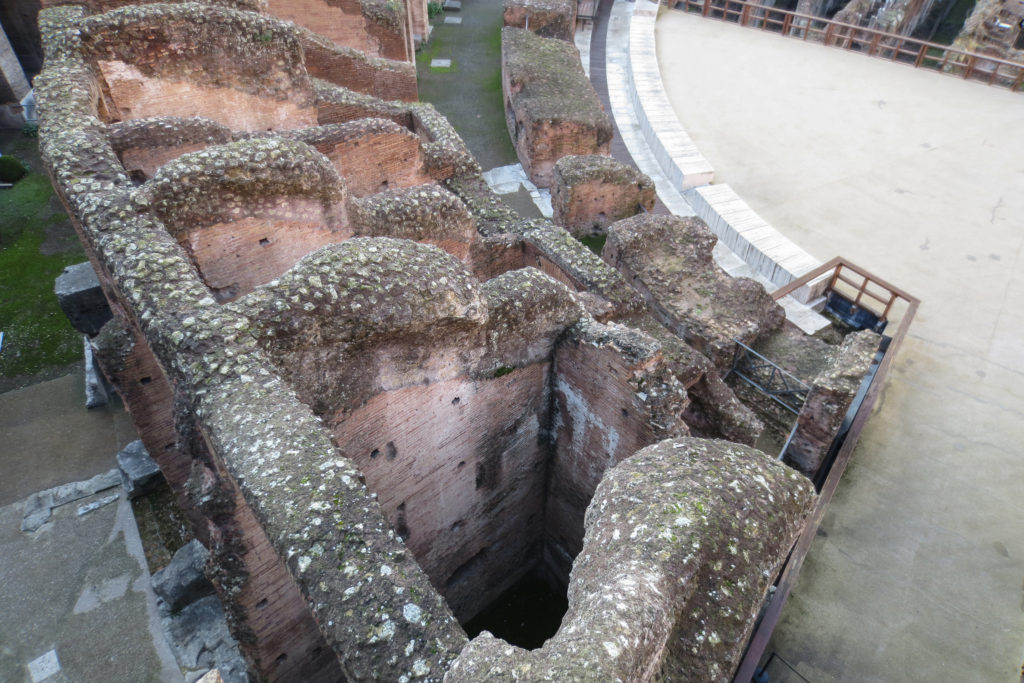
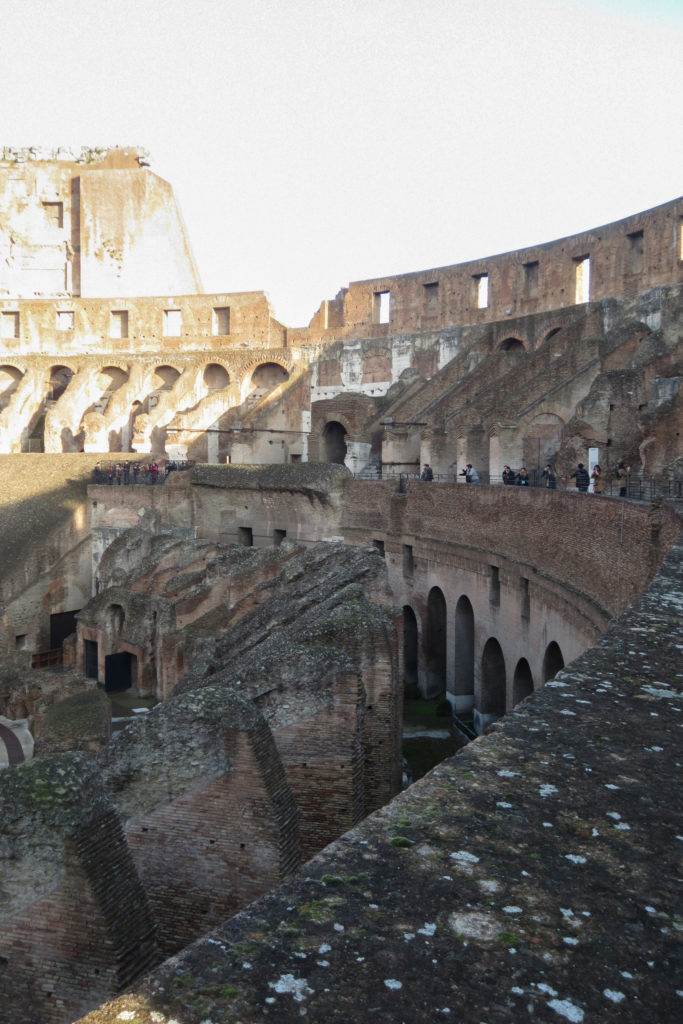
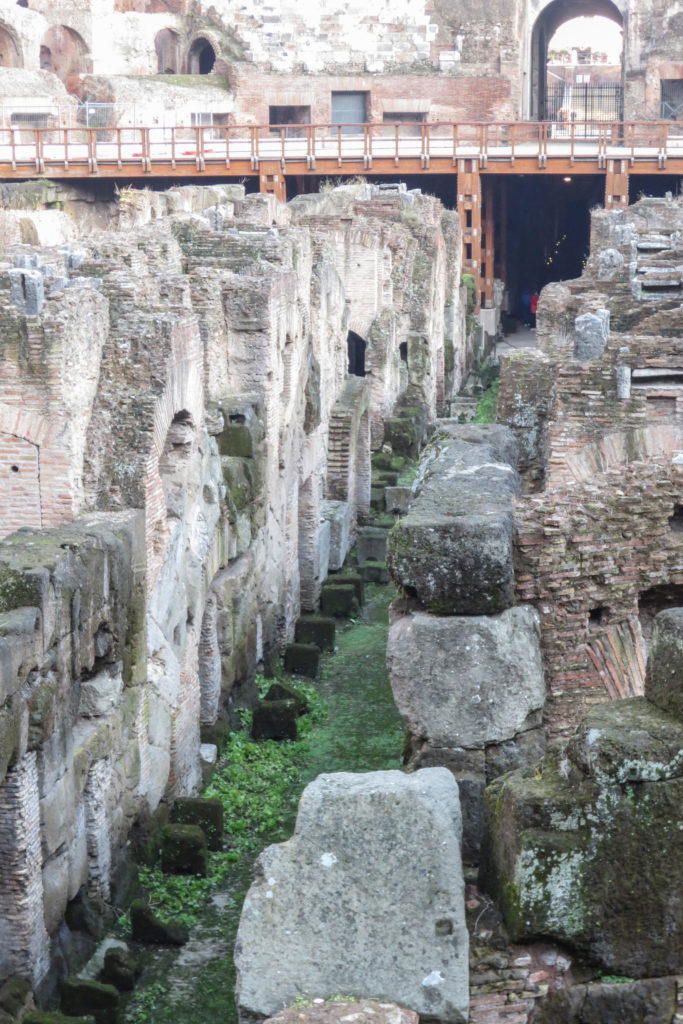
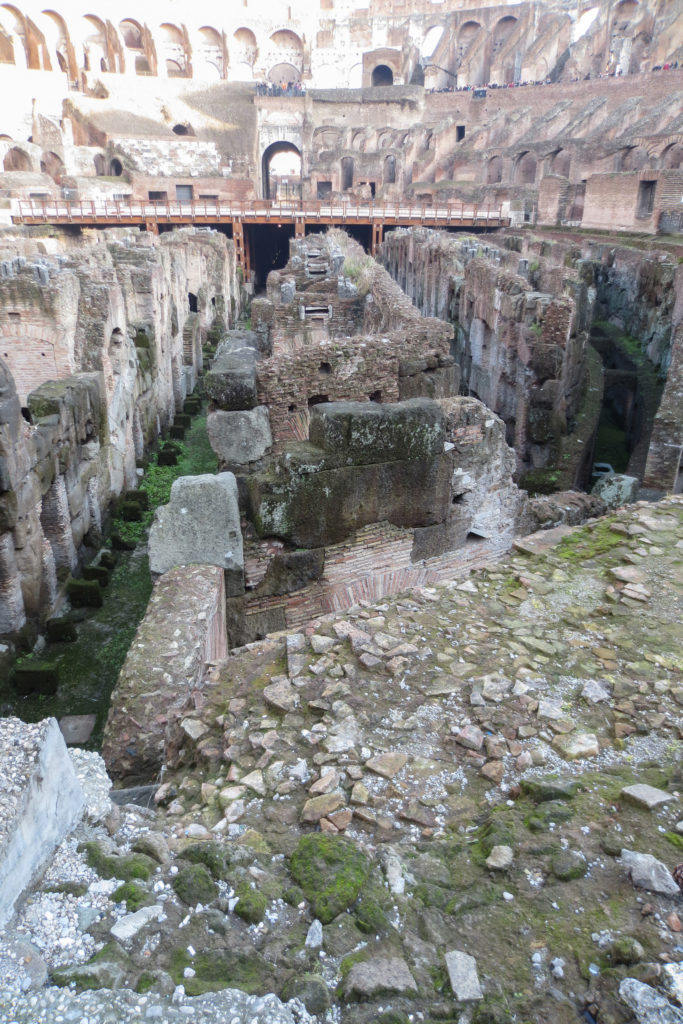
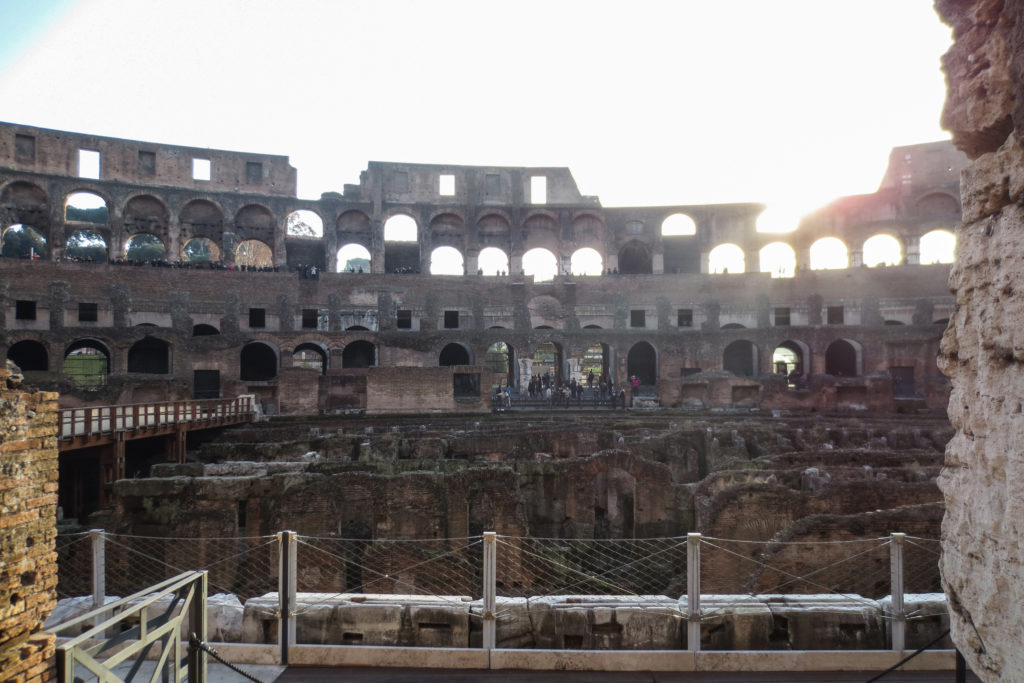
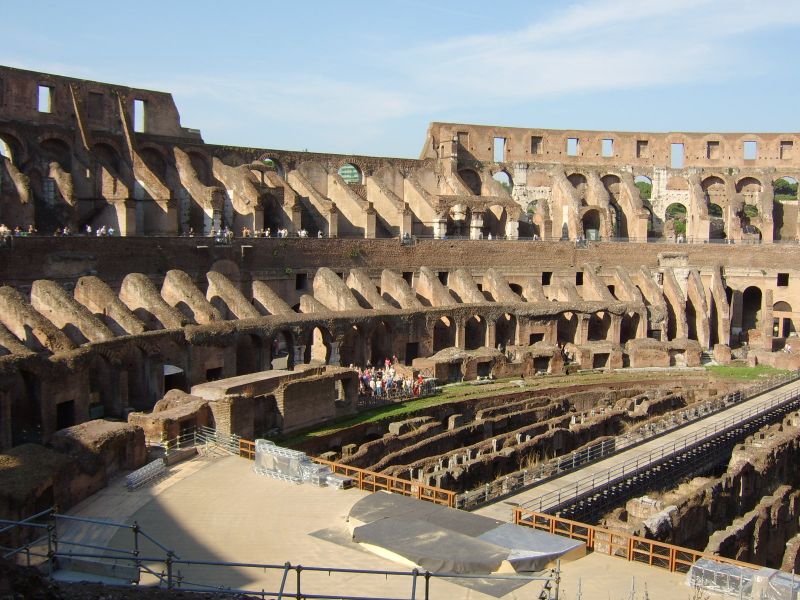
The arena itself was an oval 75 by 44 meters, and in fact it was a platform built of wood and covered with sand. Everything was an underground complex of tunnels and dungeons in which housed the gladiators, and the condemned animals. The floor had several hatches and hoists it communicated with the basement and could be used during the show.
The Harrows
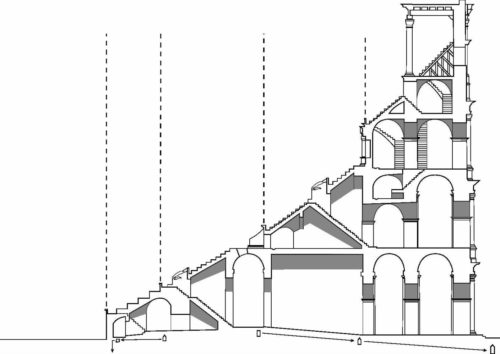
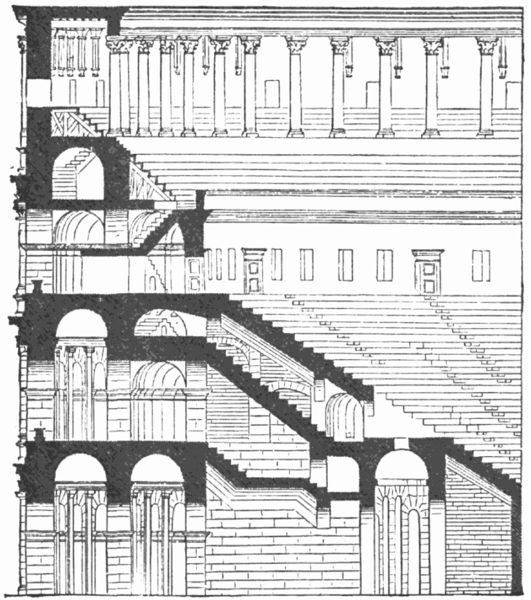
The wide differential in bleachers inside was Gradus, apartments reserved for the different social classes:
- At the podium, the first of them, sat by the Romans more illustrious: Senators, judges, priests and maybe vestals. At both ends of the minor axis had two stages: the imperial forum (pulvinar), and one reserved for the judge presiding over the games sometimes. Since this floor was the closest to the beasts, had a network of metal protection and archers posted regularly.
- The primum maenianum for aristocrats who did not belong to the senate
- The maenianum secundum divided in imum for citizens summum for the rich and the poor.
- As was the highest in maenianum summum ligneis, made of wood, and probably without seats reserved for women.
In addition, some social orders, such as the tribunes, priests or the militia, had reserved areas.
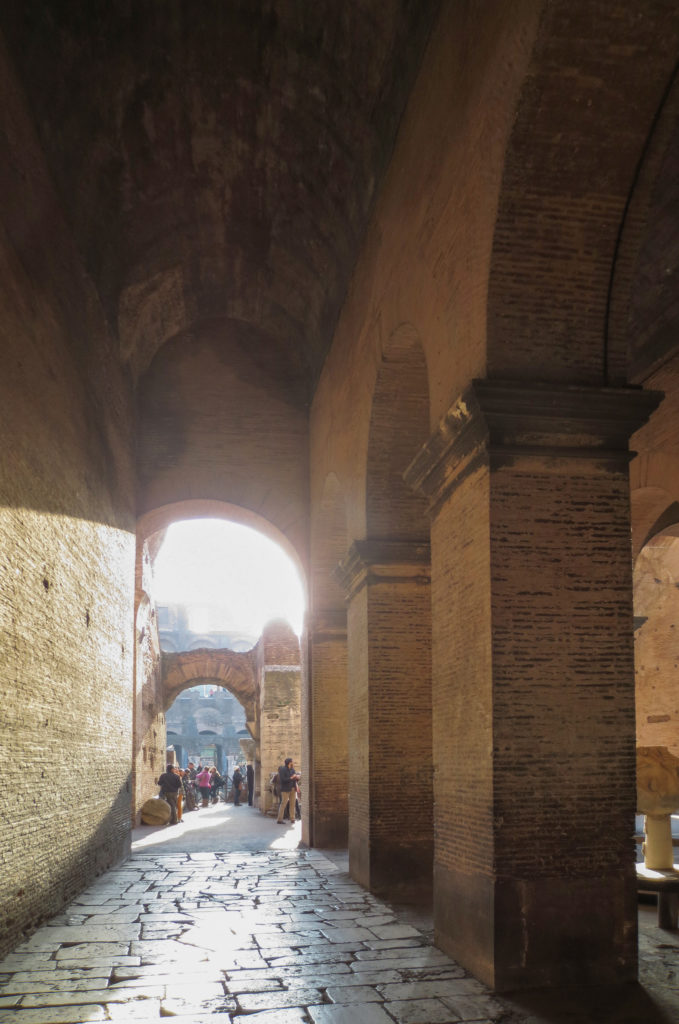
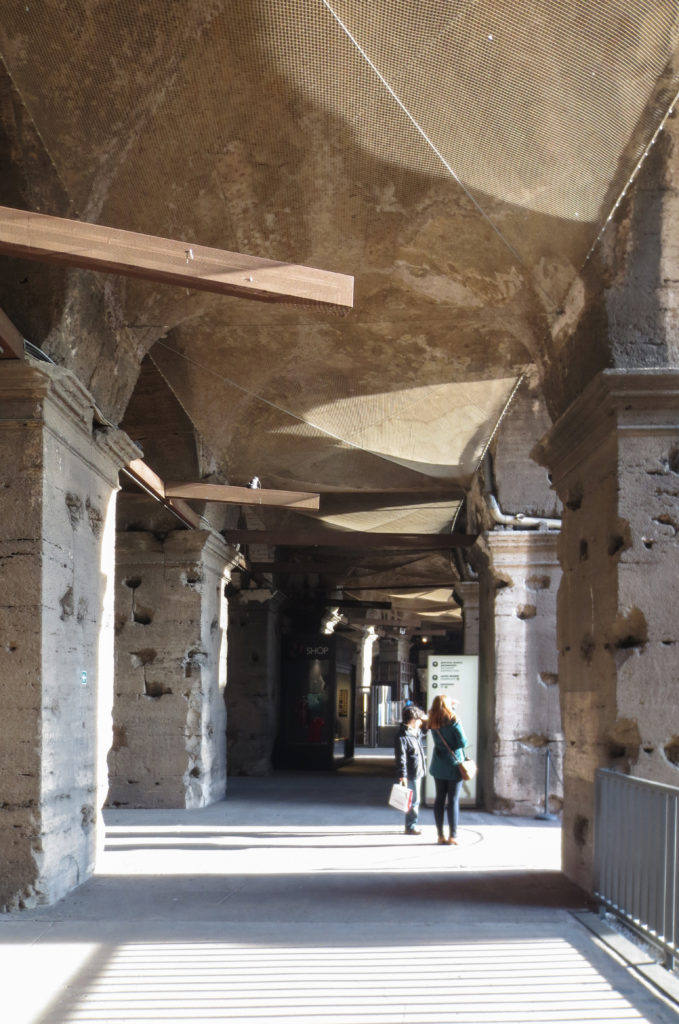
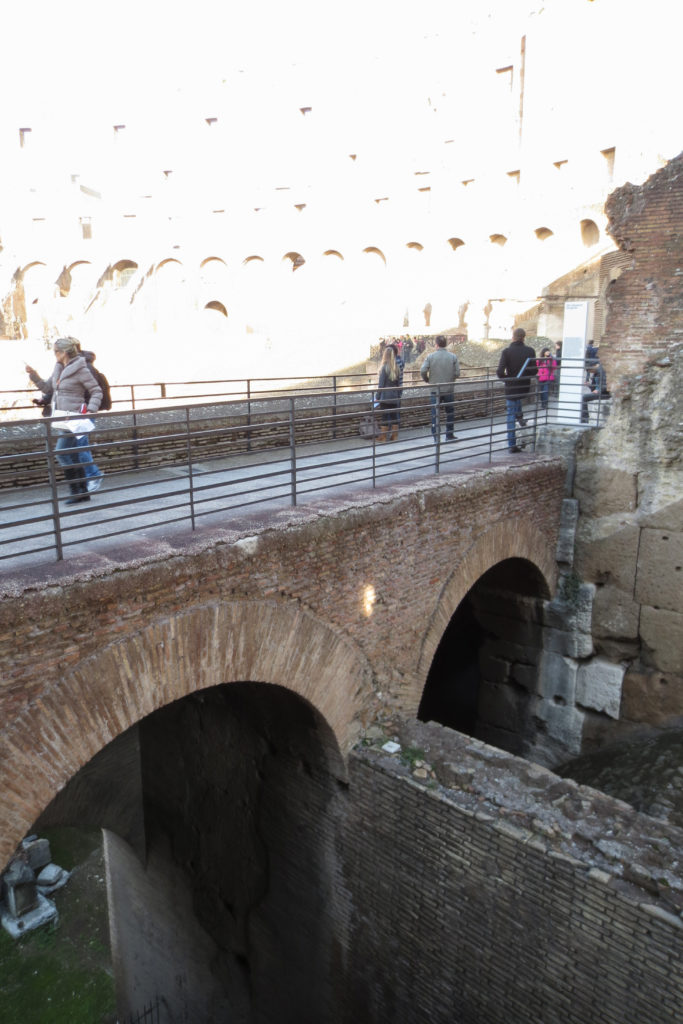
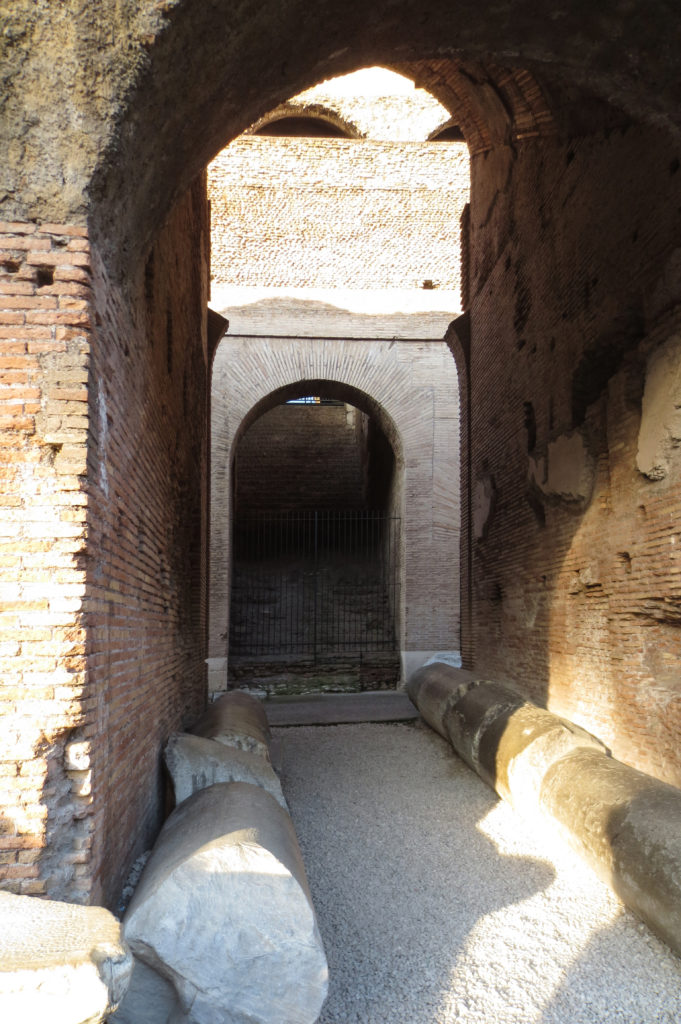
Access from the internal passageways to the stands was produced through the vomitorios called allowed to leave because a huge number of people in a short time. He was so well designed that the 50,000 spectators could be evacuated in a little more than five minutes.

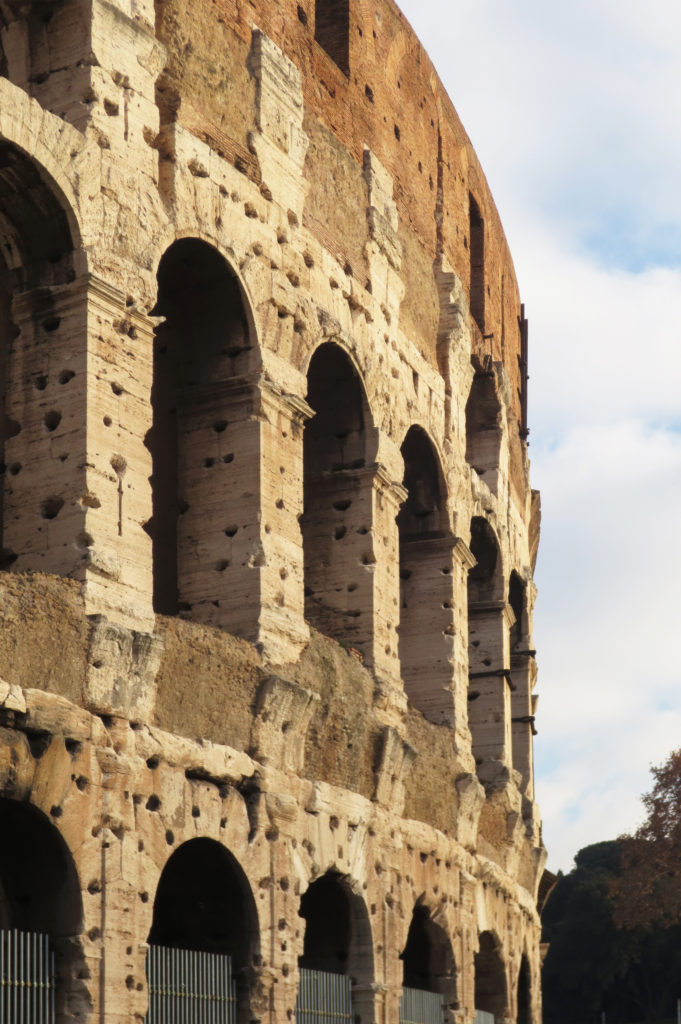
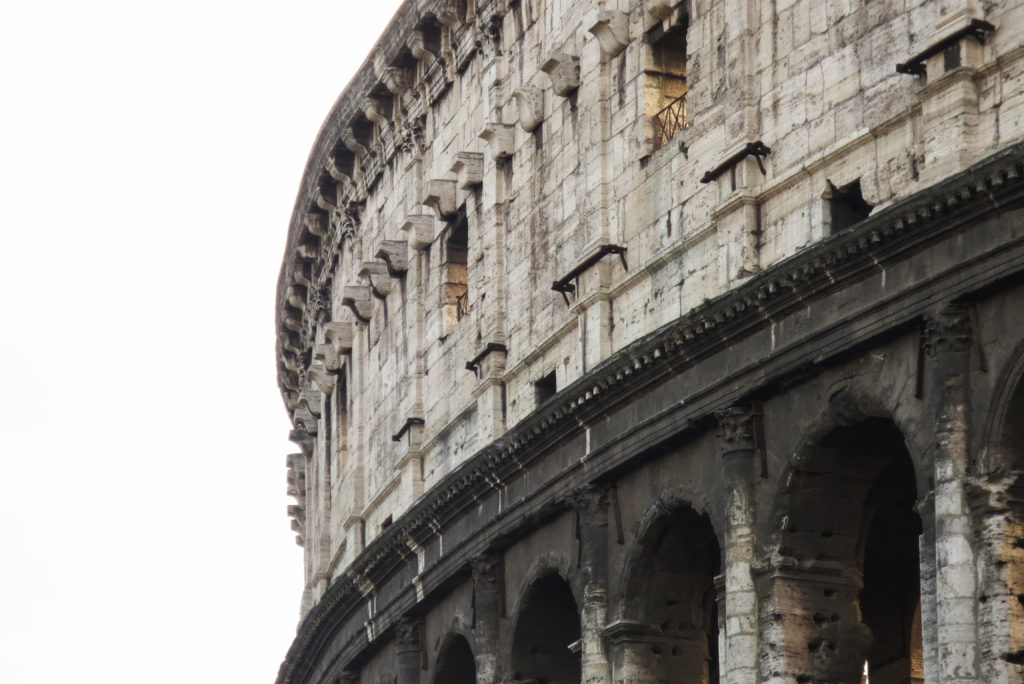
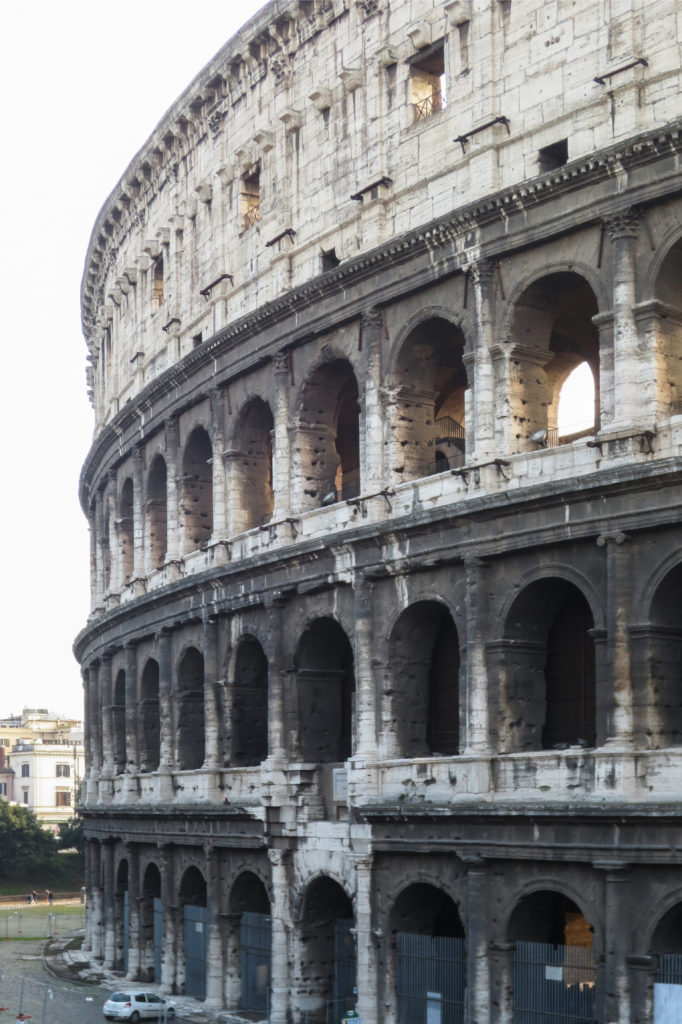
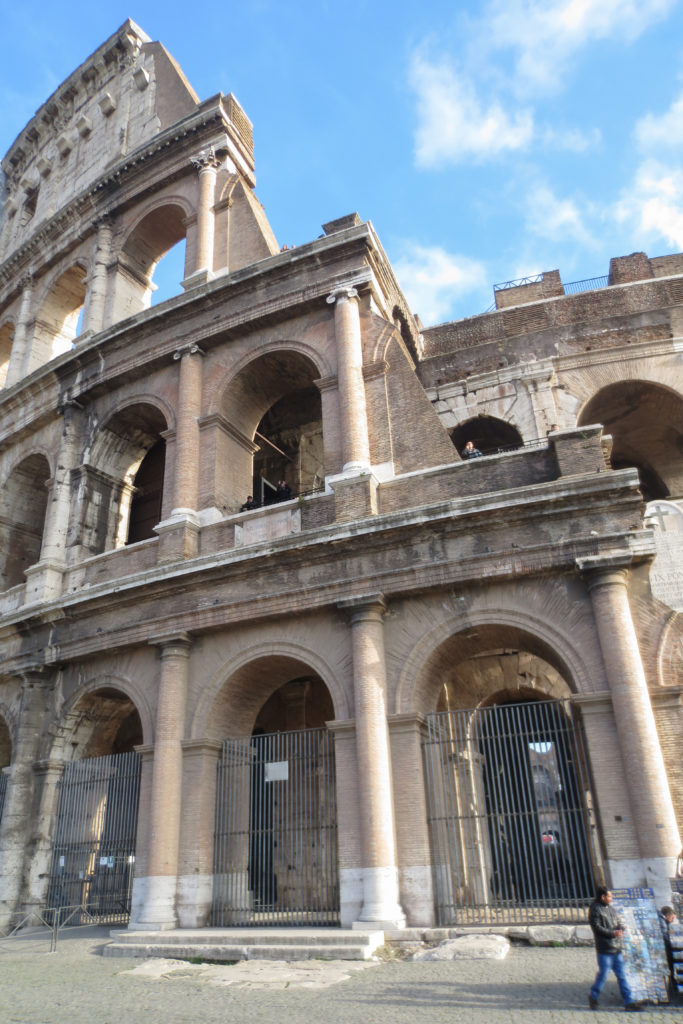
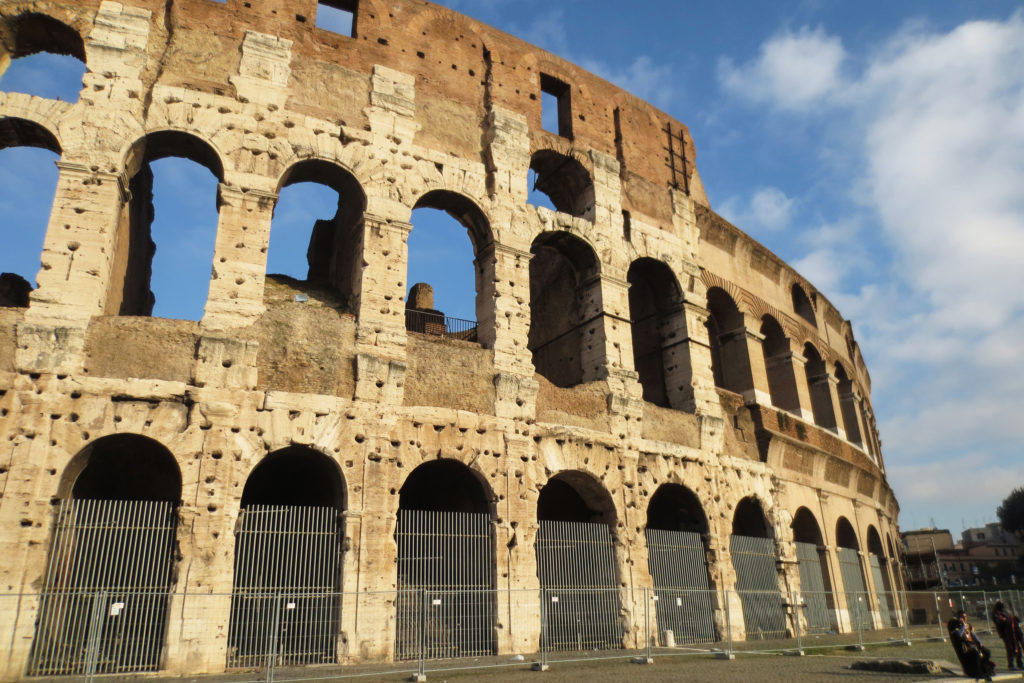
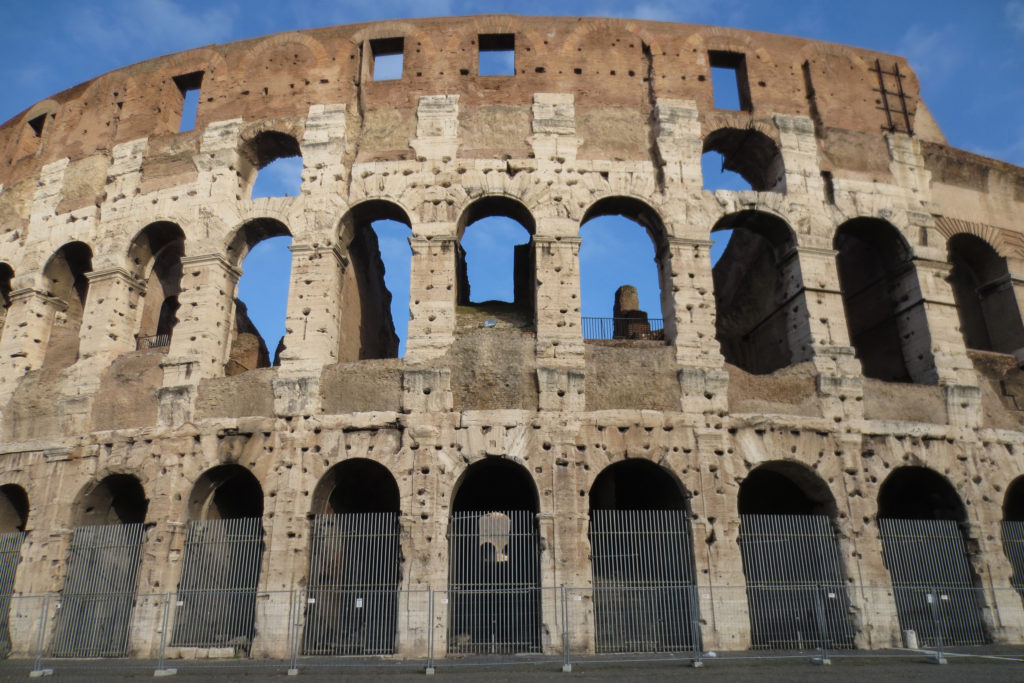
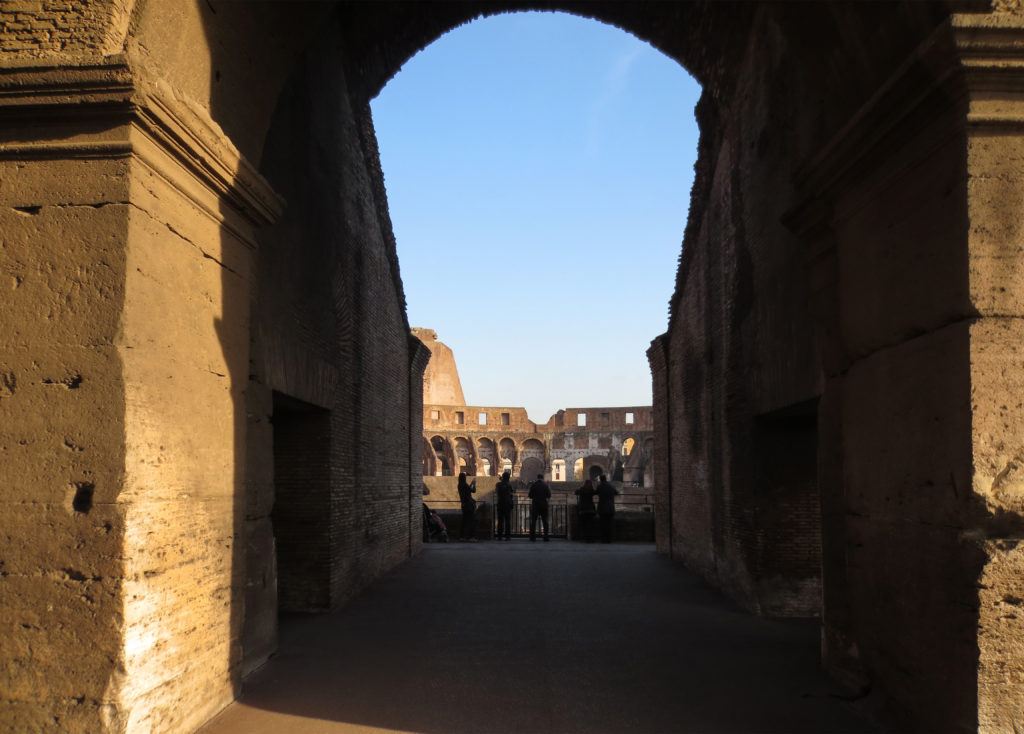
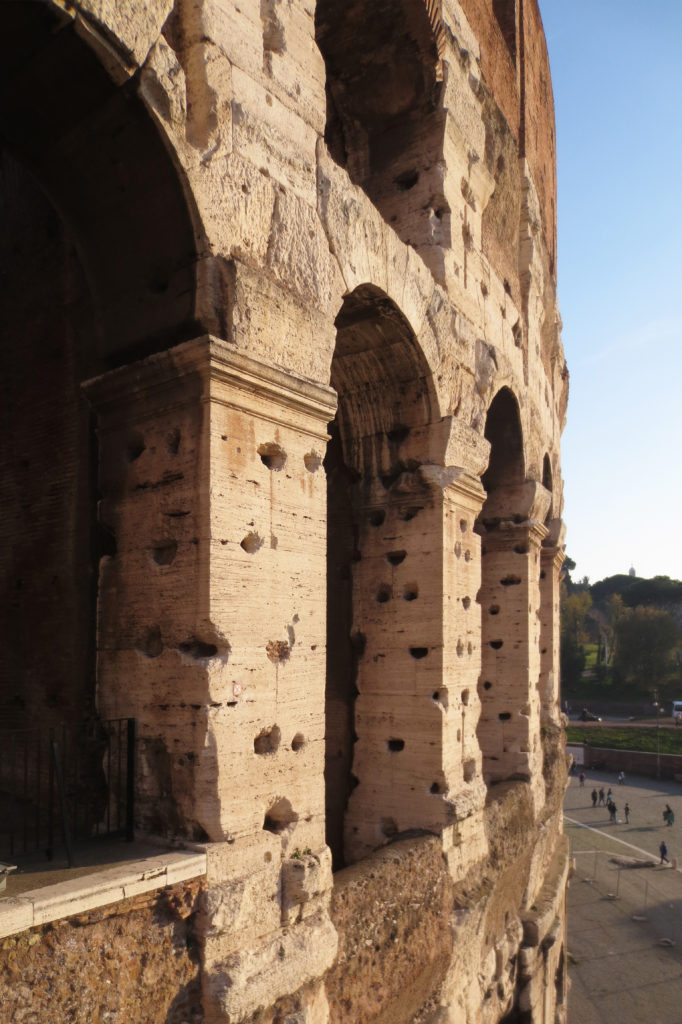
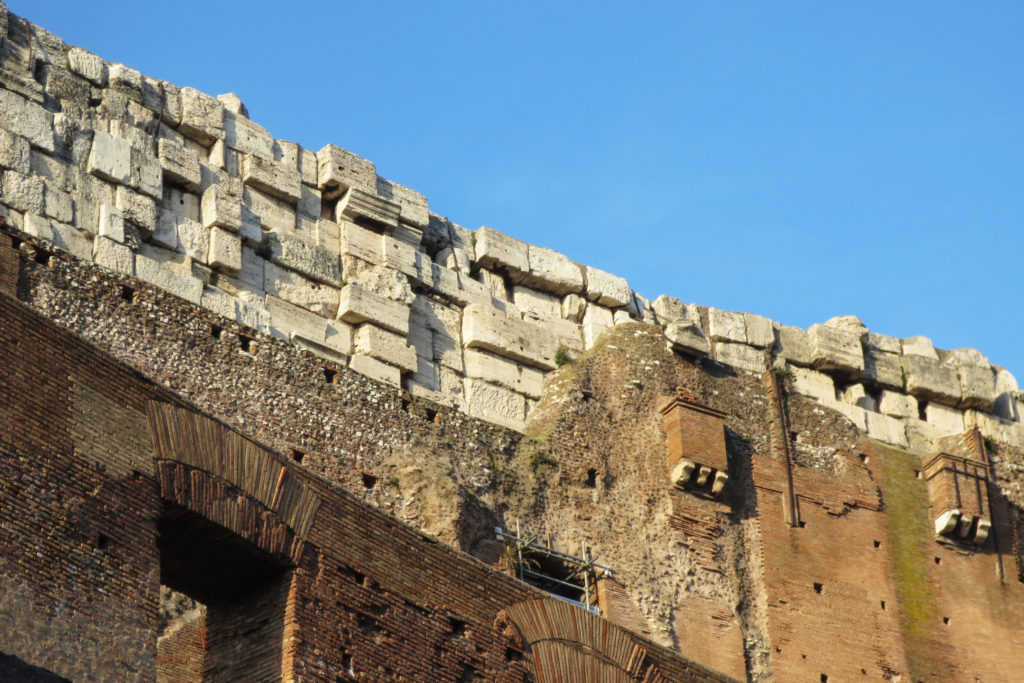
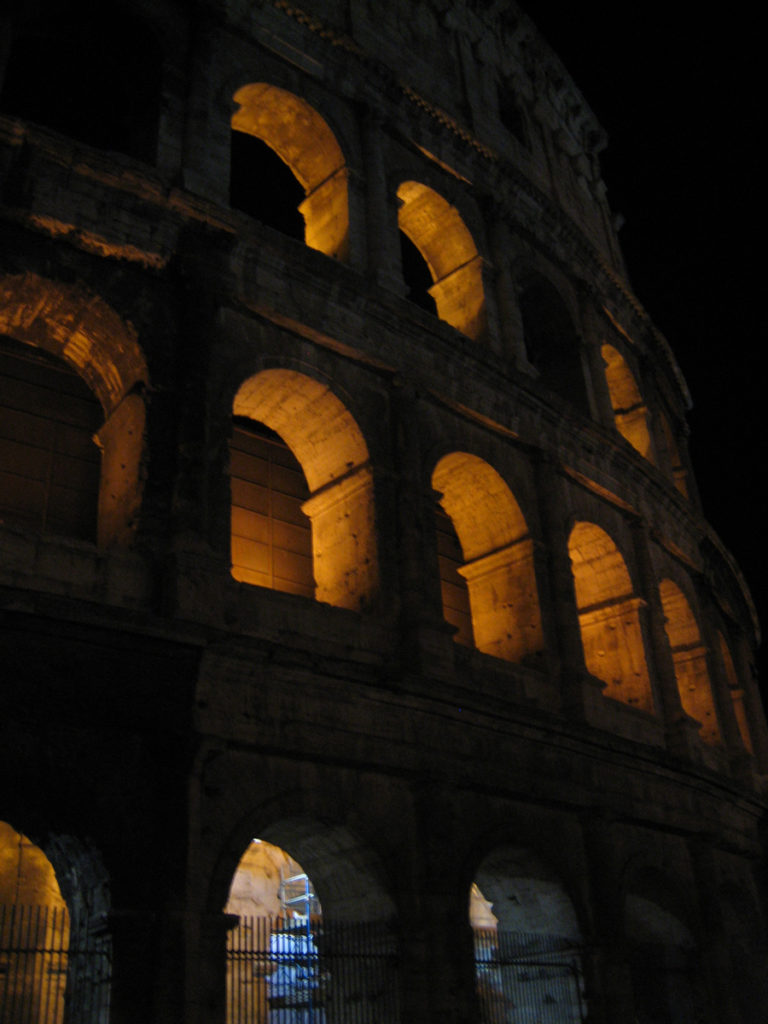
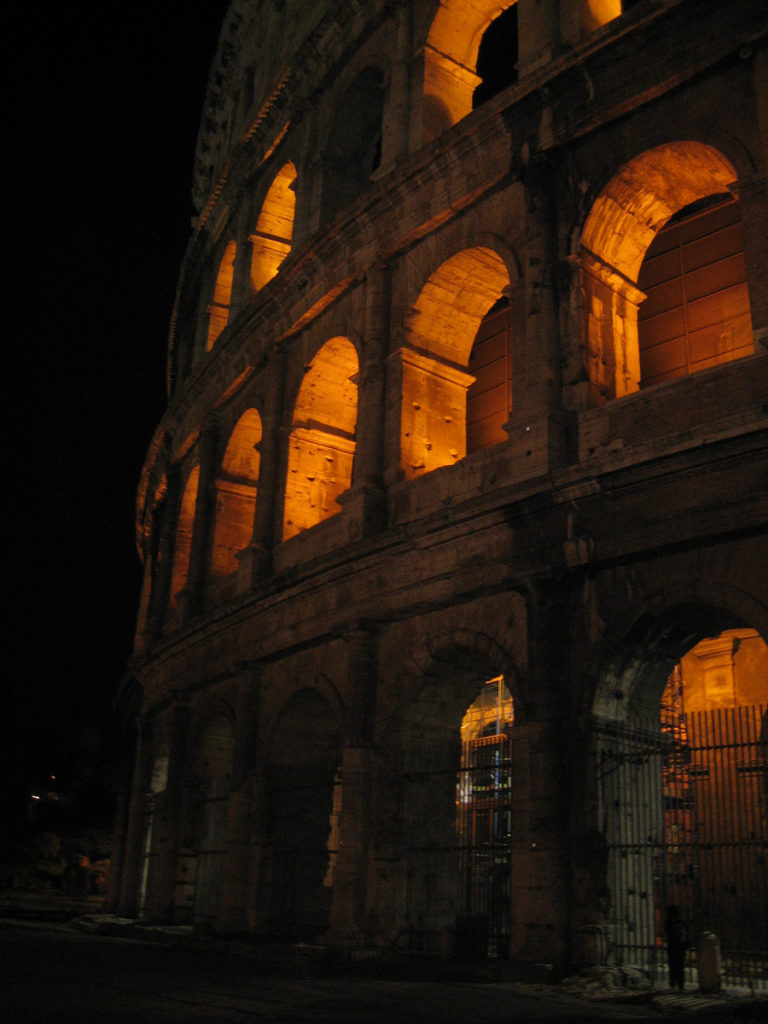
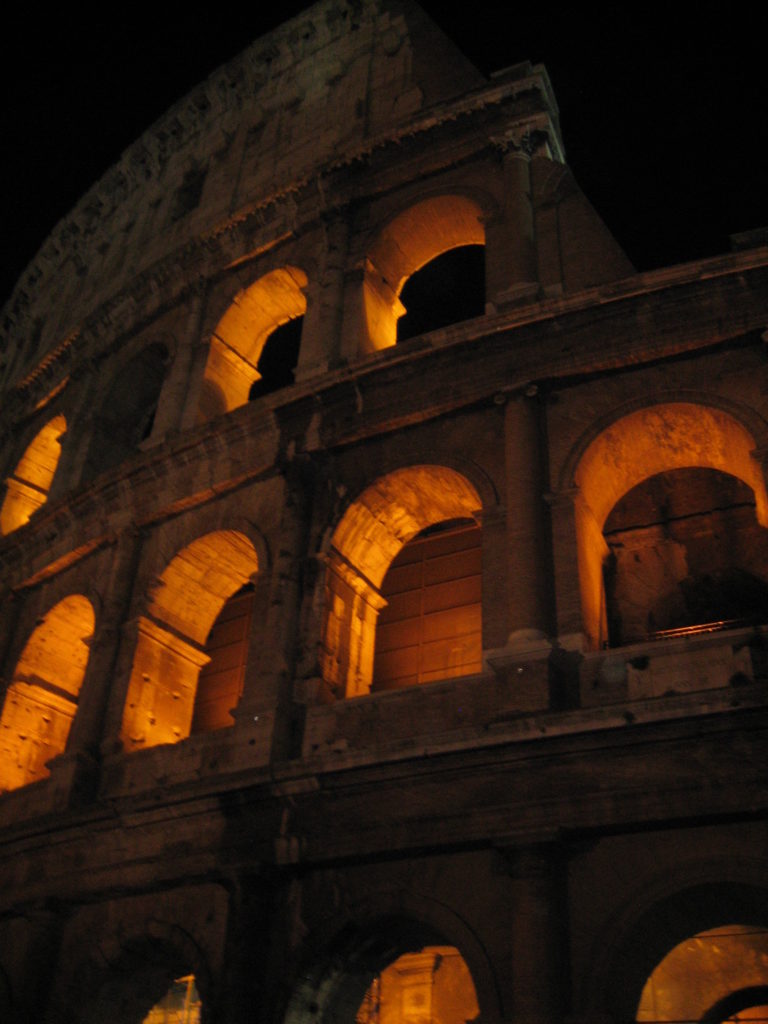
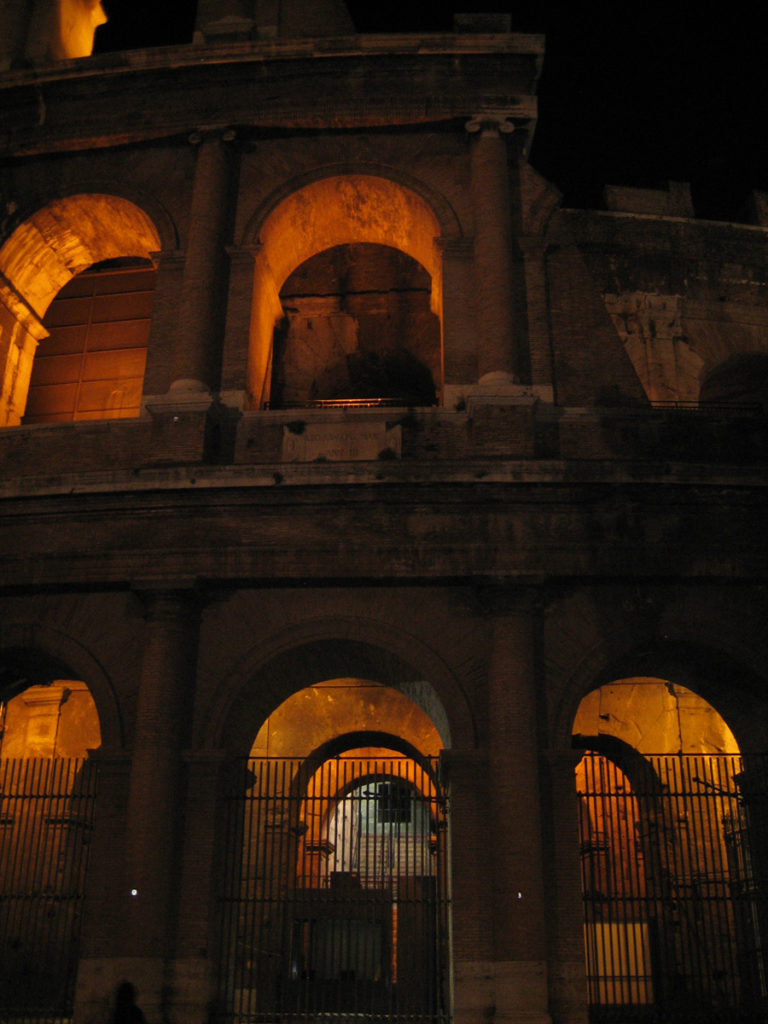
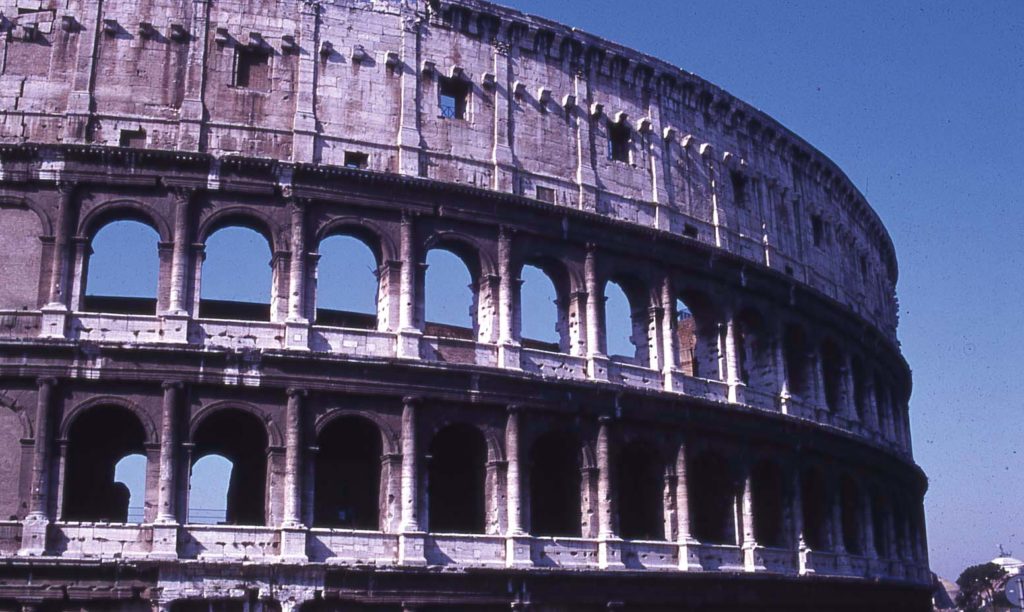
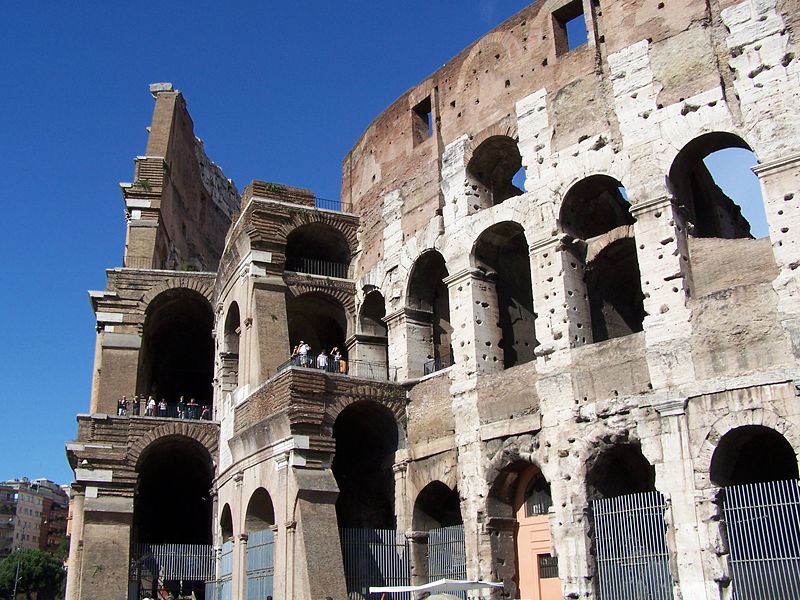
The Facade
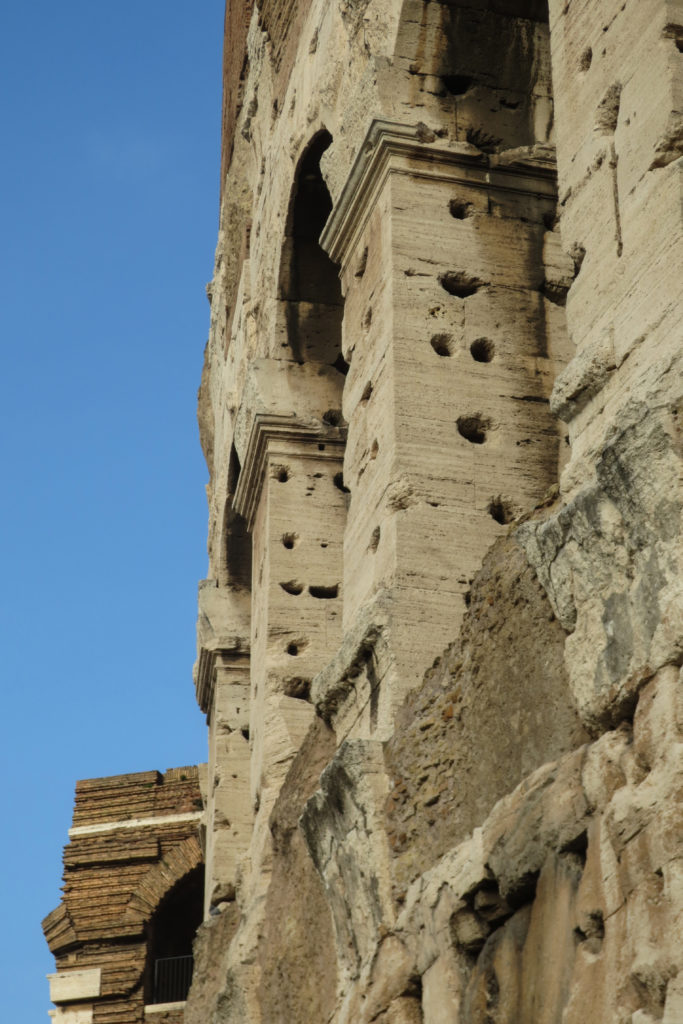
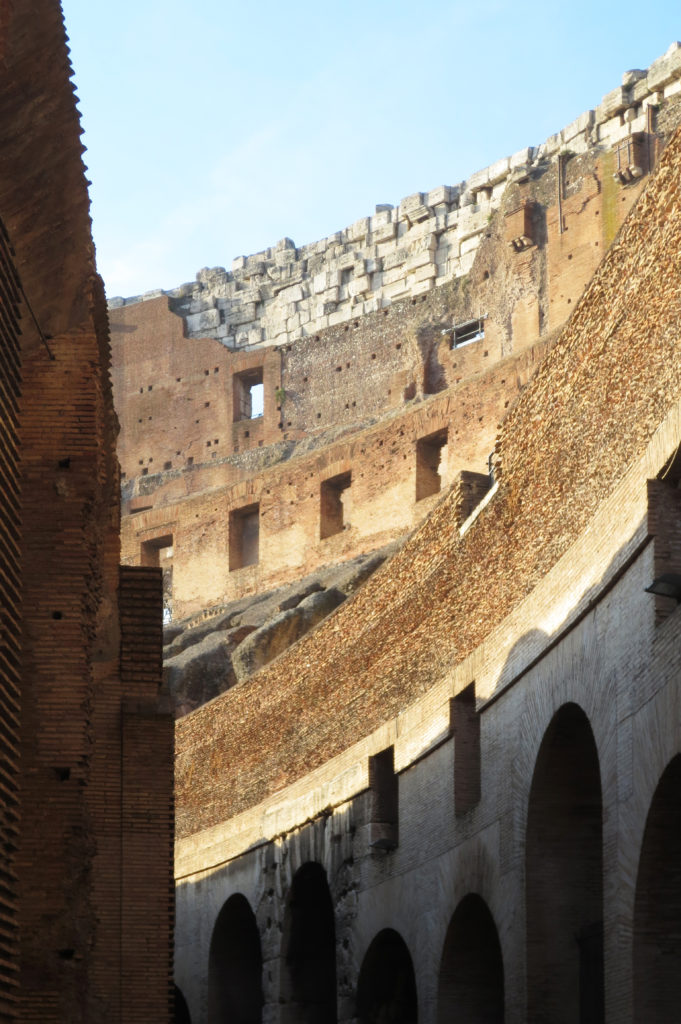
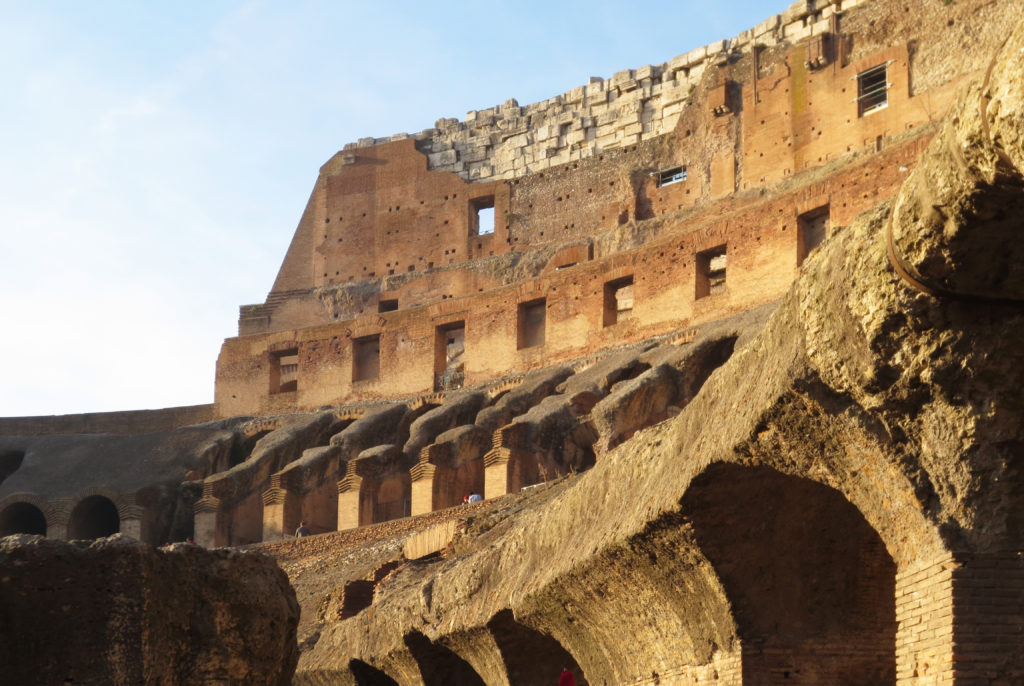
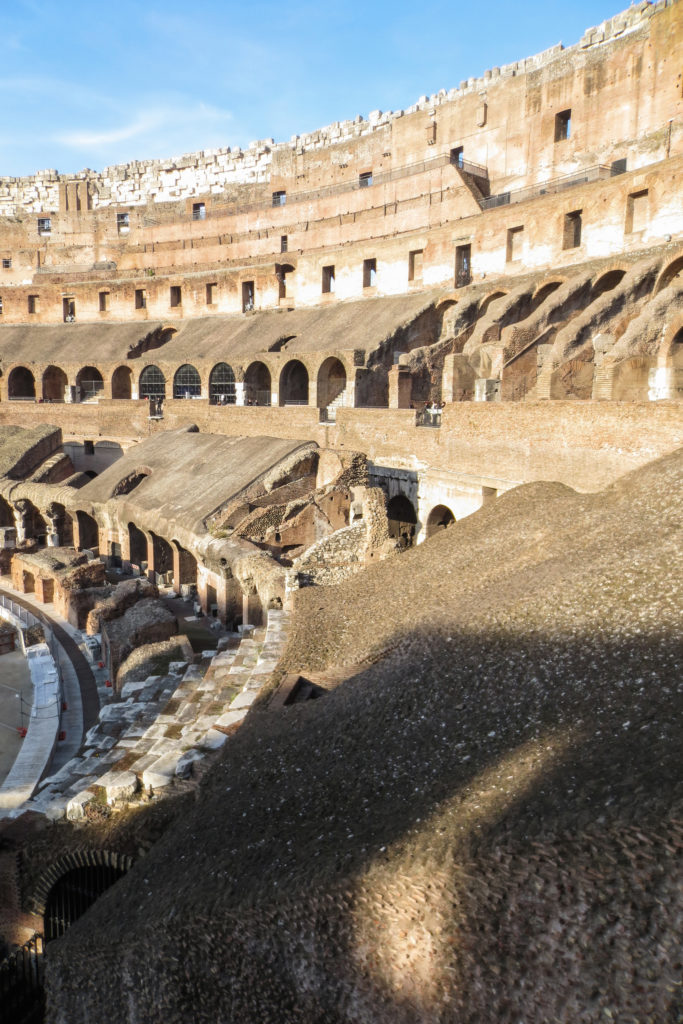
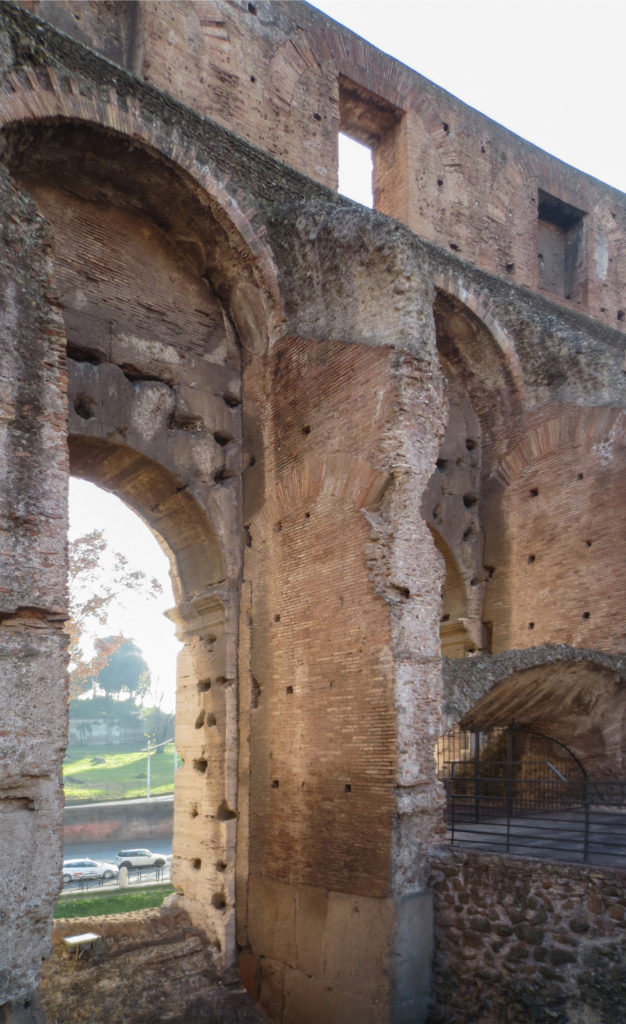
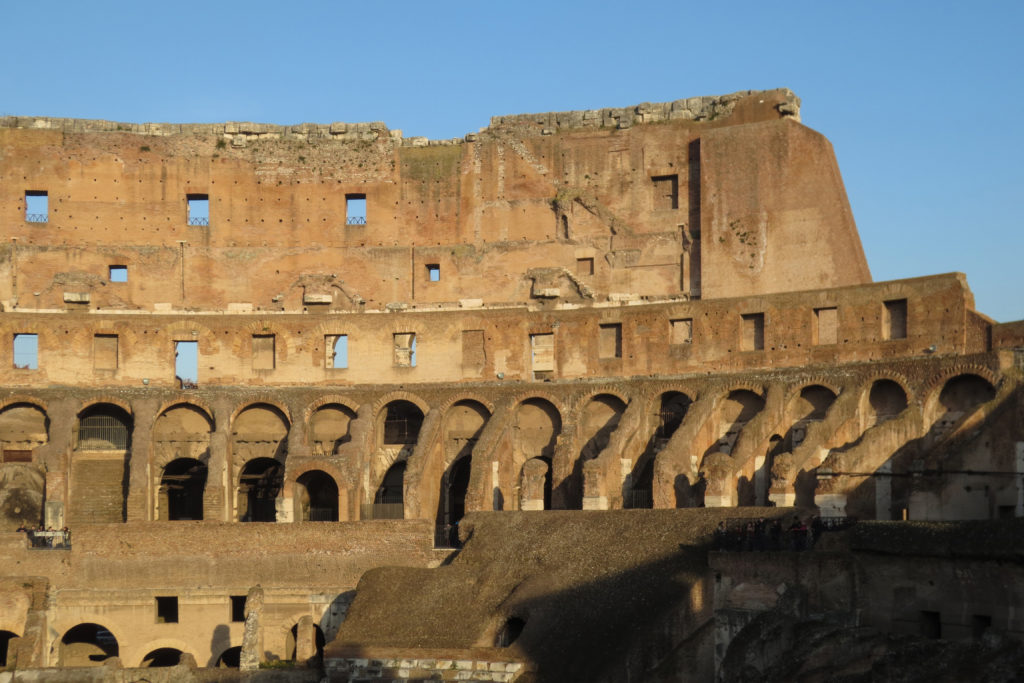
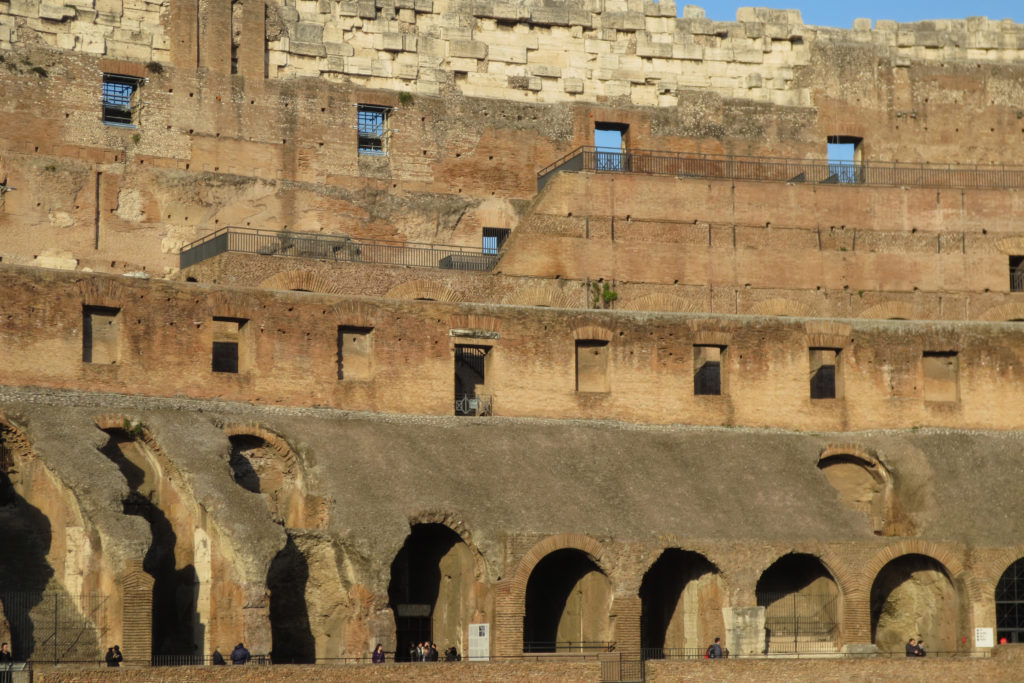
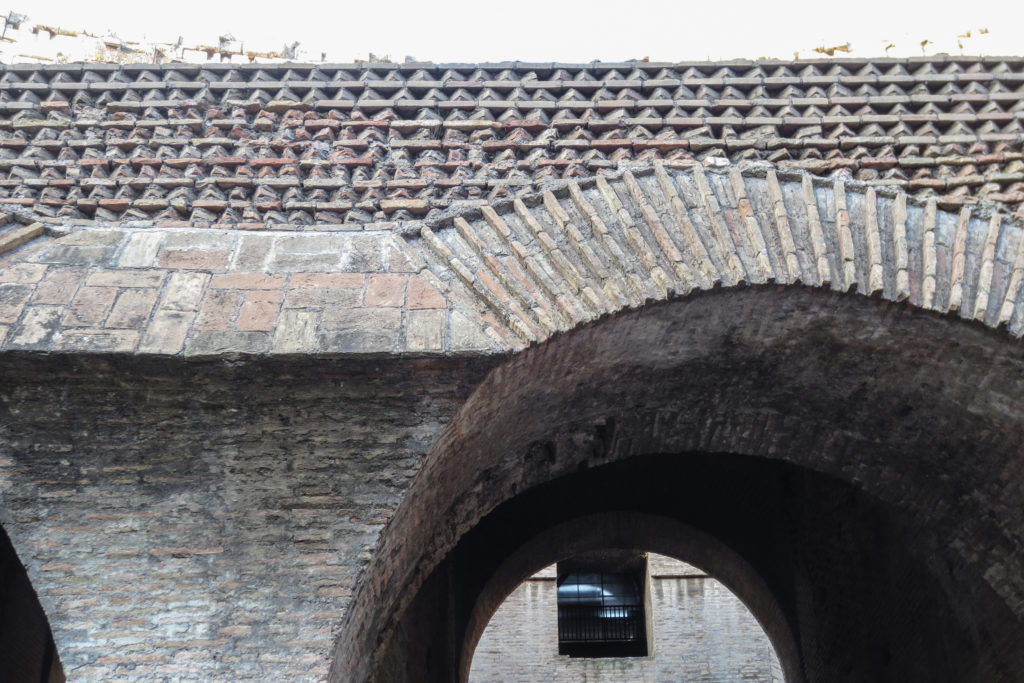
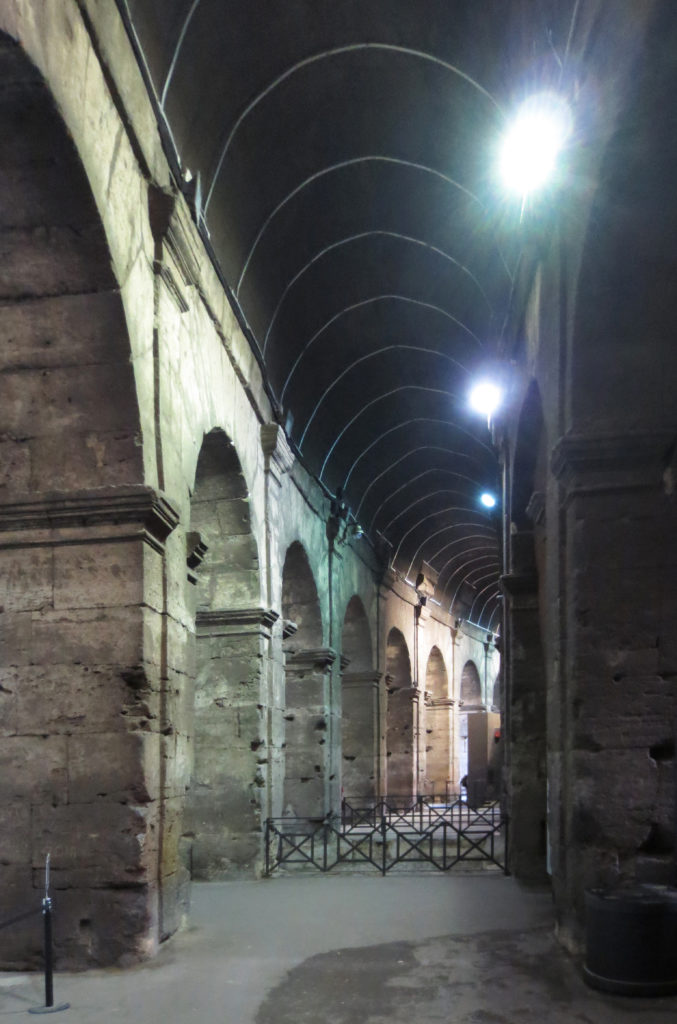
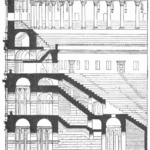
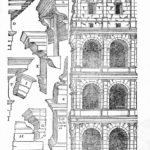
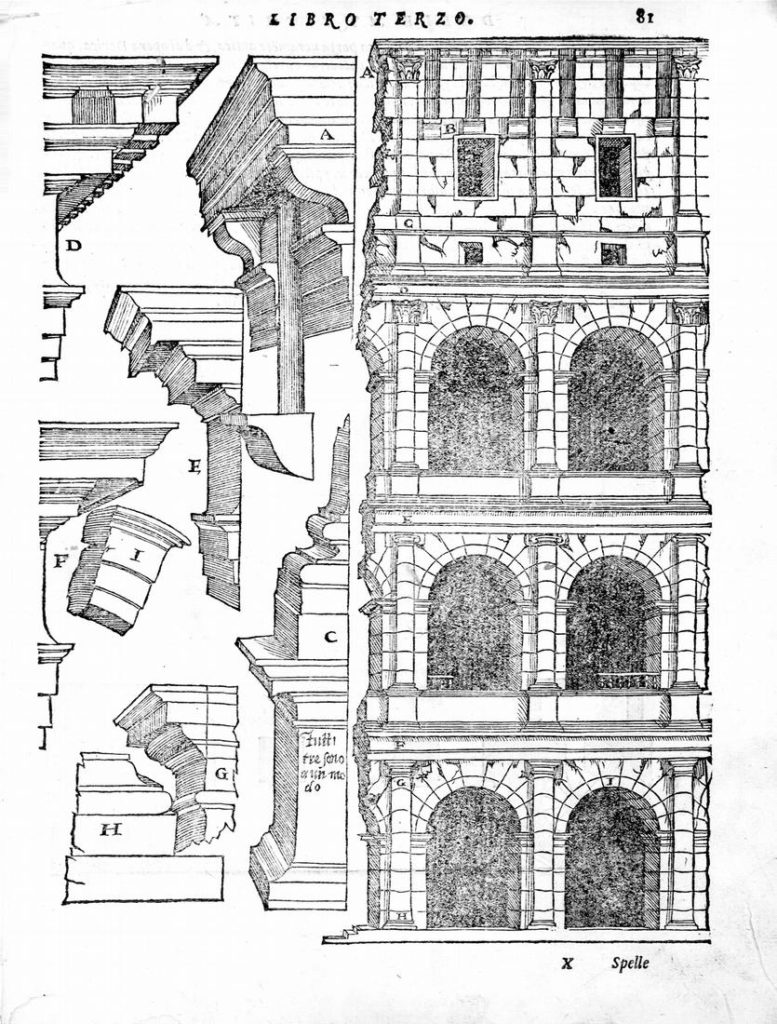
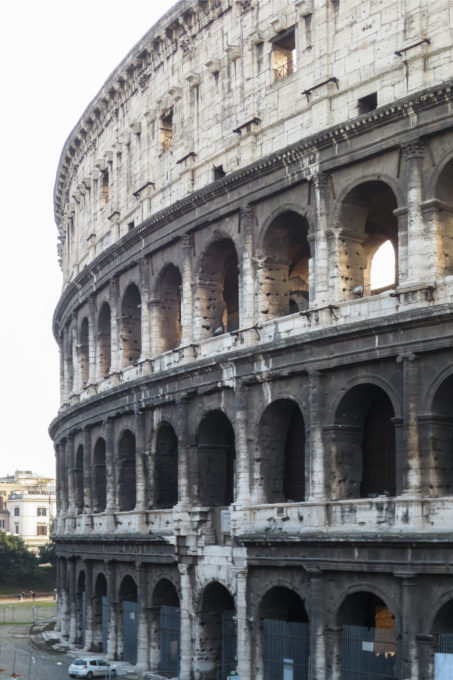
The facade is divided into four orders, whose heights do not match the interior floors.
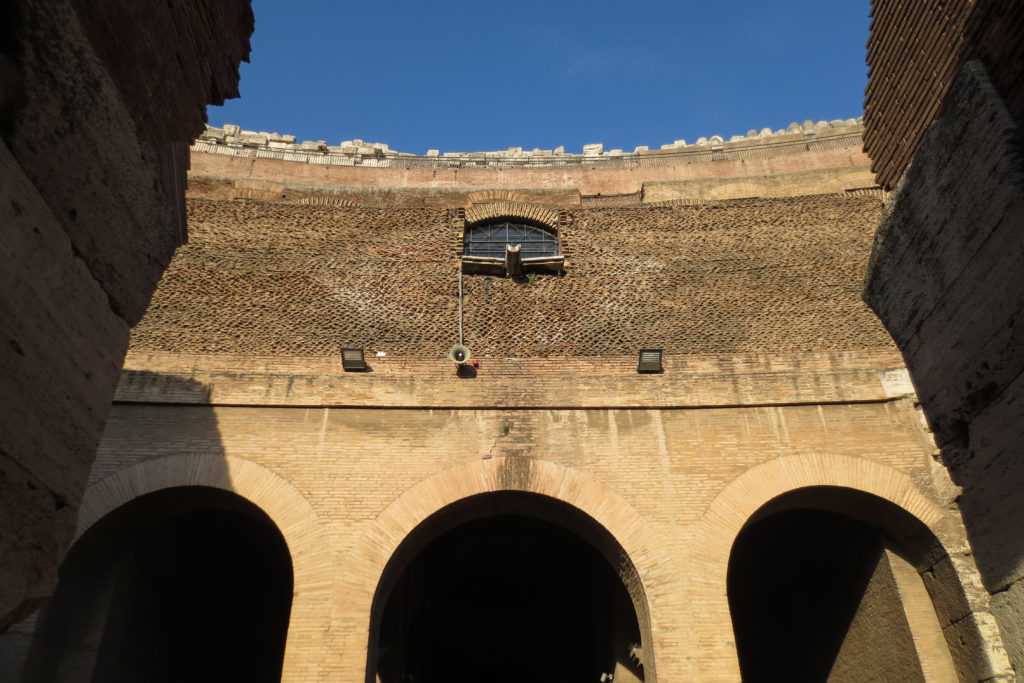
The three levels are below the 80 arches on pilasters, townhouses and semi entablature supporting a purely decorative. The fourth form as a blind wall with pilasters townhouses, and windows in every two fruitless.
The orders of each floor are successively Tuscan, Ionic, Corinthian and composite.
The ensure
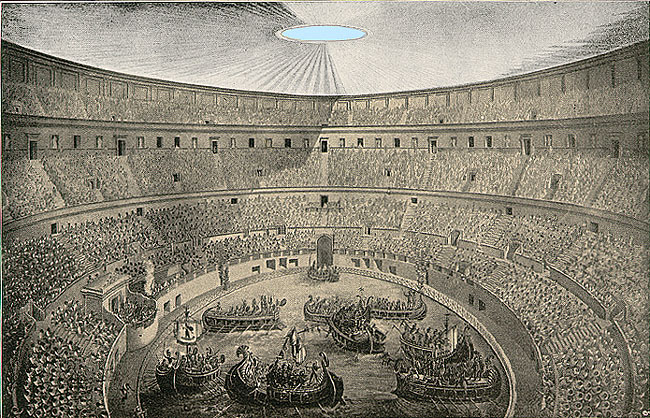
The Coliseum had a canvas cover driven down by pulleys. The cover, made with cloth sail first and then replaced by flax (light), was supported by a network of strings of which little is known. Each sector of cloth could be moved separately from around, and were operated by a detachment of sailors from the Roman fleet.
At the top of the facade have been identified where the gaps were placed 250 wooden poles that supported the wires.
Concept
The Colosseum, the largest so far built amphitheater, located in the center of Rome, capital of the Roman Empire itself was undoubtedly a great show of power by the Empire.
The amphitheater recreate an empire where a smaller scale. It held the largest gladiator fights, the bloodiest hunts, and so on. For such occasions came to the city gladiators from all provinces of the Empire to kill each other or face the most diverse creatures who lived in different provinces. On the sand could be seen as a small sample of the vast empire under the rule as warriors and animals.
The public in the capital was concentrated in the Coliseum to see the variety and extensions that could not come to imagine that they were under the rule of Emperor which were the pride of being citizens.
The fights were also atmosphere as the origin of the participants so that the attendees had the feeling of having traveled to distant lands that had nothing in common with Rome.
The Colosseum is not ceased to be a display of power. Sometimes in the form of fighting, the other hunts or even sentences and executions. The truth is that attending any events Coliseum returned home with the feeling of belonging to the largest and most powerful empire in the world. Something that was true for years.
Structure


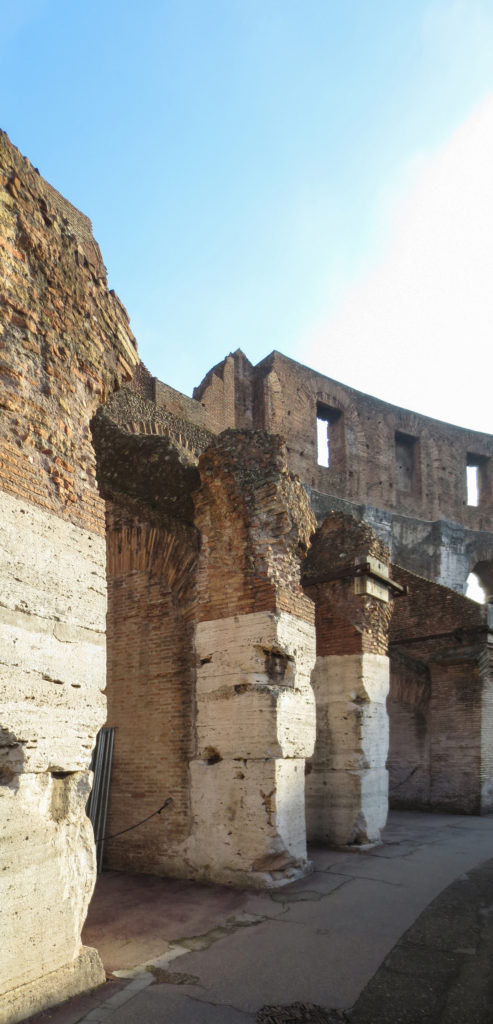
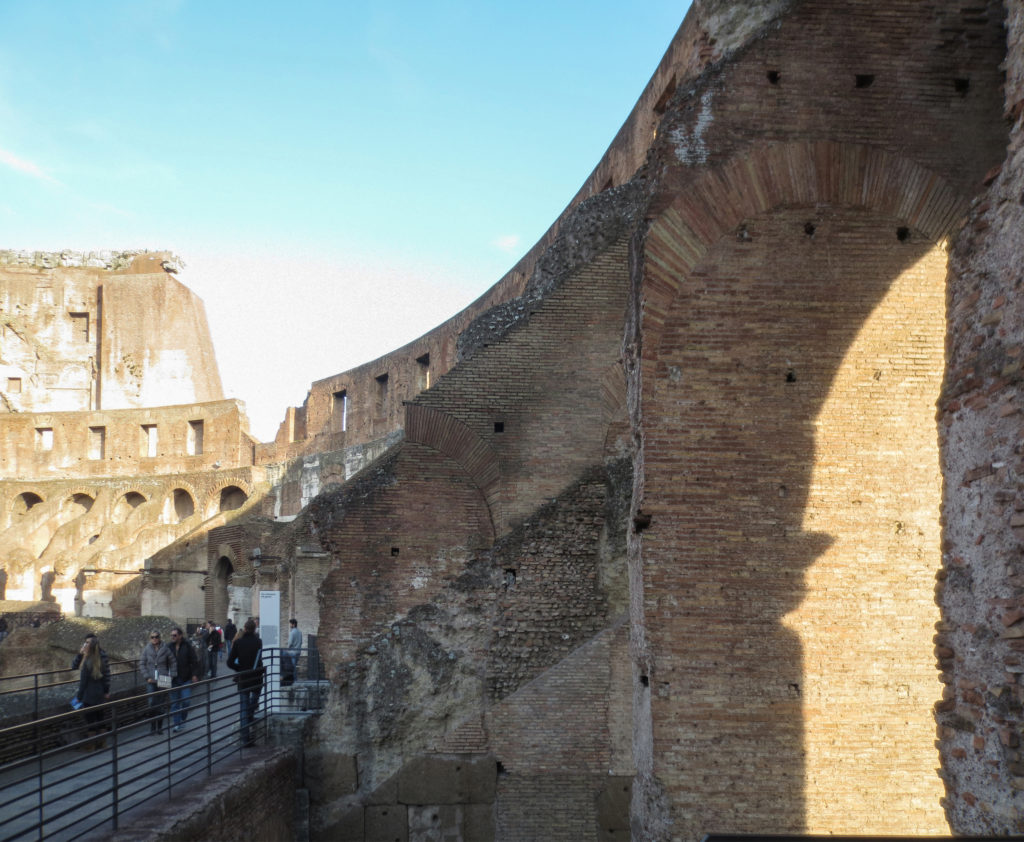
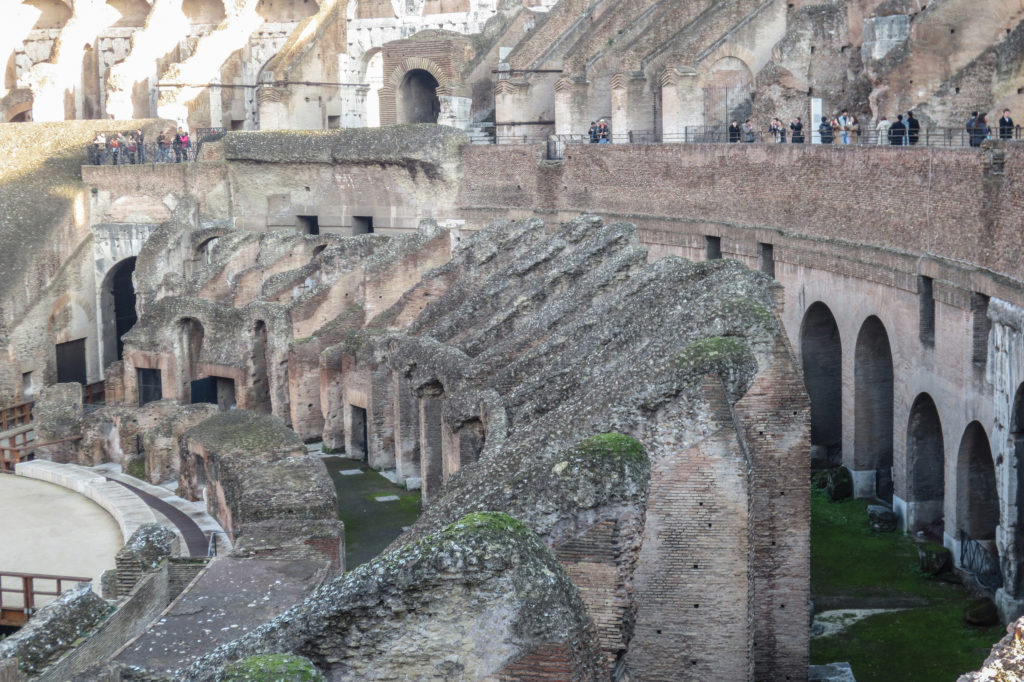
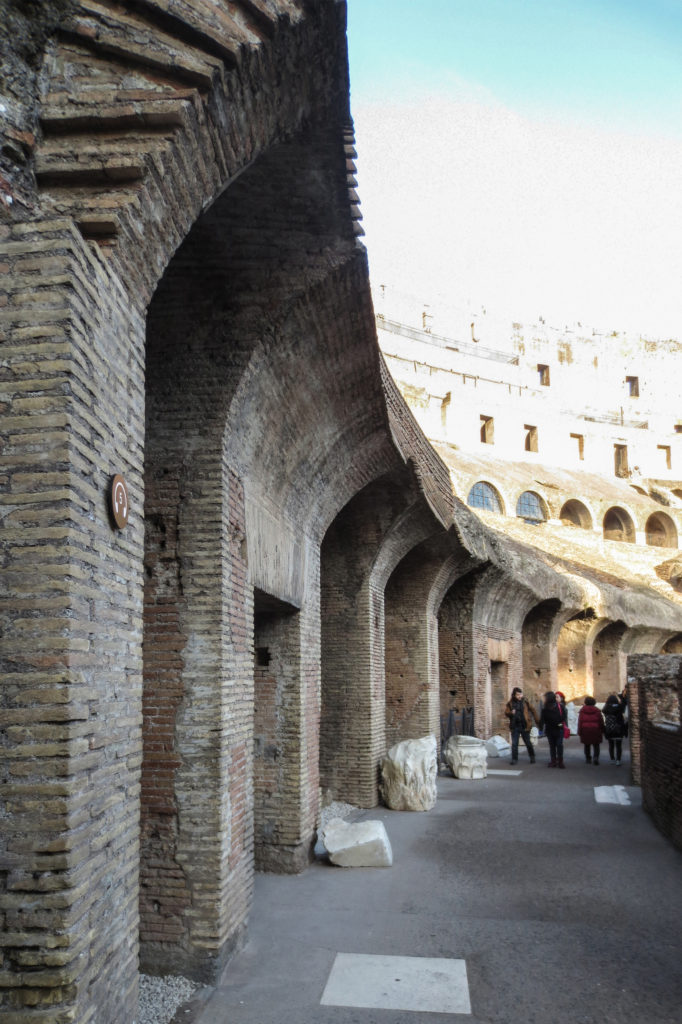
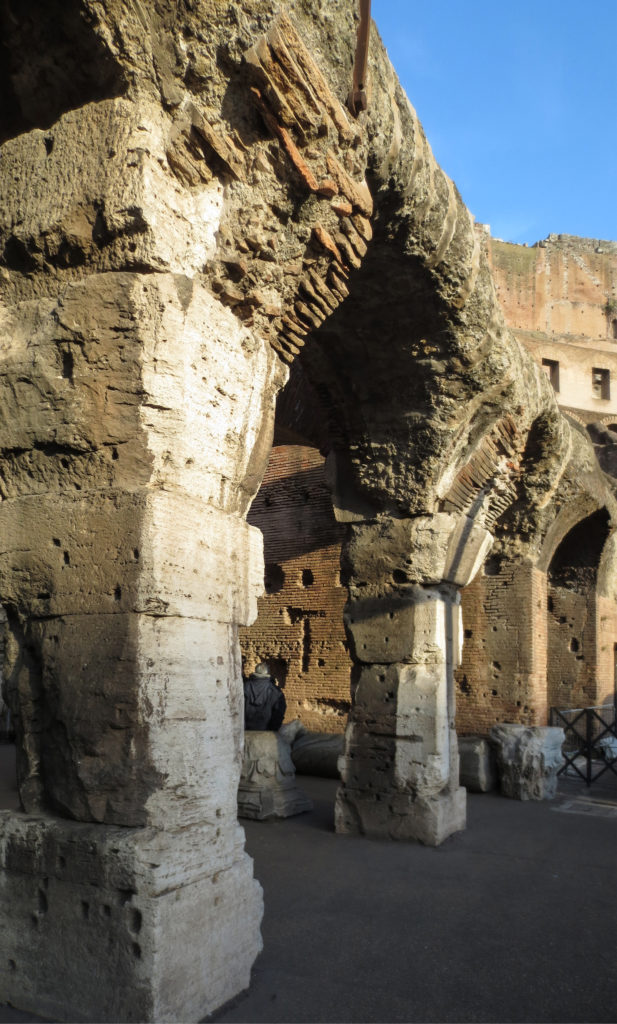
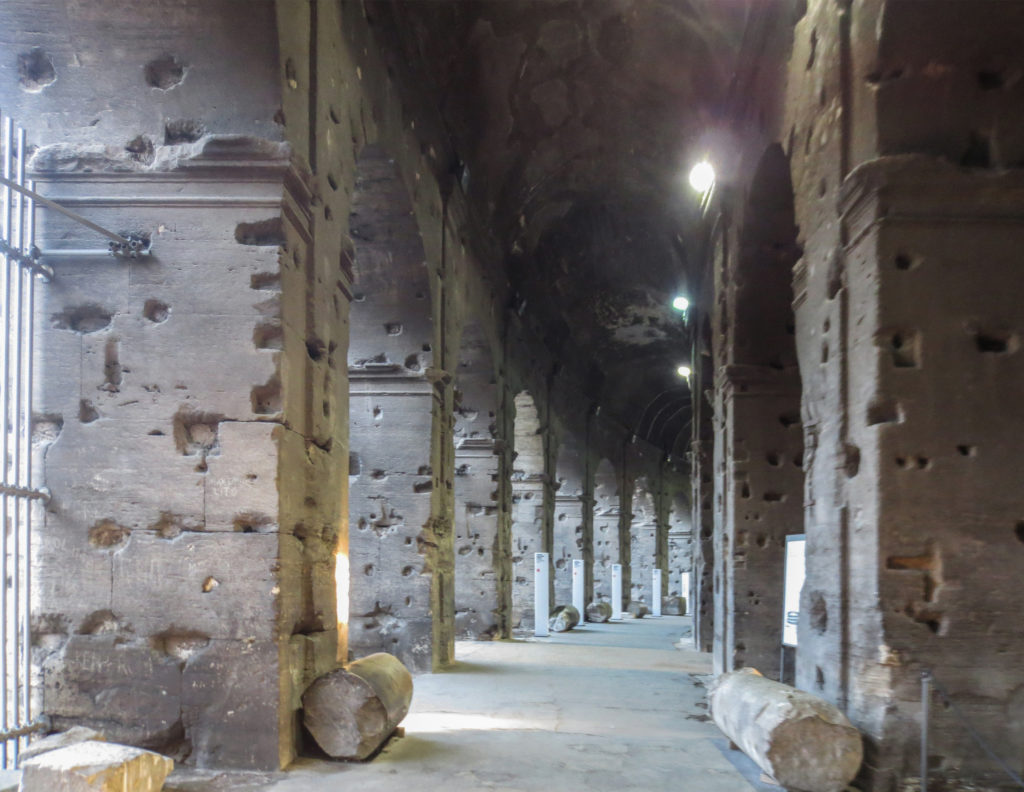
The problem with the enormous burden of the cavea or space bleachers for spectators, is solved by including powerful arches resting on strong pillars of stone and mortar and holding the annular vaults, on which different levels of bleachers are based. From the sand out 80 radial walls supporting the vaults for the area of bleachers, alleys and stairs.
Outside three lines of overlapping arches articulate the wall, corresponding to sections of the vaulted interior. The arches are flanked by half columns and topped by lintels, cornice serving separation upstairs. In the outer circumferential edge link arches and stairways each level between levels. Years after its completion the fourth level outwardly seen as a wall without arches, pilasters of composite order was added.
Sometimes there were naval battles in the arena was flooded to handle the boats. When the show ended, the sand desecaba through a system of sewers.
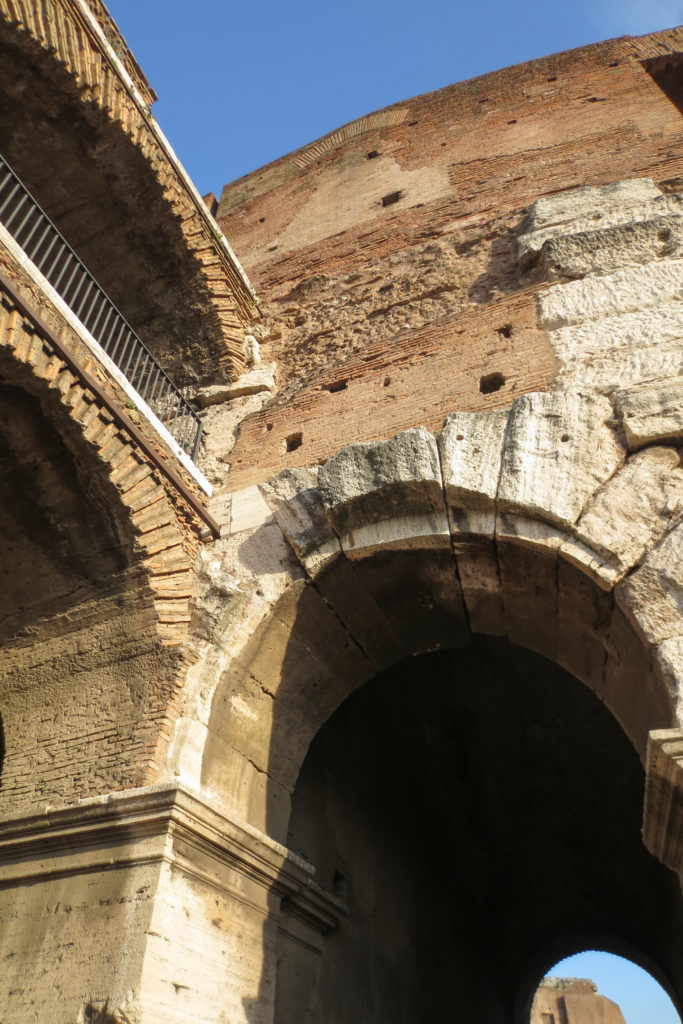
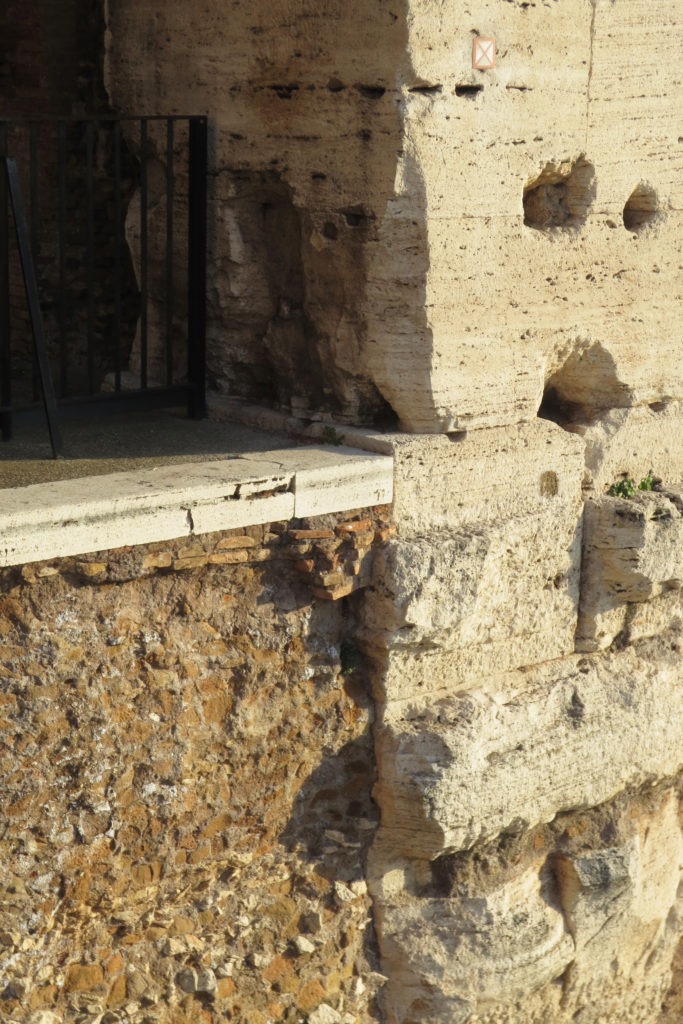
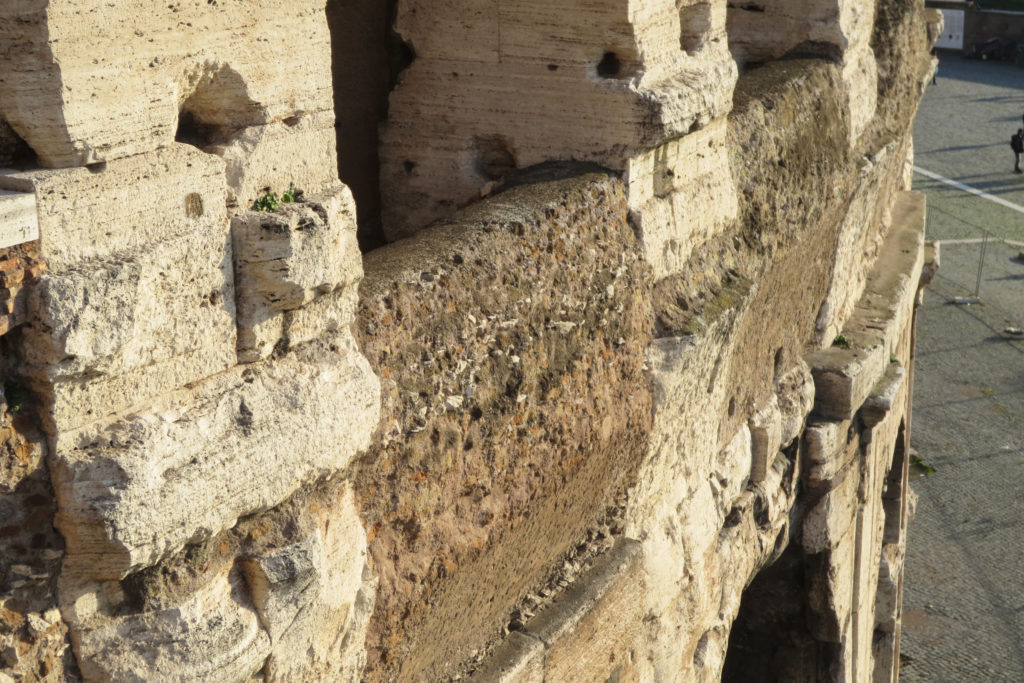
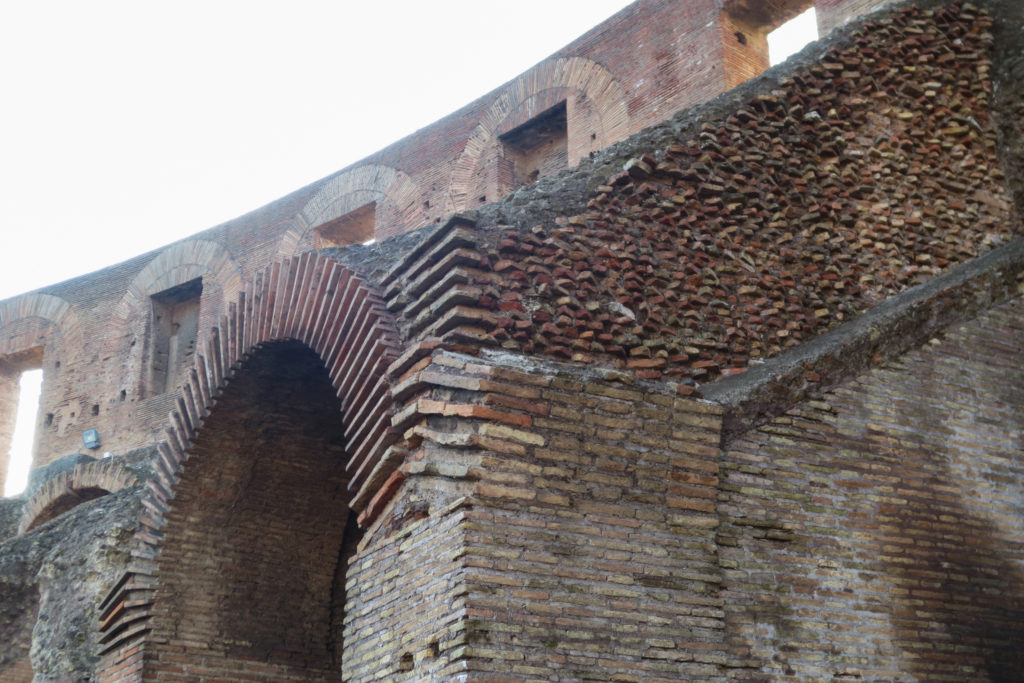
Materials

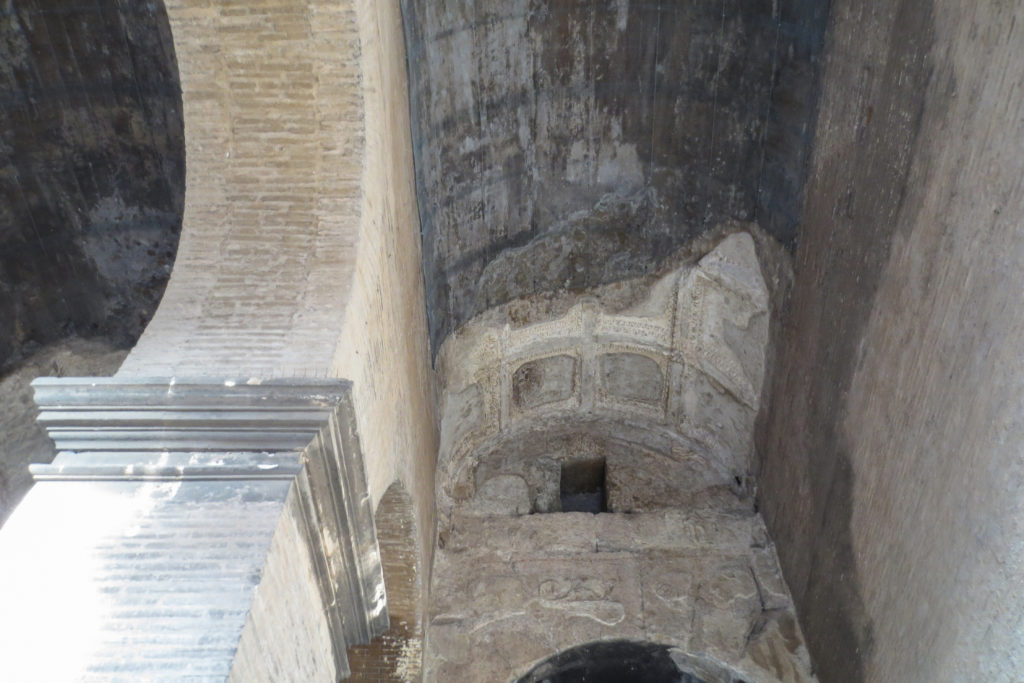
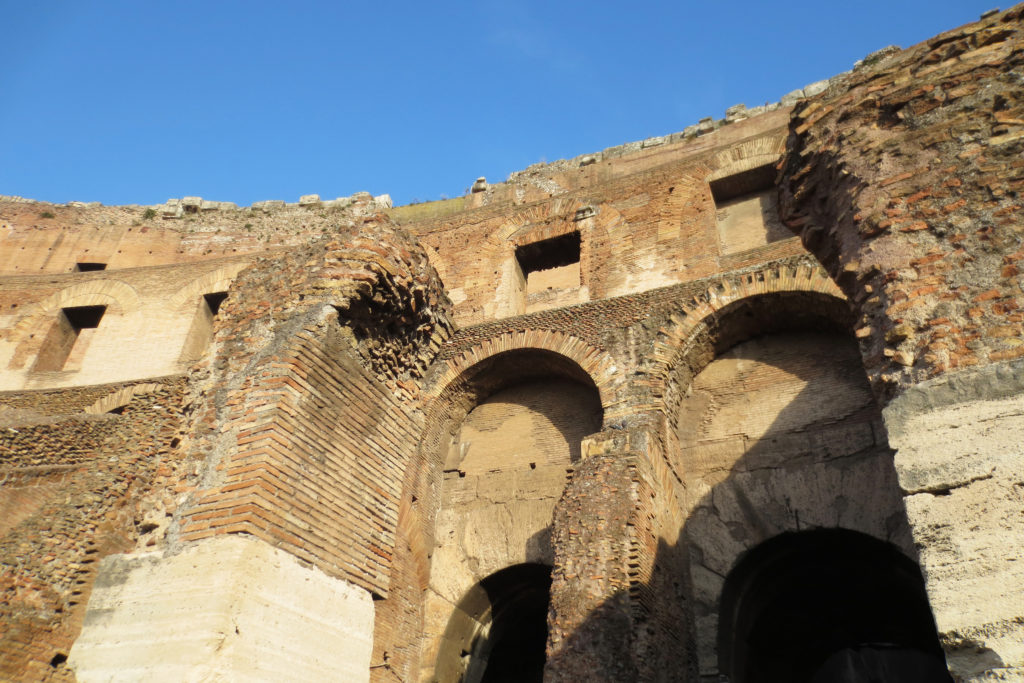
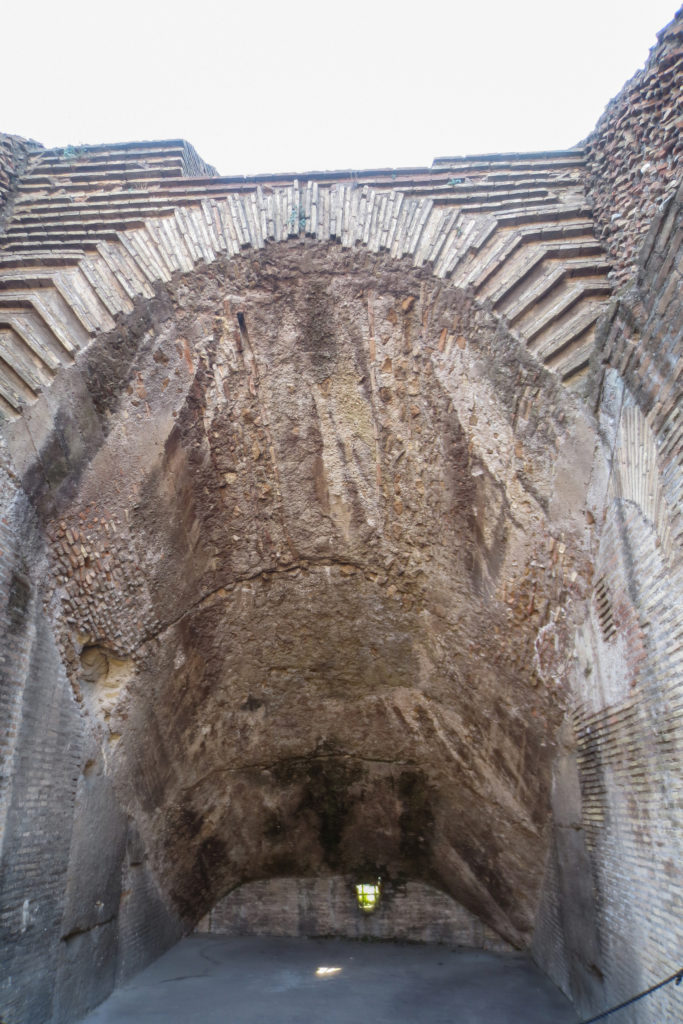
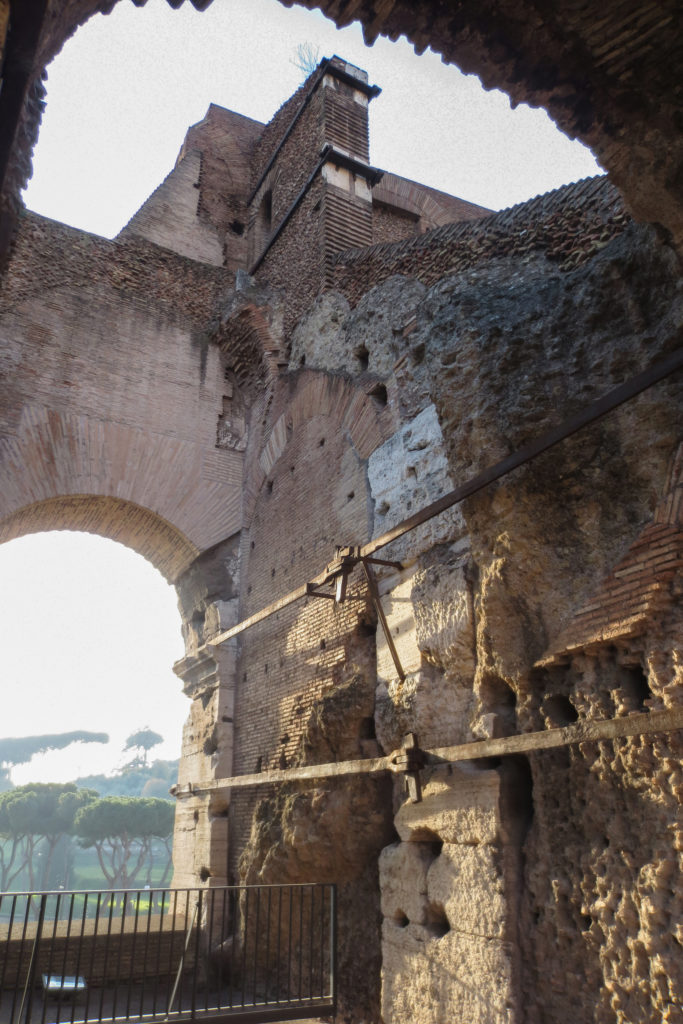
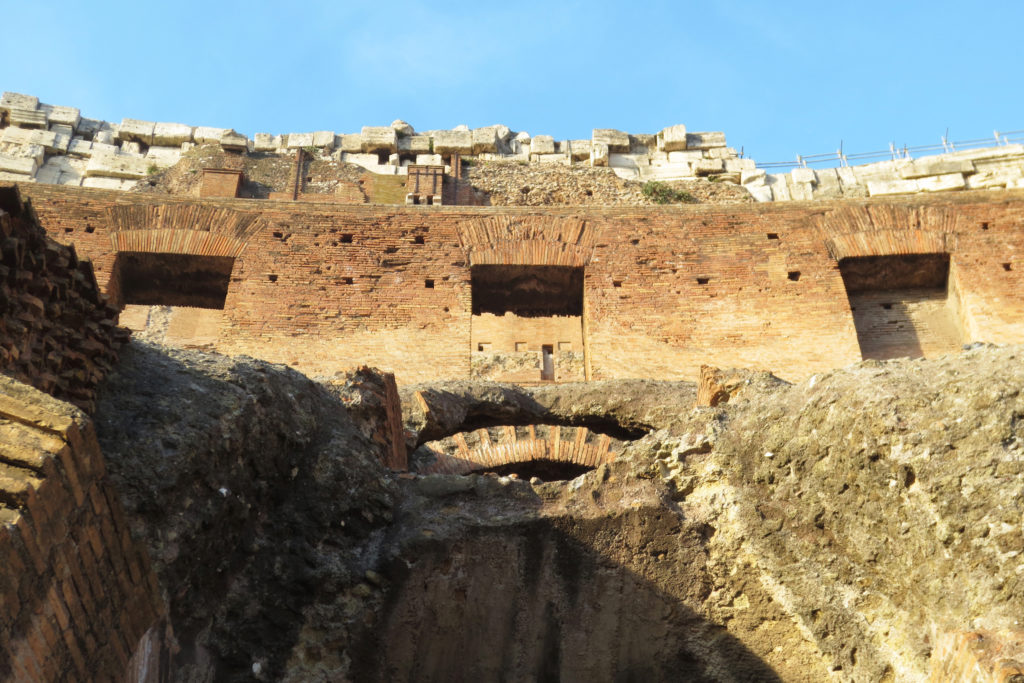
A careful combination of materials used in construction: concrete foundations, the Romans were the creators of “opus caementicium” mixture of gravel, sand, lime and water. Blocks of travertine for the piers and arcades, filled with tufa between piers for the walls of the two lower levels. The concrete brick and tufa were used to higher levels and for most of the vaults. To join the large blocks large metal clamps were applied, it is estimated that it was necessary to melt 300tn of various alloys. Marble and stucco, a mass of white plaster mixed with glue water was also used to make figures or parts that are then used to decorate the walls.
The arena where the shows took place was made of a wood parquet covered with sand, below which the complex system of passageways, rooms and vaults stretched. With the passing of the years he has nothing left of this parquet have revealed the complex system of passages and cells.
To raise the door through which came the gladiators and fairs created a system with manual lifting pulleys, while some bleachers were protected with guardrails bronze was used.
The top floor was protected in summer by an awning or velarium that bound to the masts and brackets subjects like the doors to the arena were hoisted by pulleys. During the evening shows large chandeliers on the sand were suspended.
The decor was very studied and rich in elements, with a profusion of statues, marble and stucco reliefs, bronze shields or seats travertine. From her after XX centuries of history, numerous earthquakes, plundering and other damage just some remains.
Videos