Phoenix High School

Introduction
The Phoenix Sixth Form High School Centre is the result of mind of Professor Sir William Atkinson, who was knighted in 2008, after reversing the bad reputation that the old Hammersmith School, considered the worst in the school development in Britain. With its project managed to raise 5% rate to get close to the national average.
With the new Sixth Form Centre is located next to the Hammersmith School, Atkinson has the same ambitious plans. Asked an iconic design that will inspire students aged 16 to stay and complete their education level A.
Situation
The Phoenix High School was built in Shepherd’s Bush, west of London, England. This area belongs to the London Borough of Hammersmith and Fulham, nearly 8 miles west of Charing Cross and although it’s basically residential area is the commercial center of Shepherd’s Bush Green area whose northern part is the largest urban shopping center Europe, Westfield Shopping Centre.
Concept

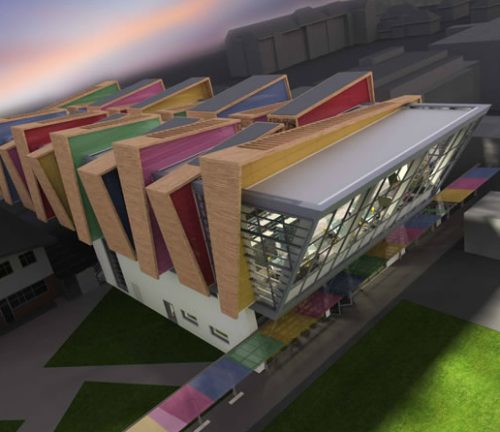
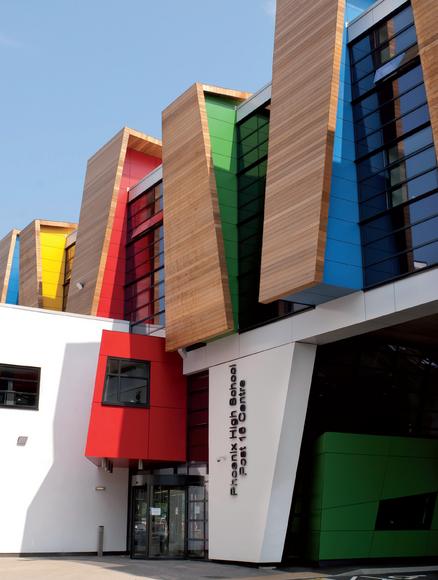
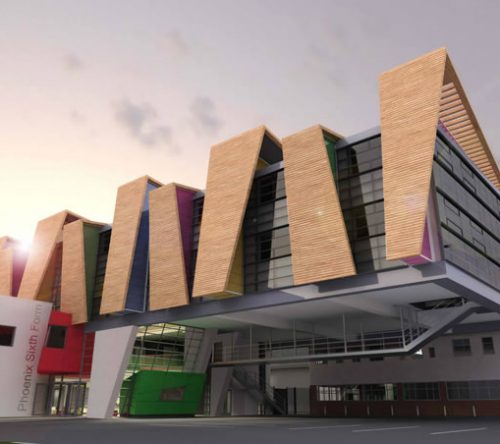
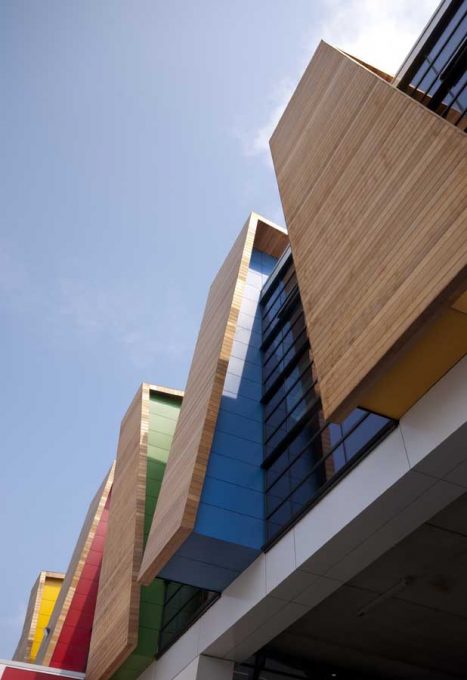
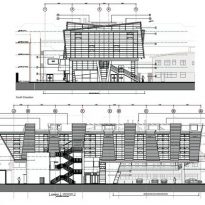
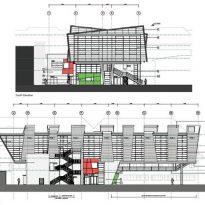
Bond Bryan Architect proposes to change the local context uncomplicated and create a real sense of spectacle. Approaching the building through an area of dilapidated housing, the first thing you notice are the primary colors: red, blue, yellow and green adorning the nine angled wooden fins, projecting and creating spin angular bodies embracing building. More than an attractive visual device, fins mask ventilation ducts and services, and provide sun protection for windows that open in the middle.
The concept of building uses wood regulated horizontally and aesthetics of glass buildings 50s existing to create an elevation composed of vertical panels of wood with several steps, which are repeated at random intervals, framed with subtle colors. These panels, projecting like fins, allow ventilation plant through the air intakes staying in their ways, at the height of the soil, maximizing the efficiency of distribution strategies ventilation.
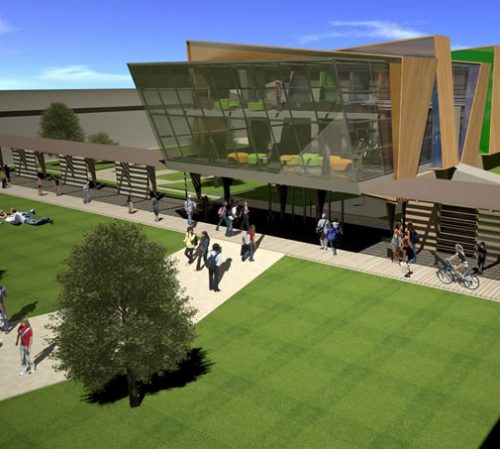
The design creates a nurturing environment for learning by introducing a dynamic concept that all students can relate to. This concept has been extended to the design of the facade, creating a visual beacon for the school and the community in general.
Spaces
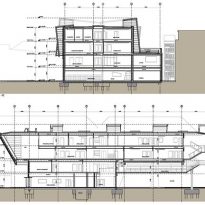
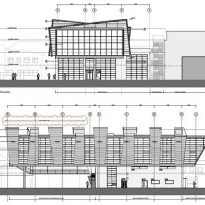
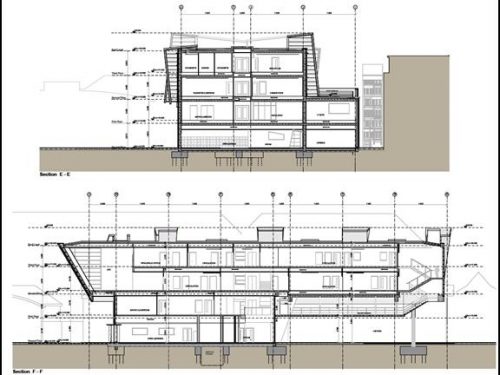
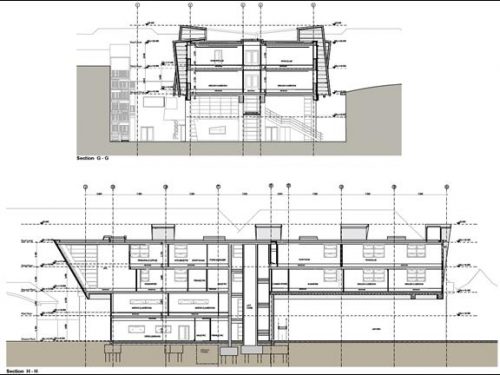
This huge concrete block, with two floors of classrooms cantilever weighs about 1,100 tons. Cantilever all spaces are arranged along a central passageway extending throughout the building and occupying a crucial provides structural support.
Space considerations and safety led to the decision to raise half of the building above the existing parking, explains Jeff Stibbons, project manager at Bond Bryan Architects: “… The staff was firm, for safety reasons, in the need for parking, but the construction of a new plant would have meant digging the field school sports or other land with high ecological value, so it was thought that the solution was to build an overhang on already existing, which in turn helped preserve the view from the classroom block… ”
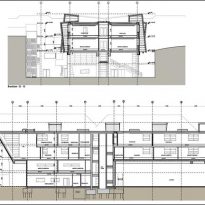
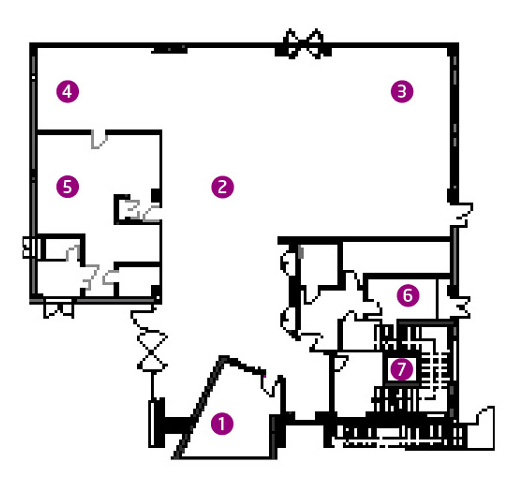
Ground floor

- Atrium
The concrete block on the ground floor covering about half the footprint of the building. It has a double height atrium with a glazed entrance, open kitchen and dining area. This floor also has ample space for movement, an open reading area, bathrooms and stairwells.
Second floor
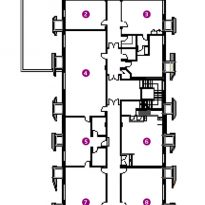
On the second floor several rooms and brightly decorated classrooms that provide private study areas are located.
Third floor
- Resource Center for Learning
At the north end of the building with double height bay window contains the Resource Center for Learning and Projects on the playground you see below. With this structure at one end and the overhang on the other, the building seems to pivot on the podium concrete.
At this level, a meeting room, offices, laboratory biology, physics lab, chemistry lab, staff room and room for various events is also located.
Structure
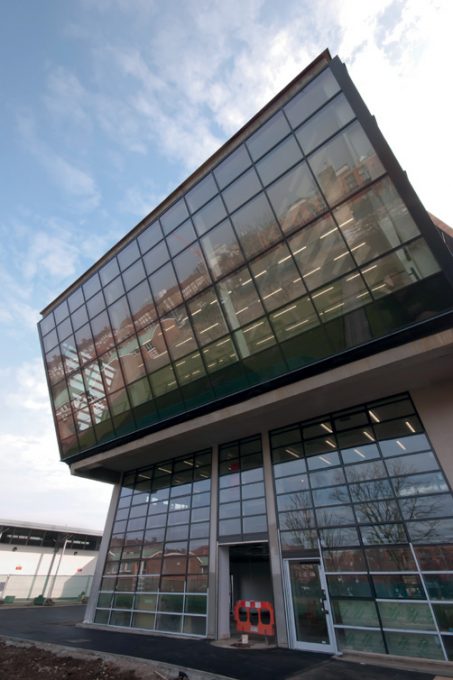
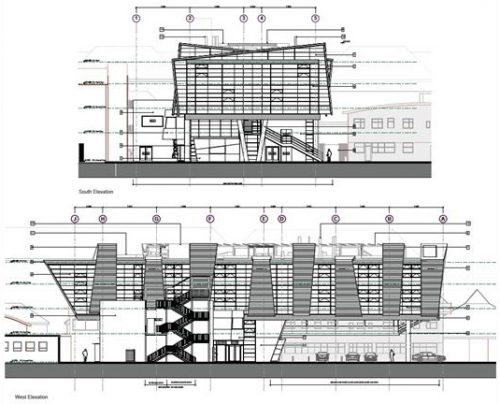
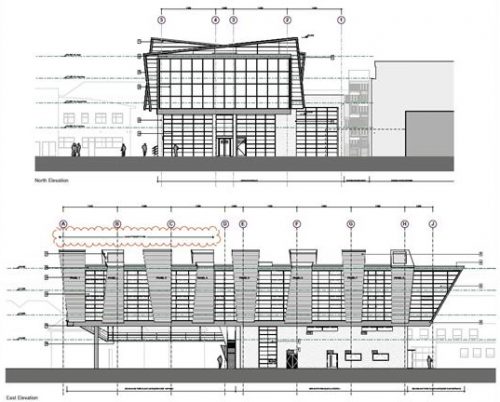
The structure of this building with its six floating forms required an advanced framework of hybrid steel and reinforced concrete, together with a complex installation.
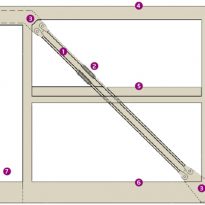
The cantilever concrete body, that the pad consists of classrooms, is supported by a column-shaped V, with Macalloy hangars. These will help to tension the concrete structure 24 meters long, about twice the area beneath the podium, at the opposite end. The total length of the building is 51 meters, defying the general rule that only 33% of a building can be extended cantilever, it has almost 50% of construction in the air.
Cantilever

This gravity-defying cantilever has been possible thanks to an ingenious hybrid structural system designed by engineers SKM Anthony Hunt and Bowmer & Kirkland, combining a reinforced concrete structure with super-deep foundation piles, two structural steel columns and also tensioning rods of steel. Designed to withstand disproportionate collapse, where failure of a structural element has a chain effect on the rest of the structure, the elements work together to support the cantilever beam and avoid skewing both horizontally and vertically, tearing the rest of building from the ground.
In most of the cantilever beam supporting reinforced concrete walls, poured in situ, precast slabs and light OmniCore in soils.
A complicated load path transfers the forces generated by the cantilevered section two tensioned steel hangers, located just behind the glass wall at the end. This charge is transferred in turn to the two walls of the central corridors, located on the concrete beams, the resulting channel supports 15,000 kN load on steel columns placed underneath.
Materials
The main materials used in its construction were reinforced concrete and steel structure. Cedar wood and material is also used in primary colors in the coatings of external fins.
The weight of the cantilever creates tensile forces in the block of the podium. To prevent cracking large reinforcements of reinforced concrete provisions diagonal arrangements and embedded within the external walls of the cantilever having a thickness of 400 mm, while the piles were sunk 25 meters deep were used. A secondary steel structure was fixed to the concrete walls for bonding wood and cedar siding colors of the ribs.