Boston Bank in Buenos Aires
Introduction
This work is the second intervention by the architect Tucuman César Pelli in Buenos Aires.
The Boston Bank tower completes the urban landscape of North Catalina.
The studio of the architect Mario Roberto Alvarez and Associates advised on the implementation on the ground in accordance with the Code.
Situation
It is located in the area of North Catalina. According to the rules established in the district, the buildings are prisms implanted in the ground, separated from each other. This area is not part of the traditional urban fabric of the city.
It is located near the river, the micro center and Puerto Madero.
Concept
The building stands as an entirely glazed, very simple volume that becomes a sculptural element as it rises.
It has two different fronts: one toward the city and Avenida Leandro N. Alem, and another toward the river and the Avenida Madero. Three of its faces are flat. The fourth, towards the city, has a series of retreats at various floors and slightly inclined planes. This creates a staggered facade that contrasts with the simple volumes of nearby buildings.
One element that stands out in the tower are the facades. Its form causes each side to have a different profile. The color of the glass on one side also contrasts with those used elsewhere in the building.
The fully glazed tower, in a gesture that seems to want to reach the sky, is no longer a simple prism but has become a city landmark.
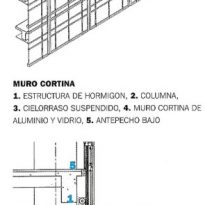
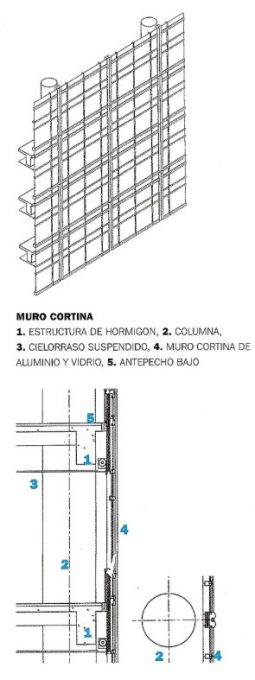
The mark of the architect is also reflected in the design of the curtain wall that covers all sides of the building.
The architect devised a plot profile of metal combined with a clear reflective glass to give the reflection of surrounding buildings, forming a tower with a dynamic image that changes depending on the reflections and the available light. The bi-directional metallic fabric is made of horizontal and vertical anodized aluminum mullions that form a regular hatch grid.
Another point of the design refers to the human scale of the building. This is reflected in the proportions of the curtain wall and also from the inside. In turn, the floors are 3.70 meters high from floor to floor which explains why the spaces are of appreciable height.
Energy saving
The air conditioning system has central union and takes in air at the 16th floor, where the machinery is located. In the balcony of that level, the first withdrawal from the south facade, is located the entry of air free from any pollution caused by traffic. In addition, a cycle-system serves to avoid a needless expenditure of energy when weather permits.