Sports Palace in Rome

Introduction
It is a building that was created for free hosting the Olympic Games which were held in Rome in 1960 and served for testing indoor sports.
Meaning
The architect Annibale Vitellozzi and engineer Pier Luigi Nervi designed the building from the standpoint of economy, speed of execution and efficiency.
Materialized work with reinforced concrete and its predilection for the static equilibrium, through the principle of decomposition of forces and the same path through the elements of the structure.
Suggested prefabrication, the apparent advantage of the perfect executive for quality assurance of the clusters and the largest developing economy.
Spaces
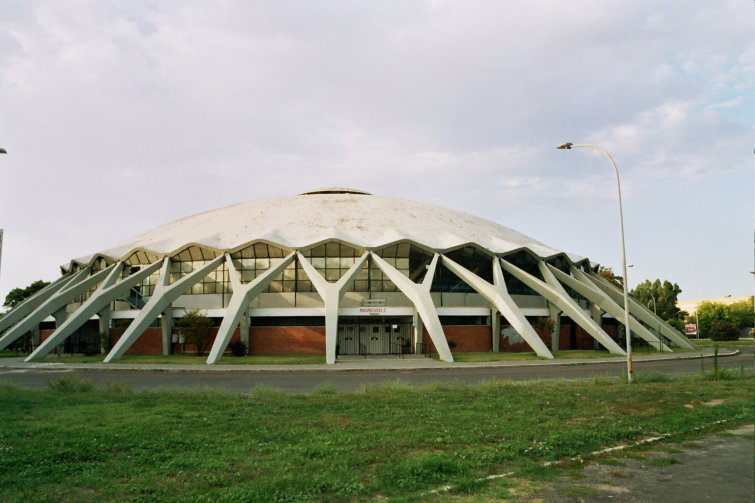
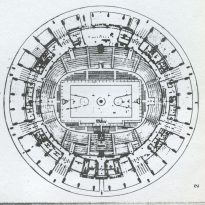
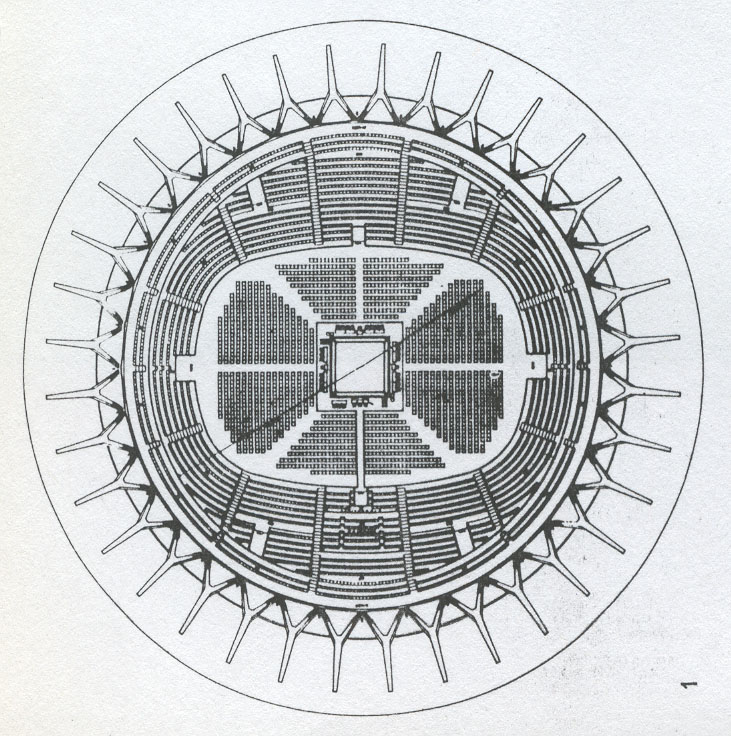
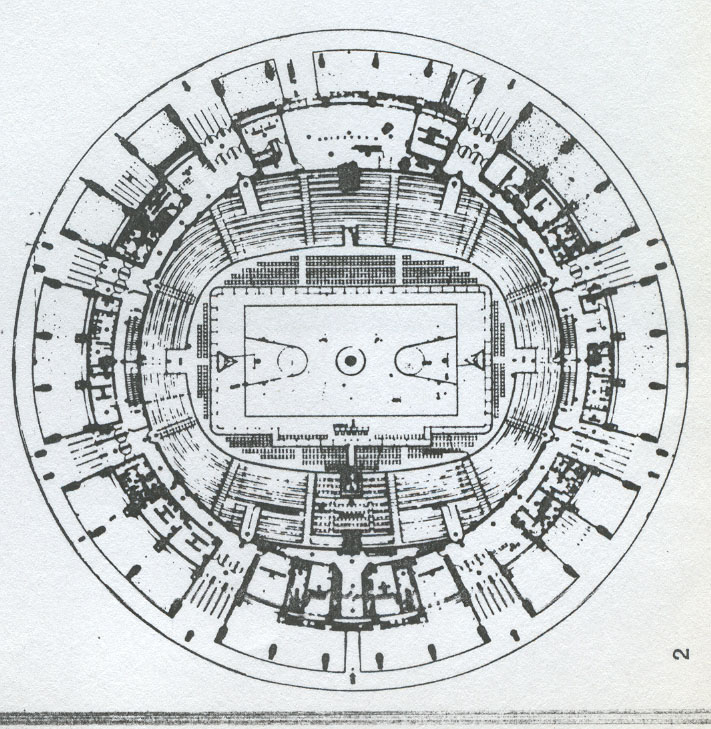
The palace is a covered stadium to accommodate 5,000 spectators in the boxing and fighting skills, and for 4000 during meetings of tennis, basketball, fencing and gymnastics; needed a game more.
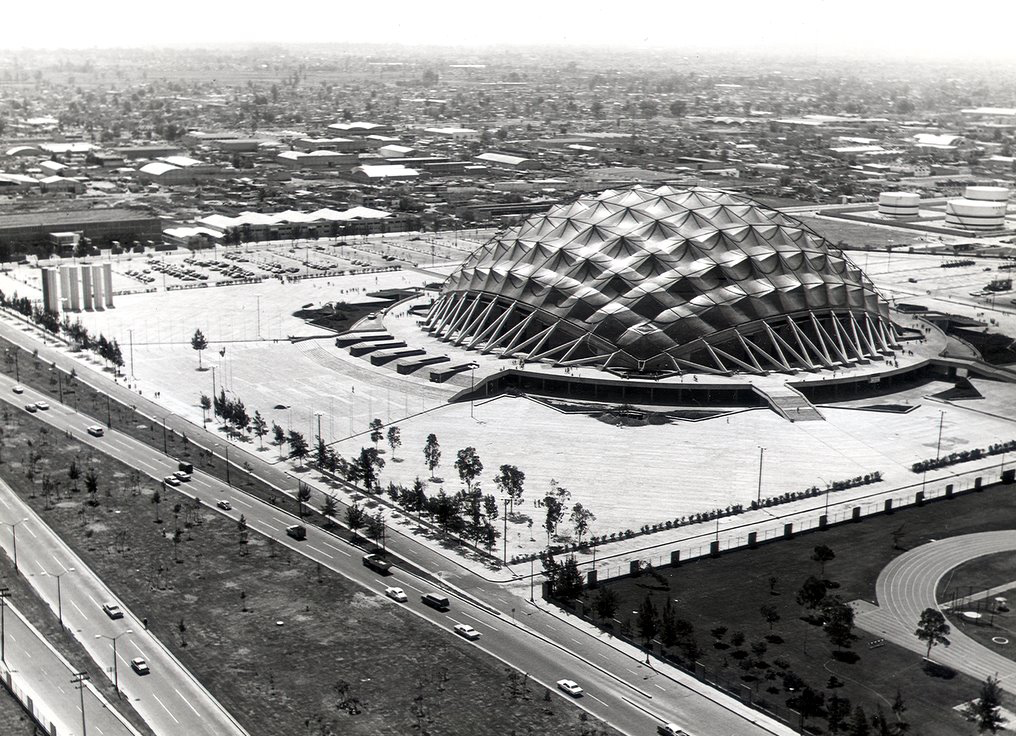
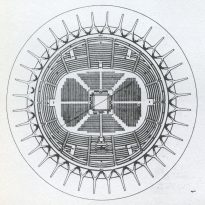
Its form is circular with a diameter of 78 m and a surface of 4776 m2.
In the outer perimeter utilities are: bathrooms, bars and first aid, including four athletic locker rooms with separate entrance, a dressing room for judges, for a medical office for an address and a telephone room with journalists.
In the ring perimeter found accommodation for the caretaker, and two cabin business transformation.
Below the level of underground facilities are: heating, cooling and air conditioning.
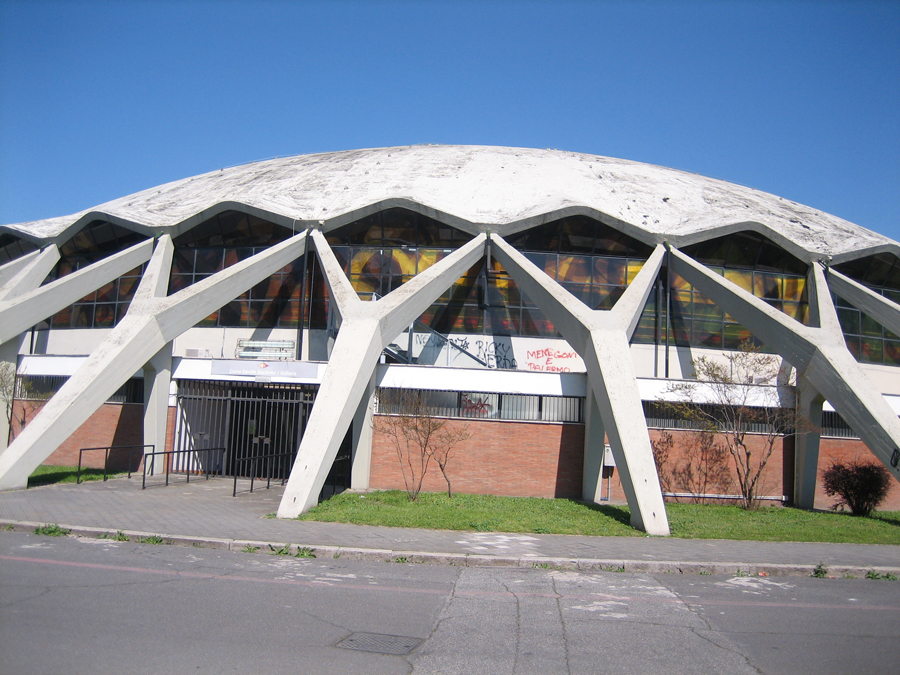
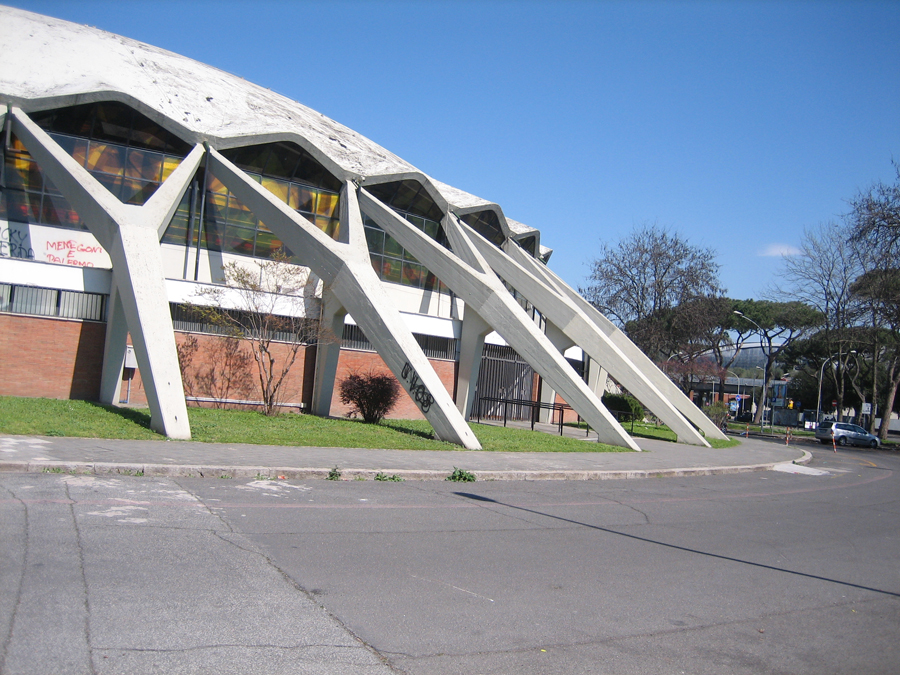
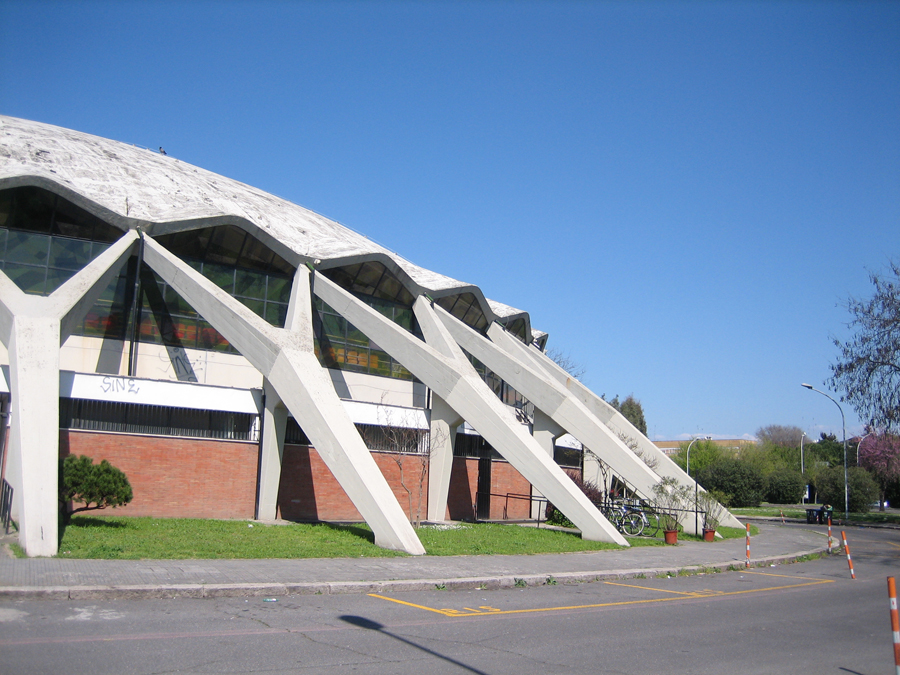
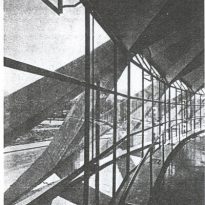
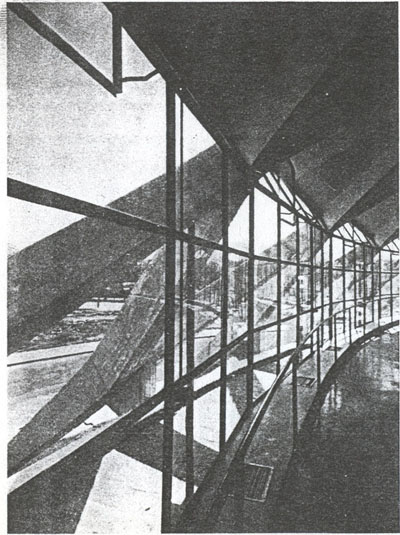
There is a contrast between the interior space and exterior. As can be seen in the forms of structure, both in the cap of the stands; abroad expression is less strong, since many of the interesting supporting structure is hidden under a glass gallery that surrounds the structure Principal, which is coupled with an overhang perimeter.
Structure and Materials
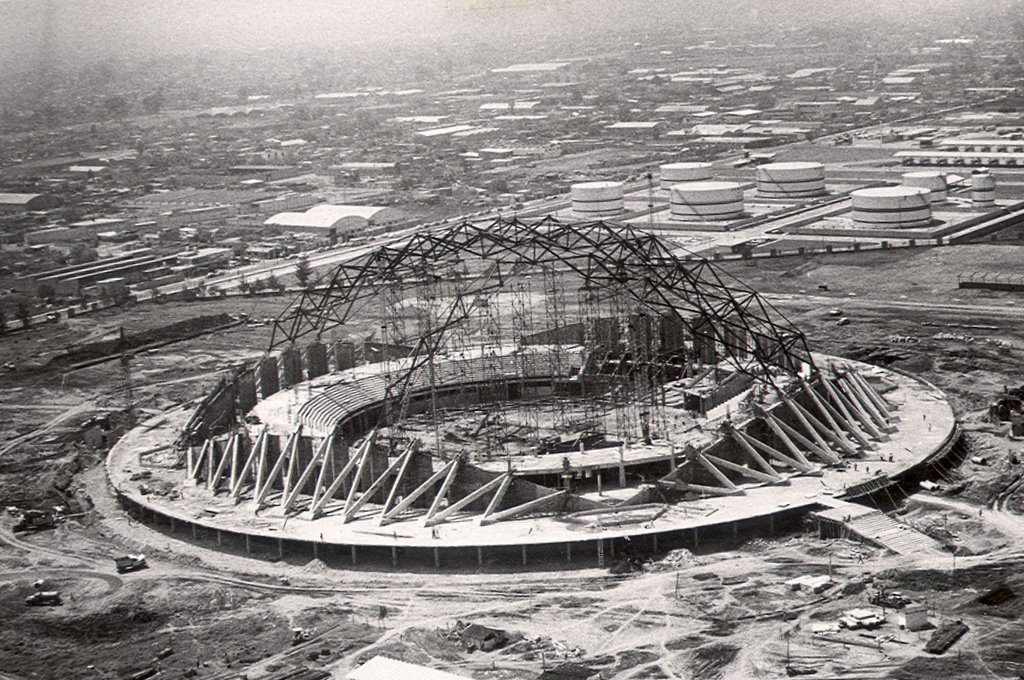
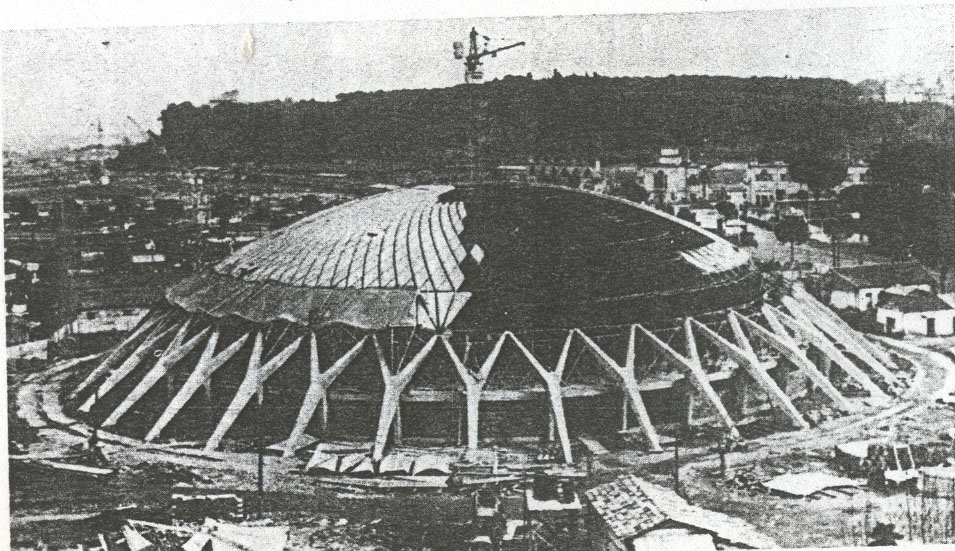
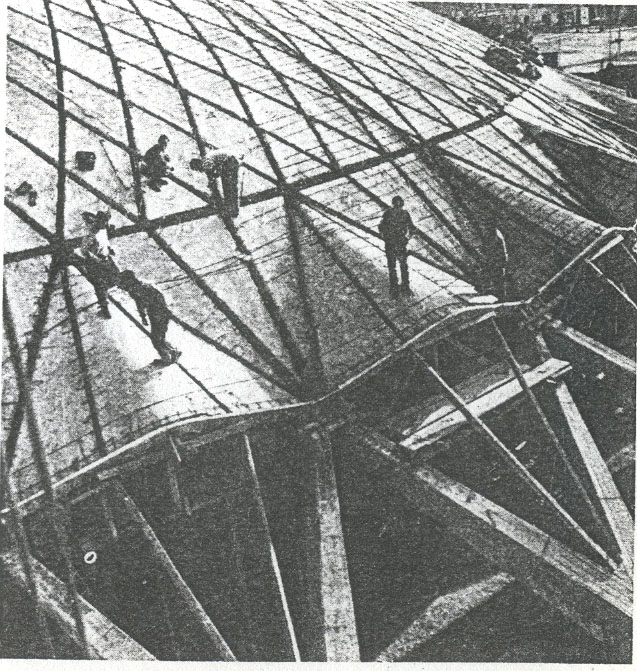
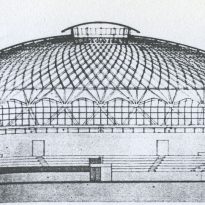
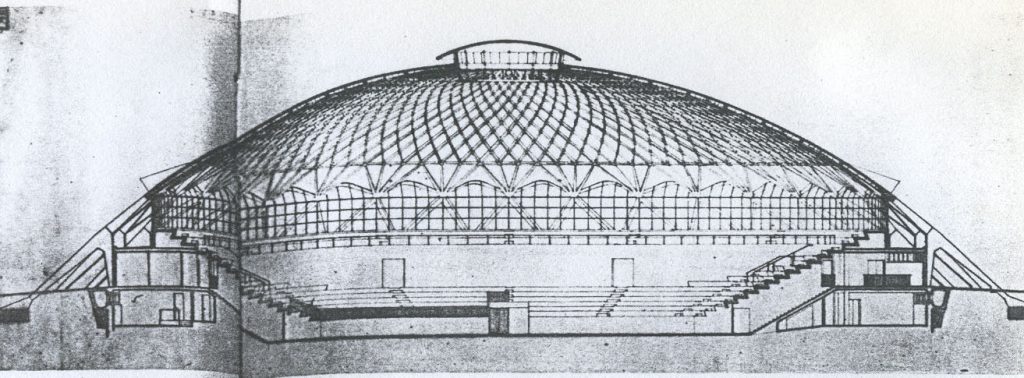
The surface is covered by a spherical cap of 69.20 m in diameter and is made of prefabricated sections 1620 ferrocement shaped diamond, linked by concrete poured into the boards to form the nerves, since these views inside.
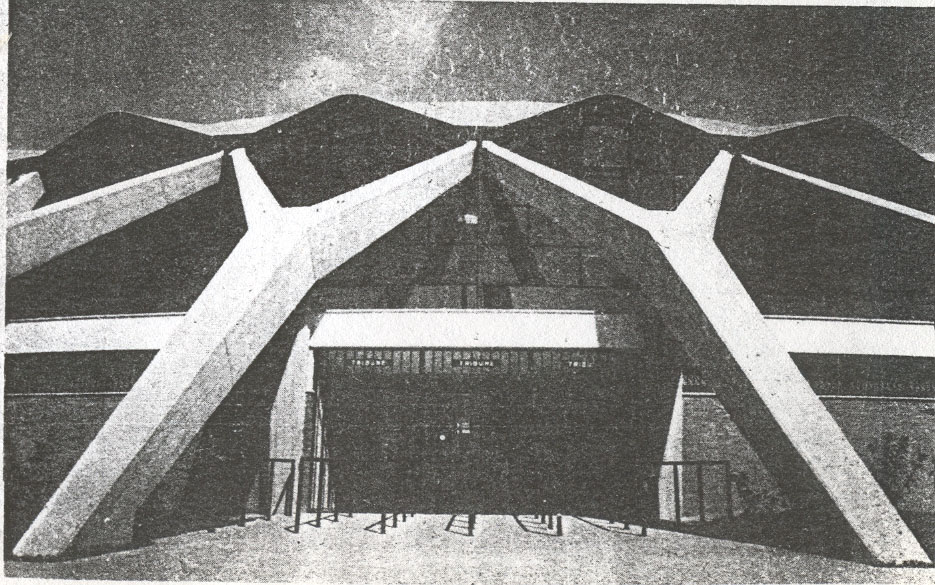
The dome is supported by an outer perimeter of 36 racks in the form of “Y” at the top, arranged in a radial and inclined.
All endings are of the rational and economical.
The main feature is the edge of the undulating contour, which gives rigidity to the whole box and is shuttering (recoverable) for the ribs.
The forum is supported by columns shaped spot beveled.
The dome was designed as a membrane structures buttresses and capable of transmitting the load to the foundation’s own weight and that of the dome.
The foundation is a reinforced concrete ring width of 2.50 m and 81.50 m in diameter.
The beauty is not the result of decorative effects, but the structural coherence.
Dome
The thickness of the dome is 12 cm. The items are prepared in molds and made on an appropriate structure that reproduces the original size, in the same sector (sector between two pillars).
Molds are cement surfaces for its perfect ending.
The frame is made of metal and a round iron wire network, which irons out of the elements.
The armed with this additional locita irons.
The top ring is the last element of trapezoidal shape and reinforced with additional armor.
The elements are based on two rails, set directly on the terminals of a metal scaffold.
Lighting
Natural lighting is done with a compression ring in the center to locate a flashlight.
Electric lighting with incandescent lamps located 18 caps metal supported by steel braces and two rows of reflectors, located in the center, illuminating the playing field, which is regulated in accordance with the requirements of the planned sporting events.