Lafayette Park

Introduction
This complex of apartments and housing towers is one of the examples Mies van der Rohe has given us on developments in American cities. Lafayette Park is located 2.5 miles from downtown Detroit, was an area prepared to issue a new city program intended for the city. After two years of study, “the Citizen’s Redevelopment Commite” decided to support and finance the proposed new development, so it presented an outline for the new development.
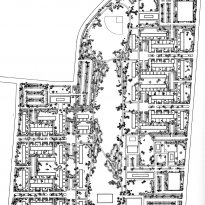
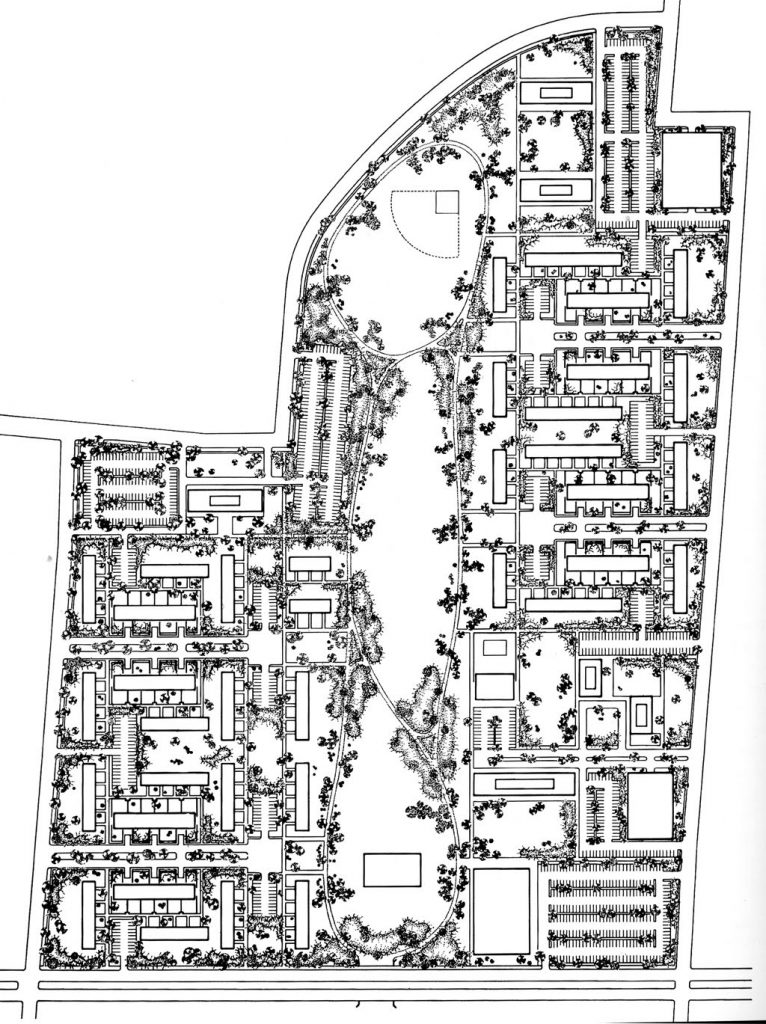
The proposal was designed by Mies van der Rohe and Ludwig Hilberseimer, in 1953 made the Master Plan for the Lafayette district of Detroit, along with partners such as Alfred Caldwell who developed the “landscape” of the whole. This had 78 acres of land, where they were able to propose solutions to problems like pollution, traffic, proximity between areas, etc.
Later in 1955-56 began the planning phase where some developers were attracted Karzin and Herbert Samuel Greenwald Chicago after a year took options for building, using the prepared by Mies and Ludwig Hilberseimer. The construction of the complex was carried out from 1960 to 1963 Greenwald.
Location
Lafayette Plaisance a district in Detroit, Michigan. Currently the complex is still in use. It is in good condition.
Concept
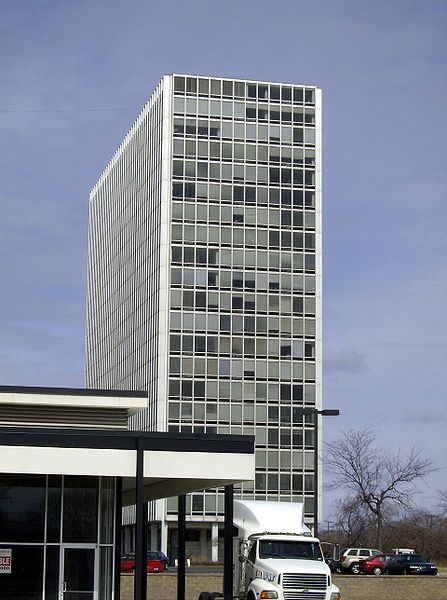
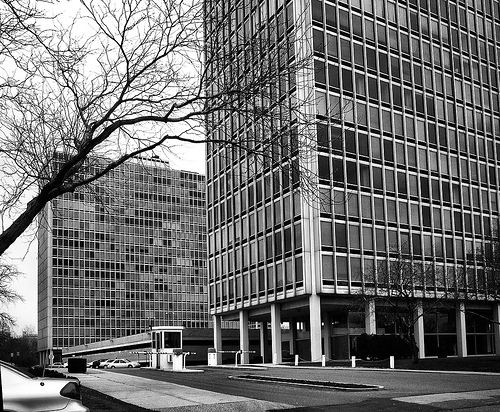
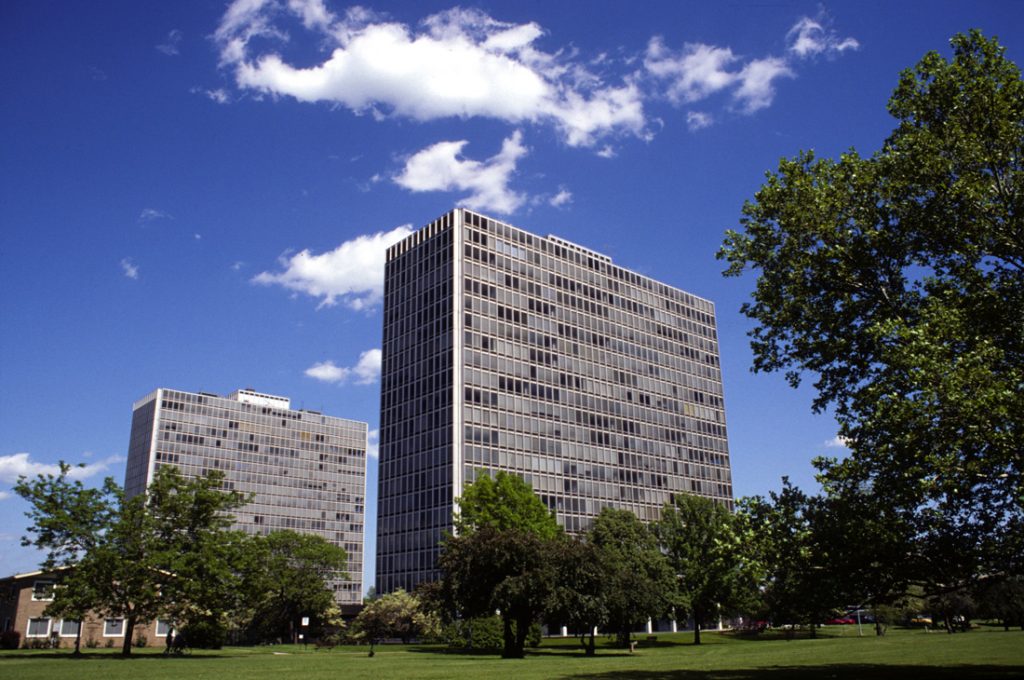
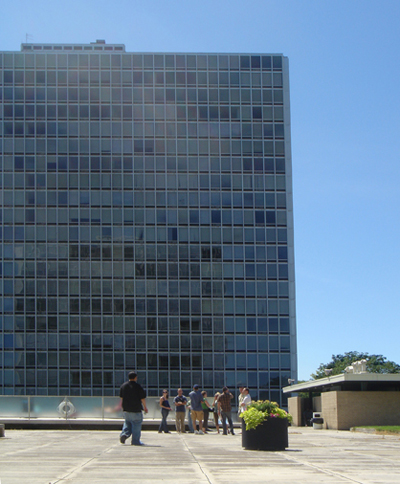
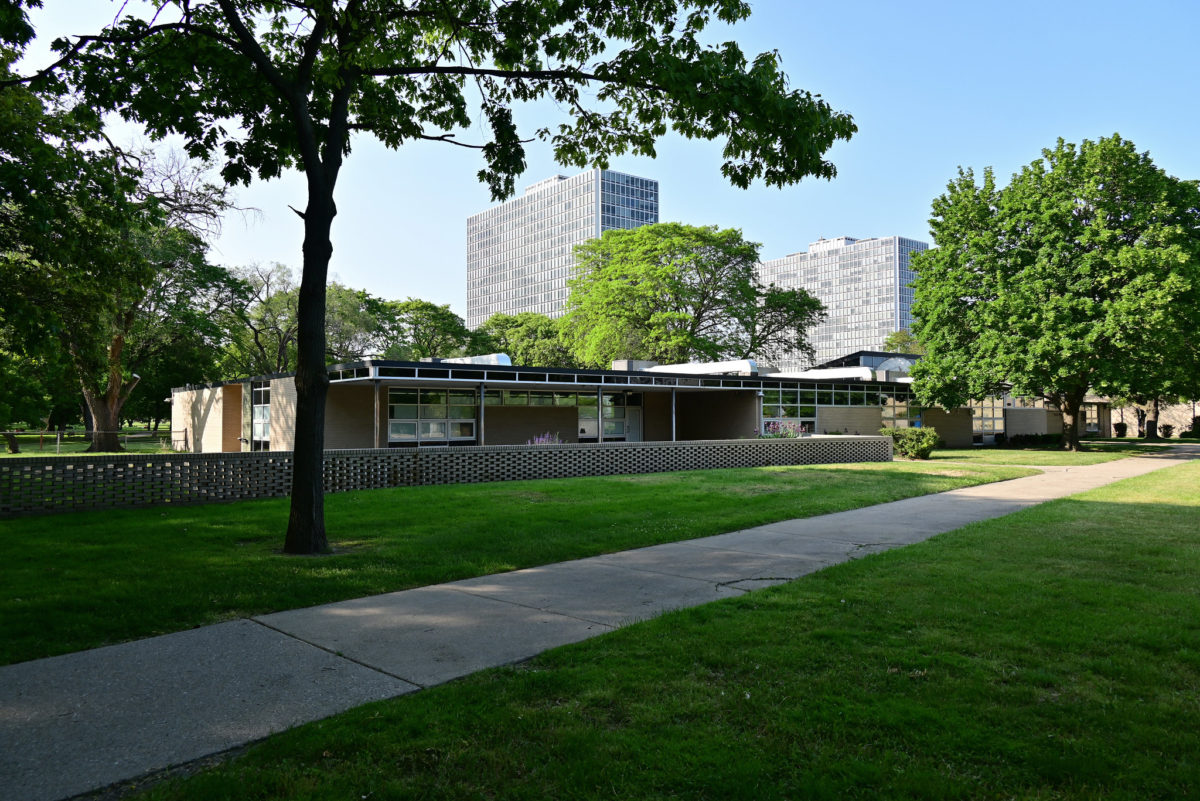
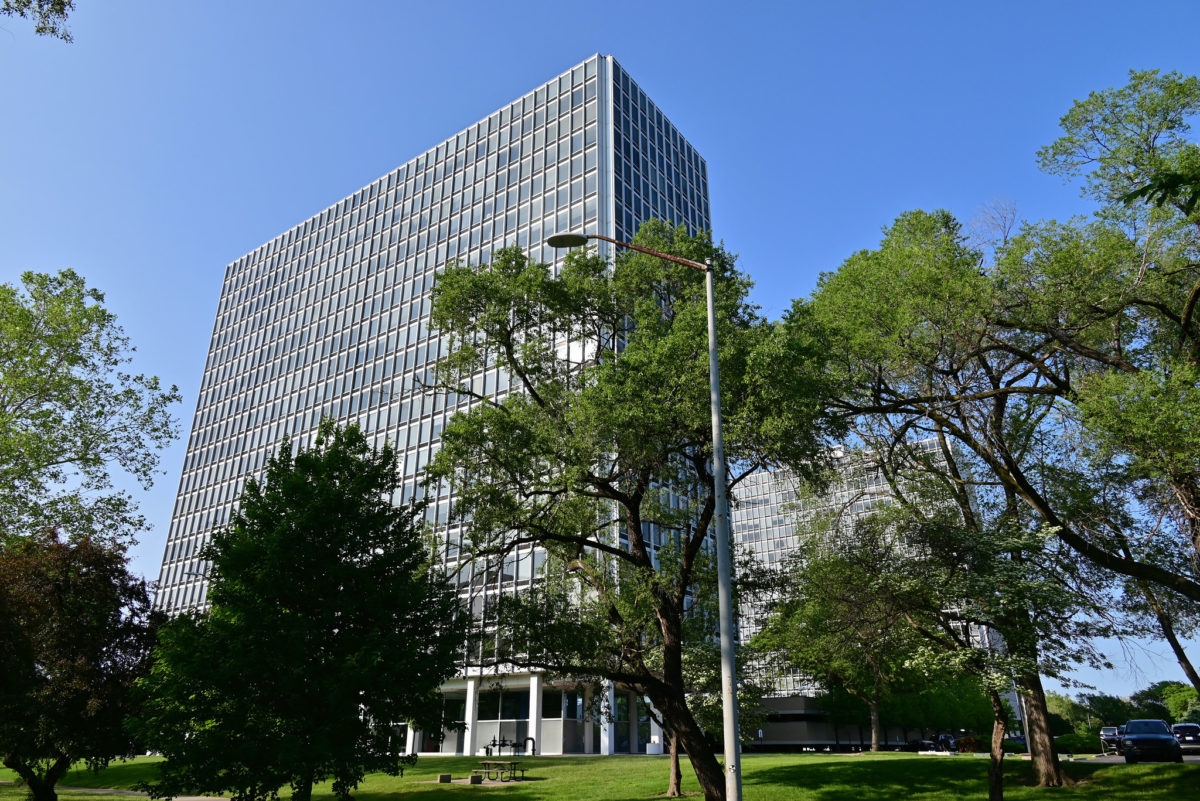
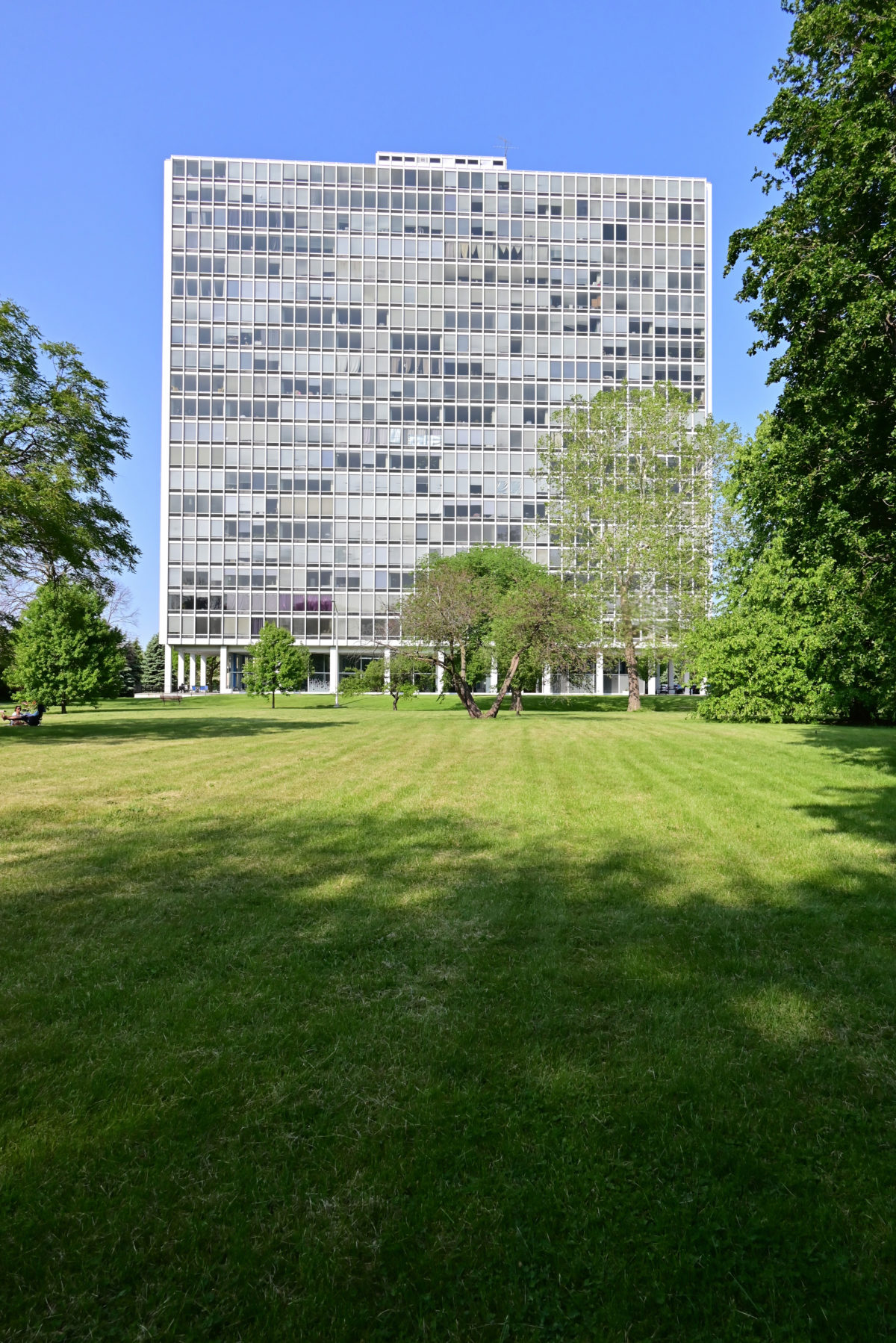
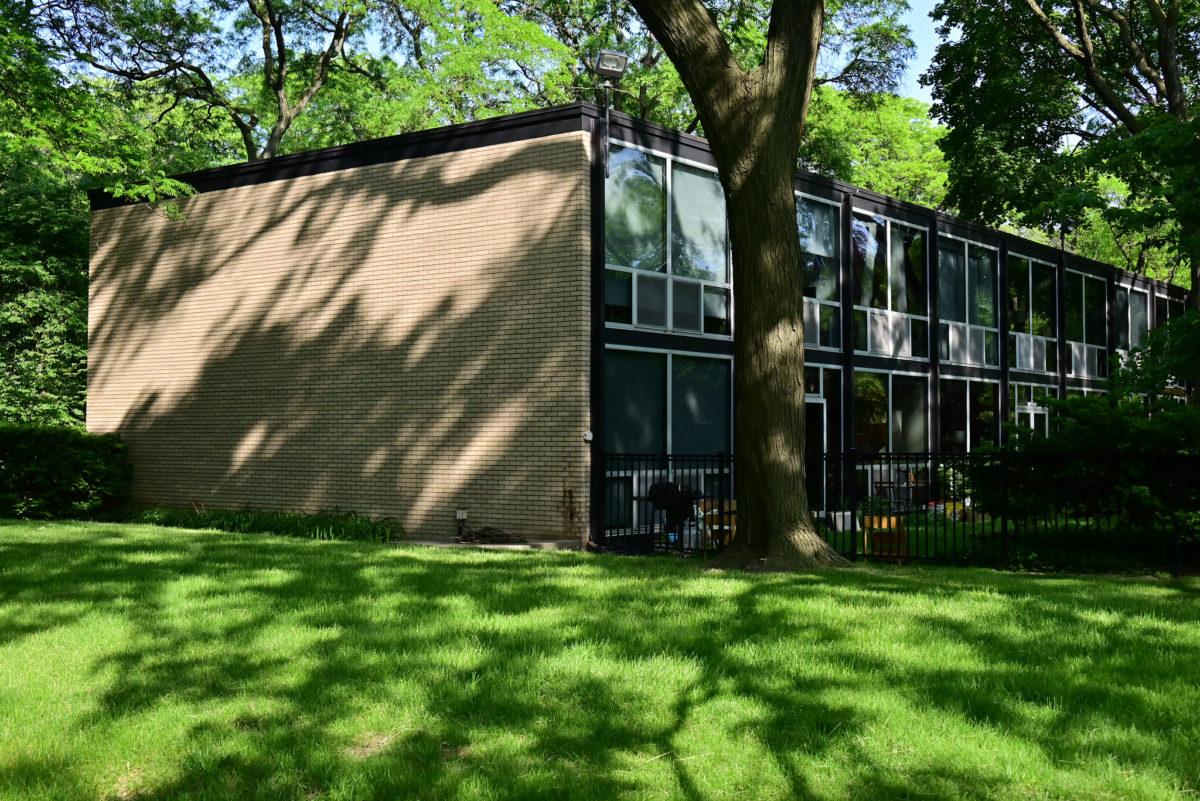
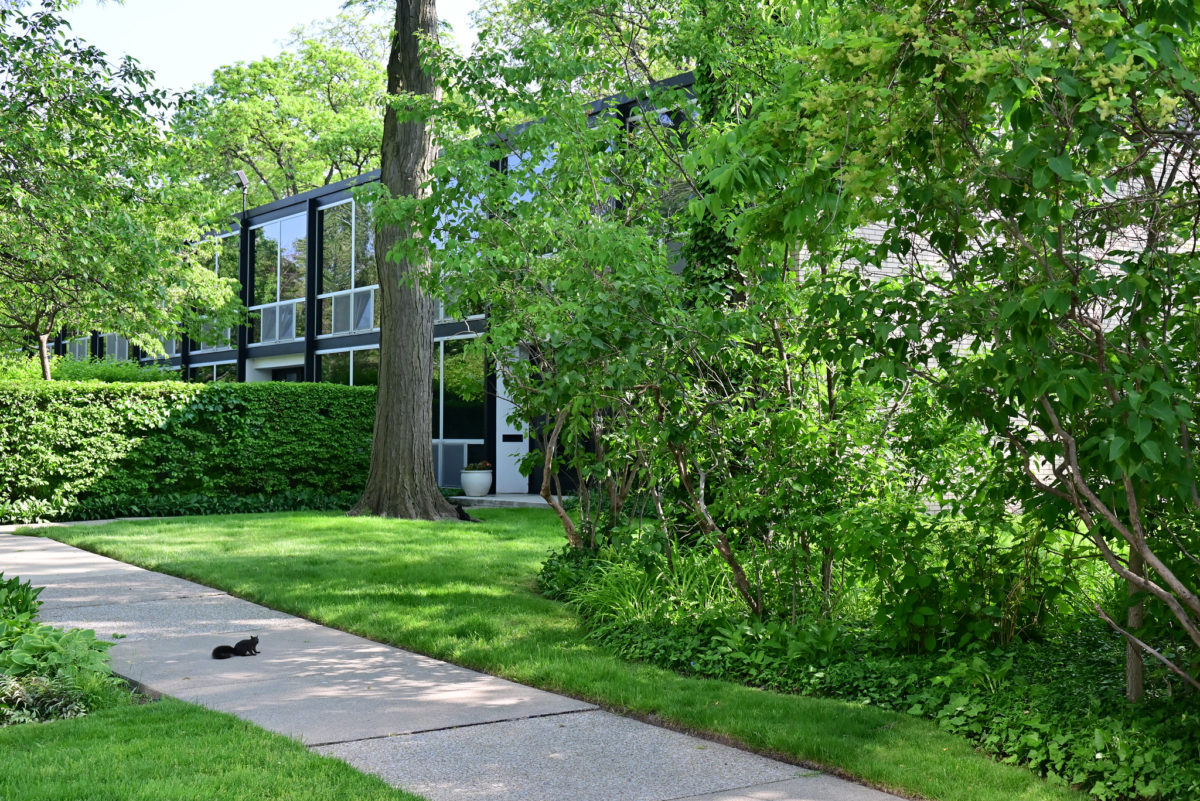
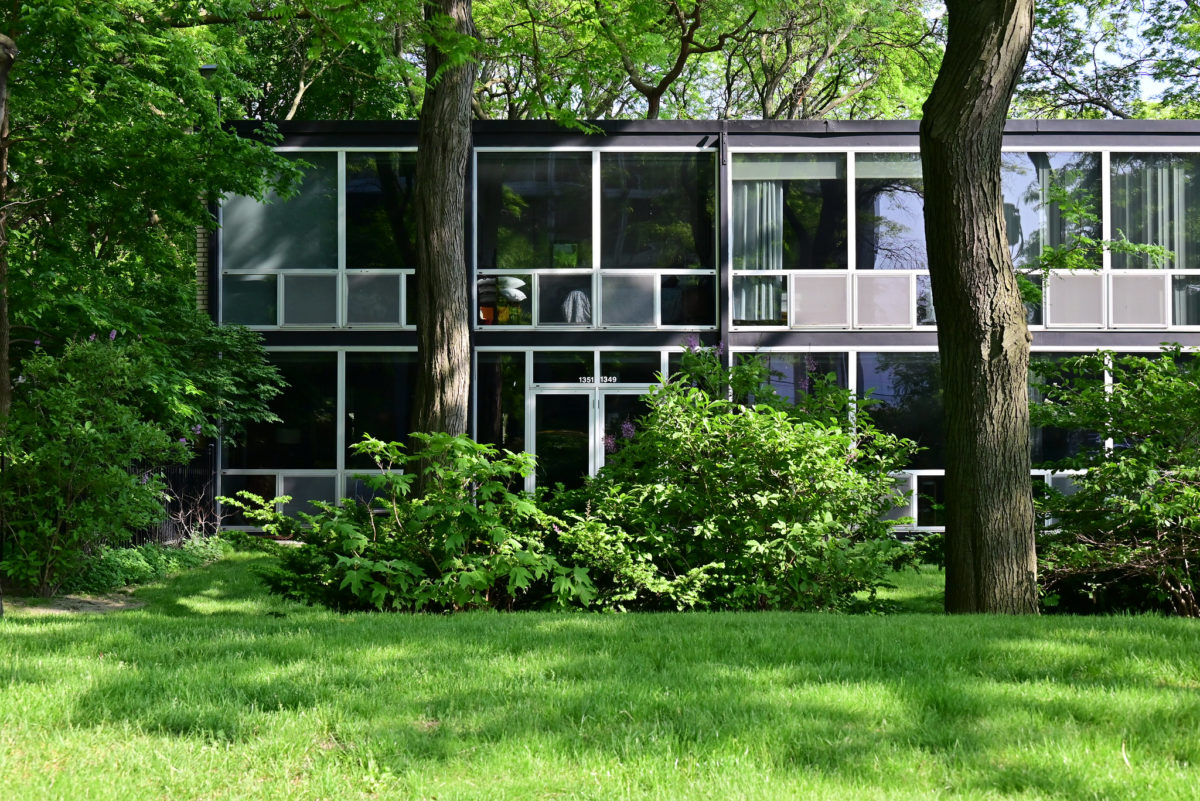
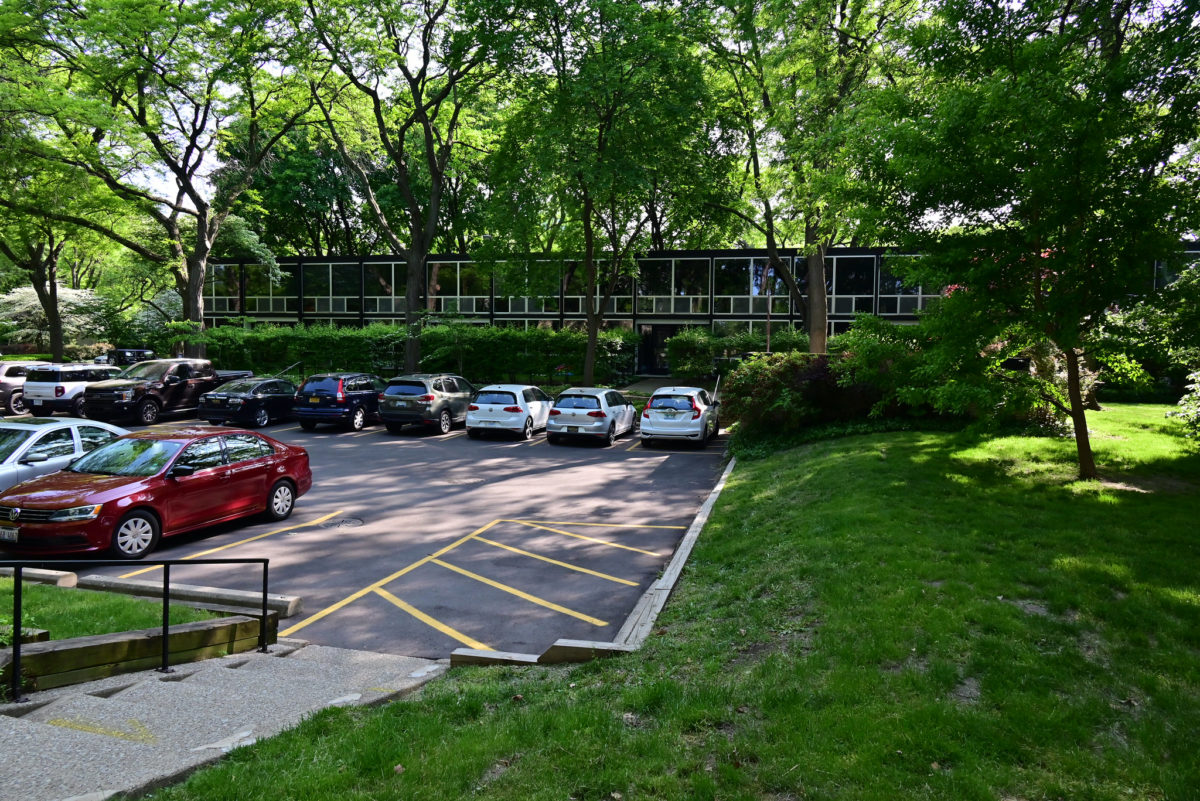
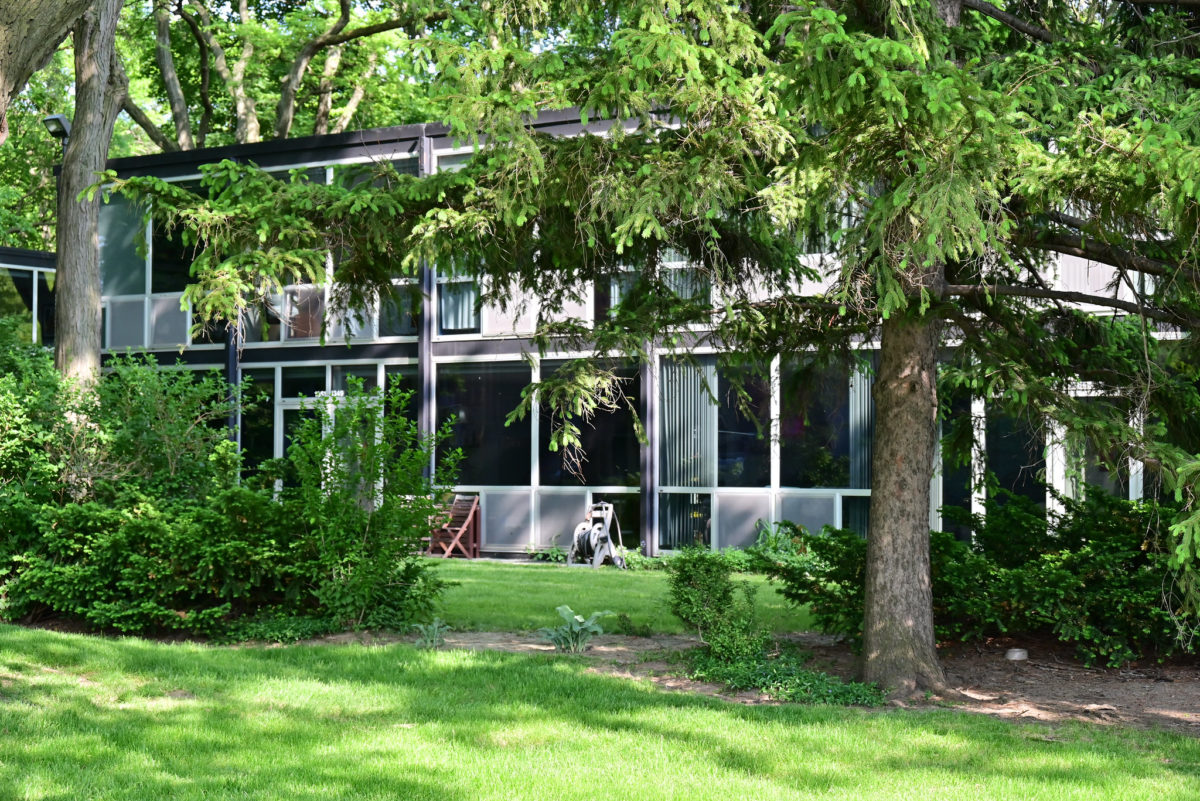
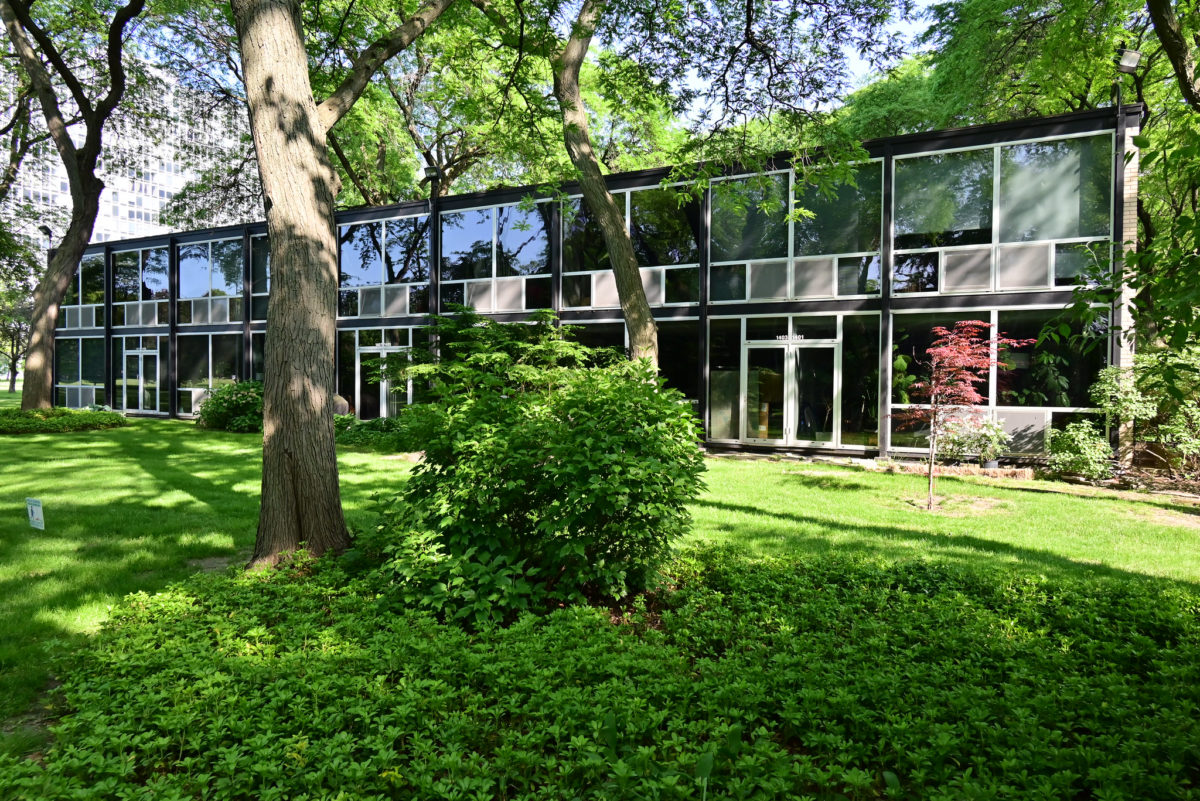
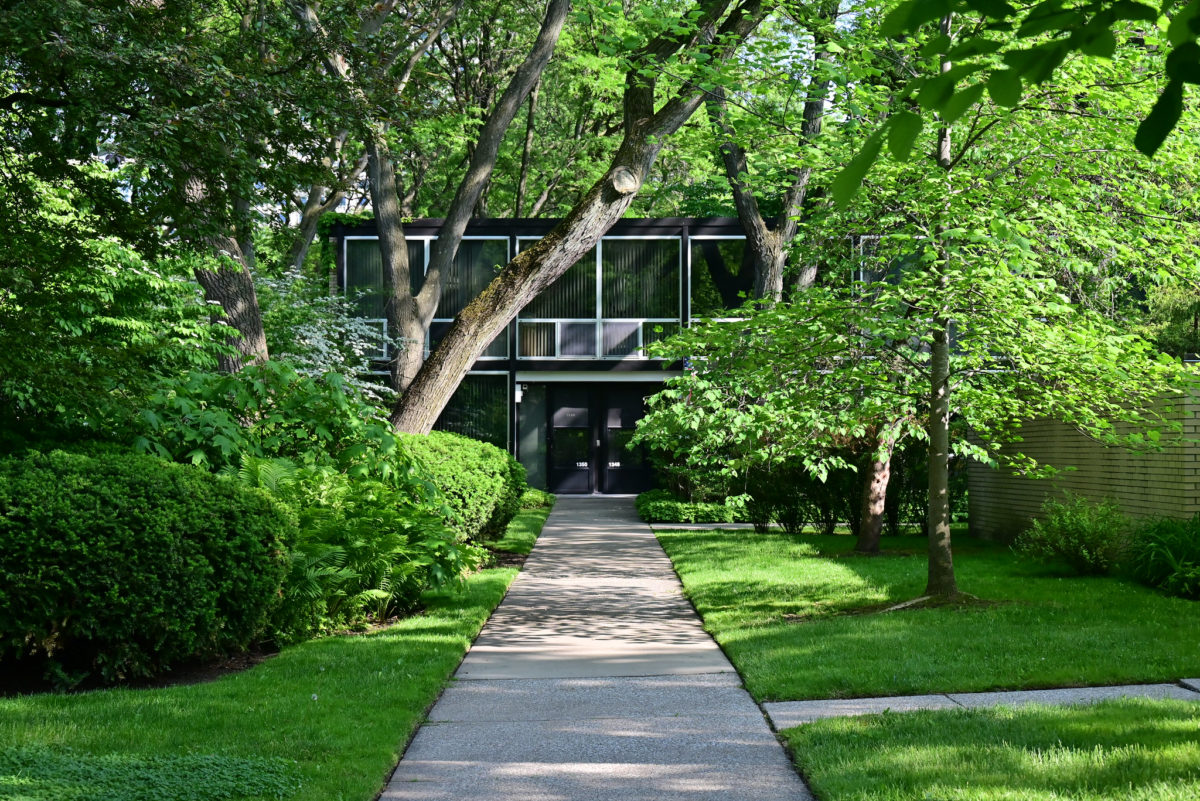
During the project, Ludwig Hilberseimer could implement his idea of “Urbs in Horto”, which was to have housing in a garden setting. By having this design, the houses were divided into two types: groups of high and low altitude groups. The high-rise consisting of four 21-story towers planned for housing with sufficient area for parking cars. While low-rise consisting of type one and type two in a row in a row, both with gardens, parking, privacy and intimacy and sheltered because of the scale of the buildings.
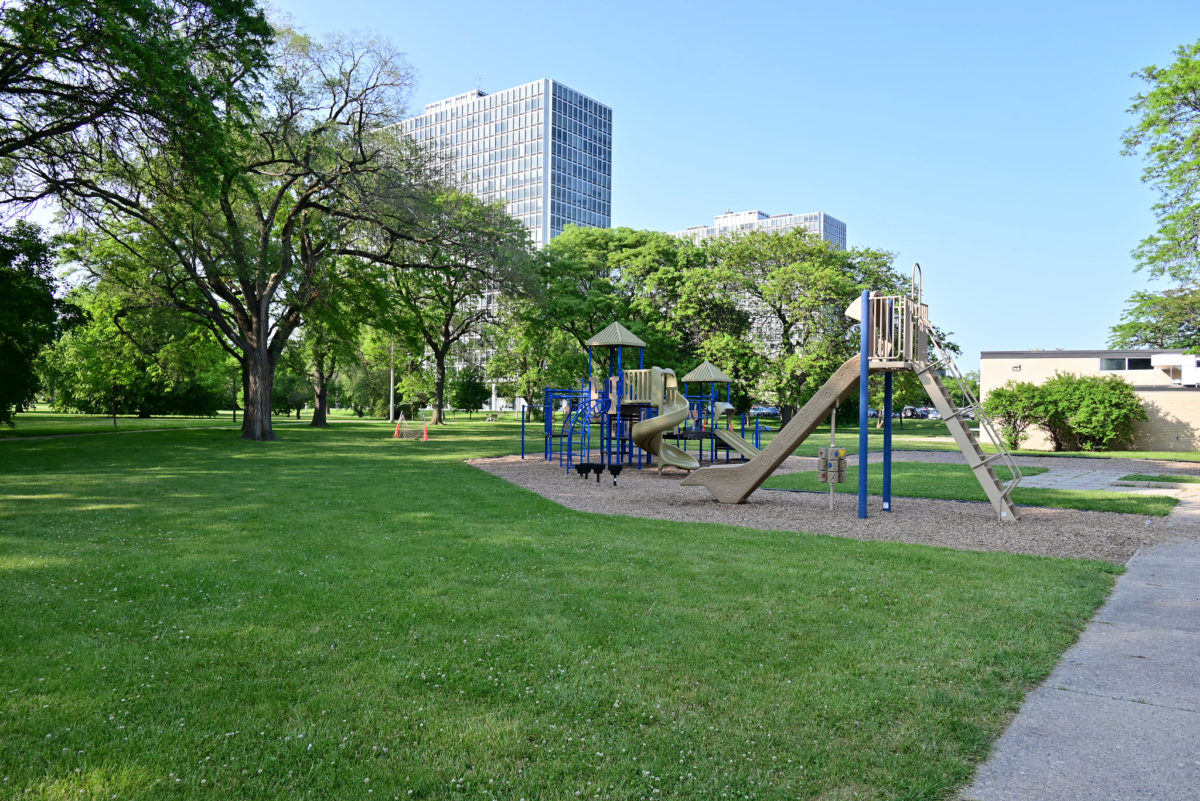
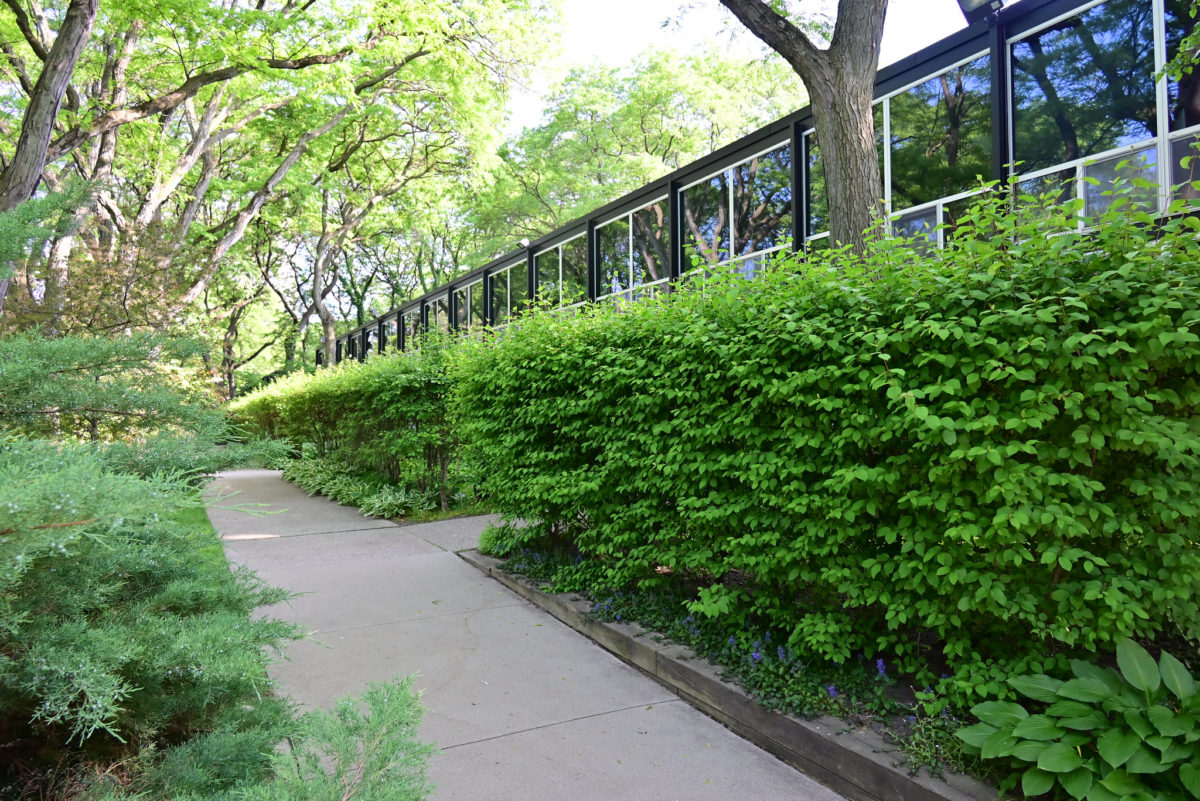
Another important feature to provide all of the above was that the accesses occur in the streets called “cul-de-sacs” that were made to create a local traffic and that does not cross the central park. Just as the work of landscape were very important because it makes the whole operation as such, since the community has access to various carriers such as a central park, playground, gardens, private patios, etc.
Spaces
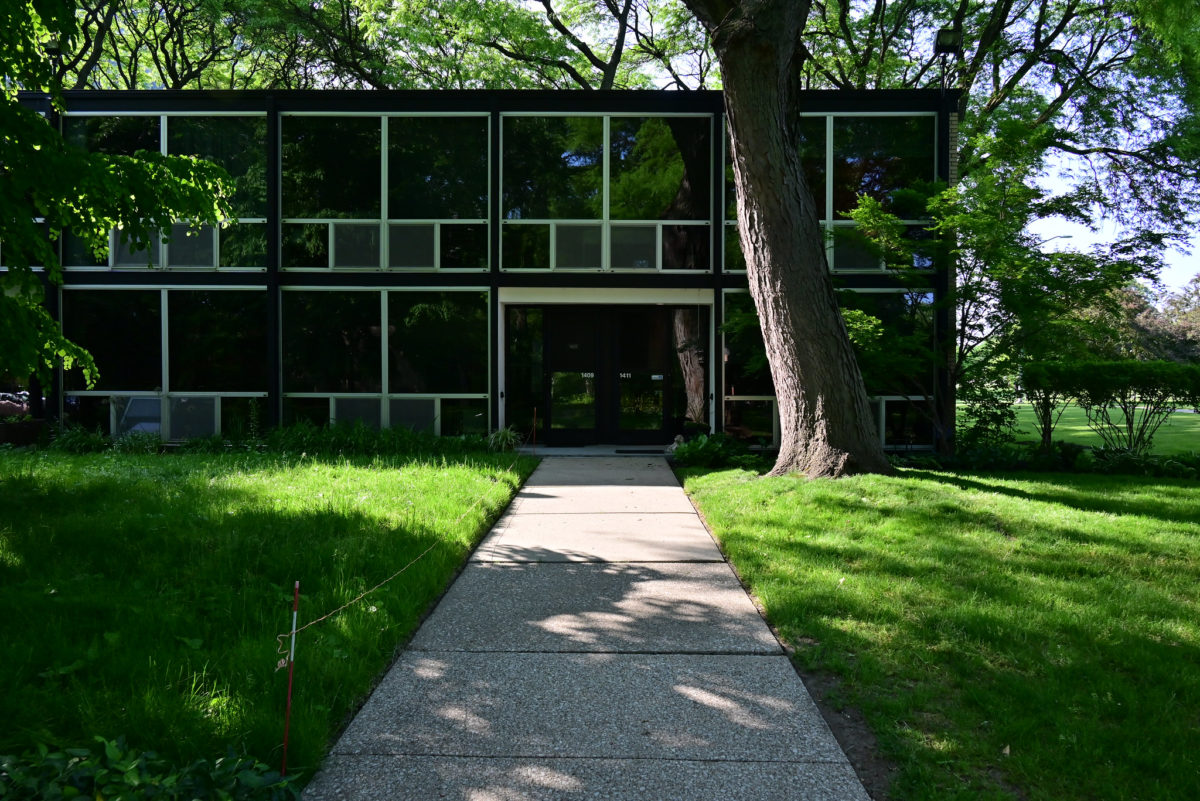
- TOWERS(high-rise buildings) The towers were designed as separate parts in the urban environment, these contained:
- Underground parking for parking
- 21 floors with 17 dwelling houses each
- Housing Types 1 to 1 room, kitchen and bathroom 2 – two bedrooms, kitchen and bathroom
- Two stairways on two ends
- Core lifts in the central part
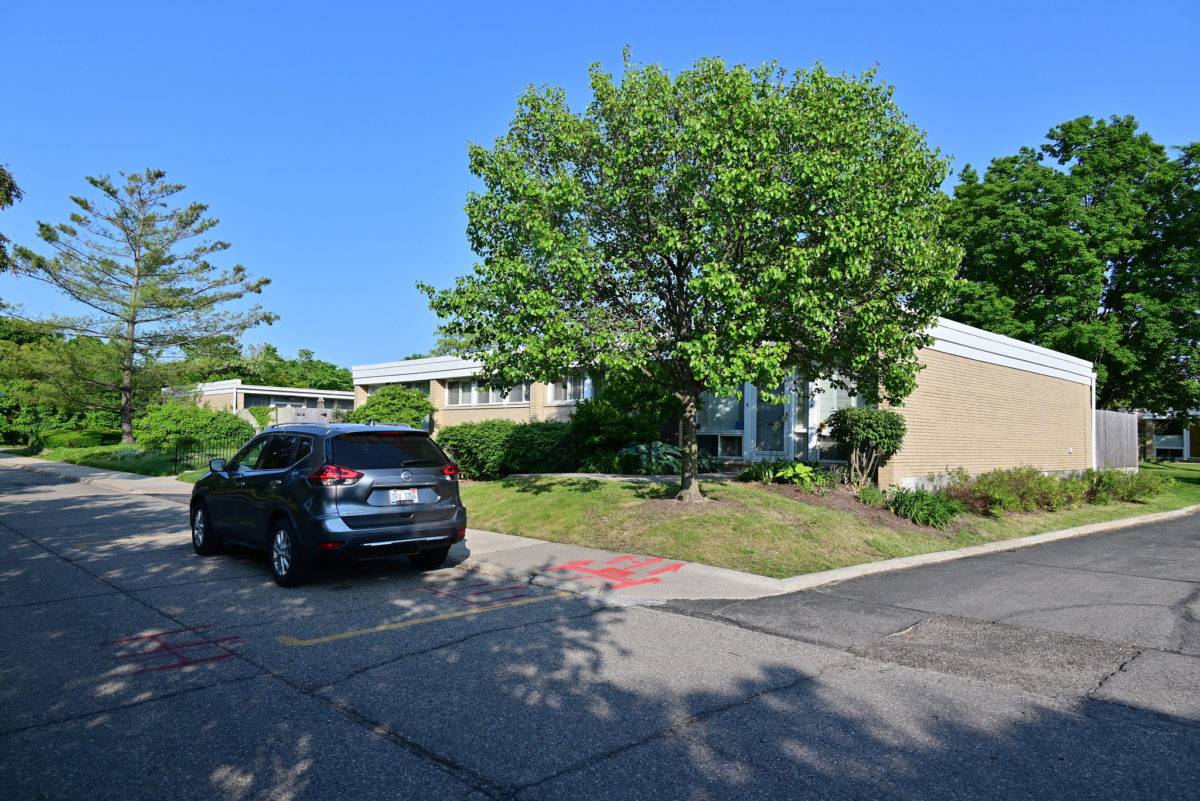
- HOUSES (low-rise buildings) The houses were divided into two types:
- Ground floor – kitchen, dining room, stairs
- First floor – bedrooms, bathroom
- Parking on site
- Access from Corridor
- Bungalow – kitchen, dining room, three bedrooms, bathroom
- Individual parking outside house
- Access from street
Structure and Materials
TOWERS (high-rise buildings)
In terms of structure is made up of box Reinforced concrete and reinforced concrete columns, with a clear grid of 6.0 meters x 6.0 meters, columns 0.60×0.60 meters. The slabs are based on a grid sheet of concrete.
In terms of materials, were used extruded steel profiles and sheet glass, some wood paneling for rooms and some areas of hormibón pabimentos in the main squares of access.
HOUSES (low-rise buildings)
Here we use the same grid of 6.0 meters each load bearing wall, unlike that used brick walls beige annealing for divisions in the housing and structural loads. The roof slab is made of reinforced concrete.
As for materials, brick walls and concrete walls are lined with steel parts laminar and extruded profiles, such as on the top of the dividing walls on the facades of the houses. On the other hand the woodwork in the beginning were made of steel profiles but with the passage of time have changed to aluminum. The wooden floor was used for the rooms, although they have emerged over time various amendments. We can also see gateways to the homes of reinforced concrete in large modules.