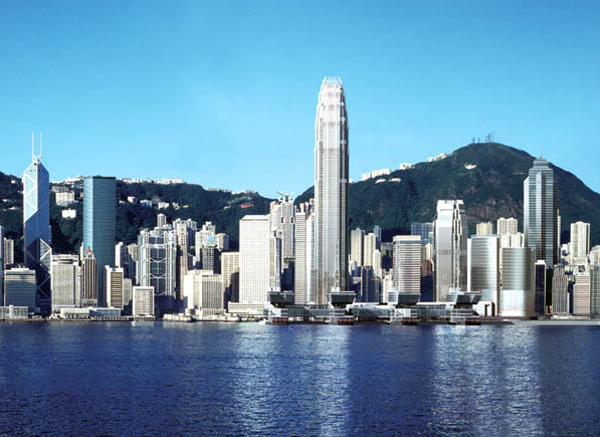
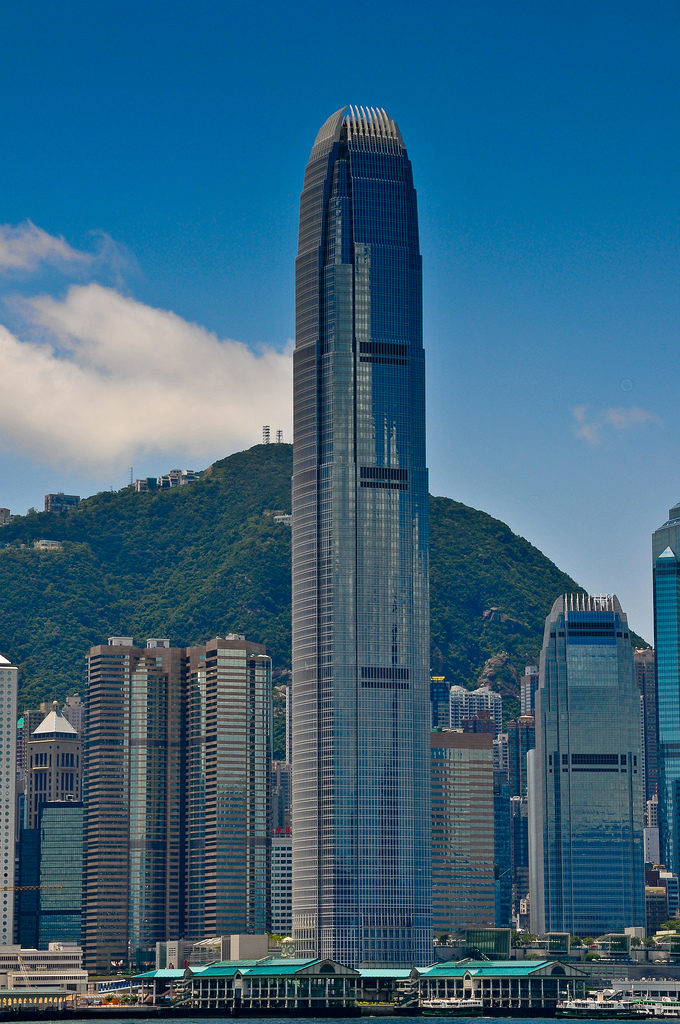
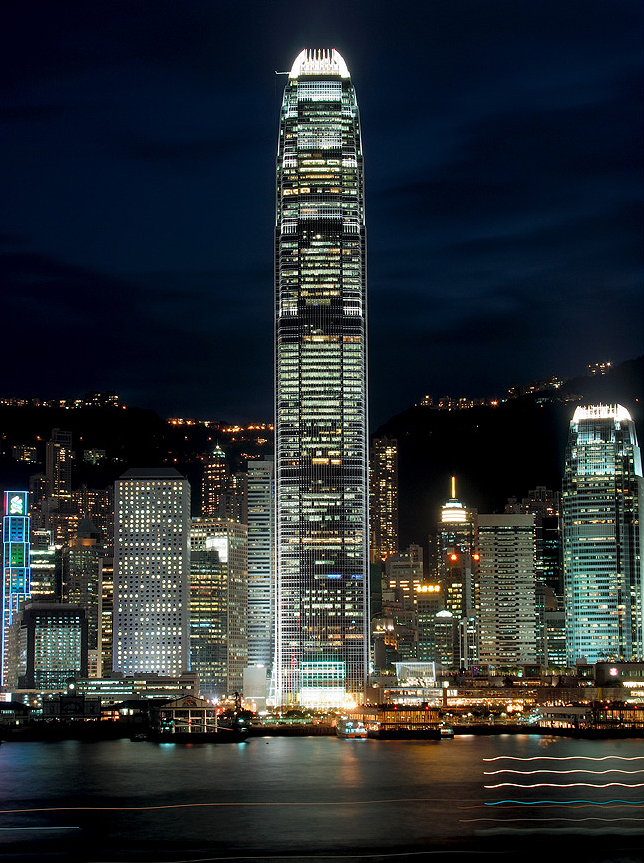
Two International Finance Centre Hong Kong

Introduction
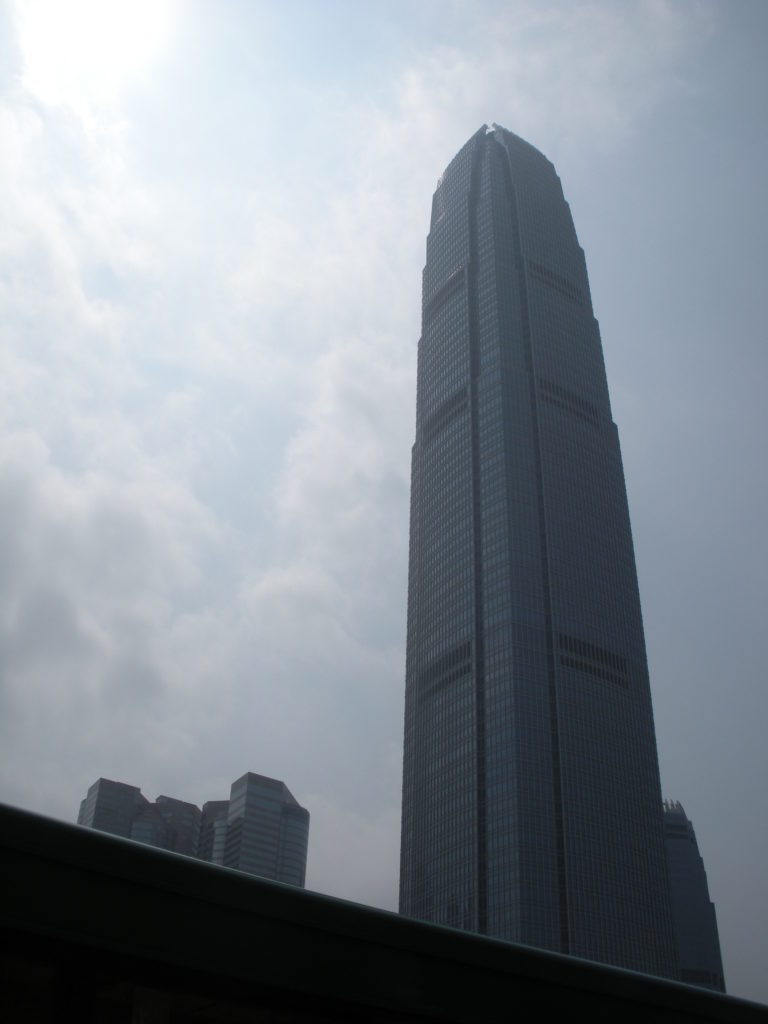
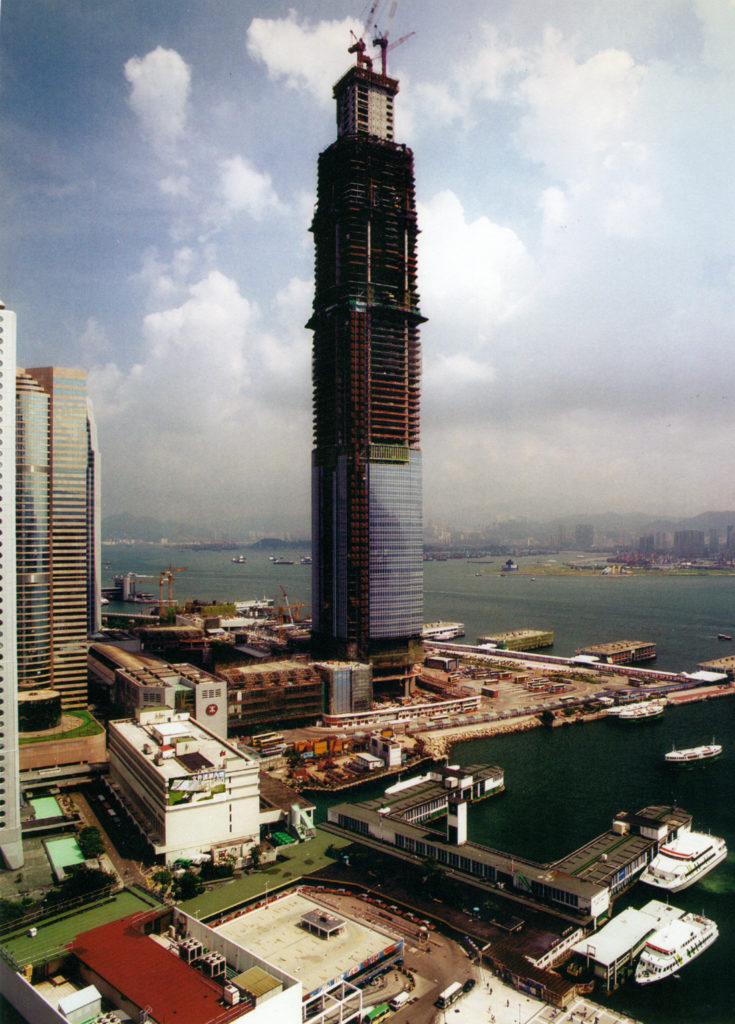
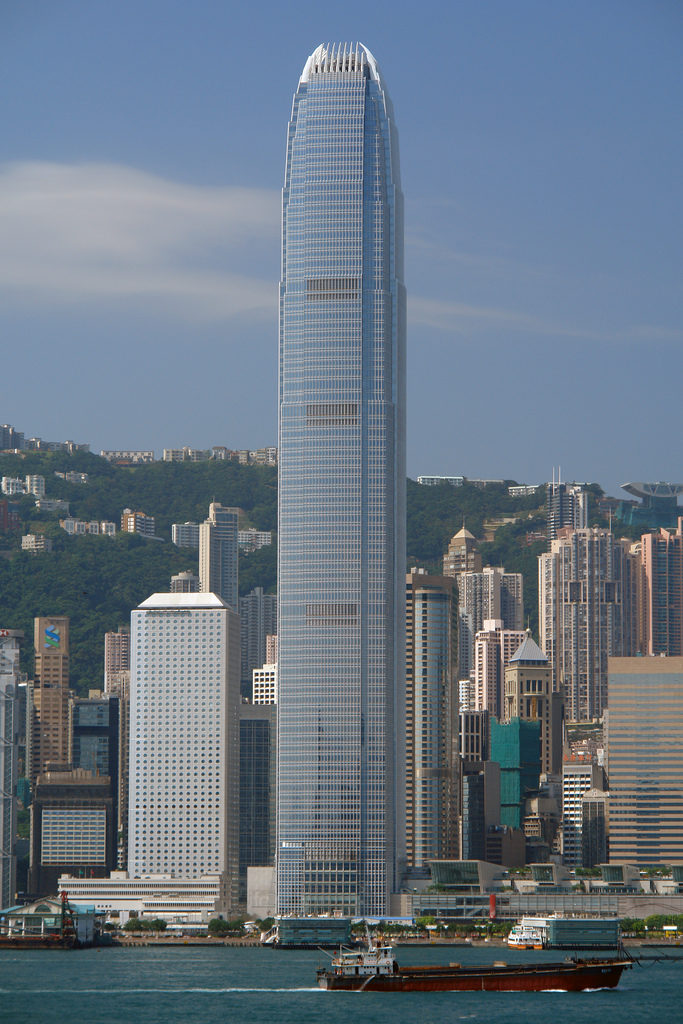
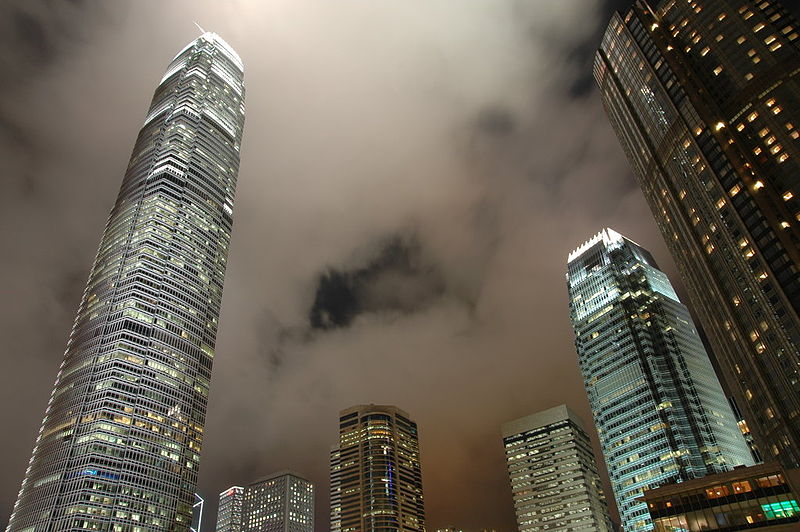
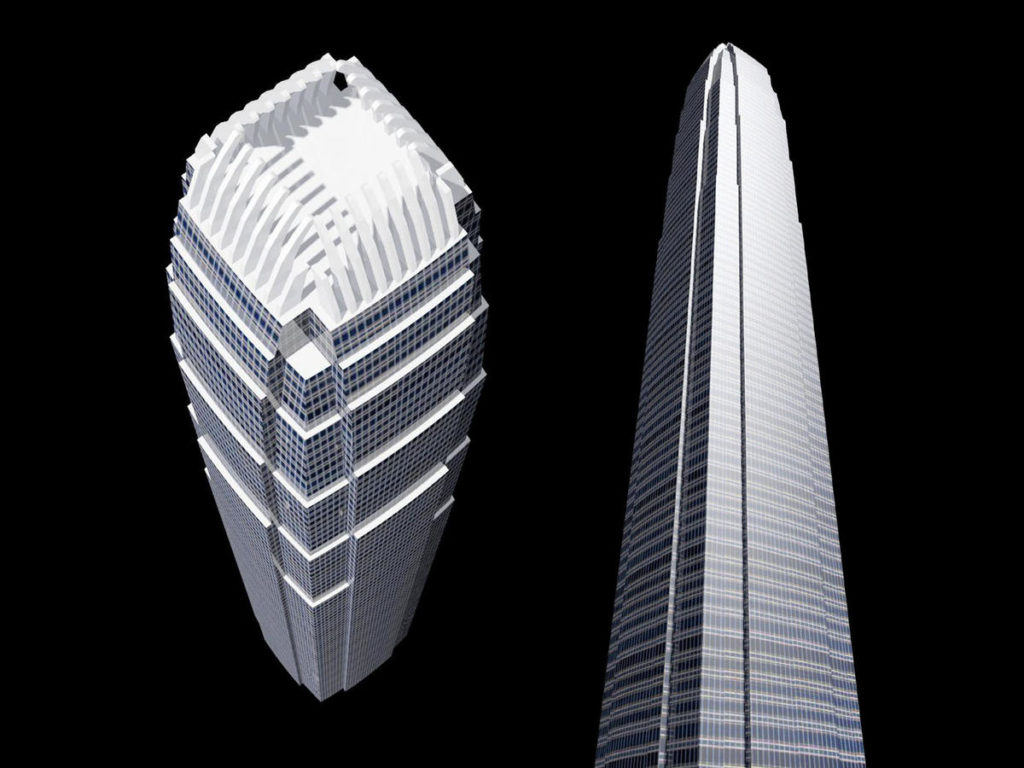
This free, attenuated and extremely slender tower is developed with 88 floors above street level whose height is increased when compared to the surrounding buildings, especially with his counterpart from 38 plants. At night, the lights frozen Hong Kong, by order of airport authorities not to confuse pilots landing at the nearest airport, favor the building model that uses “washed walls” with a retro style, recalling the futuristic designs of cities cartoonist Hugh Ferriss.
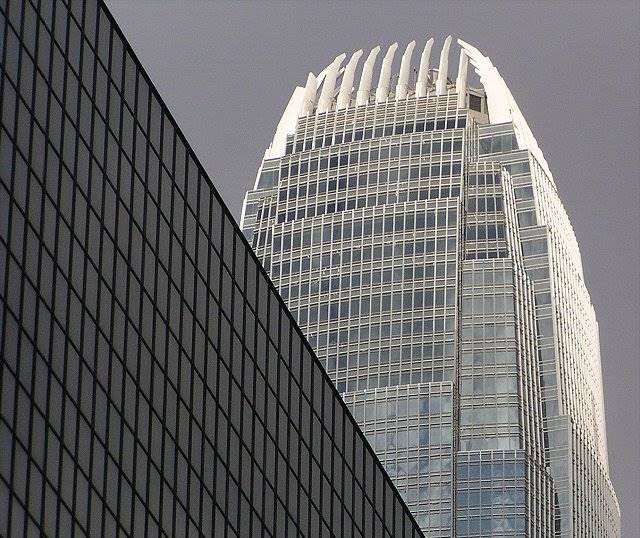
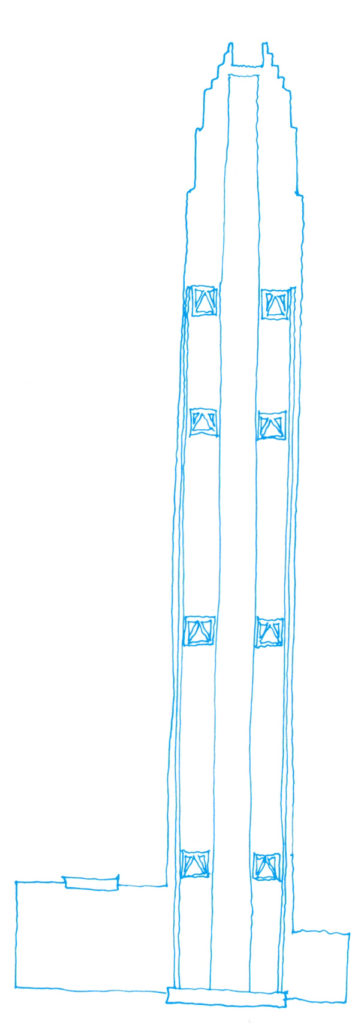
The articulating surface of the curtain facade design reinforces the verticality, ground walls are convex and center section goes a step further in some areas, giving the tower a rounded appearance, a beveled appearance.
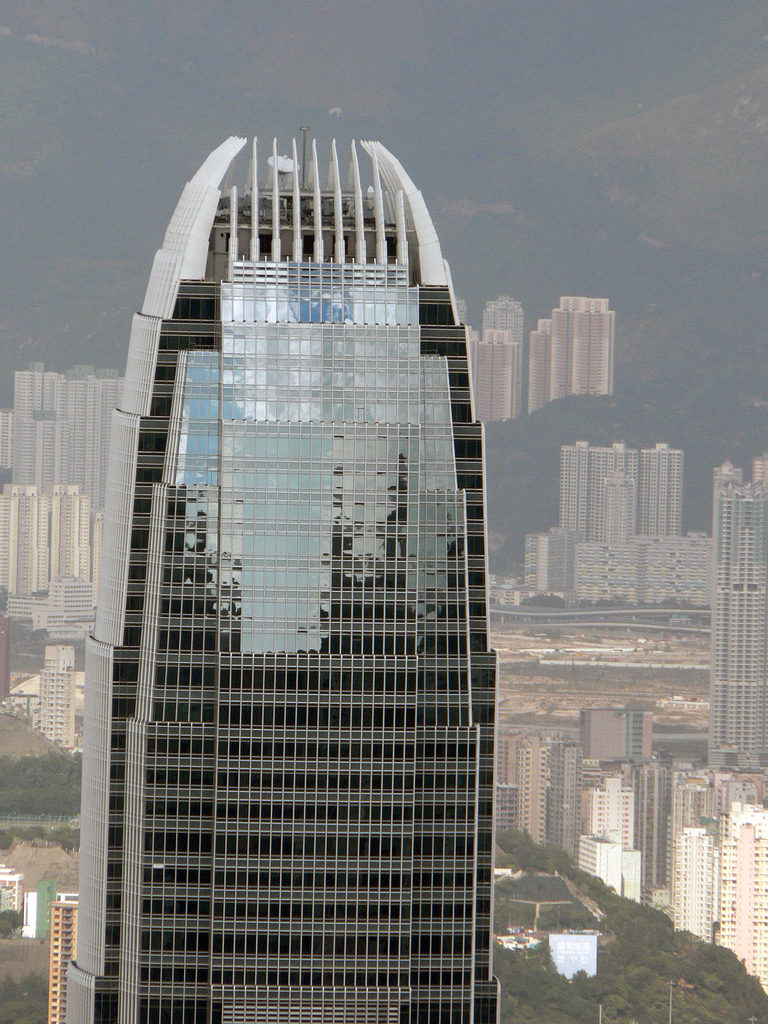
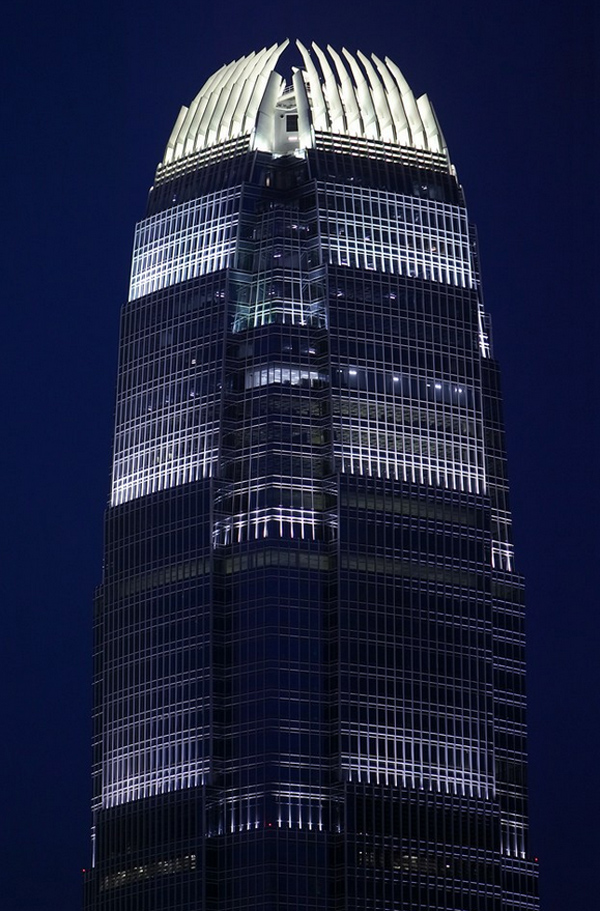
The uprights of the windows are shaped support members, drawing sharp lines from the base to the crown. The tower culminates with a sculptural crown, with an open skyward at the top design, dematerializing the building form. When night lights, the crown of the tower is visible from miles away, a welcome at the entrance of the bay.
Situation
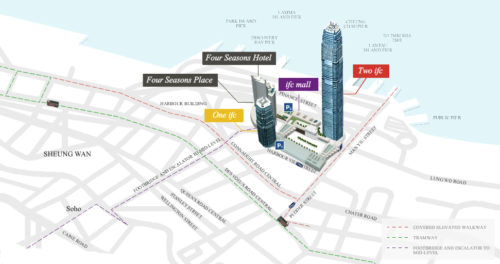
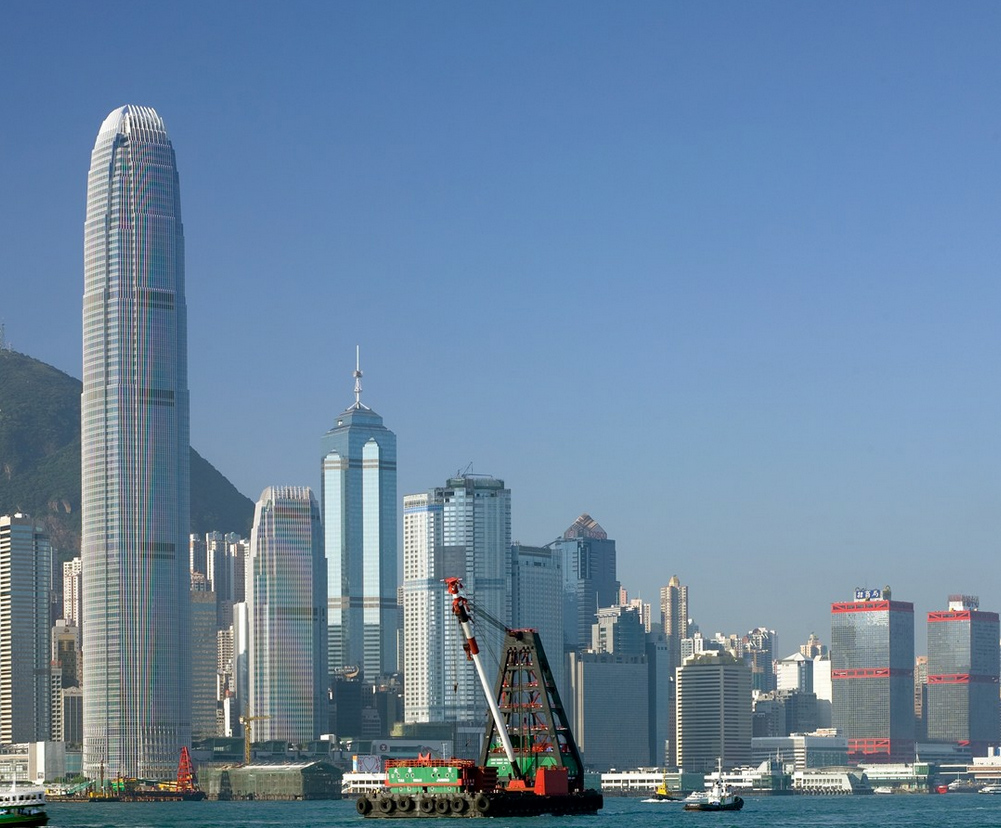
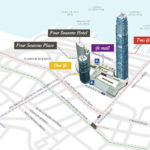
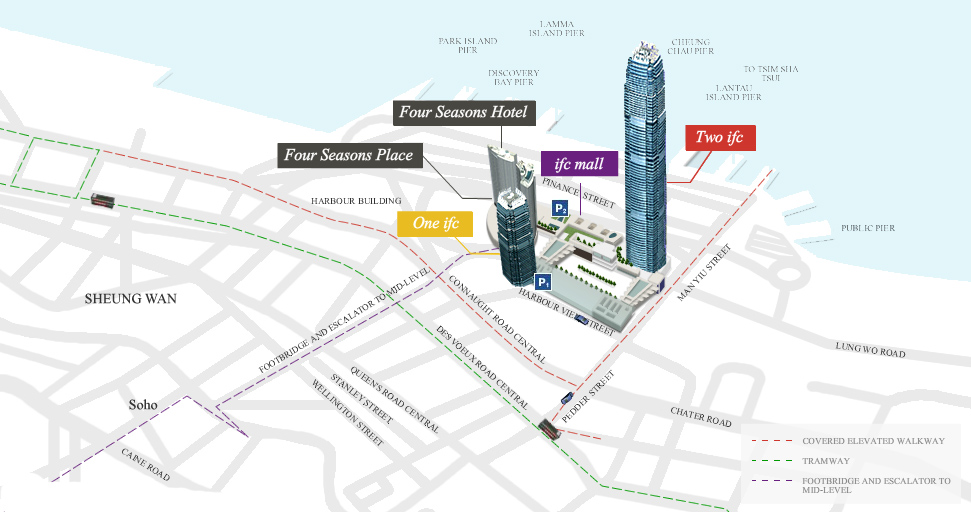
This tower, also known as IFC II was raised on the island of Hong Kong, China, by the team of architect César Pelli, in collaboration with Rocco Design.
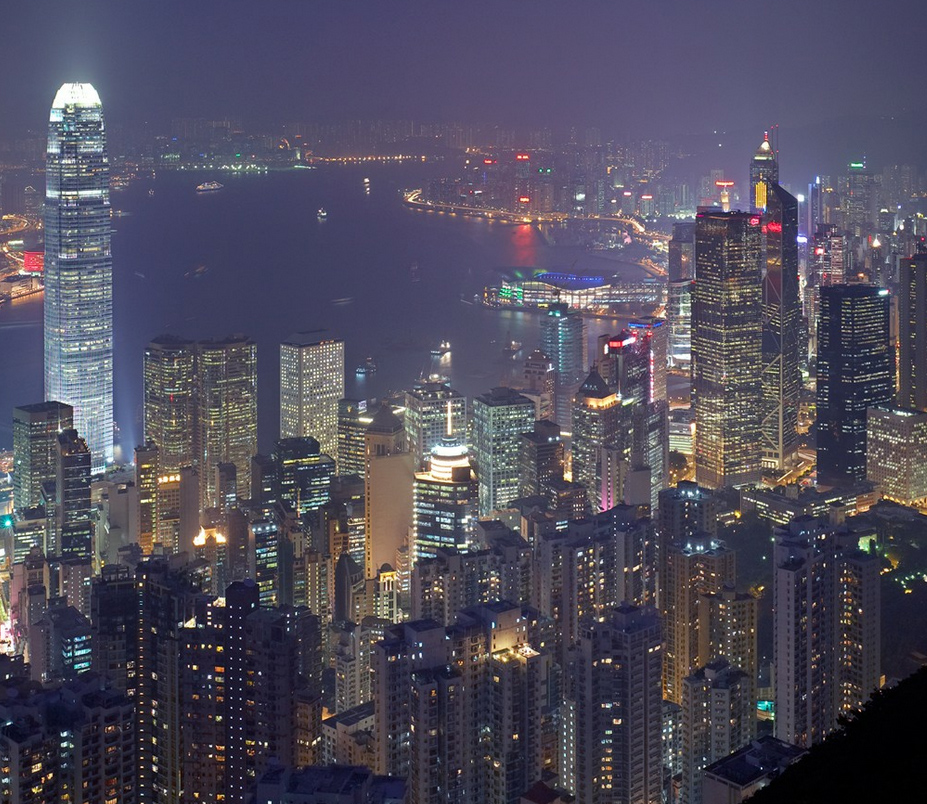
The soil used and reclaimed from the sea, belongs to Puerto Victoria, was downgraded and offers backdrop Victoria Peak and the Central District. The height of the top of the mountain known as Peak and the IFC II are the same. This new area of the city has a transport interchange equipped airport terminal, bus and rail ferry, which transports that connect the island with Kowloon Hong Kong and other cities of the continent.
Concept
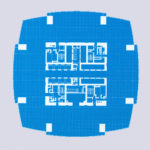
Development of Two International Financial Center, is a complex matrix of transport, public spaces and commercial use, and itself a mini city within the city.
The building has a clear and memorable, a large obelisk in the citywide presence. With its nice proportions, tapered shape tapers as it rises, expressing a vertical movement. The International Finance Center captures the spirit of Hong Kong, secure and in harmony with the natural beauty of its surroundings.
Spaces
The building was built to be used by finacieras institutions such as the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) on floors 55-56, purchased by the HKMA jointly with plants 77-88 for $ 480 million in 2001.
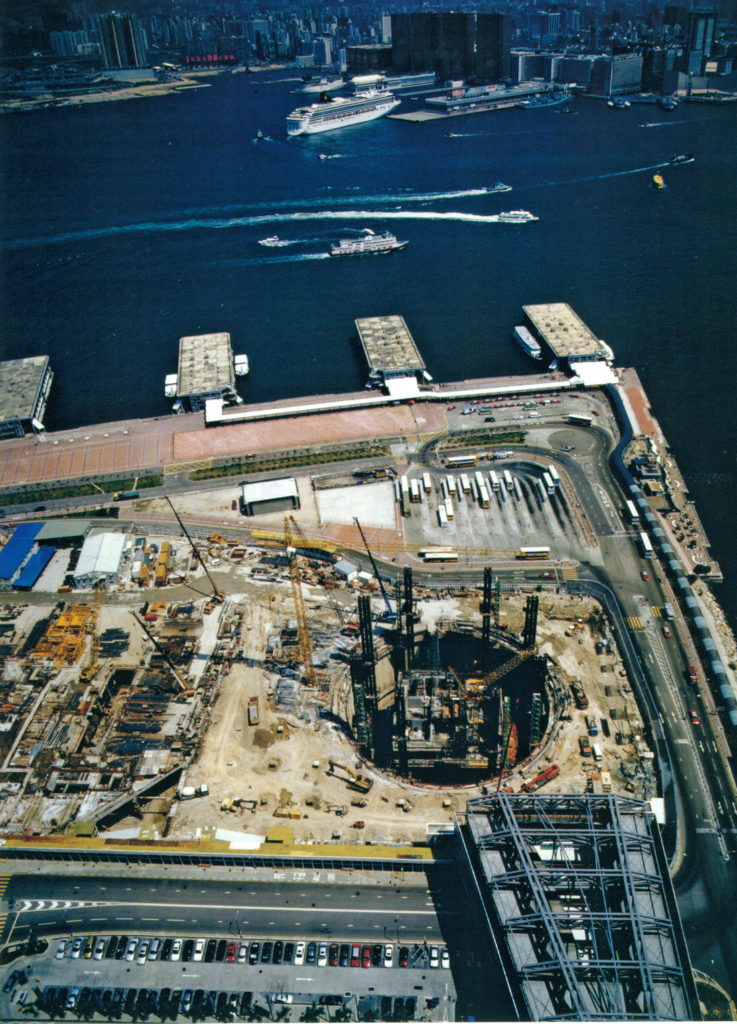
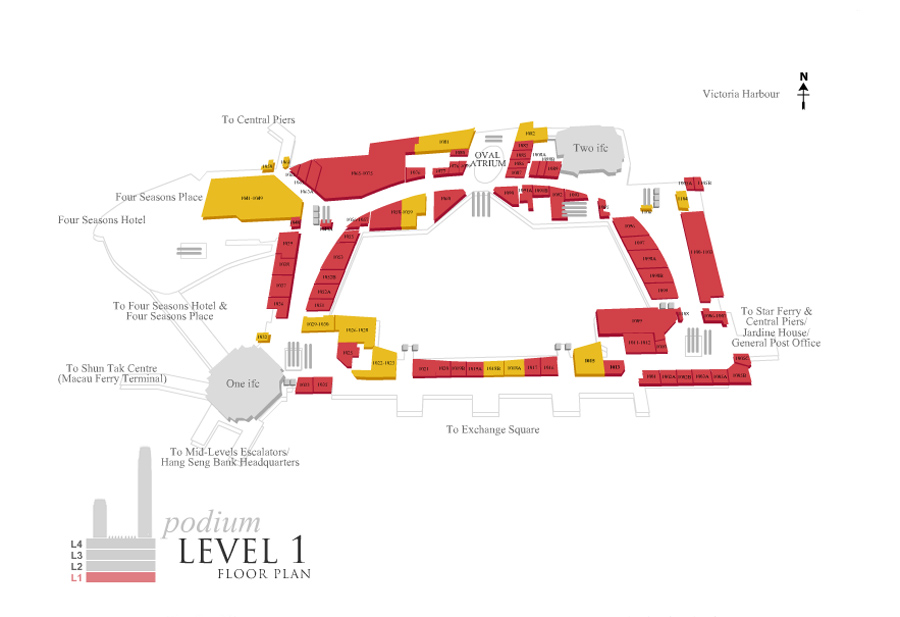
The IFC consists of hotels, offices, parking with 750 spaces, a commercial podium four floors and a public garden on the terrace. The interchange station for transport is also an important part of the Centre, connecting with the new bus terminals, the new dock for the ferry, development for land vehicular traffic and connecting with a large network of elevated pedestrian walkways.
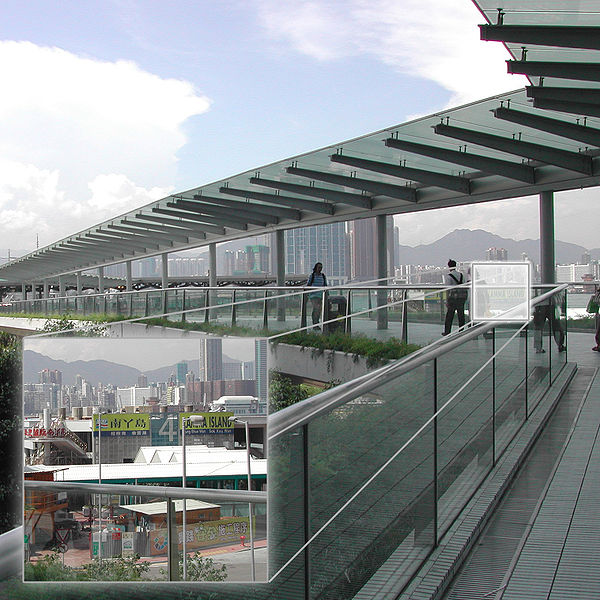
Exchange station
The concept for the design of the station was creating transparent and fluid spaces that maximize natural light, with a clear spatial configuration to guide the movement of the mass of passengers. This concept is exemplified in the entrance hall, where the tremendous height of four levels creates a space lit by a window that descends to his full height, with skylights and clerestory.
A series of large holes are located immediately adjacent to the glass wall and allow natural light to penetrate the basement.
Auxiliary spaces
In and structural components of the core spaces created every 20 plants their machinery and firefighting placed shelters, elevators and stairs.
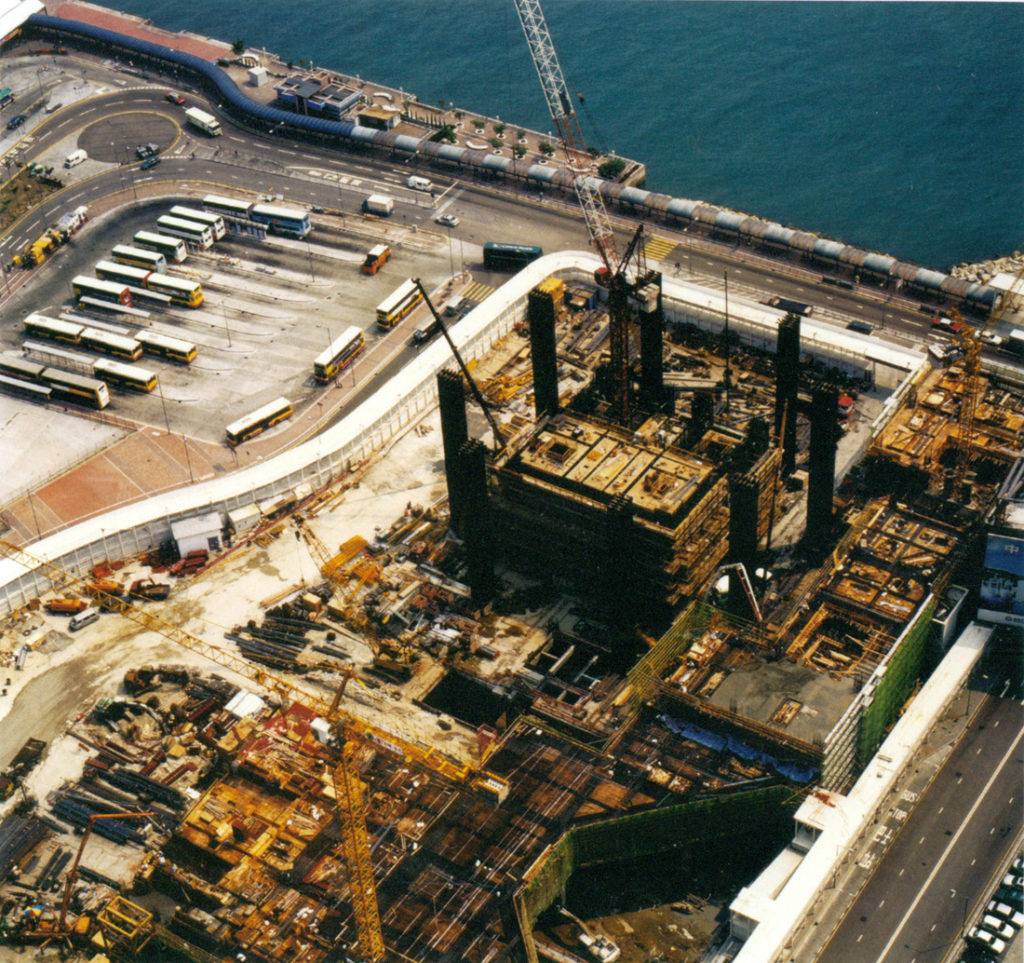
Construction
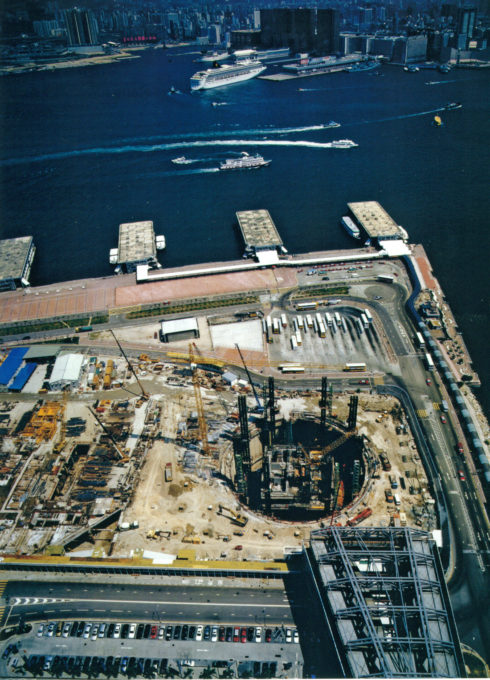

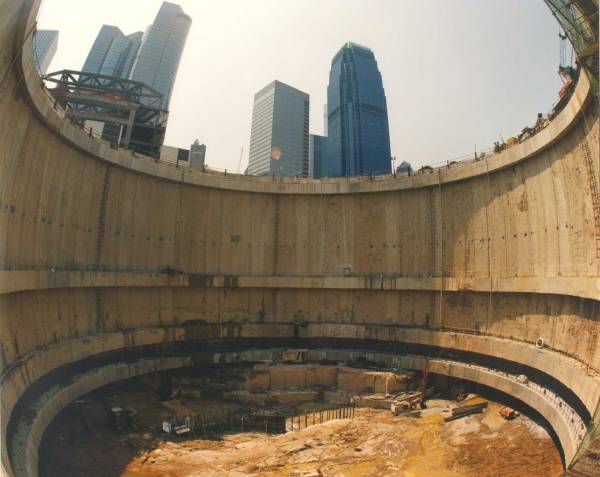
Ground and foundation
The land on which the tower was built was achieved by depositing silt dredged on a bed of rock. A deep run in the reclaimed land up to the rock, using an automatic drill trench was made. To prevent collapse of the side walls thixotropic filler sludge could be used until the concrete pump, displacing the mud layer.
As reinforcement steel cages were lowered as the material compacted, the embedded wall was removed from the inside to get a big hole that reached bedrock. From the resulting pit building work began with a simple foundation on rock exposed and properly checked. As construction progressed basements circular wall was removed.
Construction phases
The construction phase lasted three years that provide services reached 3,500 people, with conditions of safety, health and welfare rigorously detailed.
Alternate concrete steel construction is a costly decision that has potential drawbacks, both coordination between two different markets and the behavior of materials. The concrete takes longer than steel for assembly, work “in situ” require the construction, location and setting a mold and once poured takes time for settlement. Steel contrary, piece by piece, quickly providing you have a base with the required tolerance is placed.
As soon as the building reached street level, the material was removed and excavations began in the transport hub located beneath and around the base of the building.
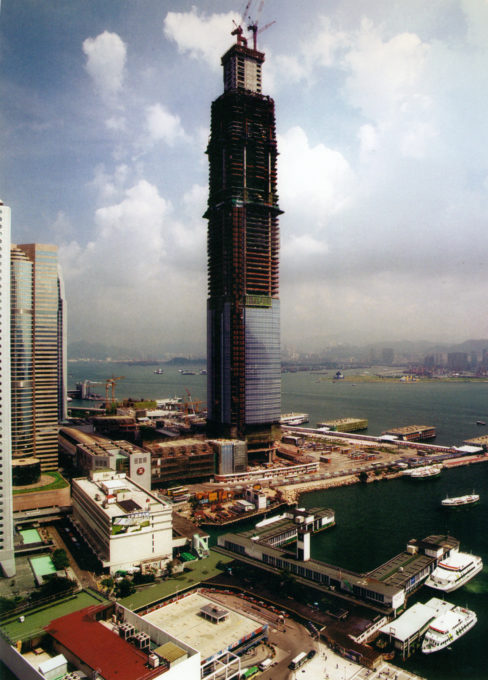

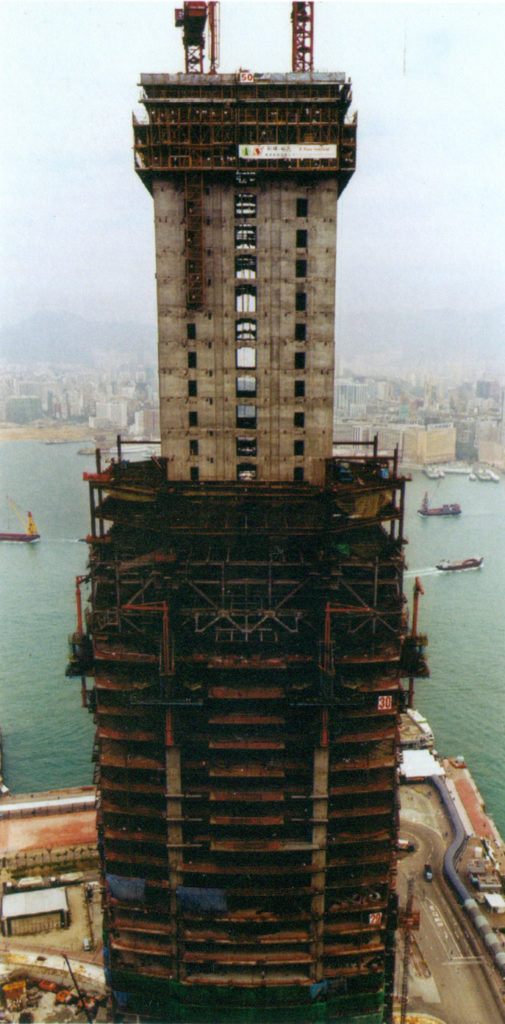
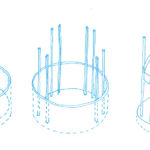
- Core
The concrete core was made to fit the hole and the surrounding soil steel, using forms “jump”. An upward rising hydraulic steel panels where prefabricated cages in which the poured concrete were placed. Once located in place, the forms themselves were contained and concrete could be accommodated. Exceeded the level rose to a new position to repeat the process.
The core was cast upstream and the central platform was holstered when work was completed. Steel inserts within the walls offering immediate communication with respect to the surrounding structure while a “pockets” on the walls were allowed to continue with the frame.
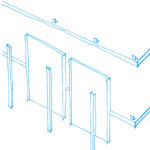
- Coating
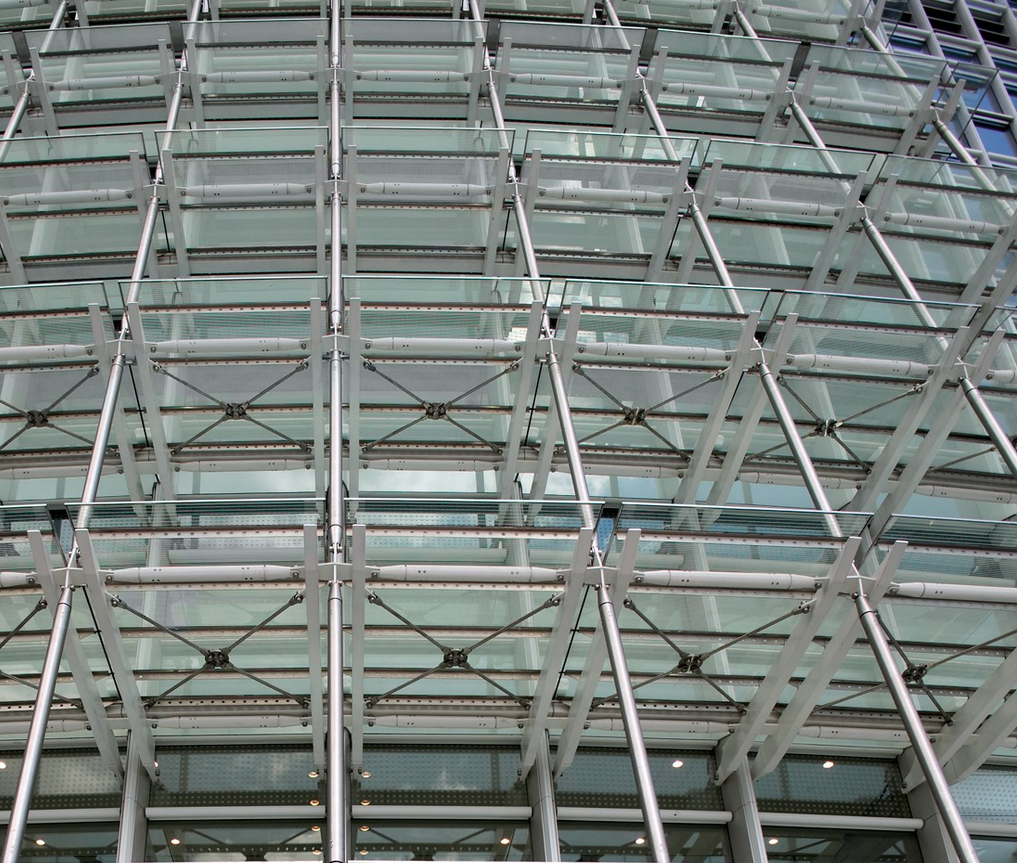
The nuclear structure, steel frame and cladding plates succeeded each other up during the construction phase. Climbing cranes and hoisting systems raised outer materials and workers.
Coating the individual panels are fitted into each block from within. Pilasters strips ensure a lasting and proper sealing against strong winds.
Structure
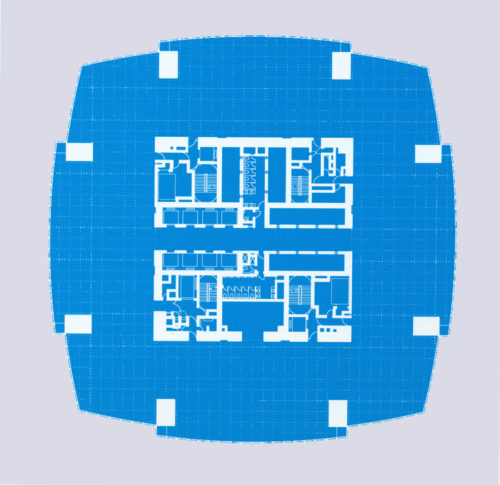
The structure of super columns with header crown, comprising a substantial core connected to eight columns of composite steel tubes filled with concrete girded by a slight secondary frame. The core housing and vertical circulation routes elevators, each comprising four areas of high open-plan floor extending to exceed eight steel columns daunting. These columns you increase their structural capacity and robustness by filling concrete. Every 20 plants the two vertical systems, columns and core are assembled by a gear overall height, in order to resist wind loads and typhoons.
Angles
The slender, fluted shape of the building is achieved by the angles of its structure, within which the most esteemed office spaces are created by users. These angles are reinforced by a much lighter secondary system that descends to a transfer structure steel shoring, located above the levels of the podium.
Materials
The design and subsequent construction work was organized in a general program, bringing the materials at the time they were to be used, avoiding storage.
Temporary cofferdam on the ground
To prevent the collapse of unstable side in the first drilling on land reclaimed from the sea, a thixotropic mud filling hardens if not altered externally used, but softens if remueve.El core circulation was made of reinforced concrete and structural steel tubing, also filled with concrete, accentuating its structural capacity and robustness.
Reaction of structural components
The different reactions of the two basic structural building materials in the building, are solved in the simplest way possible. Concrete subsides with time, as it hydrates and sits beneath the weight, while steel is dimensionally more stable. Assemblies between the core and vacuum columns topped by super possess loose shims. When the structure is subjected to strong winds in the area, the bearings are pressed and the system is closed, acting in unison. If it is found that these wedges appear fixed permanently due to the position of the nucleus, during the inspection, which is conducted annually, are replaced by thinner.
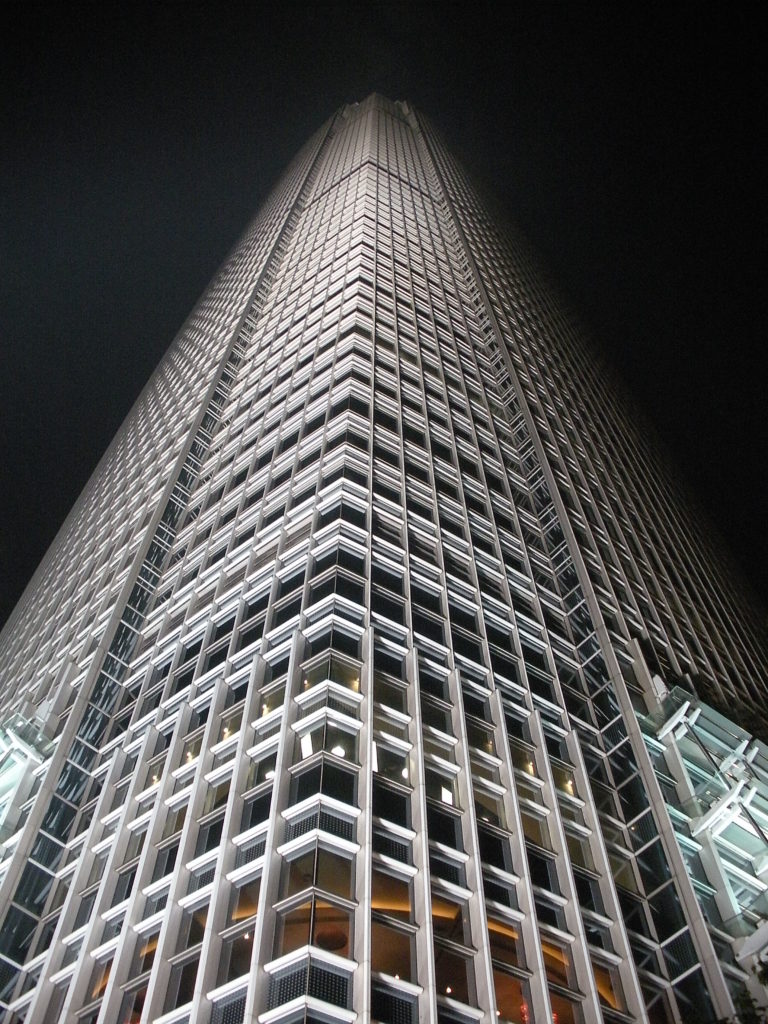
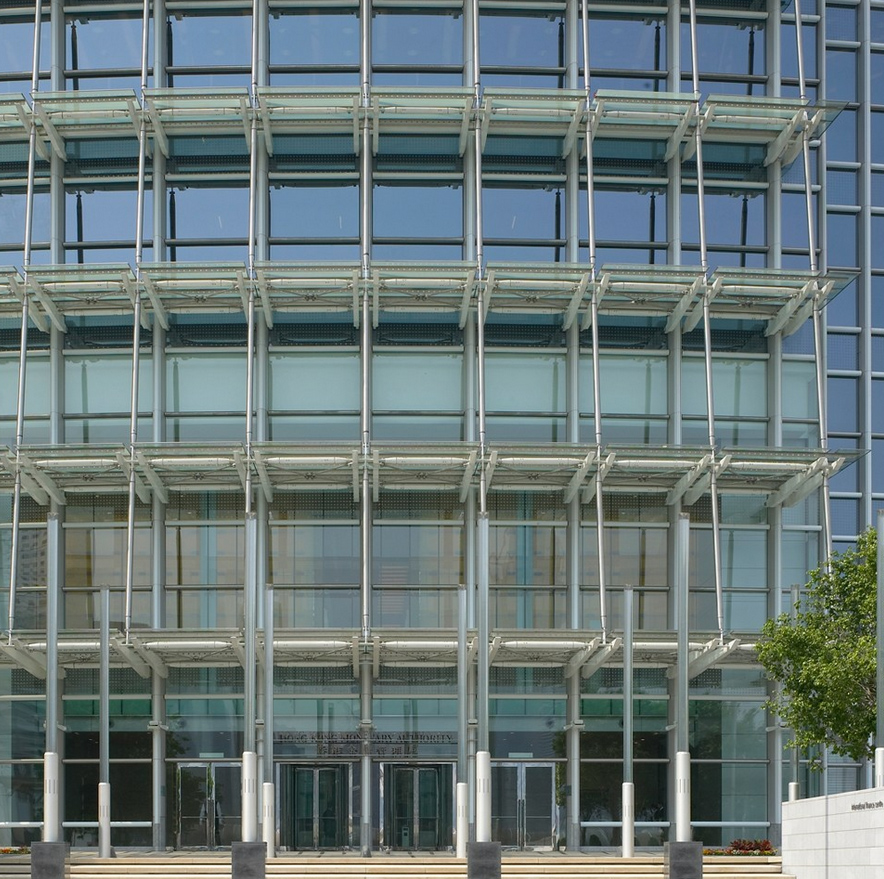
Facade
The curtain wall that lines the tower is slightly reflective glass in combination with more opaque and porous glass that helps visually smooth the surface of the tower. Aluminum components were specially colored pearly silver tone and the whole was warmly rises against Mount and the city.
Data
- During construction of basements it came to taking one million cubic meters of material 200,000 lorry movements.
- The debris were shipped to convert them into usable material in the construction of Hong Kong Disneyland.
- 38,000 tons of steel arrived by ship and 500,000 cubic meters of concrete were processed on site.
- The steel came from Spain to the basement, from Britain to transfer structures and Japan and China used in the upper structures.
- It is one of the relatively few buildings in the world equipped with double-deck elevators.
- Equipped with advanced telecommunications, raised floors for flexible cable management and almost free of columns in the building floor can accommodate 15,000 people.
Video