Great Pyramid of Cheops

Introduction
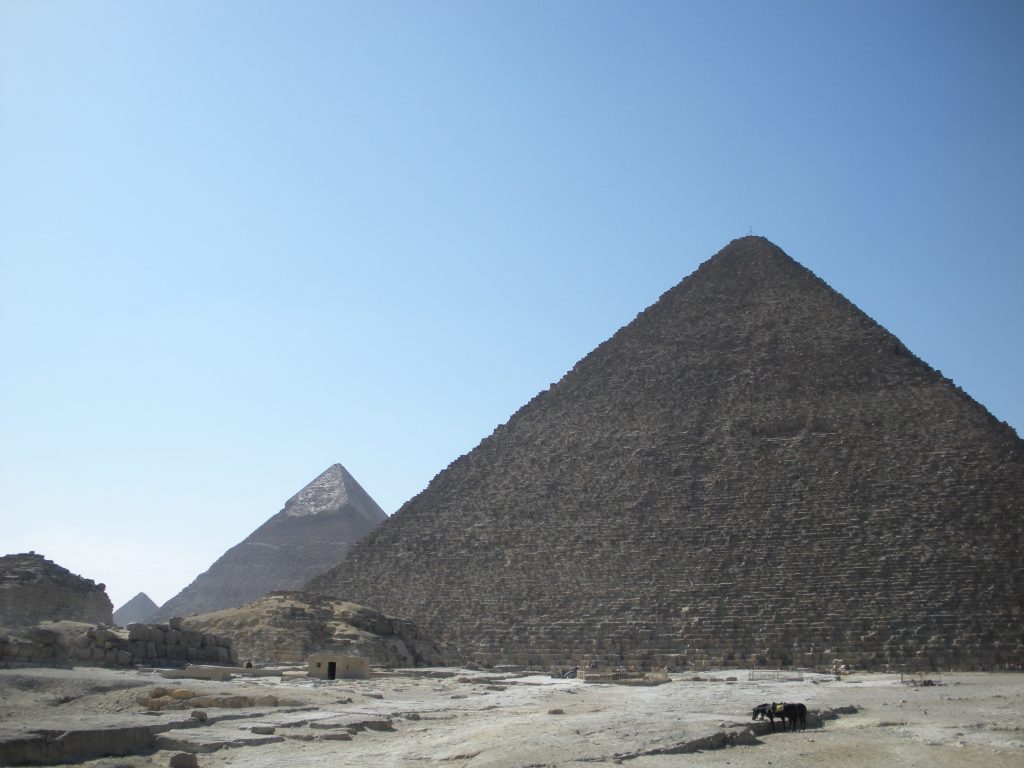
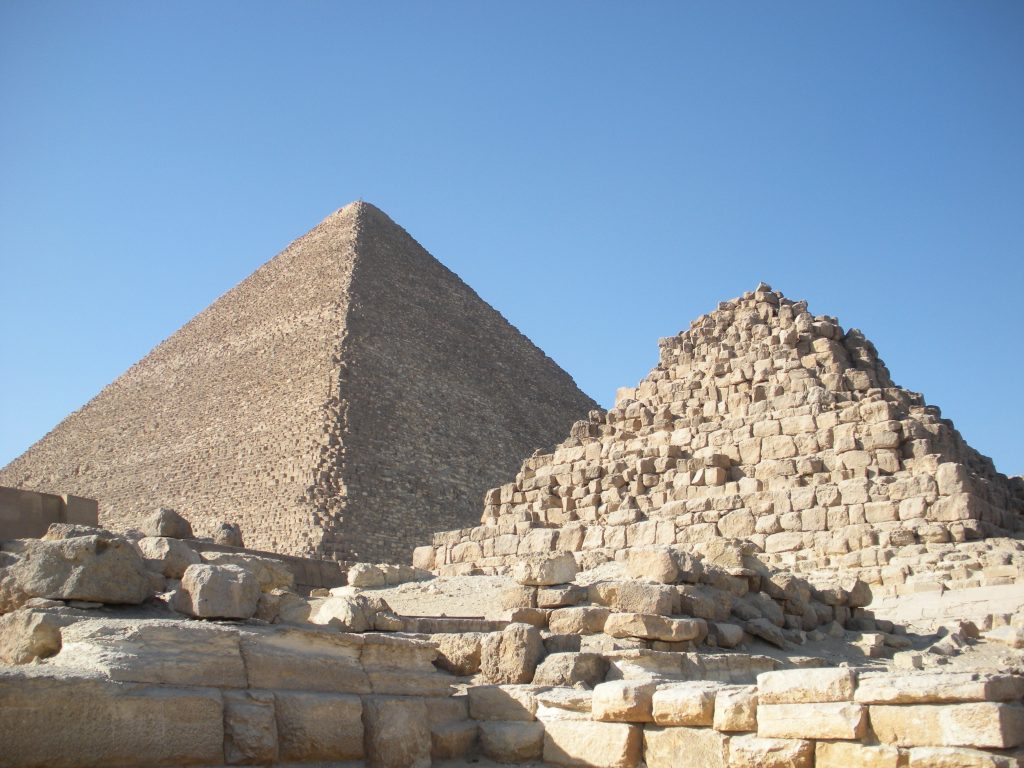
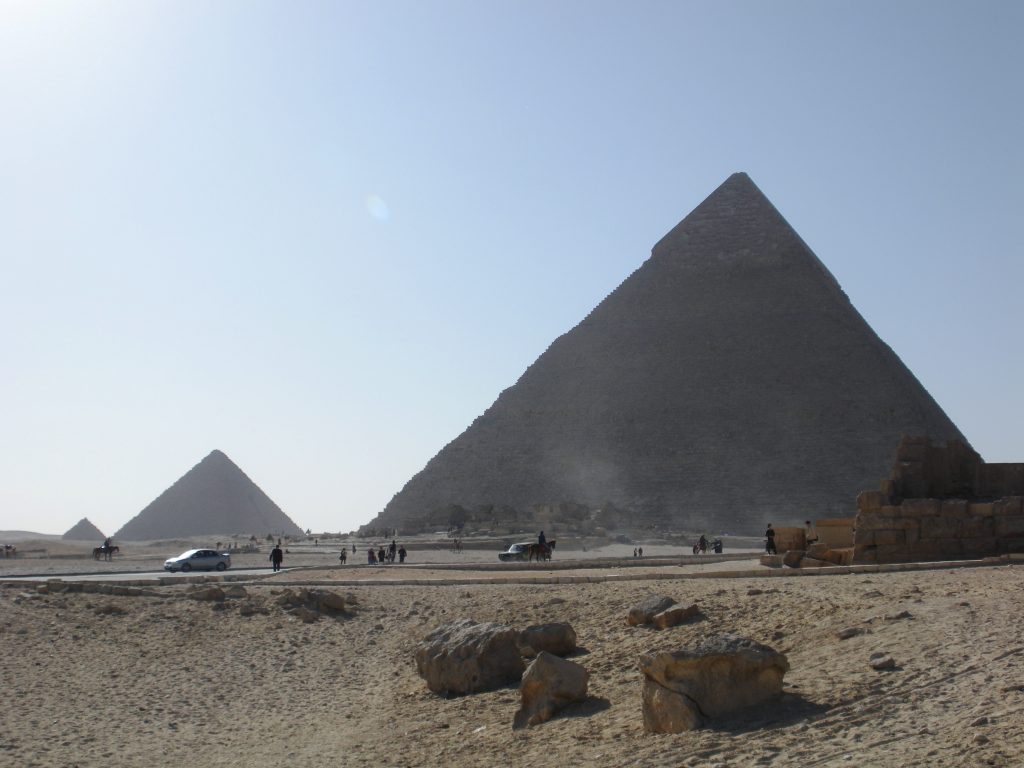
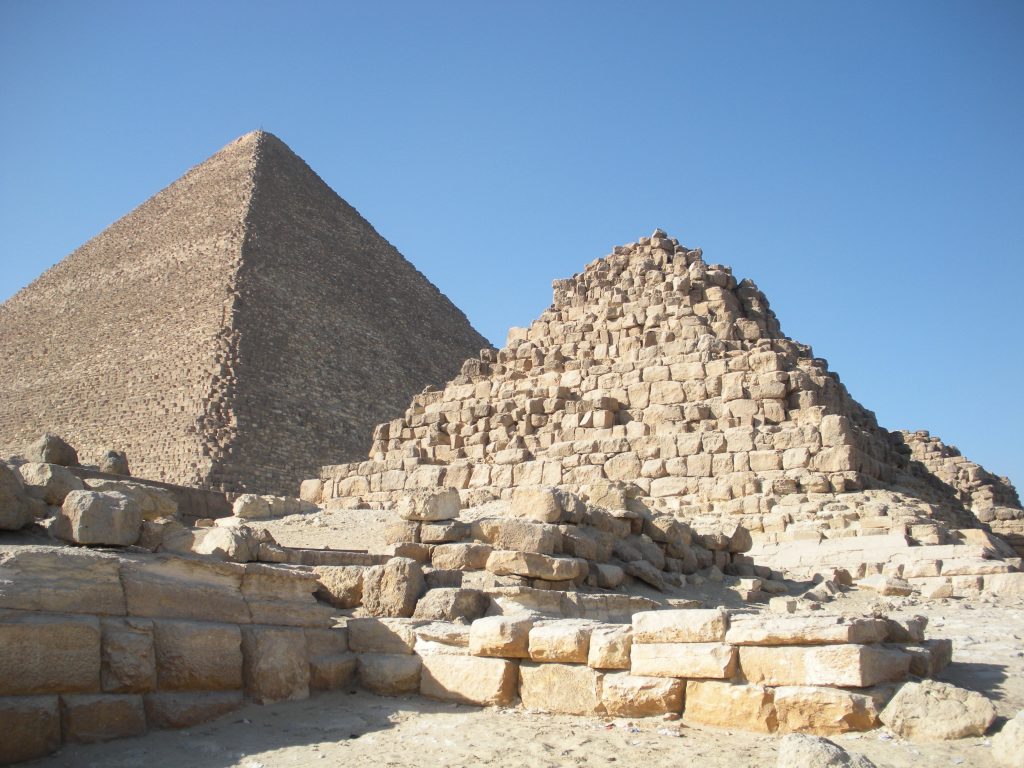
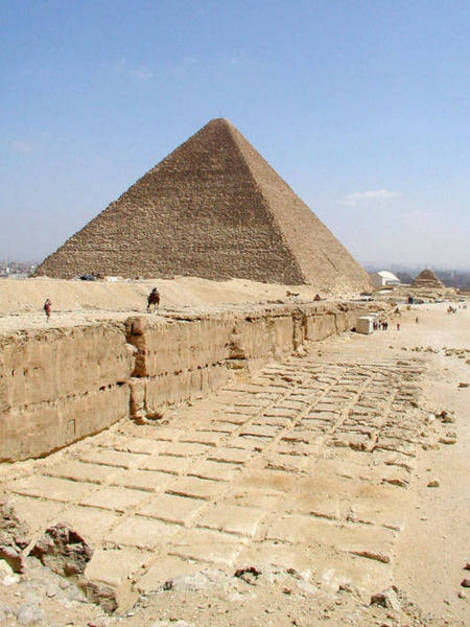
Egypt has more than one hundred pyramids of various sizes and there are nearly fifty more in neighboring Sudan. However, the three Great Pyramids of Giza have earned their reputation for being the greatest of them all. In the most famous photos, the central pyramid, ie that of Kafra (or Chephren), appears larger due to the angle of approach, since it was built on higher ground, but most of the three pyramids is the Great Pyramid Cheops, also known today as the Great Pyramid.
The Pyramid of Cheops served as a tomb for Pharaoh Khufu, also known by its Greek name, Cheops, in Dynasty IV. It is estimated that was completed between 2550-2570 years BC
It is the sole survivor of the famous Seven Wonders of Ancient World, cited by Antipater of Sidon in the year 125 AC, the other two pyramids in the necropolis (Chephren and Miceriono) are not included in these ancient wonders. Herodotus who visited the site in 450 BC stated that its construction lasted 20 years.
For some it is the logical conclusion of the road in funerary architecture, whose starting point is in the mastaba, to reach the most perfect of all pyramid. For others it is an impossible engineering feat even today. Some believe that its geometry is written the history of humanity, others that it is like a giant world of knowledge. Some see in it the tomb of the most selfish and tyrannical rulers, others a monument left by an earlier civilization known to all. Some see thousands of slaves working to whip and others believe they see alien labor. It has been said of it being a tomb, a large power plant, a scale reproduction of the Earth, a celestial observatory, a Bible written in stone…
- Treasures of Pharaoh
There are numerous and ancient stories about explorers who in many cases destroyed archaeological treasures and even disappeared or lost their lives in the pursuit of the treasures that had supposedly been buried with the pharaoh.
During the excavations made by the Arabs in the Pyramid of Cheops, slabs and boulders were found that had been used to seal the passages and chambers. We also found secret doors. This fueled the many myths about the possibility that the pyramids were a trap, and that those who came later could not get out alive.
A seventeenth-century English explorer was able to find another hole connecting the passages, but found no treasure. This leads to two possible conclusions, one, that the ancient grave robbers had stolen the treasures of the pyramids centuries before the entry of the Arabs, leaving the empty chambers, and the other that Khufu’s mummy and its treasures are still cleverly hidden within or beneath the Great Pyramid.
Location
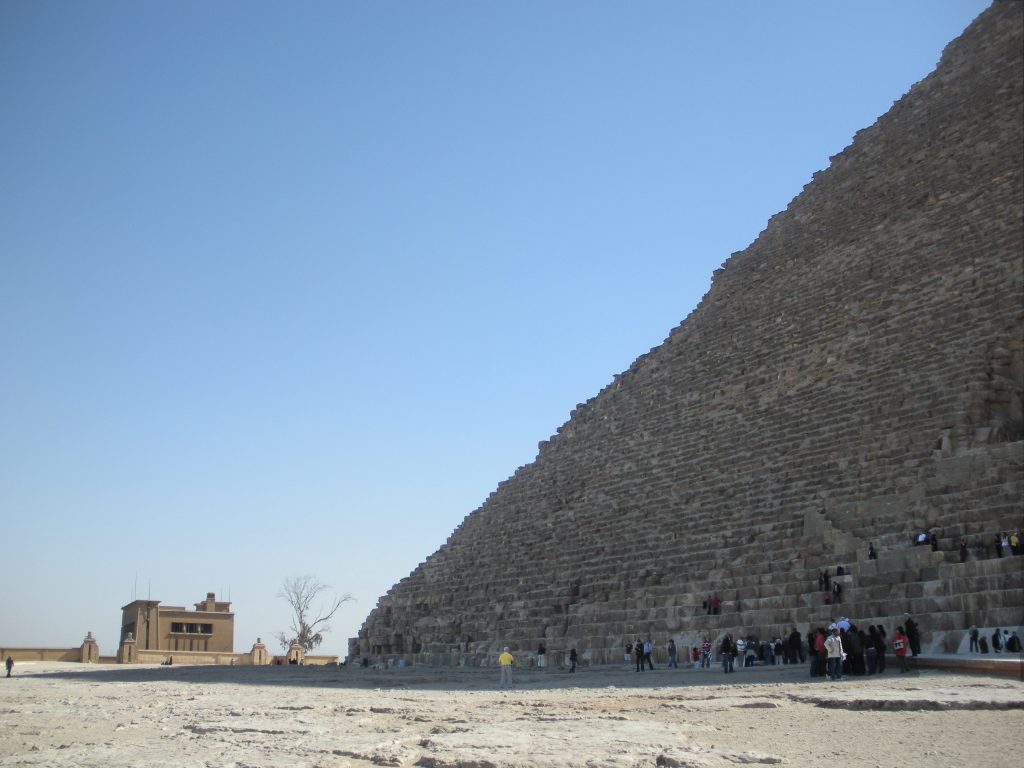
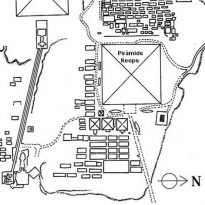
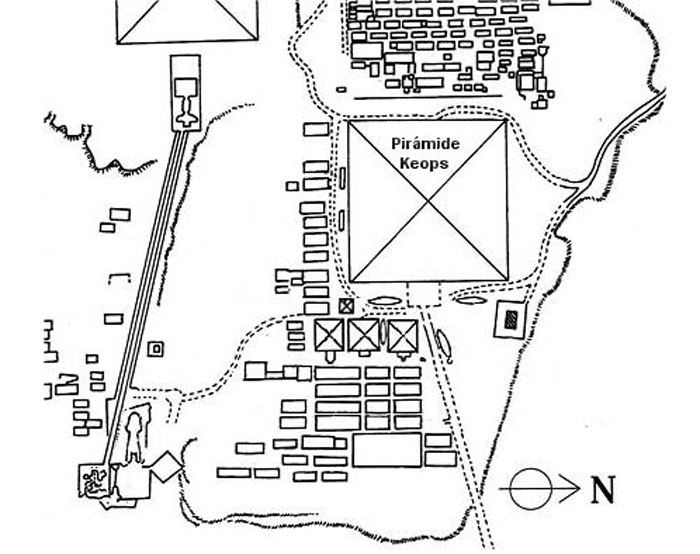
20 miles southwest of downtown Cairo and part of its metropolitan area is the city of Giza and Giza in Arabic, on the west bank of the Nile River
The Great Pyramid of Cheops was built on the Giza plateau, on the left bank of the Nile and 40 feet above the Valley of Giza, Egypt.
Description
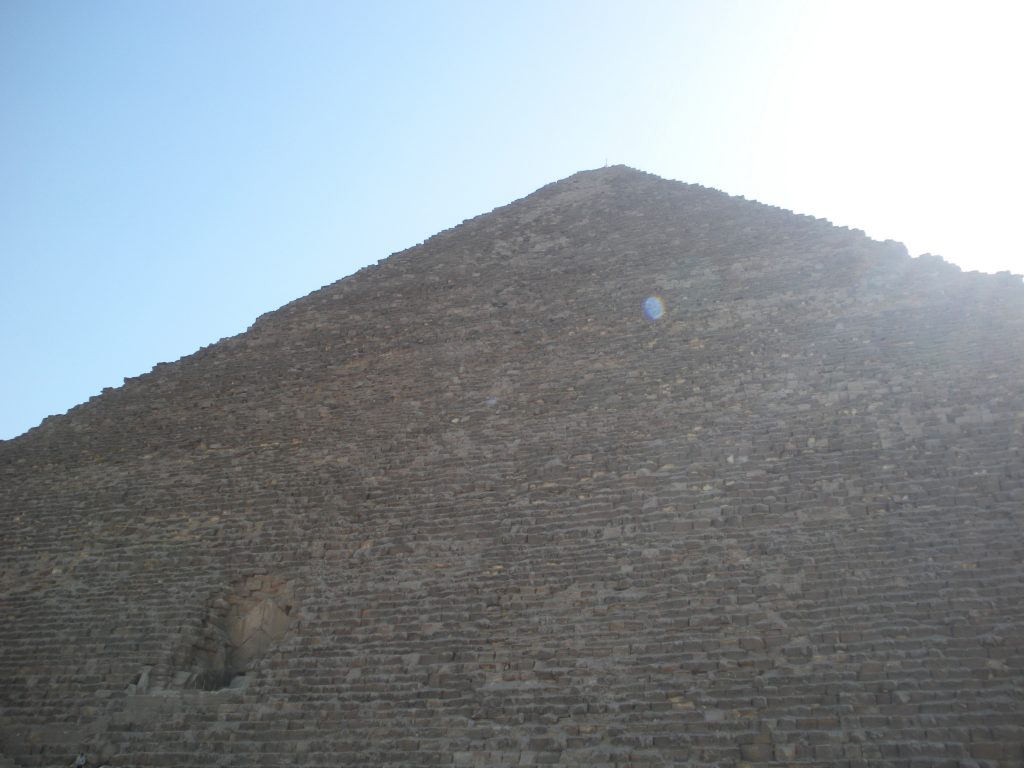
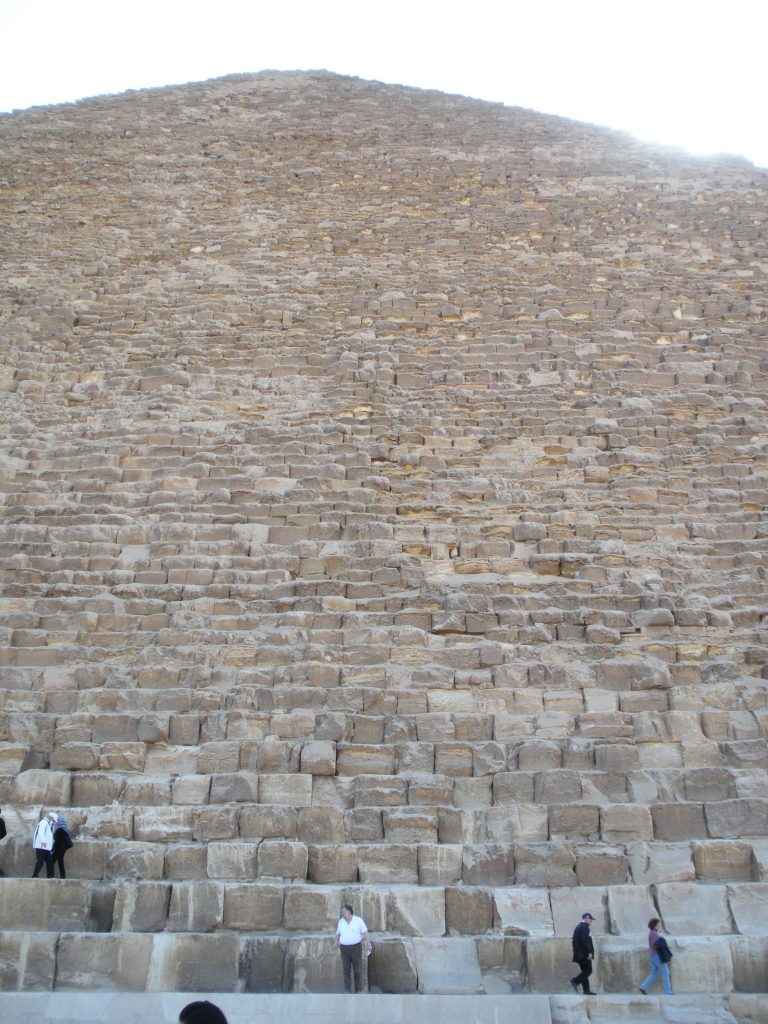
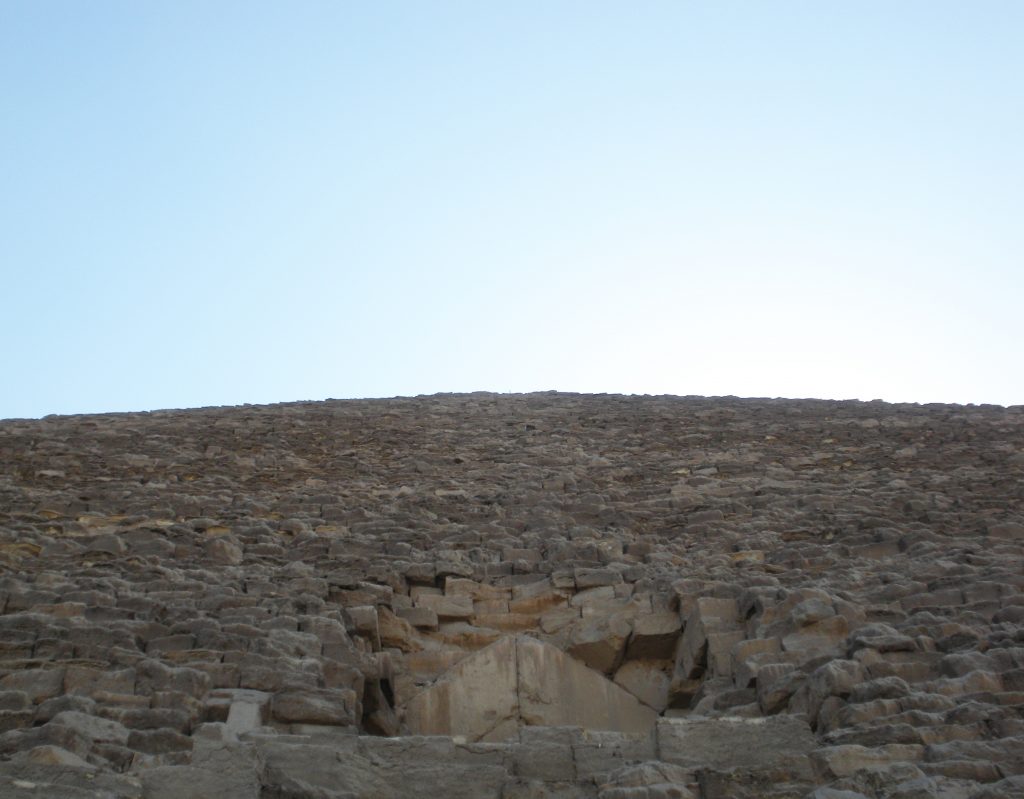
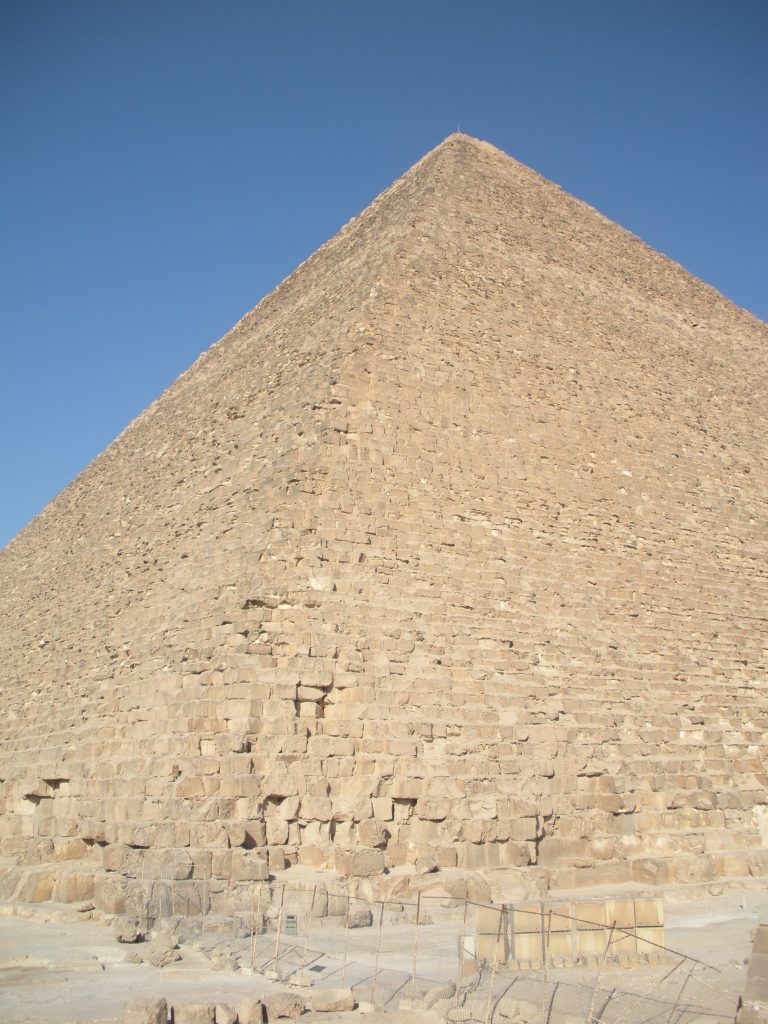
The Great Pyramid had an original height of 146 meters, but fell nine meters due to erosion and the passage of time.
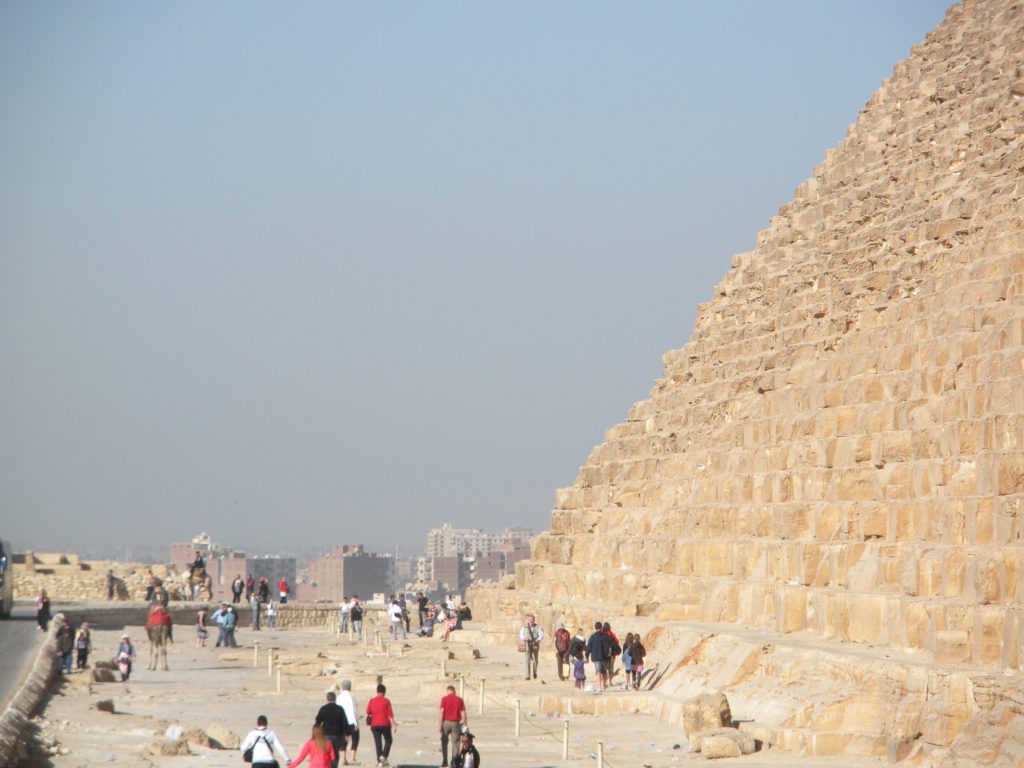
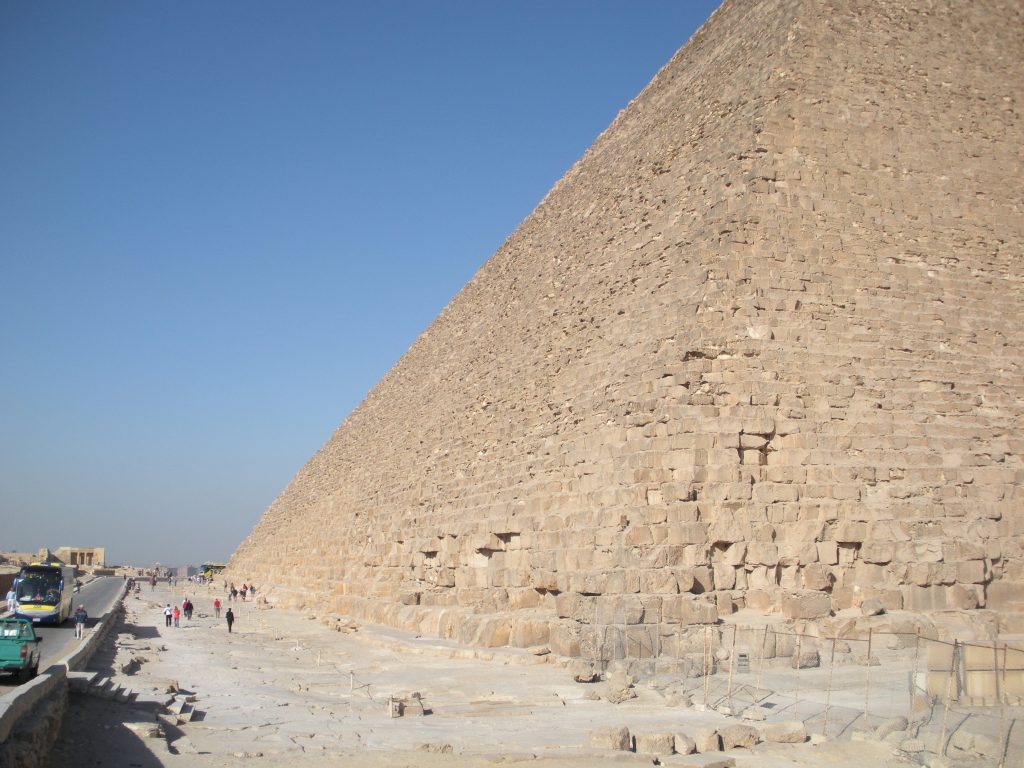
The base area is 53000m2, with 230 meters per side. This area is sufficient to hold 20 Olympic swimming pools or eight football fields. To round it is to walk almost a kilometer and its height corresponds to a forty-story building. For hundreds of years, until they built the Eiffel Tower in 1889., The Great Pyramid was the tallest building in the world.
Its sides are oriented towards the four cardinal points, so that the reflection of the shadow charged with clockwork precision the essential points of the solar year, giving the precise dates of the spring and fall equinoxes and solstices of winter and summer.
Concept
It is believed that it was erected to contain the remains of Pharaoh when he died. However, other theories abound about the pyramids, some of whom risk their belief that they were built as astronomical observatories and others who claim that their position has to do with the guidance of spacecraft.
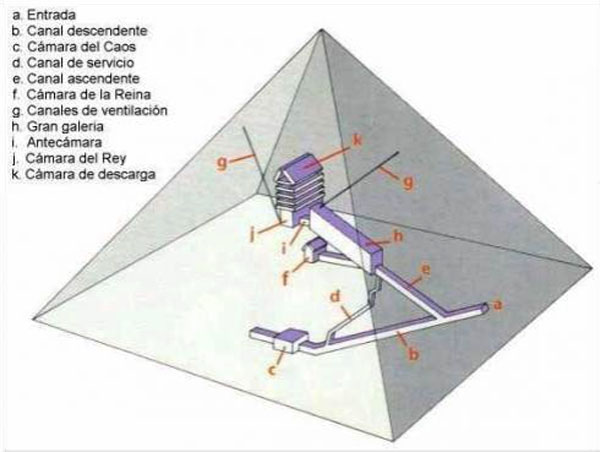
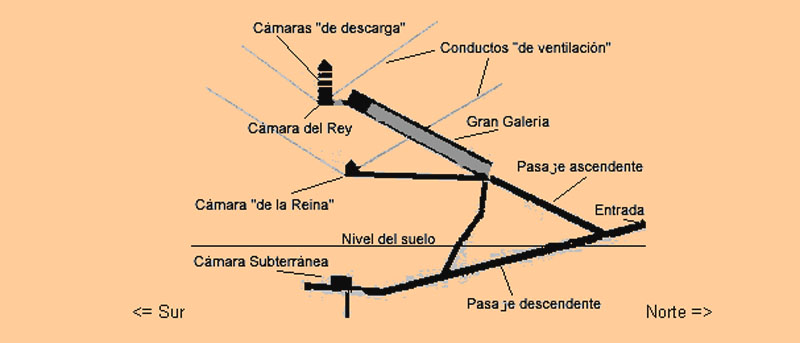
Spaces
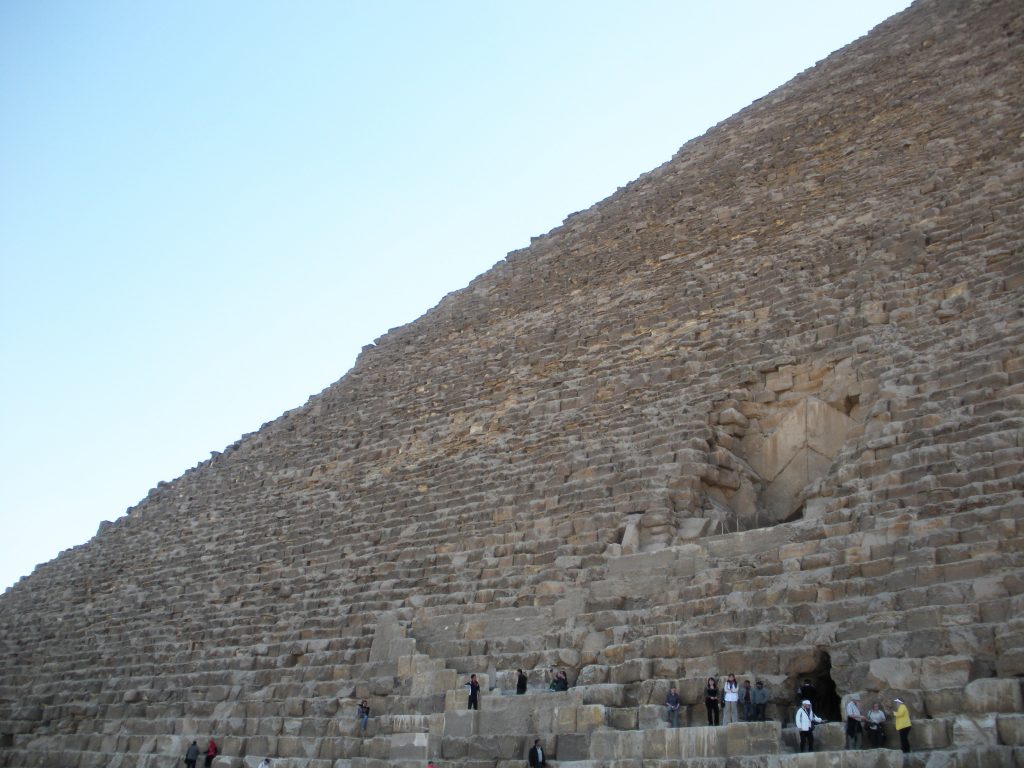
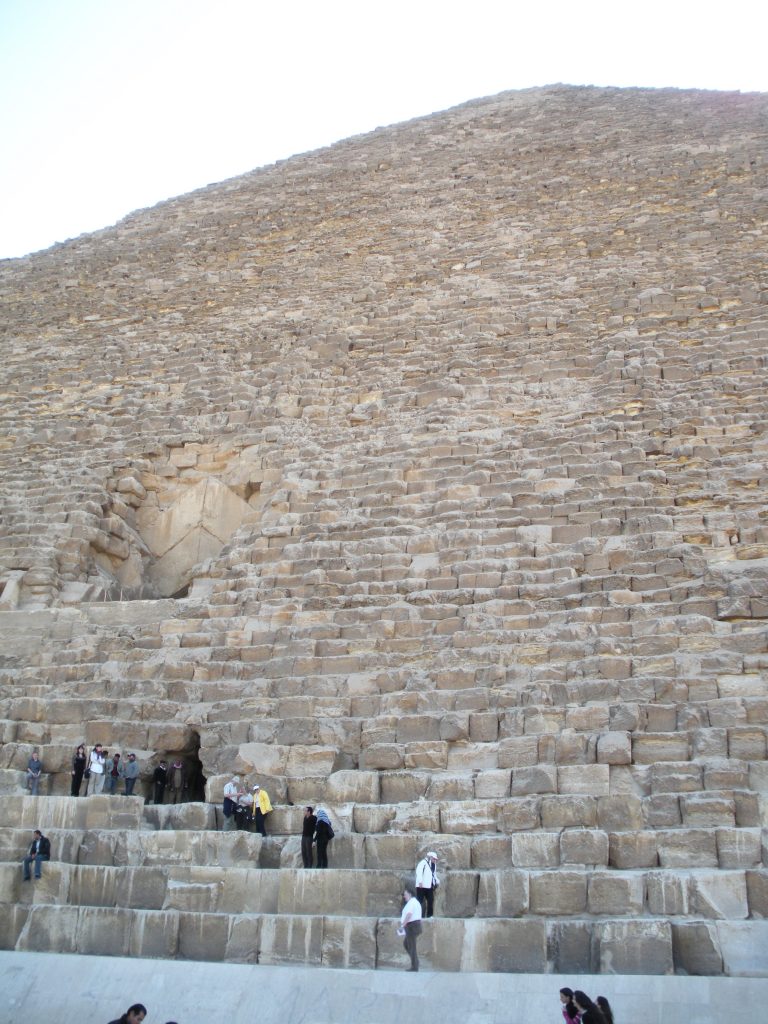
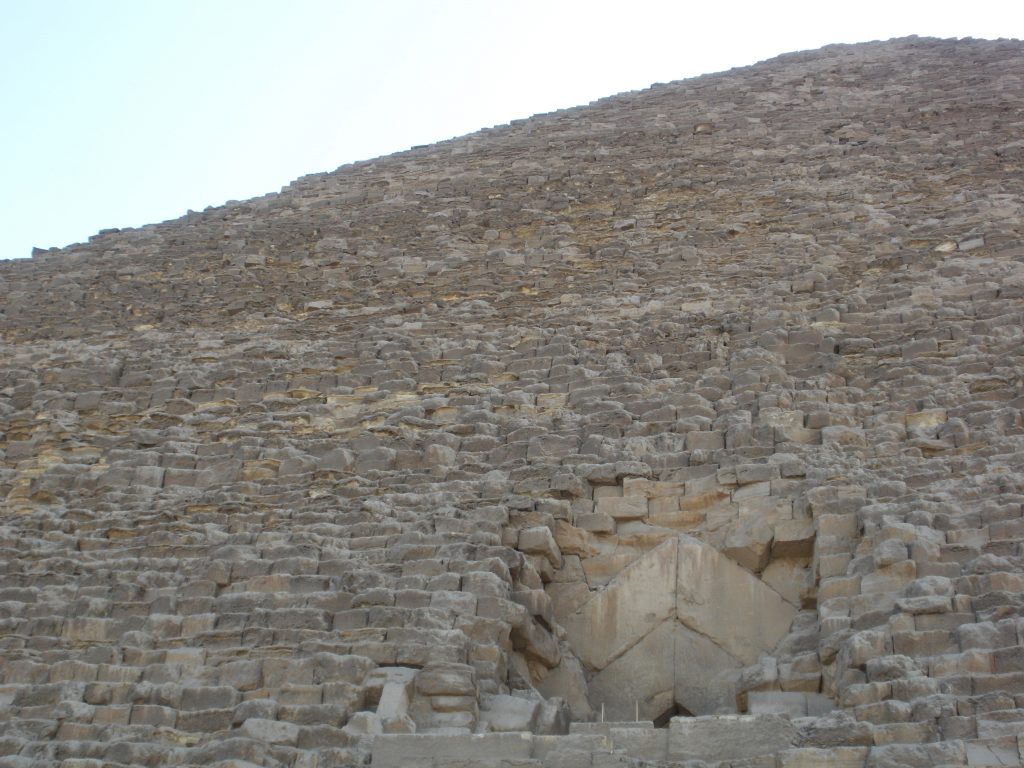
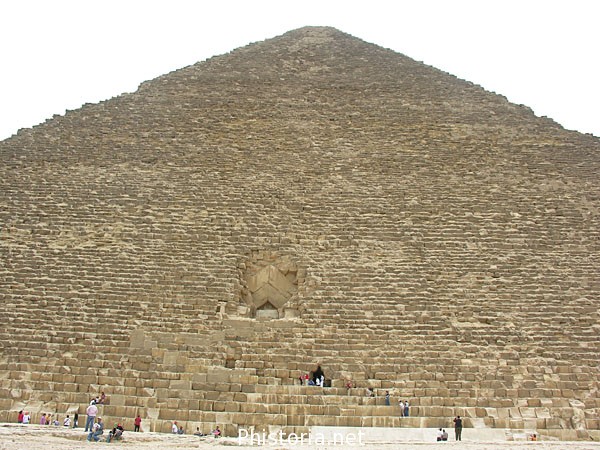
The entrance is located on the north side, at 16.75 meters high with four blocks on her discharge. It is believed that an overhead door originally known only by the priests of the highest rank hid from view. Once inside the channels and through access to rooms.
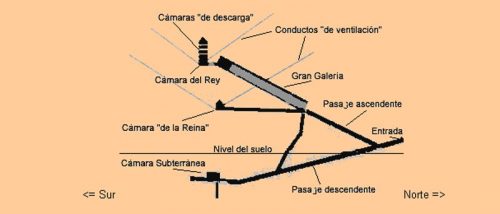
Channels
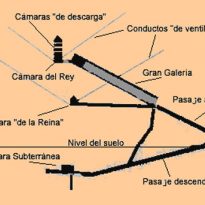
The Egyptians built two main canals to move inside the pyramid.
- Channel up
With 1.05 meters. wide and 1.20 meters. high ends in the Grand Gallery at 23 meters above the base level of the Pyramid. In the beginning there is another channel that leads to the Queen’s Chamber, the Horizontal Canal, with a distance of 38 meters.
- Channel down
This channel goes to the center of the pyramid, after covering 105, 15 meters. At the end of it we find the House of Chaos or Suberráneo Canal. The downstream channel is 1.22 meters high and 1.05 wide
- Other Channels
Both the King’s Chamber and the Chamber of the Queen, channels have been found climbing up the pyramid, in some cases such as ventilation, others have not discovered their purpose. In any case, the performance of these conduits that raise and extend the entire length of the pyramid, is a demonstration of technical and construction of its architects, because the planes could not be changed at any time, and that the channels made as construction progressed.
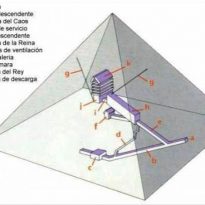
Cameras
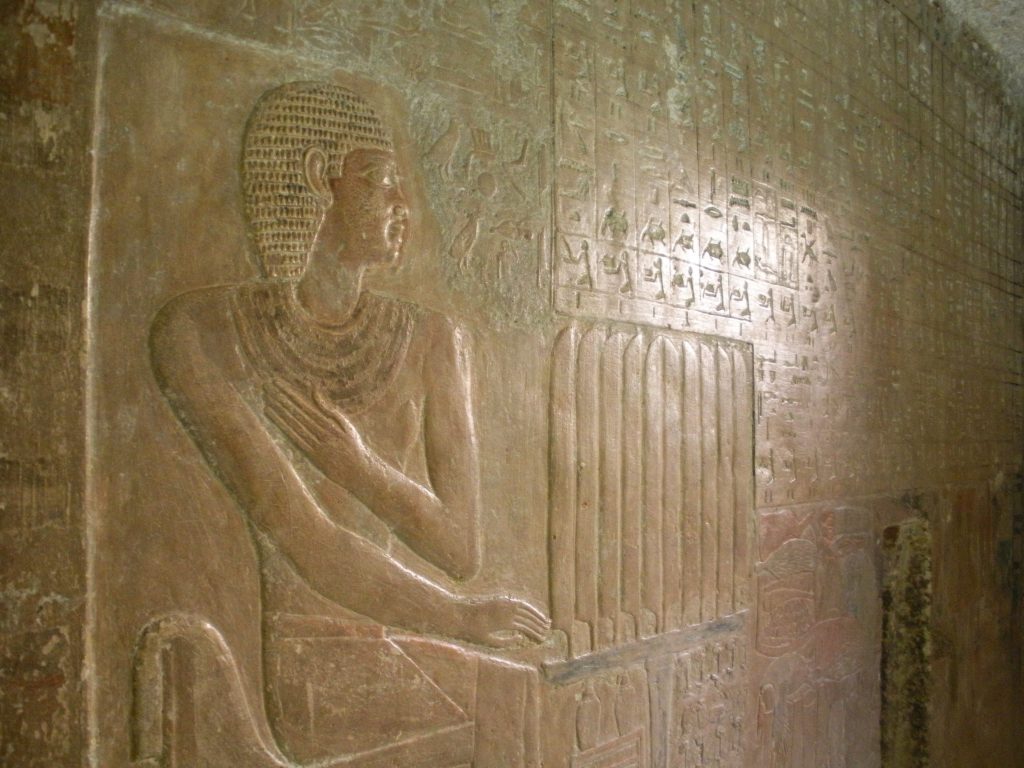
- King’s Chamber
This is located inside the pyramid, and is one of the three main chambers, together with the Queen’s Chamber and the House Underground.
This House is a rectangular slab of granite, with walls formed by five rows of stone and flat roofs, without decoration, contains a red granite sarcophagus empty, with no inscriptions. Its dimensions are: 10.481 meters long, 5.235 meters wide and 5.858 meters high.
The roof is composed of nine huge granite blocks that weigh about 400 tons and hurry away with five compartments of support, topped by a pointed roof.
This chamber is reached by a descending passage that connects the end with the Grand Gallery and the Underground Chamber.
In the north wall of the King’s Chamber there is a small aperture telescope that serves as the “Indestructible”, stars we know today as Circumpolar, ensuring the journey to eternity for their king and to all who helped in building the pyramid, according to the beliefs and knowledge of Hemiunu, chief architect of the pyramid and a cousin of Pharaoh.
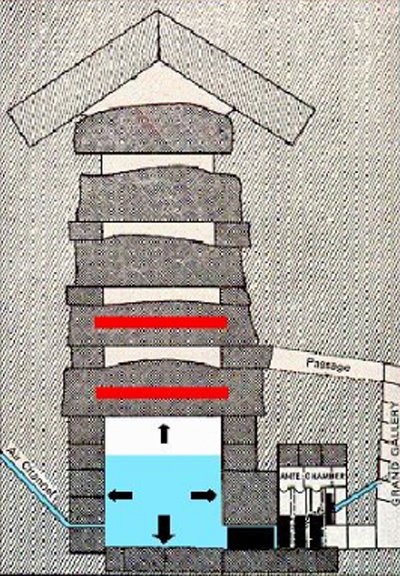
- Discharge Cameras
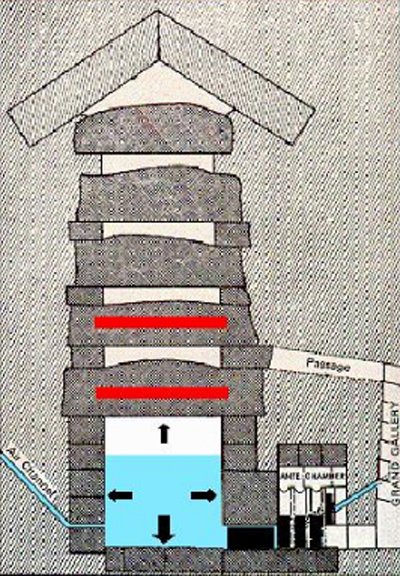
There are five and are above the King’s Chamber.
The slabs of the first, serve as a roof to the royal coffers therefore has the same surface, but with a height of 1.20 meters. On top of this camera are the other four.
The function of these cameras is to relieve the King’s Chamber of the enormous weight above him and protect it in case of earthquake. His tiles were planned with the general structure of the pyramid and have fulfilled their mission, as some of them probably have been opened because of a quake.
- Queen’s Chamber
This camera is so named even though there was never any queen is buried inside and the same characteristics as the King’s Chamber, communicating with the bottom of the Grand Gallery through a horizontal access. It is located in the center of north-south axis of the pyramid, is domed, without decoration and rectangular, 5.65 m long by 5.23 wide with a height of 4.17 and 6.30 mts.
- Underground House
It is believed that the underground chamber or “House of Chaos” more than 35 meters below the plateau level, was designed to house the deceased pharaoh but was subsequently abandoned the idea.
- The Lobby and House of Reeds
The House of Reeds, which is at the end of the Grand Gallery, was built and equipped with mechanisms that serve to prevent access to the King’s Chamber, next to it.
The three slides carved into the side walls, four vertical slots on the south wall and a few other details suggest that this camera was secured with three slabs of stone that were left to slide from above through a system of ropes.
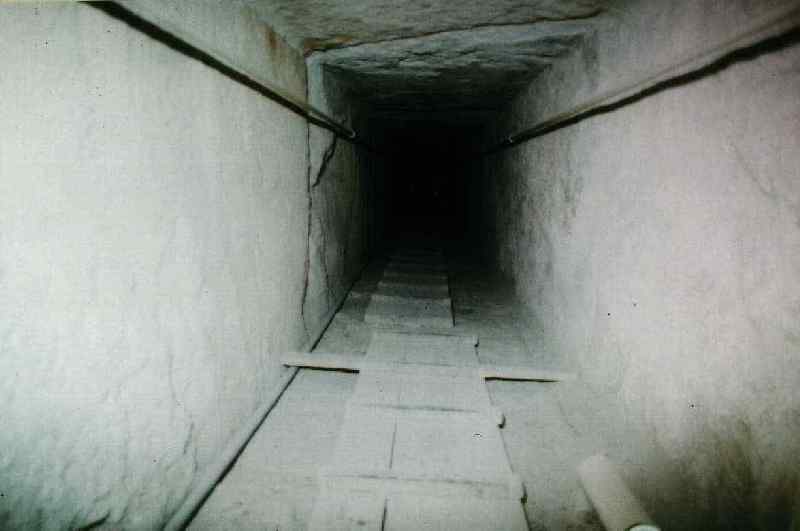
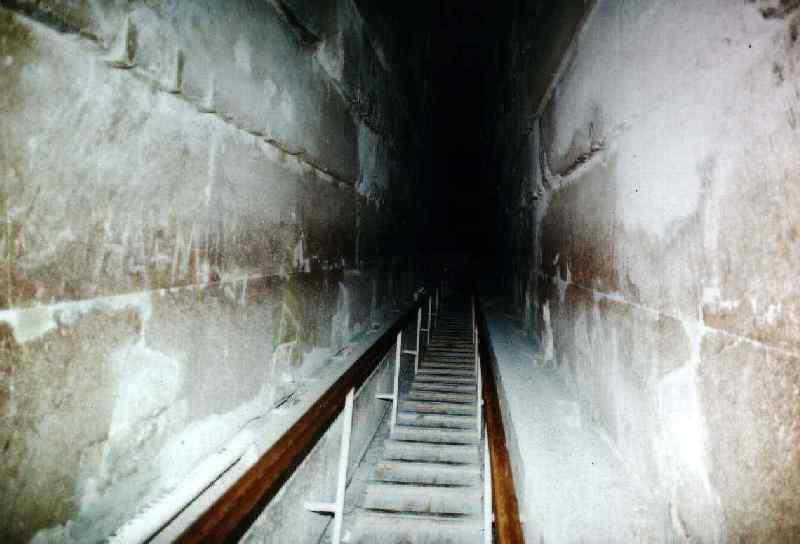
Great Gallery
The Grand Gallery is a great passage upward of about 47 meters long and eight meters high. The walls are flat to a height of two meters and from there are closing dome forming a false proxy for the courses so that the roof consists of 40 slabs overlapping like shingles have only 1 meter wide, while the soil is 2 meters.
Structure
The architects who designed the Great Pyramid, they chose a rocky elevation superstructure to withstand the heavy weight of the finished pyramid.
Its volume is approximately 2.6 million m³, and their average weight is calculated using the density is 6.5 million tonnes.
It is a pyramidal structure with 230 feet on each side and original height of 146 m made of stone step and then coated with polished stone that made it a pyramid straight and shaped ramp to the summit, at an angle of 51 º 50 ’35 ”
Construction system
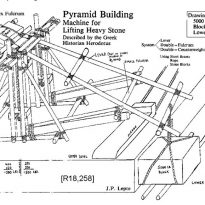
Nobody knows for sure the system was used to build the Egyptian pyramids as though several theories offer possible answers to how they moved the stone blocks, it remains to address the technical issues involving the placement and elevation of such stones, and the accuracy in placement, measurements and calculations. This construction has been attributed to aliens, Atlanteans, Egyptians before Cheops, or other cultures or civilizations unknown.
- Herodotus
Herodotus was the first to refer to their method of construction when visited 2000 years after it was built and offers the only historical account that are available.
States in regard to the construction of the monument of Cheops:
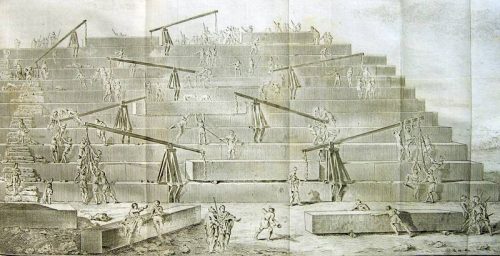
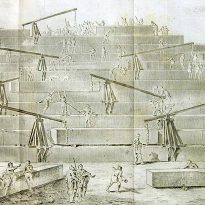
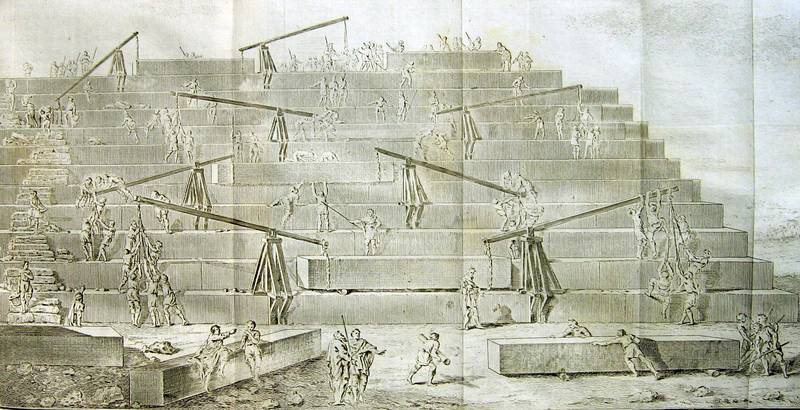
“This pyramid was built in the following way: one placed at the beginning a series of steps that some call crossai and other bomides.
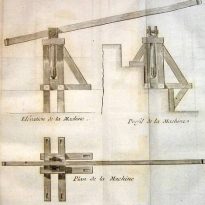
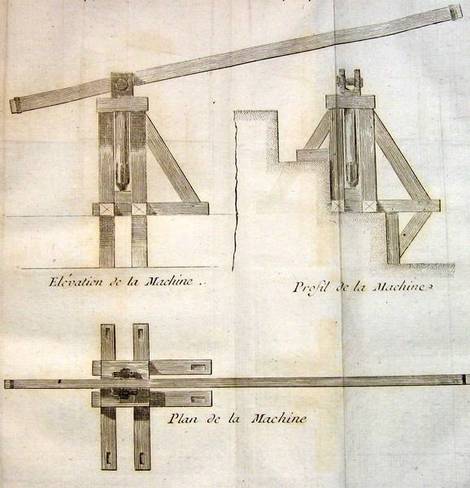
After having given to start, this first way, we proceeded to climb the remaining stones, by machines built with short pieces of wood, rose from the floor of the first platform, where the stone had arrived there, was placed in another machine installed on the first platform and passed to another crane, having as many machines as platforms. Or maybe he just had a machine, easy to transport, which moved from one floor to another, after removing the stone, indicate the two procedures, according to the two versions we have heard.
The first thing I did was to reach the apex of the pyramid, then went to the parties that were immediately below, and finally got the last touch to the floors near the ground and at the foot of the building. ”
To date no evidence has been provided to support the statements of Herodotus as a whole.
System ramps
In recent years the theory has seemed to take hold of the ramps, auque without agreeing on what kind of ramp
- Ramps envelopes
Ramps envelopes, refer to the spiral that went up on the rows of stones already placed. Those who have studied this system further consider it very difficult and contraindications for large volumetric masses used, that as they approached the summit had a much smaller space to move while the scaffolding that were mounting for a ramp capable of supporting such weight fully cover the faces of the pyramids hindering their alignment and orientation, which was perfect.
- Internal Ramp
Starting from the middle of one side, the ramp would extend into the inner core of the pyramid, leaving hollow traversed by a corridor and homeless. As they expand the number of courses of the building, increase the length of the ramp, almost to the opposite face. Arrived there, he would fill the corridor and a new ramp ride, starting on the outside, penetrate back into the interior of the pyramid to face not, repeat the process each time at higher altitudes. In the later stages should use booster side ramps and stairs.
- Ramp perpendicular

This is the traditional ramp take the stones from the quarry and would rise as the pyramid grew allowing easy placement of the last courses but has the disadvantage of the large amount of material needed to build it.
The French architect Jean-Pierre Houdin explained in April 2007 the theory, that the stones of the Great Pyramid of Giza were transported by a traditional external ramp to a height of 45 meters. From there the blocks were uploaded by a spiral ramp, mounted inside the pyramid itself
Over the years arquiólogos and scientists, even the architects have thought of many other types of ramps in combination with systems of checks and pulleys. This method may have been based on archaeological evidence, but there is no clear evidence it was used as the unique way in the Pyramid of Cheops, so everything is in the field of theories. To date there is no way of knowing with certainty that the ancient Egyptians used methods for lifting blocks of Giza.
Materials
Even today, 4,500 years after its construction, the Great Pyramid of Cheops is one of the largest structures built by man.

- Stone Blocks
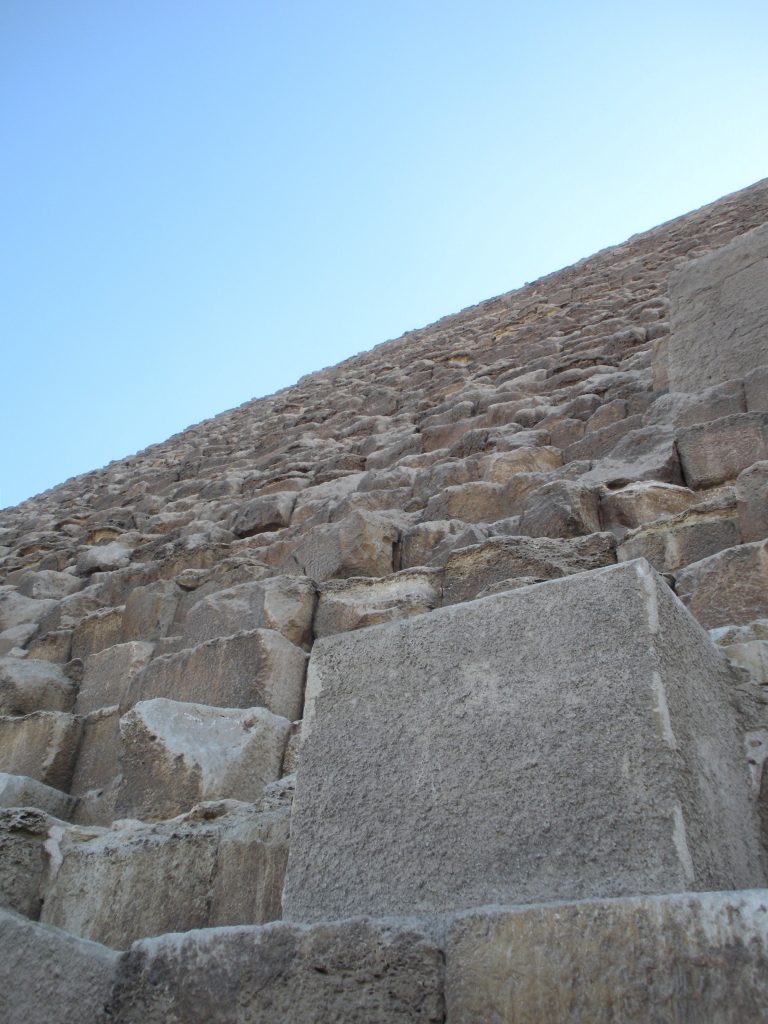
The Great Pyramid is composed of 2.3 million individual blocks of stone about each of them with a weight between 2 and 60 tons, a fact which makes it an architectural triumph and one of the Seven Wonders of the World.
- Limestone
At the time of Pharaoh was covered by 25,000 polished limestone blocks, also weighed several tons, but the coating came off as a result of strong earthquakes in the region. Later the Turks dismantled and fragmented in order to transport these blocks and to build various buildings in Cairo.
The King’s Chamber is completely built of granite from Aswan.
Video