Salisbury Cathedral

Introduction
Gothic architecture is developed in Western Europe in the late twelfth century after having been under the domination and civilization of the Roman Empire.
France is the cradle of this style is from here and across Europe.
England, with its Norman kings, had possessions in France and thus was related to the movement of Western Europe. Thus both by external influences such as its own, comes to develop its own unique gothic of this country.
Situation
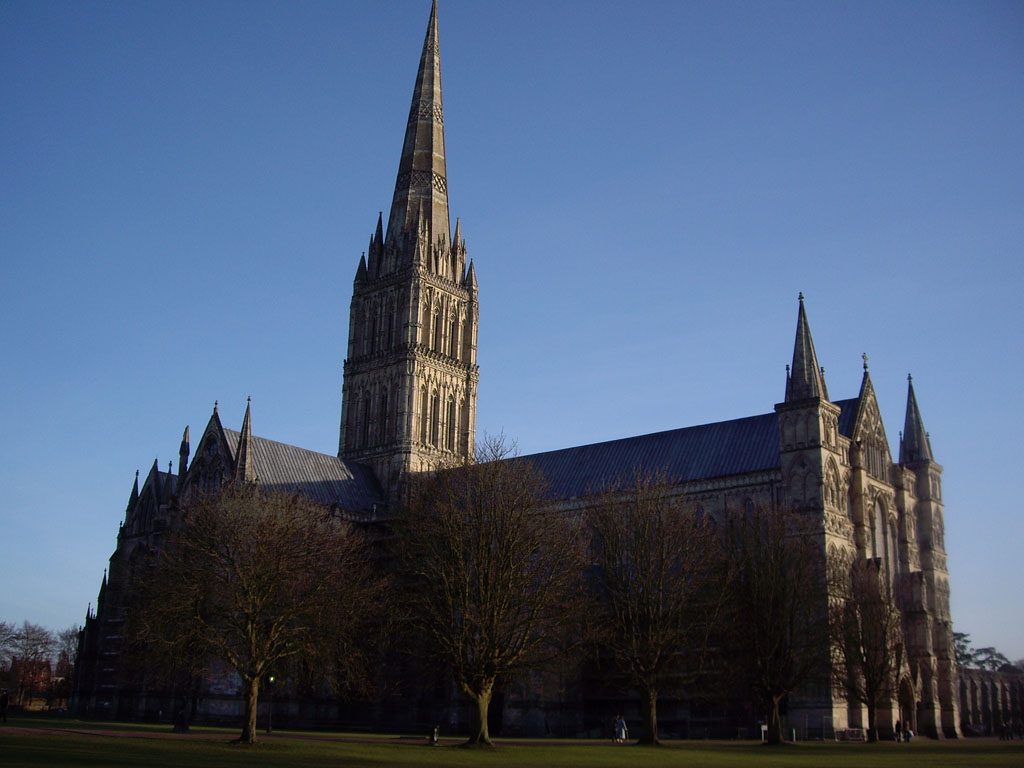
Cathedral of imposing its isolated location of buildings, located in vast green spaces, on the outskirts of the city.
This situation differs from the Gothic cathedrals of the continent that often surrounded by houses and shops, close to churches or rodeándolas, generating a hierarchy.
Concept
The great power and domination of the church that existed at the time, is reflected in the floor of the cathedral with notable additions and modifications; emerging special chapels for worship the saints and the Virgin Mary, a shrine for the further expansion increase of the clergy, deambulatorios for processions, funeral chapels and cloisters.
Salisbury Cathedral is an example of this great development of Gothic architecture, resulting in an elongated and more narrow than in the first buildings of this movement.
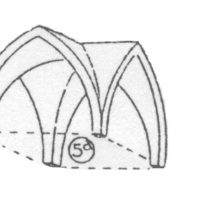
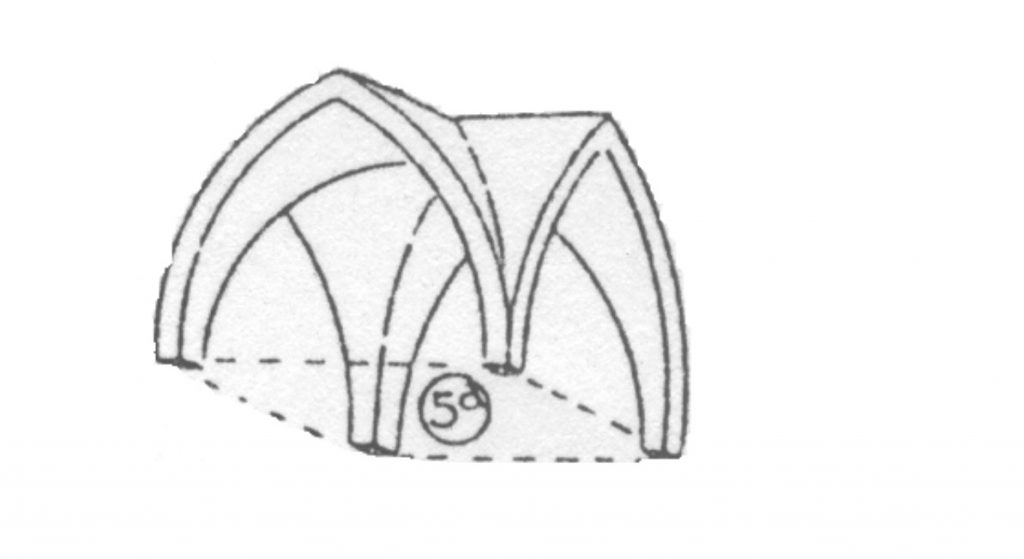
Following the Romantic that each arc of the roof falls in a support pillar in the system continue ogival these nerves become vertical.
Gothic buildings with their skeletal system, they differ from the Romans where it forms a joint constructive solid wall surrounding the building and supports a continuous canopy.
Both the Greek architecture ogival express its structure, as in both styles is essential in the artistic work. Ogival in its elements are determined mainly by its strict structural utility, and the new layout of the capital to support the super structure, such as the arches of the roof indicating its role in sustaining the nerves or ribs plementía.
Spaces
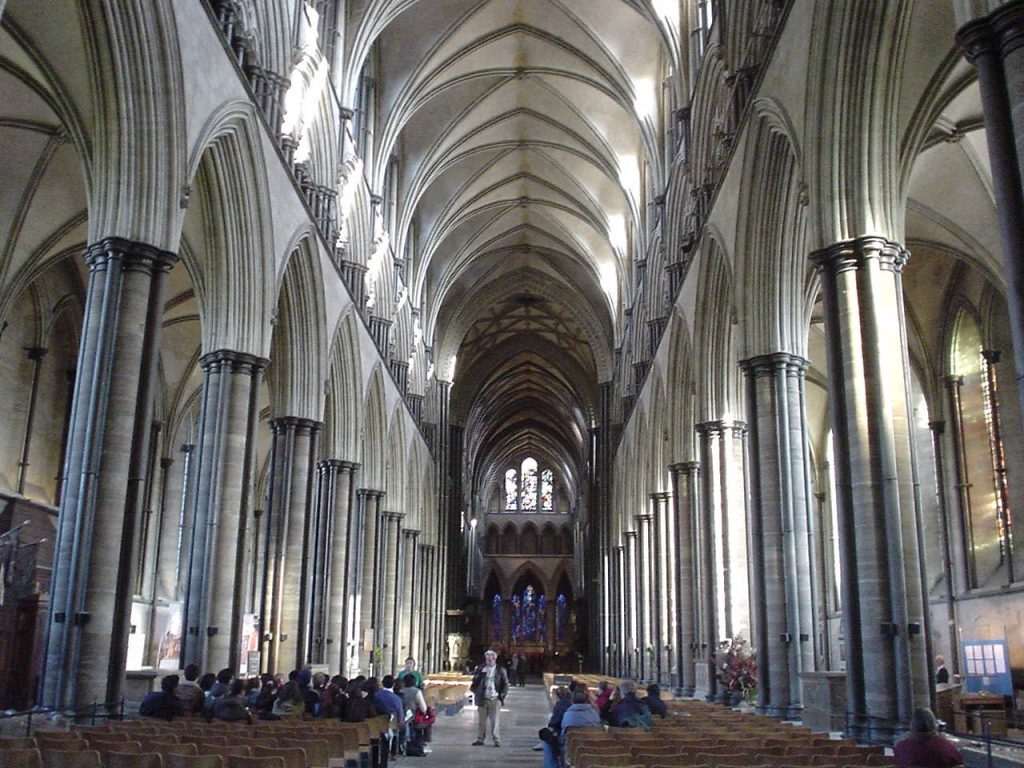
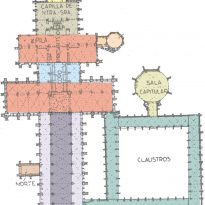
The plant is in the form of patriarchal cross with two well-marked cruisers. The main hall has a length of 142M and the transept more measured 61.5 m. The same length as the nave of the body West.
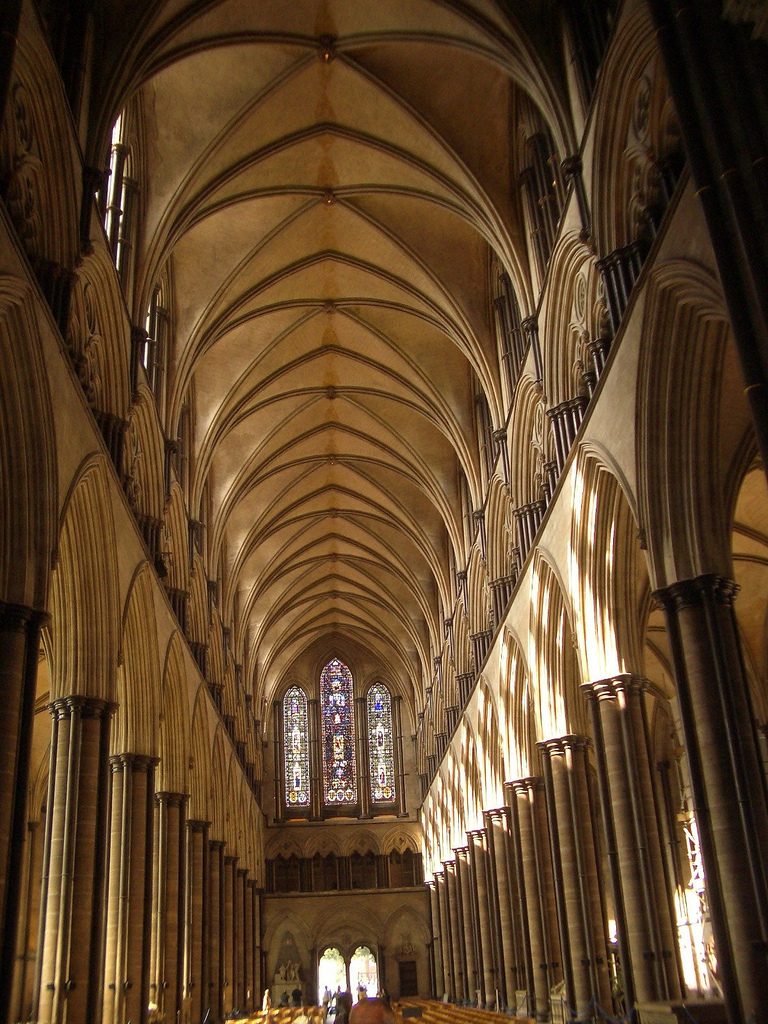
The body is divided into three Western ships: one is the largest central 12m wide and 6m two sides of each. The most important part is the head flat, very typical of British buildings. After the head is the presbytery. Is located between the two transepts a small choir. All the cathedral is built with quadripartite ribbed vaults.
In the year 1284 SHALL BE AFFIXED a large cloister. It is dominated by a central building polygonal plant built in 1263 call chapter house, which rests on a single umbrella central pillar.
At the junction of the nave and transept more highlighted a flashlight (tower crowned with a needle that is over 120m in height).
The main entrance is N to S is where a gate guard.
Structure
Ogival structure is divided into parts (which are the nerves, pillars and buttresses buttresses) and passive parts (formed by closing the walls, large windows and elements).
The structure is a skeleton made up of pillars, buttresses, ribbed vaults and arches. The thrust of the vault is due to their oblique arched shape, which is transmitted to the robust buttresses by transporting buttresses outside. The efforts are the vertical buttresses and pinnacles located above these gravitatoriamente for overloading.
Materials
The inner wall of the nave is divided into three levels: the first part called “Arcade”, where the pillars separating the ships and walls bear arms. Above is the “triforium” formed by a gallery with no windows surrounding the church through the pillars and in the space corresponding to the lower deck of the ship. Finally, in the upper part is located the “Clerestorio” where there is a composite archery with high windows that illuminate the ship and the system of ribbed vaults can be raised to the height of the espinagada. On the roof of a covered timber and very high slope.
The ongoing constructive approach as the Roman, where the arches are built as permanent cimbras on which then puts the thin elements.
The capitals are simple moldings and a very marked color contrast in the interior, through use of black marble in certain areas.
The facade of the building is made with sillarejo or small blocks due to the ease of transportation.
In this cathedral windows were expanded to encompass the entire space between the buttresses, covering windows with color biblical episodes.