Center for Ecological Activities Sluňákov

Introduction
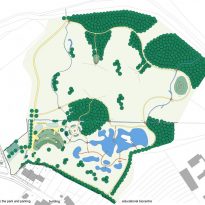
The Center for Ecological Activities Sluňákov was designed as part of the project long term Sluňákov, whose facilities started to build in an area of 15 hectares located in the city of Olomouc, are intended for ecological activities as well as biocenter education, explaining to the public issues on the environment and its processes and deepening environmental awareness.
Its facilities are taught seminars for professionals on environmental issues and education and awareness about school groups about the value of conserving the environment. The building has been designed so that energy ahorrardo work also constitutes an example of green building and sustainable development.
Situation
It is located in the northwest of Olomouc, in the valley of the Morava River, near the village Horka nad Moravou in the Czech Republic and serves as an information center and gateway to the protected nature reserve Litovelské Pomoravi. The main objective of the park is to protect a valuable set of river ecosystem complexes composed of riverine forests, wet meadows and marshes.
Concept
Architectural Design

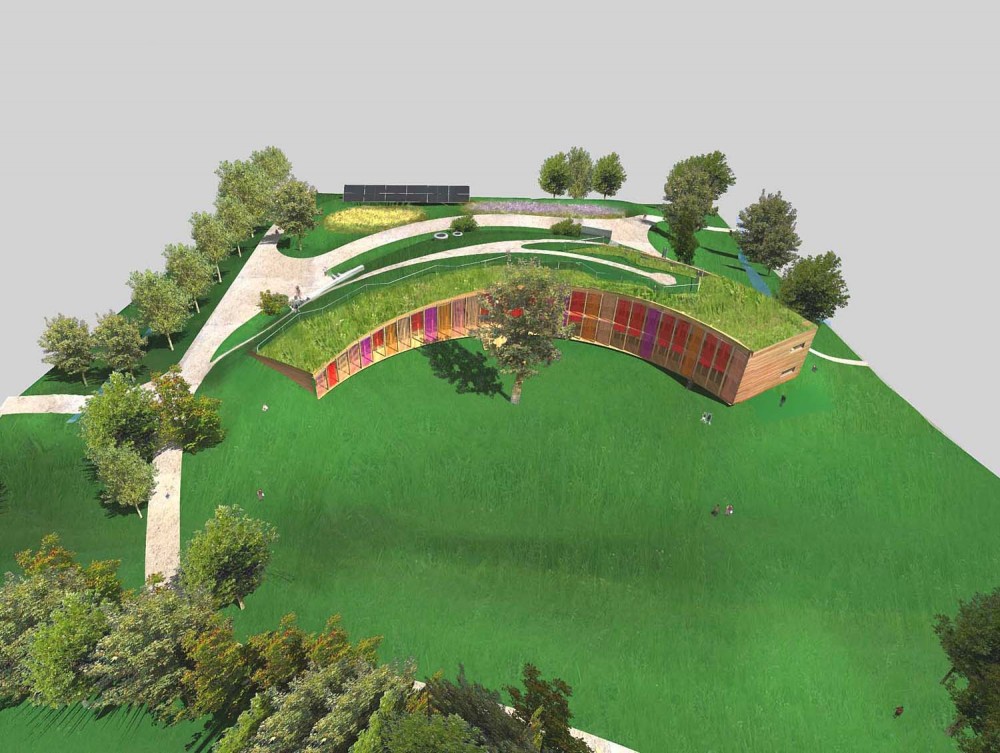
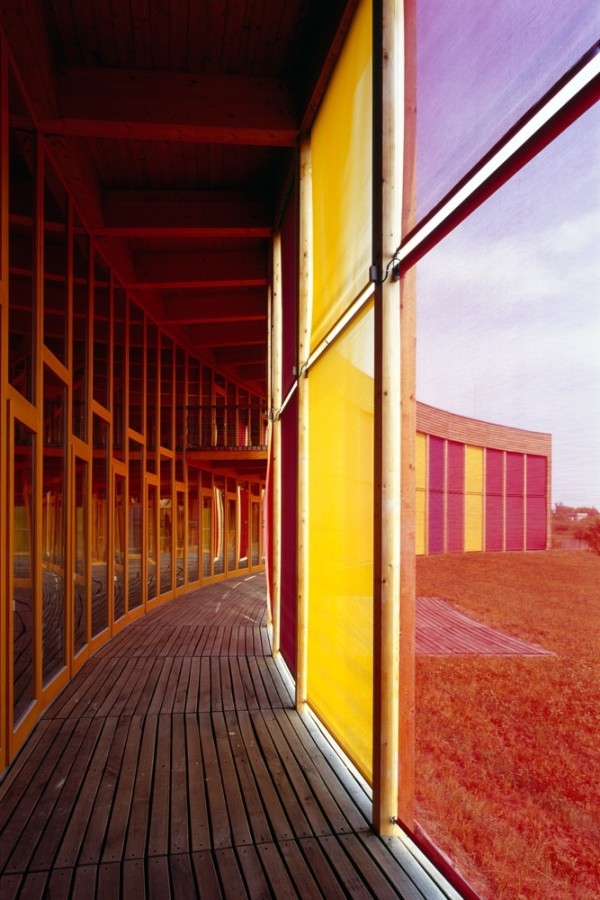
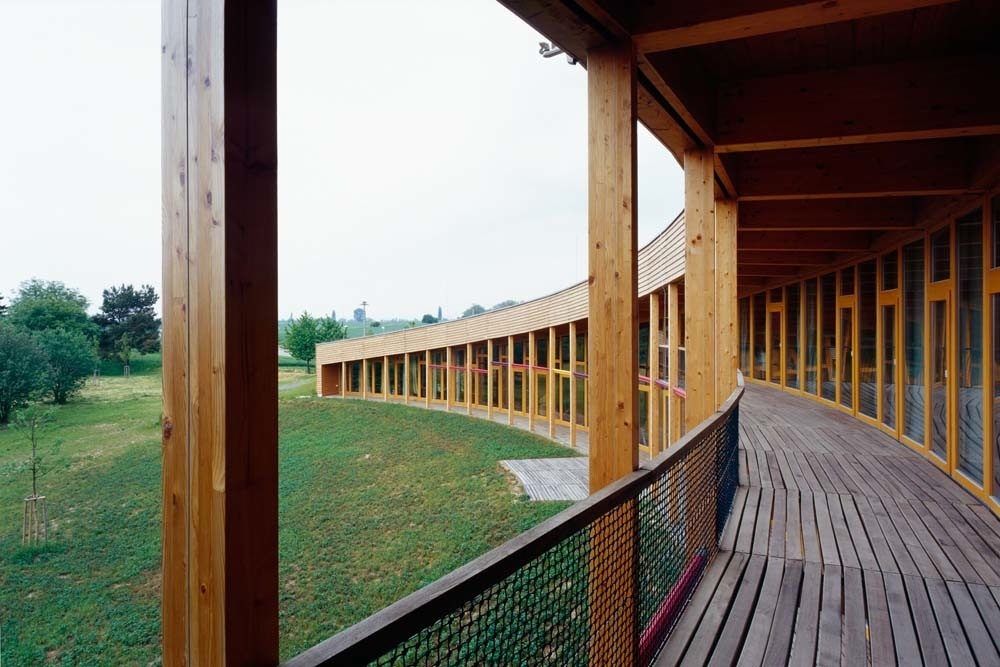
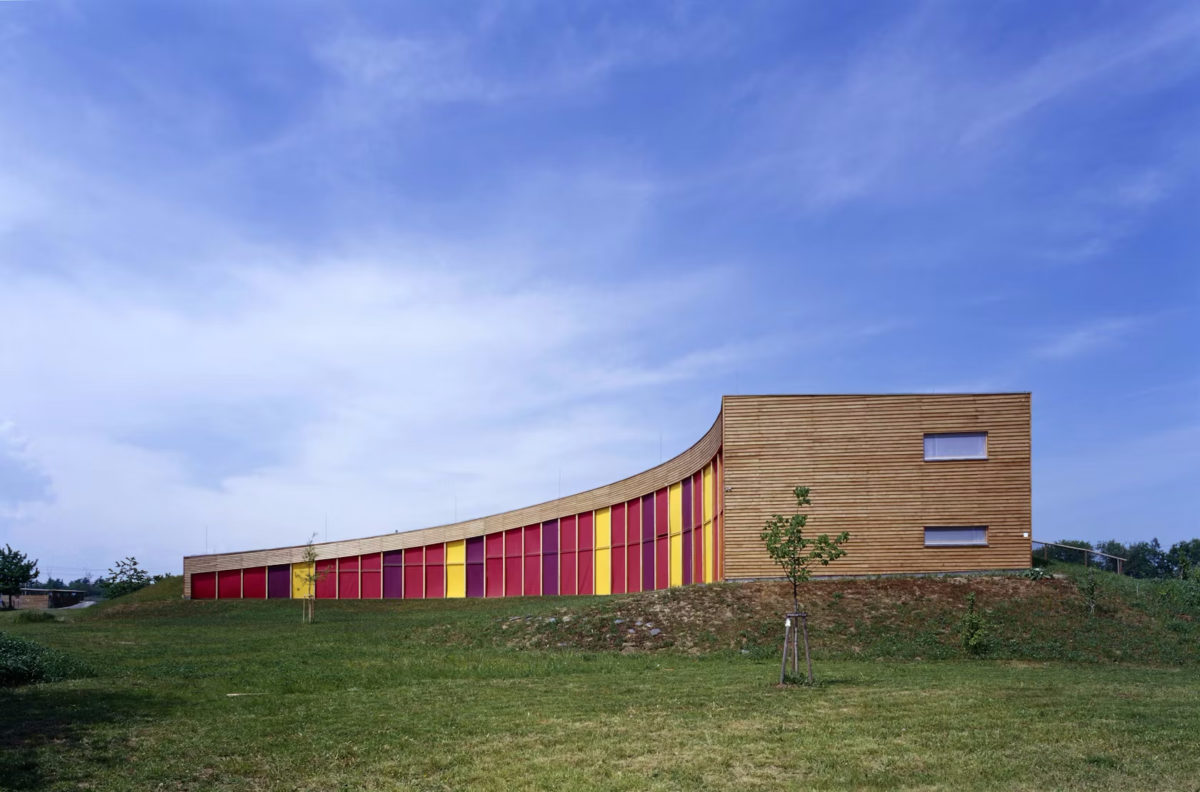
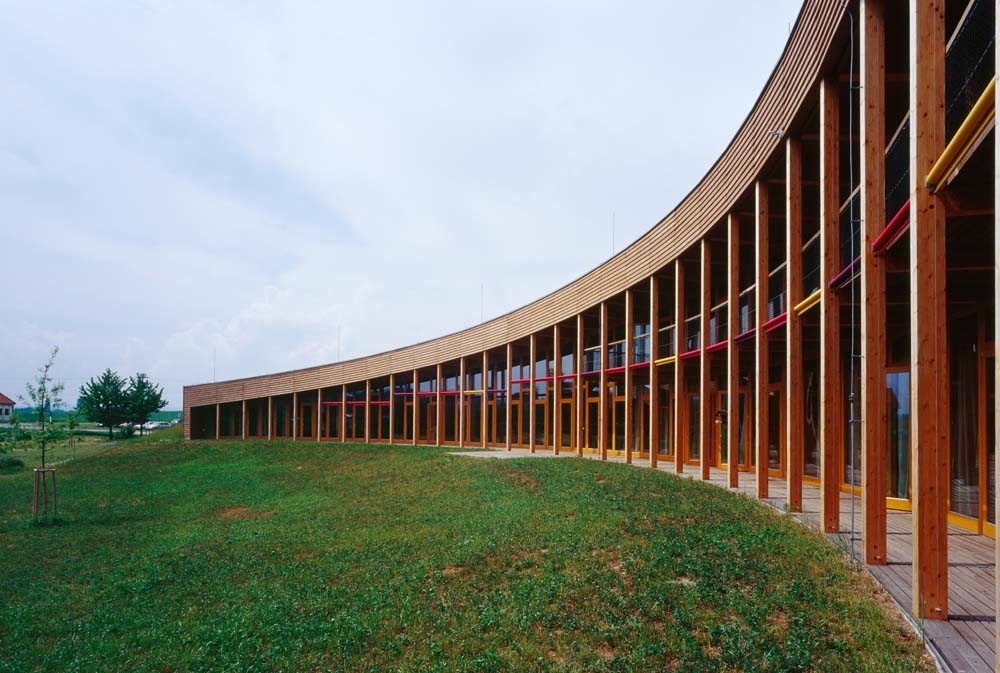
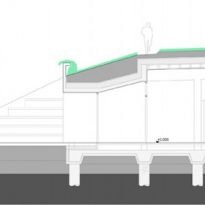
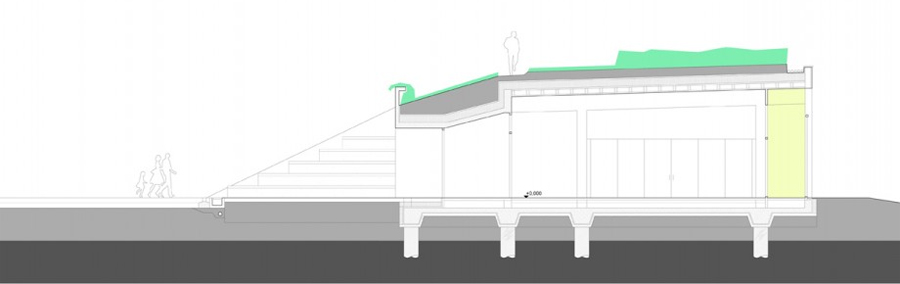
The building was designed as a living terrestrial wave curve and merges seamlessly with the surrounding ground and symmetrically follows the north-south axis. The architectural design faces south through a glass facade protected by movable solar fins. On the north side there are two entries embedded in the ground.
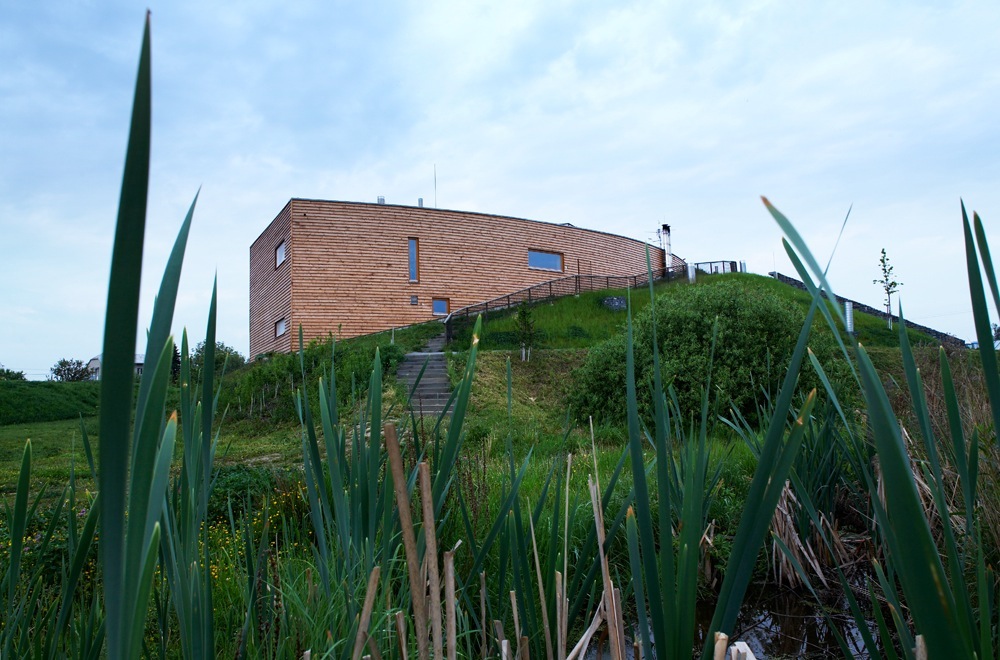
The east side of the building rises, symbolically, from ground level to allow entry of sunlight from the southwest.
The north side protected by terrain, joins smoothly to the green roof of the building, which gradually increases in height from west to east.
The unusual style of the proposed outcomes for the edification of the building derived from a process of finding new ways in ecological buildings that not only integrate with the environment, but also using solar power and take advantage of the protection offered by the ground against unfavorable weather.
The initial figure was inspired by traditional low and rustic buildings found in Hana, east of the Czech Republic. The form of solar eclipse served as inspiration for the curve of the building. The spine of the building is the hallway that runs its length and has access to all spaces.
Flexibility, which is conceived as a benefit in all green building concept, highlighted in solving the floor plan, causing it to rise to ensure it is higher than the flood level.
Spaces
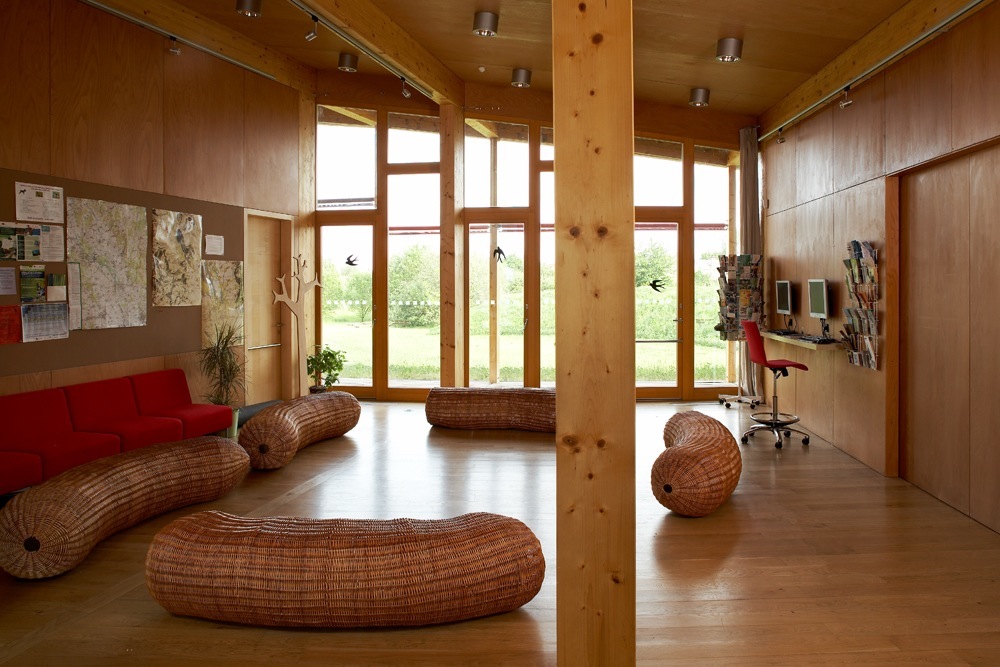
The road that leads from the main entrance on the “peak” of the building continues to the point “cusp” featuring a gazebo with a unique view of all Biocentro. The area between the building and the artificial mound in front of the south facade is used as habitable section of the garden for guests and visitors.
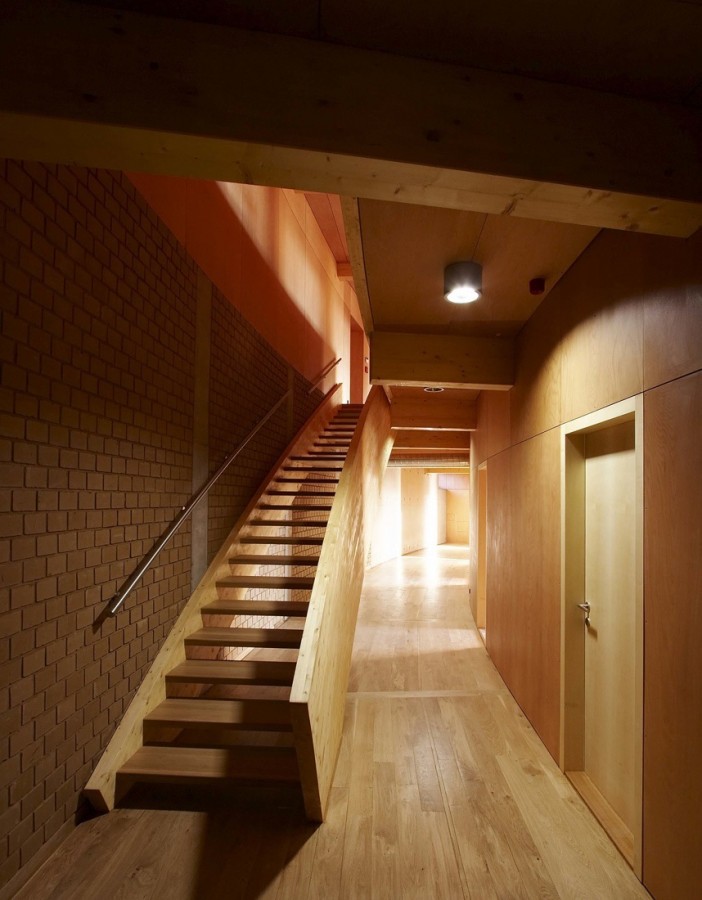
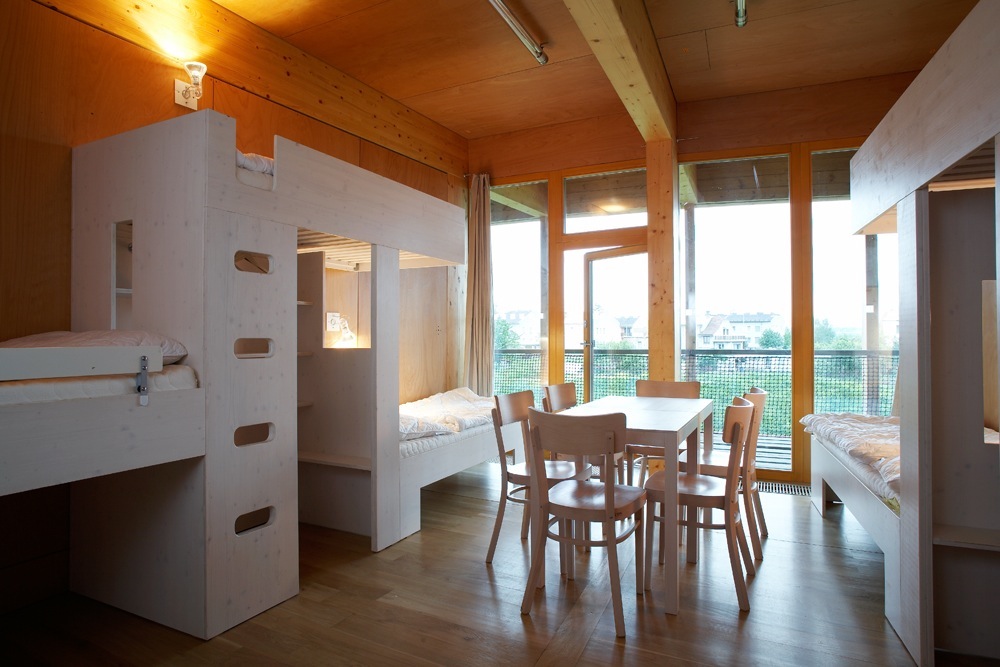
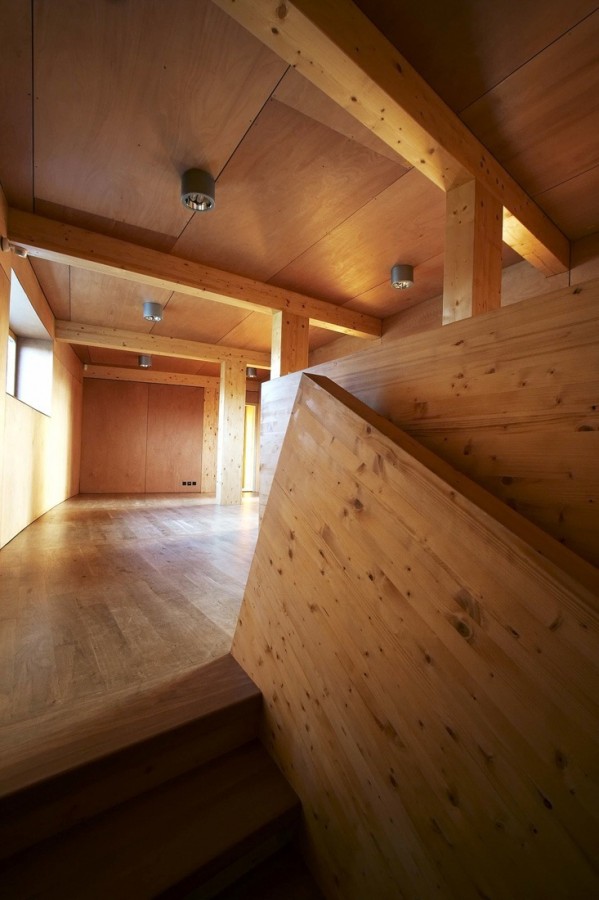
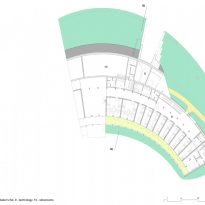
All floor rooms are accessible from the long corridor that runs through the building.
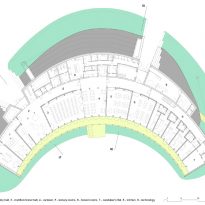
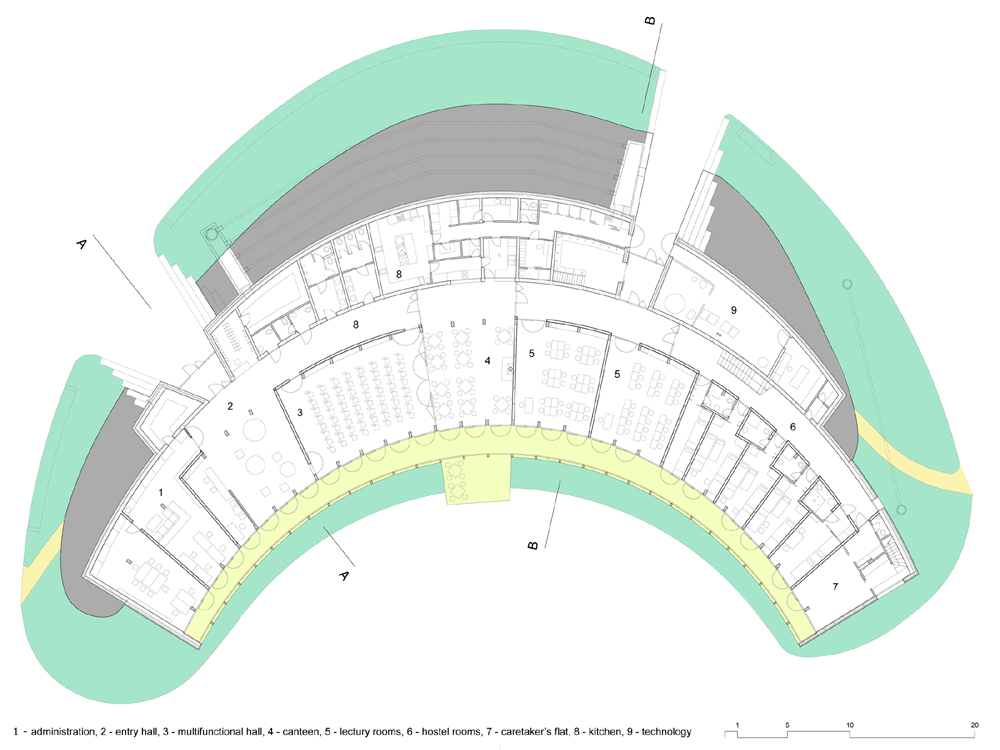
Distribution plants
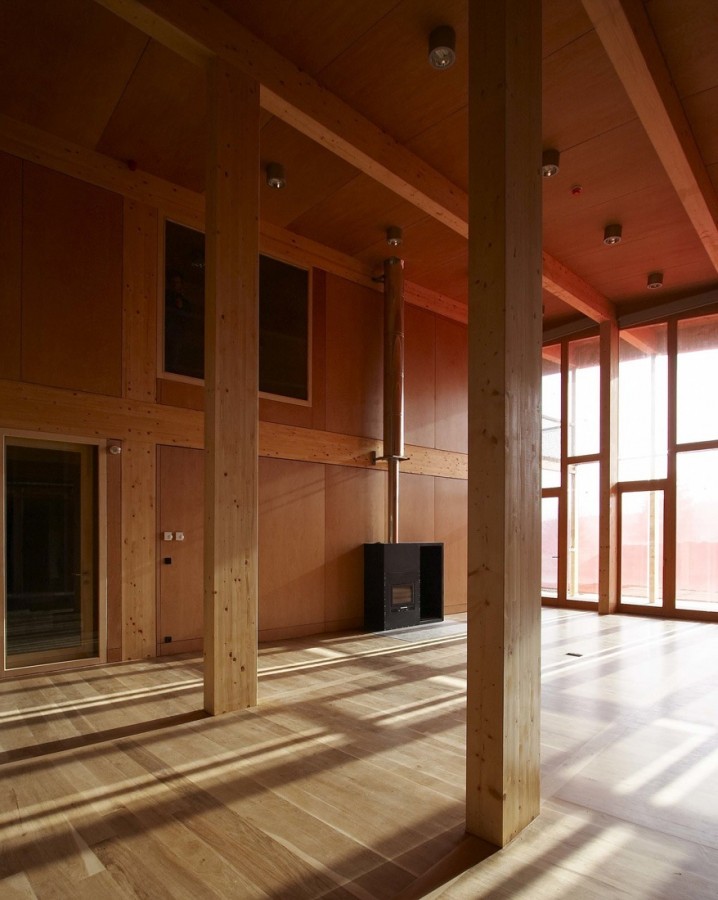
In the sunny area, south of the corridor, a residential area is located, half of the ground floor occupied by a multifunctional hall entrance, a conference room, a dining room, kitchen, reading rooms, classrooms and offices being. In the other half of the plant’s upstairs, is the area of hosting and concierge department, while on the north side of the top floor teams are located.
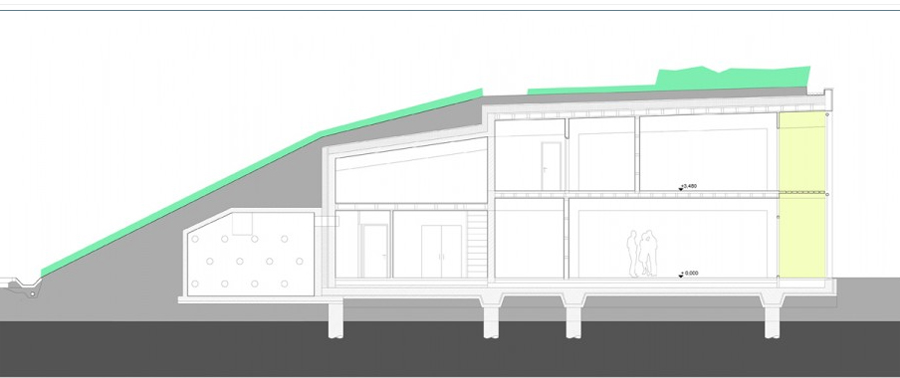
Structure
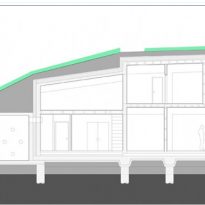
Similarly to the distribution plant, the building is divided, from the construction point of view, in two different types. The northern part was built with a reinforced concrete structure, while the southern part, which comprises the main hall, is made with a supporting structure made of wooden timber framework.
Construction systems
The building combines passive and active building systems. Liabilities in the glass facade facing south or in the natural protection of the land in the north, allowing you to save energy. Assets in the ventilation system and partial space heating and geothermal heat exchanger. All systems are also used for demonstration and educational purposes.
Materials
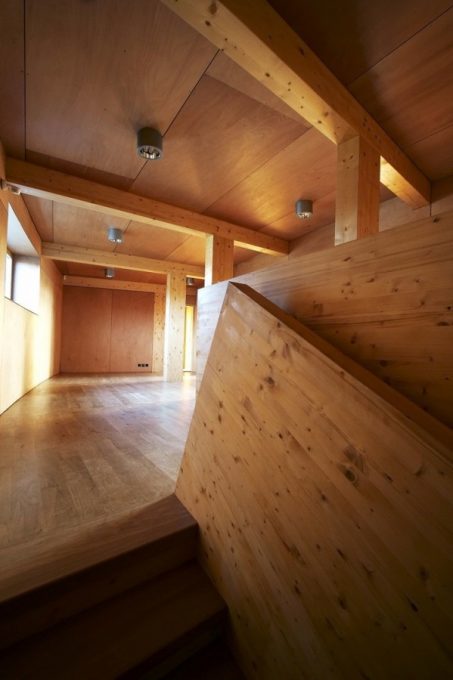

All materials used are traditional and have been chosen for their environmental compatibility. The facades are covered with wood, glass, concrete and stone masonry.
The interior finishes are made primarily of wood, glass and unfired brick walls and plaster.
For structures of the technical rooms and wet areas have been used baked bricks and concrete.
Most floors are covered with wooden planks and wetlands and engine rooms with epoxy seamless.
The whole concept of interior and exterior of the building is based on the nature and takes into account the use of the same colors taken both individually protruding surfaces and characteristics of each of the materials used in the construction of structures building.
Energy concept
Its energy concept was designed to respect the basic principles of sustainable development.
The building was divided into six separate ventilated areas. The Centre is ready to run an entire year with a four-month season heating is supplied using a combination of renewable energy, biomass and solar energy.
Ventilation with fresh air and warm heating reaches every corner of the building by conventional air circulation and heat recovered from air emissions. Geothermal heat exchangers are mainly used to provide fresh air in the summer months and are located at the rear buried.
Two boilers supplied with wood pellets are the main sources for heating and production of hot water. For the latter a system based on solar energy that covers 70% of the hot water demand and 20% of energy needed for heating was also placed.
Energy scheme
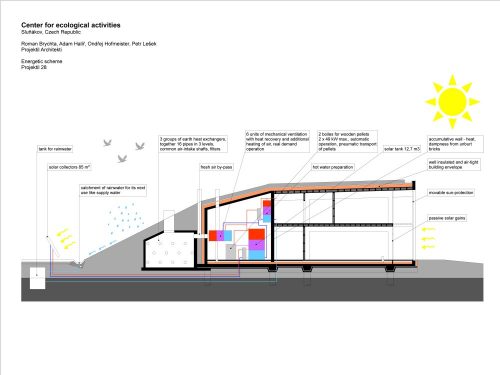
- One-tank rainwater collector
- Solar 2-manifolds 85m2
- 3-Collector water for later use
- 4-Three groups underground heat exchanger pipes 16 in 3 levels
- 5-By-pass of fresh air
- 6-Sies units mechanical ventilation with heat recovery and additional air heating. Operation according to actual demand.
- 7-Two boilers wood pellets maximum 2×49 kw, automatic operation, pneumatic pellet.
- 8-Preparation of hot water
- 9-Tank Solar 12,7m3
- 10, Brick Wall, accumulation of heat and moisture
- Airtight and insulated 11 Wrapper
- 12-screen mobile solar
- 13-gain passive heat