Trajan’s Forum

Introduction
Trajan’s form, known in Latin as Forum Traiani, is a forum designed by the Roman emperor Trajan. It is part of the vast complex of the Imperial Forums in Rome. Its construction, carried out between 107 and 112 was performed by the architect Apollodorus of Damascus.
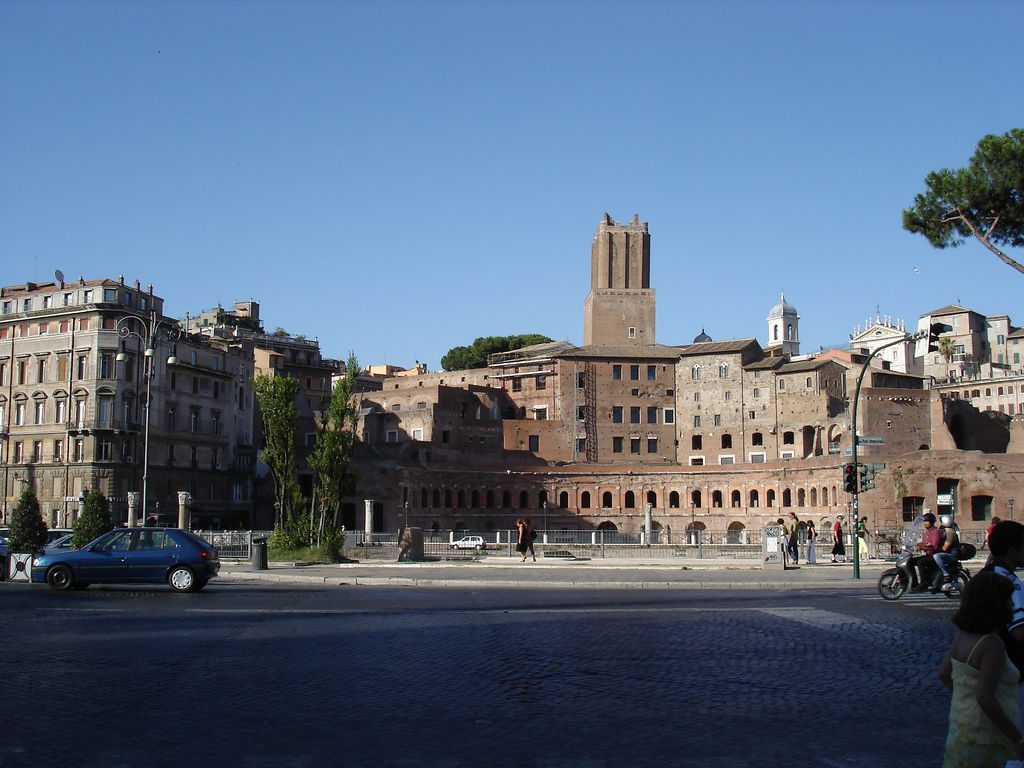
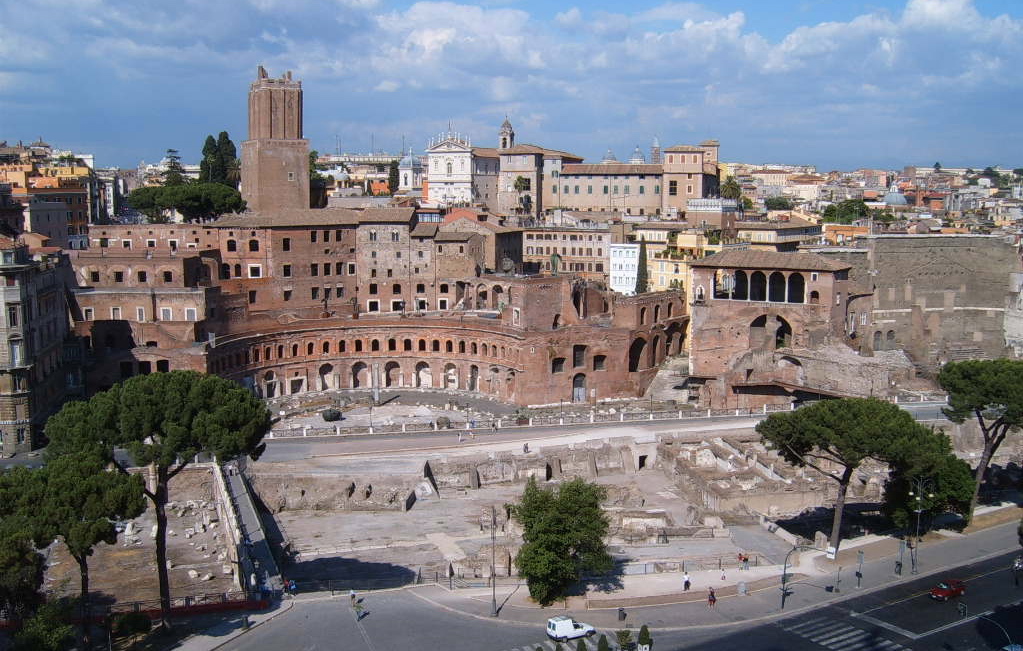
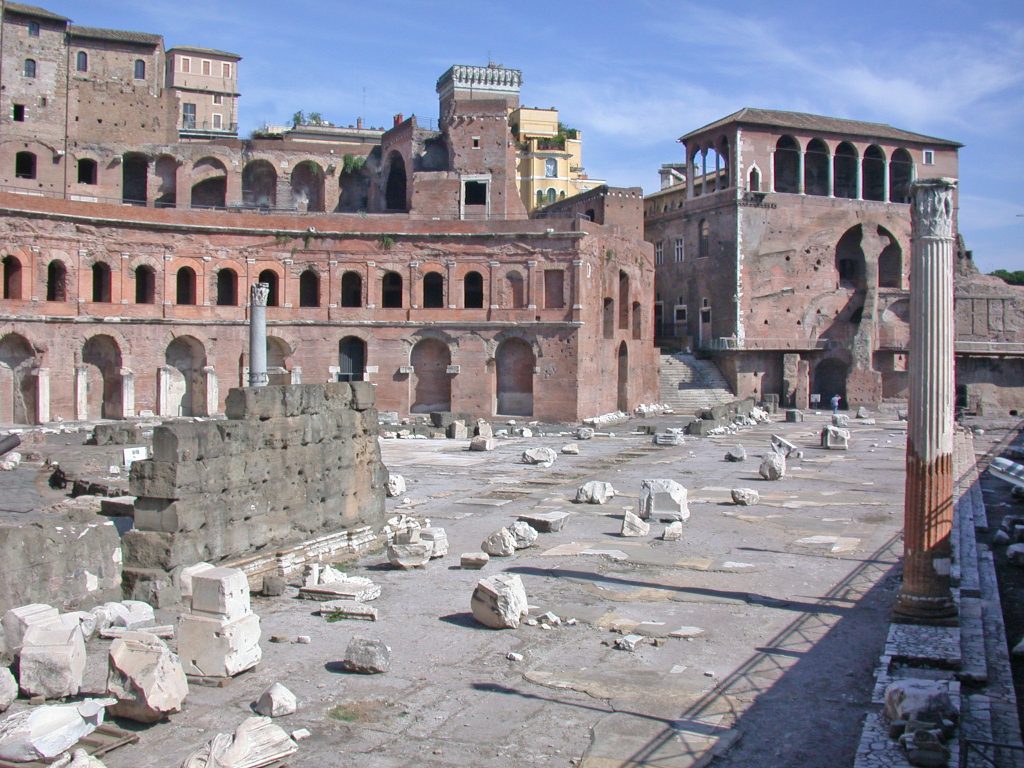
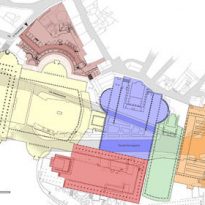
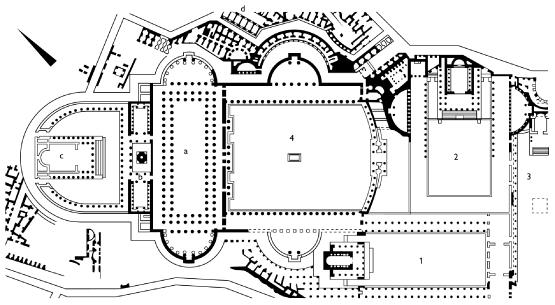
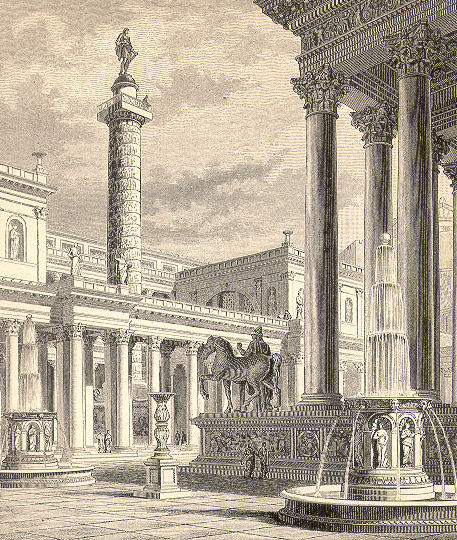
This spectacular complex is the largest forum of Rome. Has the squares, the Basilica Ulpia, Trajan Column and the Temple of Trajan.
The forum was built by the Emperor Trajan with the spoils of war brought after the conquest of Dacia, which had ended in 106.
The lack of available space in the valley of the forums as a solution imposed only for the opening of a comprehensive step towards the Campo de Marte, destroying the hill, the Atrium Libertatis and a stretch of wall Servianos it occupied. For the construction of this monumental complex were to make extensive excavations.
It is possible that the excavations were begun under the mandate of the emperor Domitian, while the draft of the forum was completely in charge of the architect Apollodorus of Damascus, who also accompanied the emperor Trajan’s campaign in Dacia.
The Forum of Trajan is chronologically the last of the Imperial Forums in Rome.
In the mid-ninth century, marble blocks from the square were systematically to be reused in other buildings, due to good quality. Simultaneously, the floor was restored pedregullo, which is an indication that the site was still being used as public space.
Situation
The lack of available space in the valley of the forums as a solution imposed only the placement of the forum in an area hitherto unknown in the city: the Campo de Marte.
To reach this area was necessary to open a large step toward the city from what would be the Champ de Mars, destroying the hill, the Atrium Libertatis and a stretch of wall that was occupied Servianos.
Meaning
The Forum of Trajan is inspired in its general design, in the near Forum of Augustus, but at the same time introducing many innovative features.
One of these is represented by the position of the Basilica Ulpia, placed transversely to close the bottom side of the square of the Forum, normally occupied by a temple front seat.
But the most important detail is that the package shows obvious similarities to the military camps. These camps were indeed a main square where they were the tents of the commander and the tribunes and where the troops arengaba Square which was closed in one of the sides closer to a basilica, there were just over the military archives, in correspondence of which to be recorded in the forum the two libraries, and finally, the column is usually at the site occupied by the sanctuary of vexilla or weapons Legionari.
Spaces
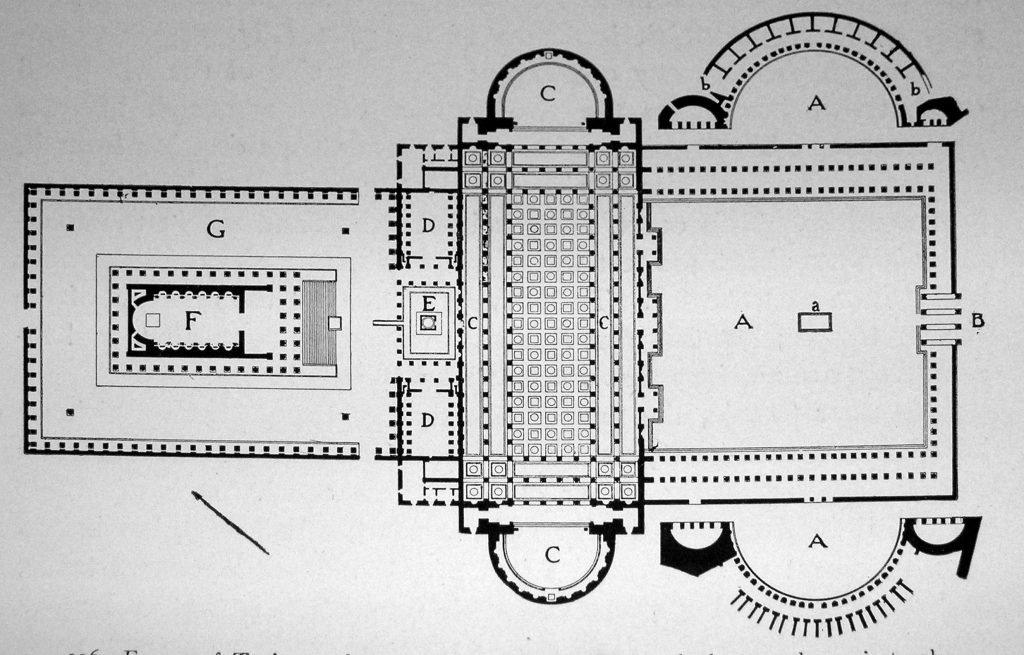
The forum was built from a large square surrounded with porches measuring 200 x 120 m with exadrae on both sides. The main entrance to the forum is for the south side, where it is located a triumphal arch topped by a statue of Trajan in a coach with six horses. Ulpia the basilica is located on the north side of the square, it was covered with rectangular blocks of marble and decorated with a large equestrian statue of Trajan. On each side of the market square is also hosted by exedrae.
North of the Basilica had a smaller square, with a temple dedicated to Trajan deified on the north side. Immediately north of the Basilica Ulpia on each side of the Forum had two libraries, one containing the documents in Latin and the other documents in Greek. Between the two libraries stood Trajan column of 38 m in height.
Only one area of markets and Trajan column have come to today.
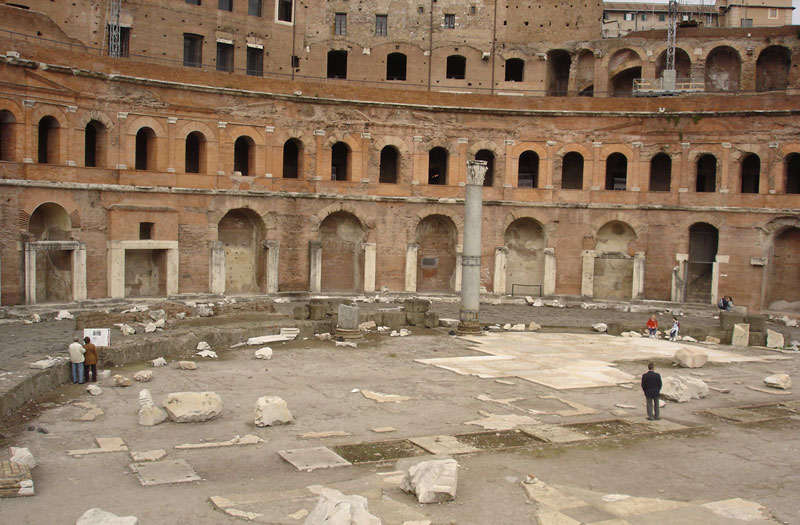
Basilica Ulpia
The Basilica Ulpia, which closed the plaza by the fund, has only been partially excavated. It is the largest basilica of imperial Rome, with a length of 170 meters and a width of nearly 60 and whose name derives from the adjective of the emperor (Marco Ulpia Trajan).
Had access to the southeast, with a central opening of three arches and two sides of a single arch, framed by columns and crowned by groups of statues, as we confirm the reproductions in the currencies of the time.
The interior of the basilica was formed by a monumental nave, separated by imposing granite columns of the four lower than the surrounding buildings on all four sides; under these ships were divided among themselves by rows of marble columns. Closer on the sides of the building opened two large semicircular exedras, which followed the same route to the square. In exedra southwest Trajan placed “Libertatis Atrium, where the ceremonies took place for the liberation of slaves, who previously performed in an old building, destroyed to make room at the Forum.
In the northwest side of the basilica, two openings entering the courtyard where today stands the Column of Trajan.
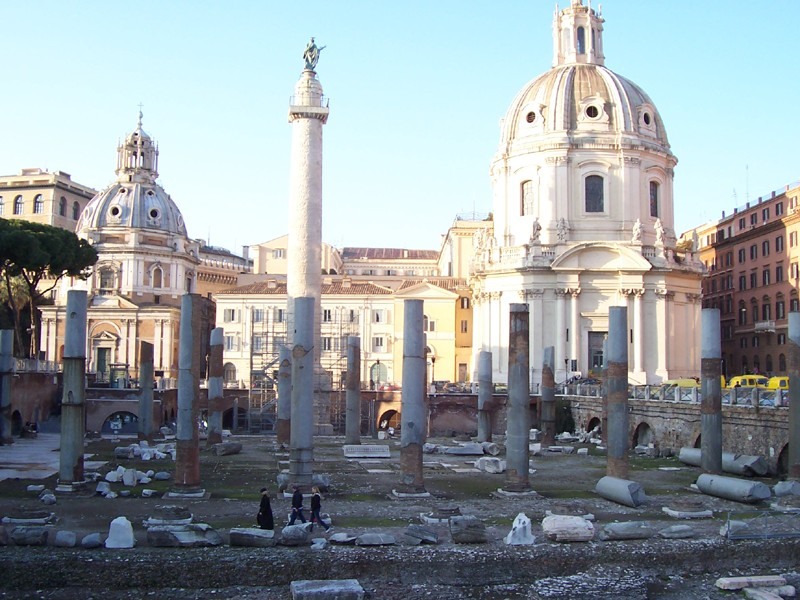
Column of Trajan

The column was a gift from the Senate and the Romans did to the emperor during the victories in the wars against Dacia (Romania village). Completed in the year 114, is a column of 30 meters in height (38 including the pedestal on which) covered by a spiral bas commemorating the victories of Trajan.
The column consists of 18 huge blocks of marble from Carrara, each of which weighs about 40 tons and has a diameter of about 4 meters. The frieze sculptures complete and is about 200 meters is 23 times around the column. On the inside of it, a staircase of 185 steps provides access to a lookout platform at the top.
The purpose of the Column of Trajan was threefold: to identify how far the mountain moved by the forum, cover the ashes of the emperor and celebrate the conquest of Dacia as a victory of Trajan.
Originally, the column was topped with a statue of an eagle, and later was put in place a statue of Trajan himself. In 1588 it was replaced by a statue of St. Peter by order of Pope Sixtus V, which is still preserved.
The relief
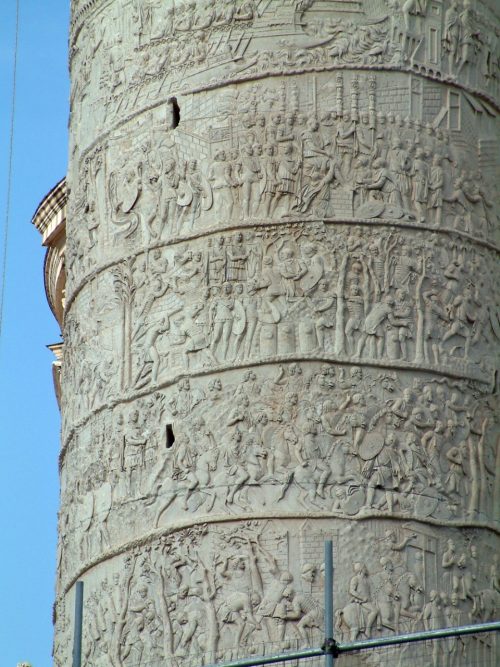
The story highlighted two victorious campaigns against Trajan Dacian in the bottom half of the first column shows the (101-102) and the higher the second (105-106). Both sections are separated by the personification of Victoria.
The relief was completely polychromed. The figures are carved in marble of a chronic nature, so it does not matter sculptural technique but the message that tries to convey. The sculptor (or sculptors) little attention to the perspective, using several different in one scene.
The metaphorical language used has features not only the representation of the gods, but the Danube is also represented by an elder. This is why so many simplifications are observed, such as isocefalia. The chronic form is helical and chronologically, narrating scenes of the various campaigns dacias we could find the life in the camp, the construction of an aqueduct or a siege of the city. A total of 2,500 human figures: the emperor appears 59 times, always seen in a realistic way, not superhuman. The relief is a valuable source of information on the Roman army.
Registration

The following inscription is on the pedestal:
SENATVS • POPVLVS • QVE • ROMANVS
IMP CAESARI • • DIVI • NERVAE • F • NERVAE
Traiano • AVG GERM • PONTIF Dacic
• • MAXIMO TRIB POT XVII • VI IMP VI COS •P•P•
AD DECLARANDVM • QVANTAE • ALTITVDINIS
MONS ET • Both LOCVS <…> IBVS SIT • EGESTVS
Translated:
‘The Senate and the Roman people, the emperor Trajan Nerva Caesar Augustus Germanicus Dacic, son of the divine Nerva, Pontifex Maximus, a tribune for the seventeenth time, the emperor for the sixth time, consul for the sixth time, the father of the nation, to show that the height reached the hill and destroyed the place now like this. ”
In other words, according to the column entry is as high as the hill that previously existed in the same place.
Is perhaps the most famous example of writing quadrata (uppercase Roman square), a type of writing often used in epigraphy, but less frequently in the manuscripts. As is designed to be read from below, the letters are slightly smaller than the above, to produce the proper effect of perspective. Some but not all divisions of words are marked with dots, lots of words, especially imperial titles-in abbreviation. At registration, the numbers are marked with a titulus, a bar above the letters. Missing a small piece at the bottom of the registration.
These letters are formed from geometric shapes such as square, circle or a triangle, and were cast for the capital letters in our alphabet today.
The modern typeface Trajan computer, designed in 1989 porCarol Twombly (who worked for Adobe Systems and Bigelow & Holmes), is modeled on that used in the inscription.
Libraries
Trajan column was flanked by two libraries in which they also retained the emperor’s private archive and a collection of decrees of pretores. In one of these texts were in Latin while the other Greek texts were preserved.
The library, located in the southwest, has been discovered under the Route of the Imperial Forum, is a rectangular enclosure, with niches in the walls on three high steps and surrounded by a double row of columns, which were placed in cabinets containing volumes. On the back wall opens up a bigger niche with marble decorations, which should contain a statue of a deity. From the upper floors of the library could provide the frieze of the column of Trajan.
Temple of Divine Trajan
Northwest of the package was located the Temple of Divine Trajan Plotinus and the Divine, which closed the Forum.
It was erected in the year 121 by Adriano, in honor of Trajan. There are no news about this temple, which arose on the site where today stands the church of Santa Maria de Loreto and should take colossal scale, with eight Corinthian columns in front and eight on the sides, with a height more than 20 meters.