Tokyo Sky Tree

Introduction
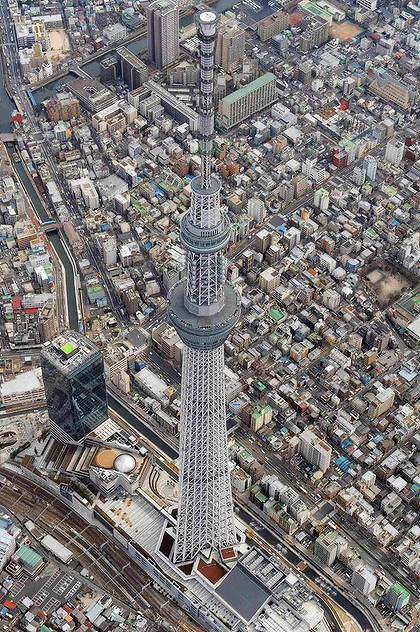
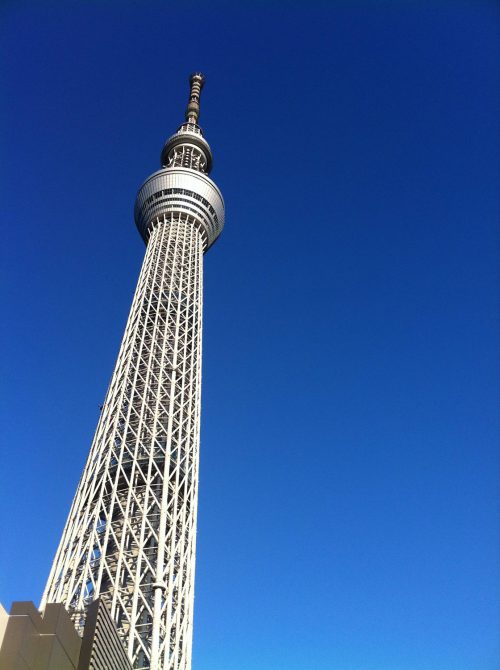
The Tokyo Sky Tree (東京 スカイ ツリー), is a new television and radio tower that has become a symbol of the Japanese capital and centerpiece of the Tokyo Skytree Town in Sumida Ward, not far from Asakusa. With restaurants and observation platforms, reaching a height of 634metros. It is the tallest building in Japan and the second tallest structure in the world at the time of completion. At its base is a large shopping center with an aquarium.
The study Nikken Sekkei has worked closely with professionals and experts in different disciplines to achieve this project, from the first sketches to planning in the posing of the project, through the modulation of design environmental assessment and design district cooling heating, correlation with the environment and urban landscape. In the end, more than 100 architects, engineers and planners have participated in the project design.
Location
Tokyo Sky Tree is near the bridge and Area Narihira Oshiage along the Sumida River, was once the center of the glorious culture of Edo, in the eastern part of Tokyo, Japan. It is surrounded by traditional downtown areas such as Asakusa and Mukojima, and is a key center of rail transport, subways and metropolitan bus Tobu water.
Tower relationship with the surrounding
The work is located in the center of a triangular plane surrounded by the three axes, the Sumida River and Arakawa River, and south, the railway lines that run east-west and some roads. Perpendicular to each axis, several streets converge towards the focal point which is the tower, so that it is designed to have three doors, inviting people to come along these streets.
Concept
The planning of the structure began in February 2005 when Tobu Railway Corporation expressed his desire to build a tower that would provide broadcasting services and house the administrative authorities of Sumida-Ward. At the beginning of this project, the client asked the designer to create in this area “a new landscape beyond time and space.”
The design was based on three concepts:
- Merging a futuristic design with the traditional beauty of Japan
- catalyst for the revitalization of the city
- “Security”, contribution to disaster prevention
Design forms
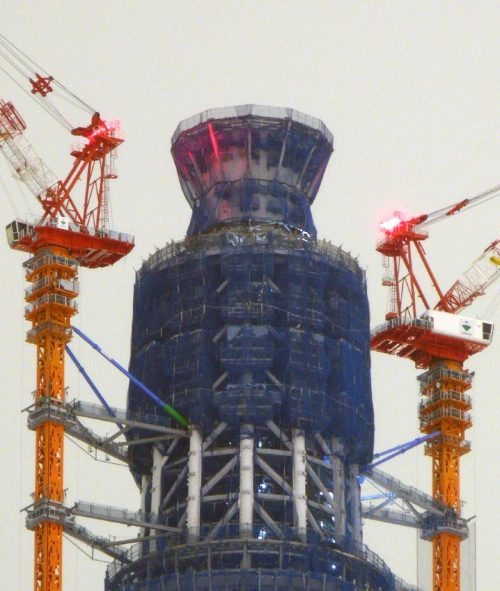
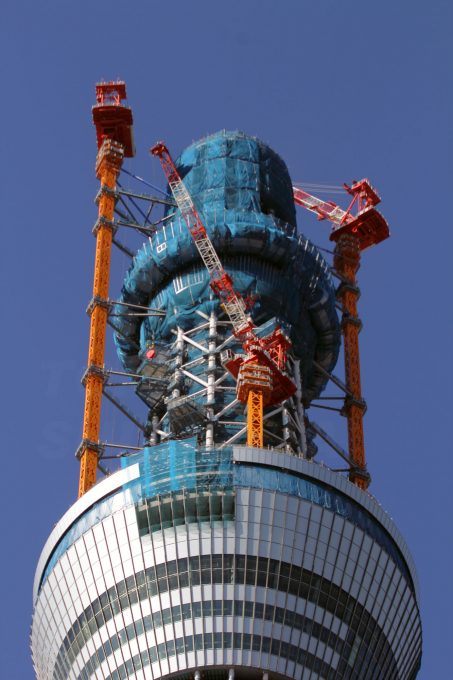
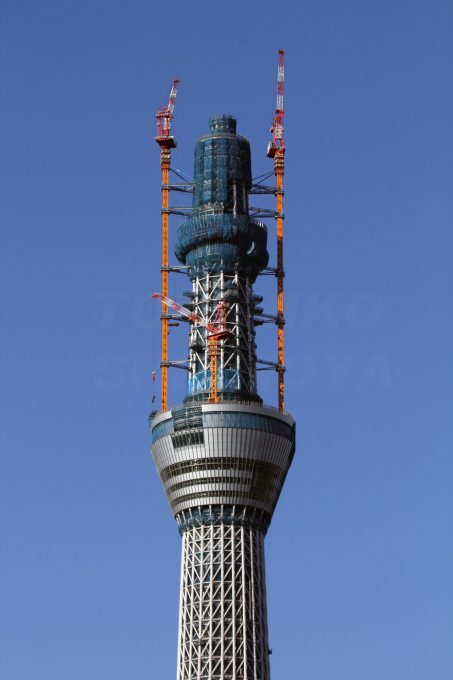
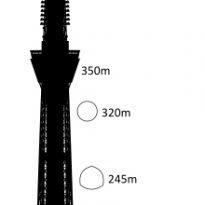
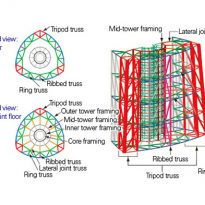
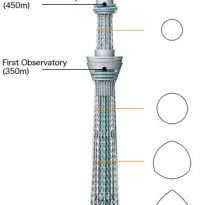
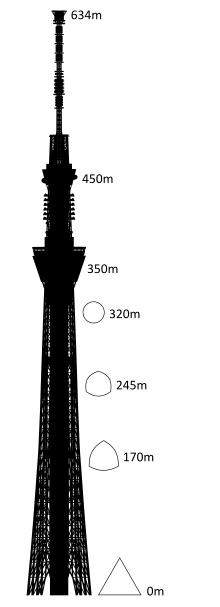
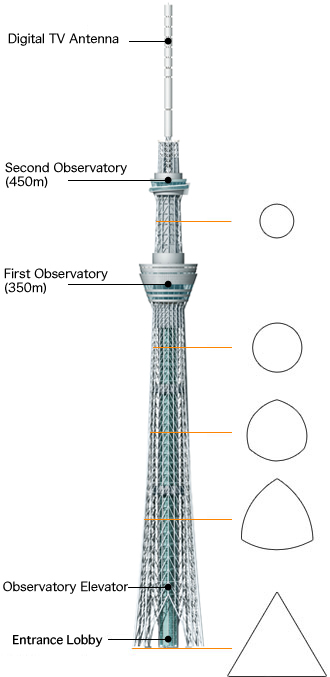
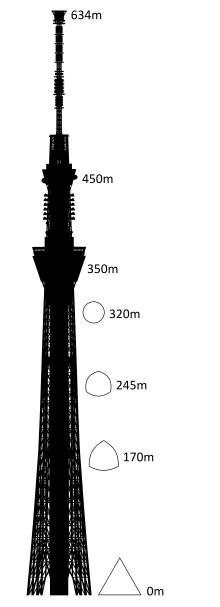
The footprint of the Sky Tree is an equilateral triangle, each side is approximately 68m. Of the three vertices are extended lines, which converge to 50 m above the level, where the lines extend further to 600 meters. The ratio of length to width is approximately 9:01, thus creating a thin vertically.
The three legs on the bottom, resembling a boiler tripod or a tripod for the camera, to a height of 350m. In ancient China the concept of self-standing anywhere, with three legs themselves, was used ceremonially giving people who seek a vague sense of security. Also, the smooth triangular shape results in a structural analysis solution is secure, despite having fewer structural elements. This will not only reduce tightness in the minds of the neighbors, but also reduces the structural steel tonnage used, both beneficial to the environment.
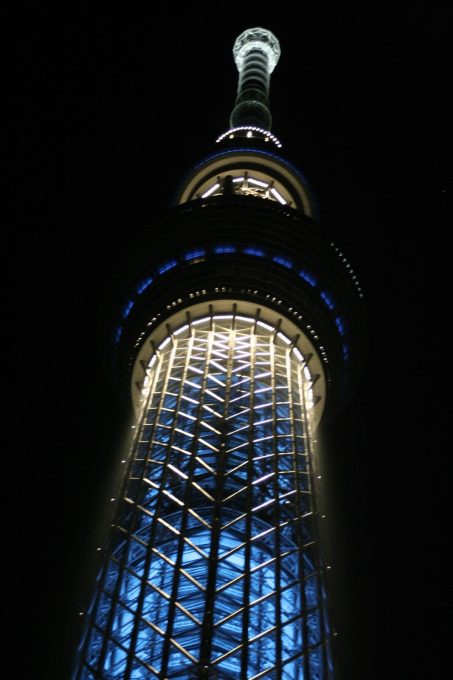
Meanwhile, to the observatory, has selected a round, thought is right to look at, 360 °, above the vast plain on the outskirts of Kanto.
The change in shape, from the triangle to the circle, also means “warp” and “fall”, which are traditional forms of Japanese culture. The ridge line of the triangle has a “warp”, usually seen with Japanese swords and the transition section where the triangle changes to a circle is the “fall” seen in the central columns, gently expanded the architecture in the Traditional temples of Nara and Heian eras.
The tower thus created is an unprecedented way in the world, at the base rectangular gradually changes to a circular plane to a great height.
Function
This tower is designed primarily to serve as a transmission of radio waves for broadcasting new generation of ground wave television, and is also expected to become a symbol of the redevelopment of the city center along with the maintenance of the cultural tradition of the area, in partnership with Asakusa, a famous tourist attraction rich cultural traditions of the Edo period.
Spaces
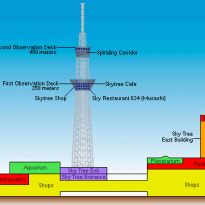
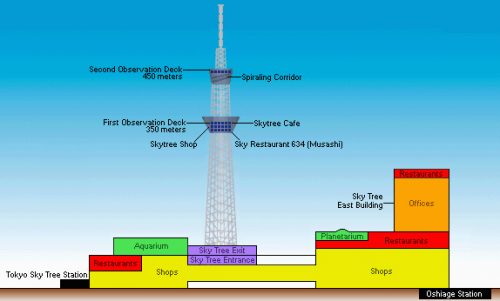
At the base of the Tower Skytree, has deployed the largest shopping center in Tokyo, the Tokyo Solamachi, with over 300 shops, restaurants and entertainment, as the Sumida Aquarium (すみだ 水族館, Sumida Suizokukan) located in the 5th and 6th floor of Tokyo Solamachi Mall. With good design and modest size, is home to over 10,000 sea creatures.
The tower itself has two public open areas, observation platforms.
Platforms

At a height of 350m, which ends the tripod, stands an observatory, Tembo Deck, with capacity for 2,000 people and a second at 450m, with a capacity of 900 people.
- Tembo Deck
Tembo Deck extends over three levels, with excellent views in all plants. The upper floor has large windows, which offer some of the best 360 degree panoramic views of the city. The middle floor has a gift shop and Musashi Sky restaurant, serving French-Japanese fusion, while the ground floor has a cafe and glass panels in the floor, from where you can see all the way to the base of the tower.
- Tembo Gallery
An elevator group Tembo Deck deck connects to the next, Tembo Gallery, at 451.20 meters high. Dubbed as the “world’s highest bridge”, the Tembo Gallery consists of a sloping ramp, spiraling, gaining height as it flows through the tower. The steel construction and glass tube allows visitors to look down from the dizzying heights of the tower and along the Kanto region at distances spectacular.
Structure
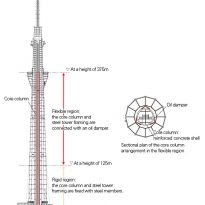
Structurally, the tower was built as a giant tree with deep roots in the ground. At the base, the steel tubes of 2.3 meters in diameter and 10 inches thick trunk form the base of the structure, a series of armor and joints branches. The middle column concrete is structurally separated from the steel structure that surrounds an earthquake-resistant design similar to the legendary temples pagoda.
In structural engineering, the Sky Tree and concrete develops the essence of advanced technology in structural designs to ensure the highest degree of structural safety. The “alleged” taken into account in the structural analysis are: an earthquake with its epicenter in the metropolitan area, such as South Kanto Earthquake, or the Tokai and also a catastrophic storm with a wind speed of 70-80 m / s for an average of ten minutes, as this may be once every 500 years.
Various structural analysis methods and assumptions were introduced:
1-A from research in a new area
The height of the Tokyo Sky Tree is approximately 634m. The tower structure of Japan, outperforming the Tokyo Tower, also designed by Nikken Sekkei Group, which was completed in 1958, 333m above the level. For the study of wind conditions at 600 meters above the ground, blew up a balloon radiosonde for measuring meteoric and get the data on the distribution of wind speed levels and disturbance conditions at that altitude.
On the other hand, besides the conventional subsurface investigation, we conducted a special study, a micro rotating measurement, not usually required, for the formation of soil to a depth of 3km. Through this special measure is to know their behavior during an earthquake and cause fluctuations that place in the structure.
2-anchor the tower to the ground
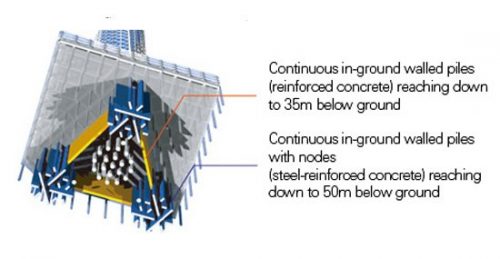
The more you raise a building, its foundations are subject generally proportionally greater traction and thrust down.
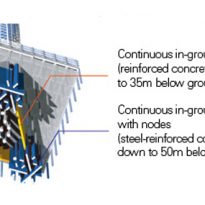
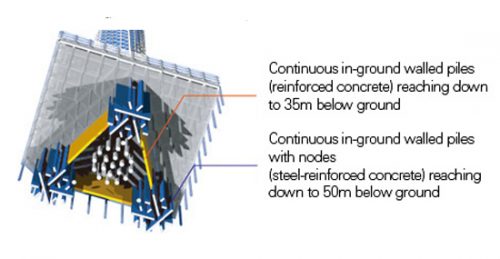
In the case of the Sky Tree Tower, its structure is particularly subjected to a greater force. Its foundations must be designed to withstand such forces, making nodular forms on the walls of the batteries to increase the frictional resistance. The nodes are battery based on the pins of the nails of the shoes. Also to be connected continuously, in radial directions, these walls serve a similar function to the roots of a giant tree monolithically integrated on earth.
The steel beams are connected rigidly to fully charge the external force applied continuously on the ground. Noting the entire structural system can be said to be “a giant tree growing from the ground.”
3-Composition monolithic structural beams
The main structural elements, the Sky Tower Tree tubes employs high-strength steel whose strength is double that of a standard steel channel. The steel tubes used in the base of the tower are huge, the diameter is 2.3 m and the thickness of the tube is 10 cm.
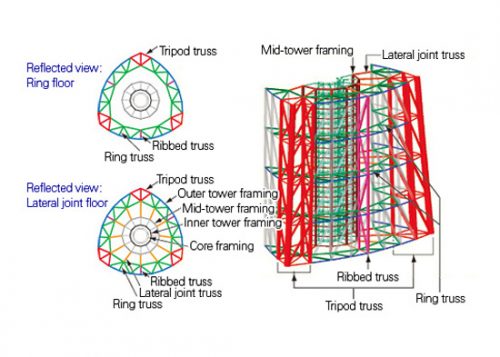
The entire structure of the tower consists of items “lattice”, each of which is a combination of triangles, comprising a main member, a side member and a diagonal member, each member in plural number. These members are joined together by joints branching, ie a section of the bypass pipe connected by welding directly to a main line without using any other attachment plate members. This type of joint is very simple in appearance and advantageous for preventing rust. This set is rarely used for a building or structure on land, generally used for marine structures, for example, an oil platform jacket, so that the board is designed according to the rules fixed for such construction marina.
4-Control of vibration of the structure
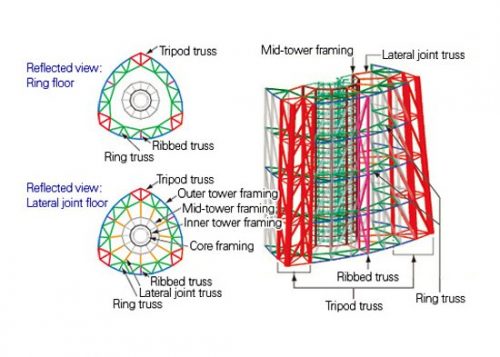
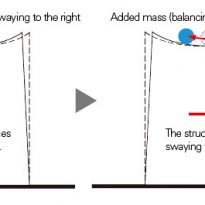
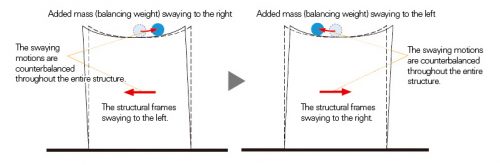
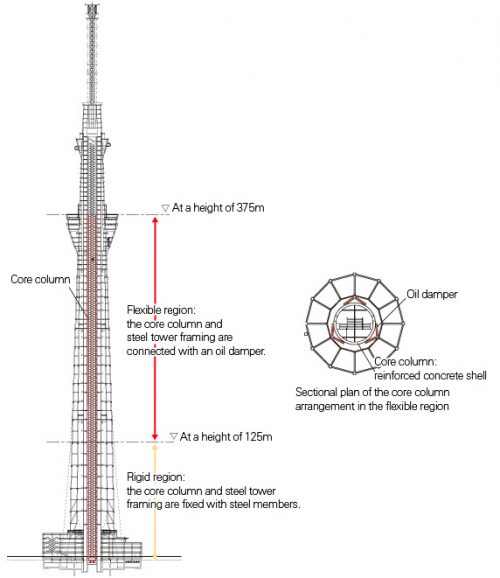
The cylindrical core concrete tower is structurally isolated from the peripheral steel structure, causing the top of the central column to function as “counterweight”. This control system is, in principle, a new application of the modern “crowd control mechanism Added” and can reduce the response of the cutting force by 40% during an earthquake.
In Japan pagoda with a height of 5 floors, never been dropped during an earthquake, so far, due to “Shimbashira” or “Middle column” of the temple, built in the center of it. In the construction of this super structure have blended traditional techniques with other high-tech, creating a vibration control system called by its builders “Shimbashira-Seishin”, “Central Column Vibration Control”
5-Crowd control mechanism added
This mechanism is to control the oscillating motion of a structure as a whole during an earthquake, providing an additional mass (balance weight) to move with a slight delay from the rocking motion synchronized, as a counterweight, to compensate for movement structure by movement of the weight. Usually, concrete or steel ingots are used as added mass, and sometimes systems for construction equipment, a heat may be used for example for the same purpose. At the Tokyo Sky Tree, the center column created as stair box is used, first in construction, such as added mass.
Materials
The structure of the tower is made of steel and reinforced concrete.
The tower was constructed with extremely strong steel tubes around a central concrete column, two pieces are structurally separated from each other in the middle section of the tower. In the case of an earthquake, the concrete core and steel frame are designed to compensate each other and reduce the overall motion of the building.
- Trellis
The outside of the tower lattice is painted a color called officially “White Skytree”. Is an original color based on the traditional Japanese bluish white called “aijiro” (蓝白)
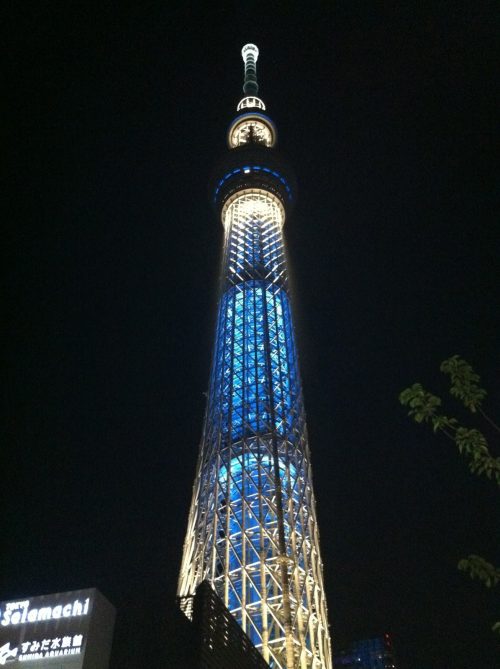
- Lighting
The lighting design consists of two patterns, the Iki, elegant and stylish, in a sky blue tone and Miyabi, more refined, in purple. These patterns are used alternate days. The tower is illuminated with LED lights.
It takes about 50 seconds on a high-speed elevator rack with glass roof, in getting to the first observation deck at 350m in height and 30 for reaching the upper deck, at 450 meters.
Video