Notre Dame Cathedral

Introduction
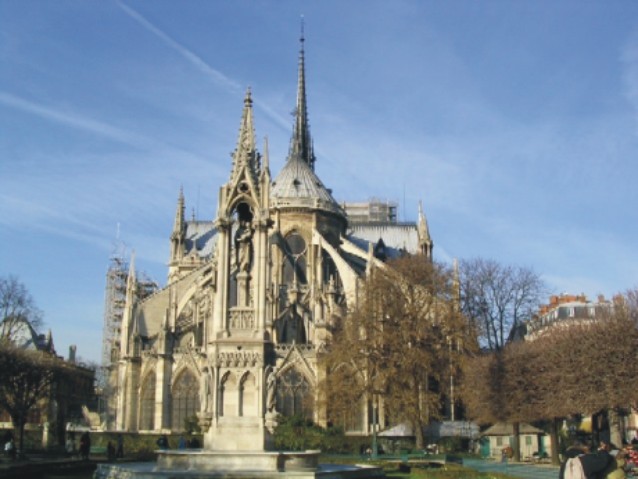
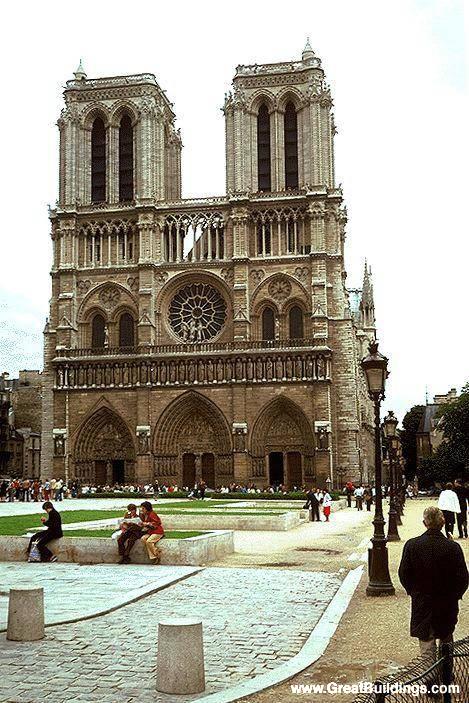
Notre Dame de Paris is undoubtedly one of the symbols of the city. While not the largest cathedral in France, is one of his most remarkable Gothic art.
Bishop Maurice de Sully began construction of the new cathedral from 1163 on the site occupied by a former church dedicated to St. Etienne.
The construction coincided with a period of prosperity and increasing dominance of the city, so the work should reflect this power. Thus, the building was done without interruption because of economic problems, but only ended in mid-fourteenth century, after many changes and interventions by different architects and craftsmen.
The cathedral underwent many changes and restorations, the most significant undertaken in 1844 by Viollet-le-Duc and Baptiste Lassus, which lasted 23 years. More recently, in 1965, excavations under the cathedral revealed the existence of the catacombs of Roman and medieval rooms.
Victor Hugo wrote in his 1831 novel “Notre Dame de Paris”. His poetic illustration of the architecture of the cathedral enabled many to discover a different way.
In 1804 he was crowned in the cathedral Napoleon Bonaparte in 1909 and was beatified Joan of Arc.
Particularly emphasizes its magnificent Cavaillé-Coll organ,
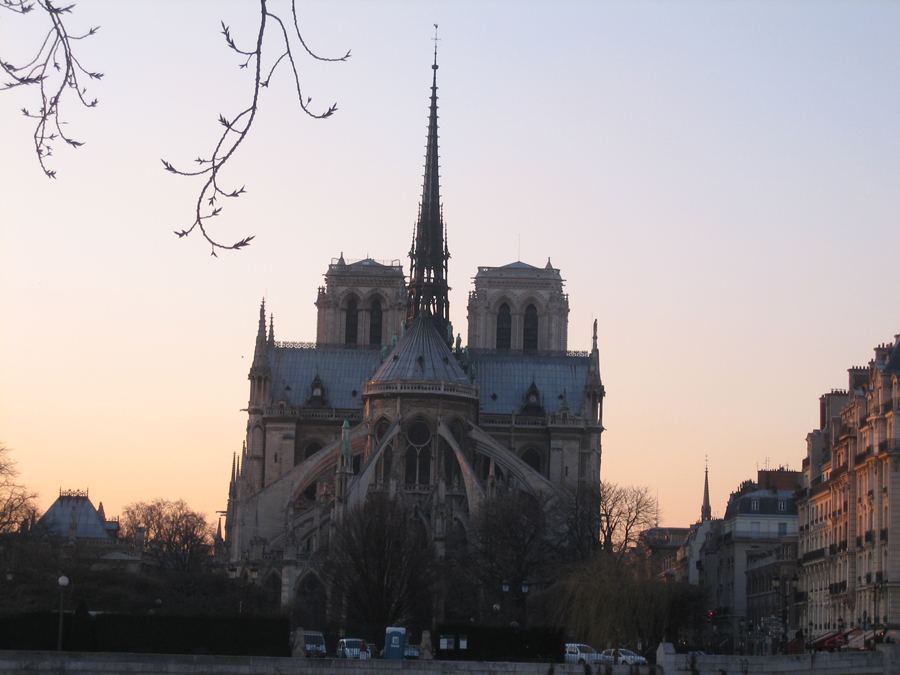
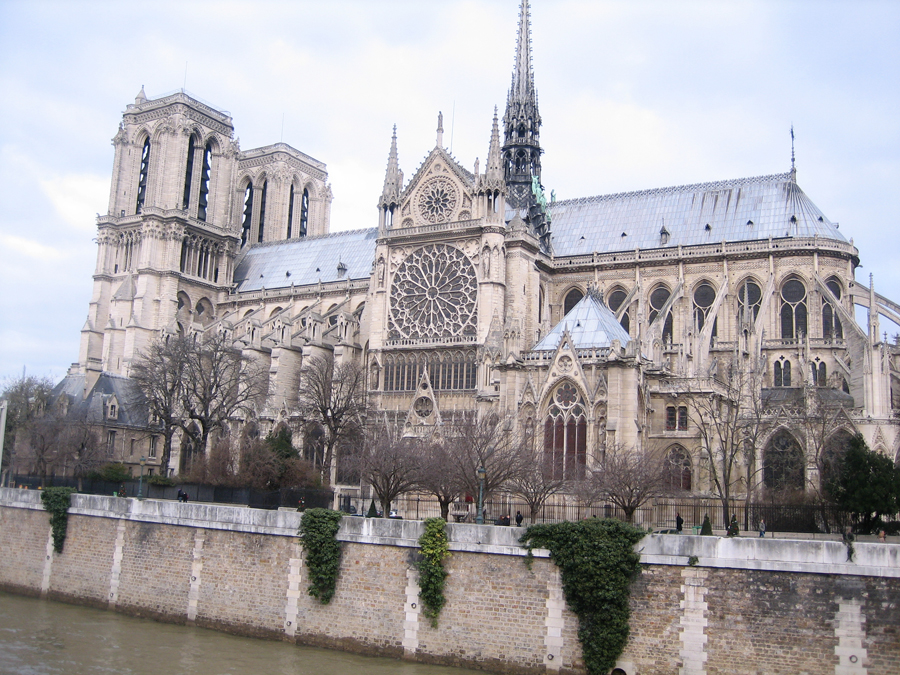
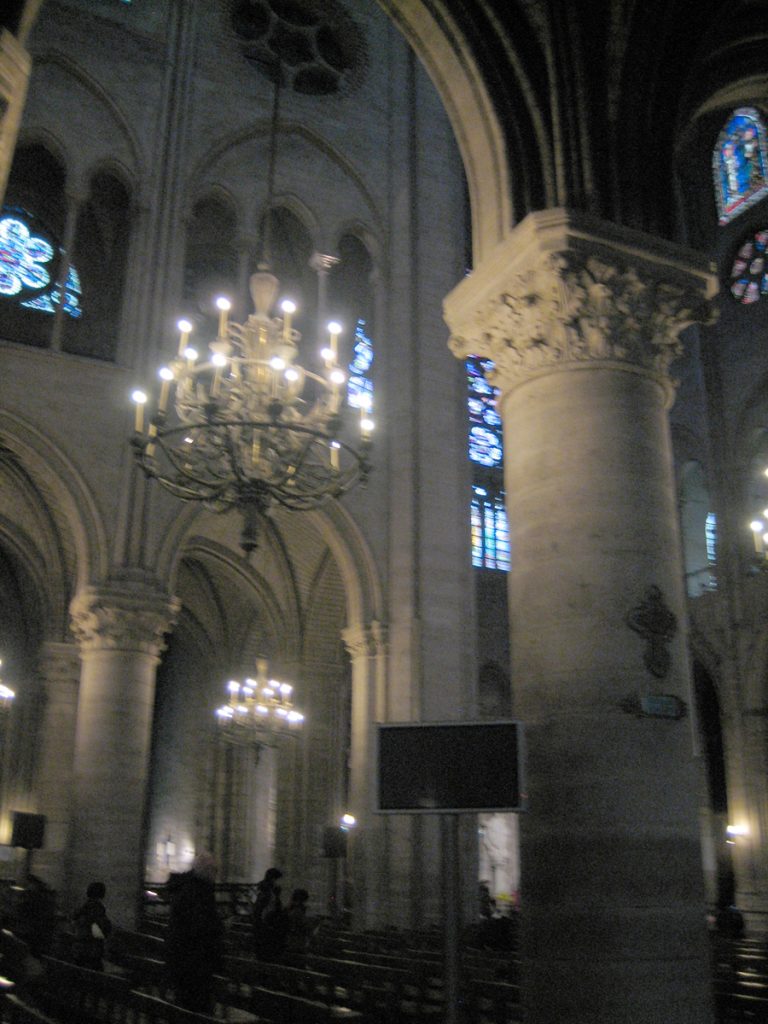
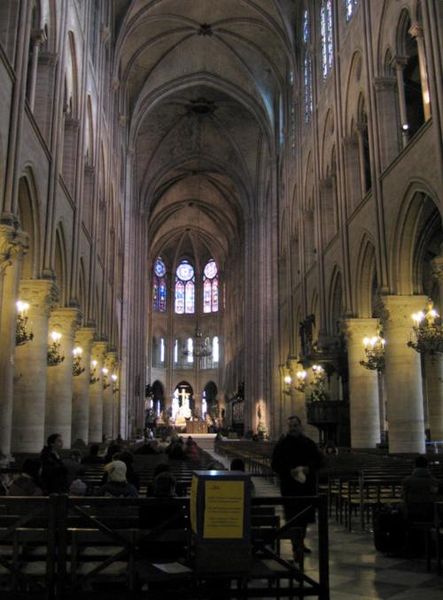
Like most Gothic cathedrals, is dedicated to the Virgin Mary. Is notable for its large size, the regularity of its elegant design and the introduction of a new technical element, the flying buttress.
Situation
It is located in the eastern part of the Ile de la Cité that by their defensive situation is giving rise to the city of Paris.
It is surrounded by the river Seine, with gardens front and rear. Its facade looks toward the west and overlooking the square Notre Dame, where the zero point from which all distances are in France.
Concept
There is even a cathedral in this duality of stylistic influences: one is reminiscent of Norman Romanesque, with its strong and compact unit, on the other hand, and innovative use of Gothic architectural changes, which give the building a light weight and apparent ease in building vertical and support the weight of the structure (with the skeleton of structural support visible only from the outside).
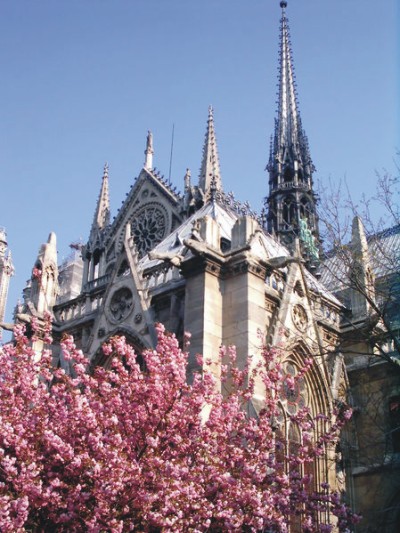
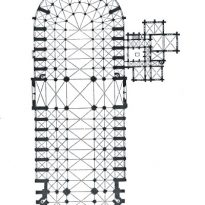
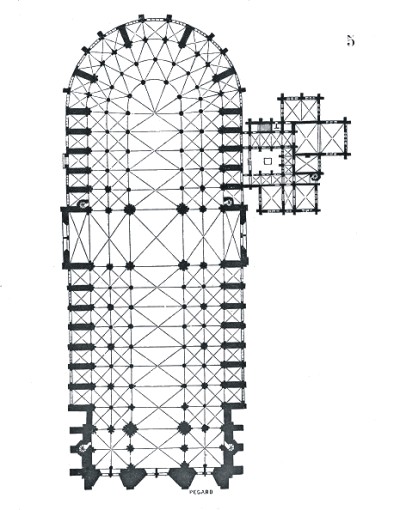
The plant is demarcated by the Roman cross training oriented to the West, increased longitudinal axis, and is not noticeable from the outside. The cross is “embedded” in the building, surrounded by a double ambulatory, which circulates in the choir at the top (east) and runs parallel to the ship.
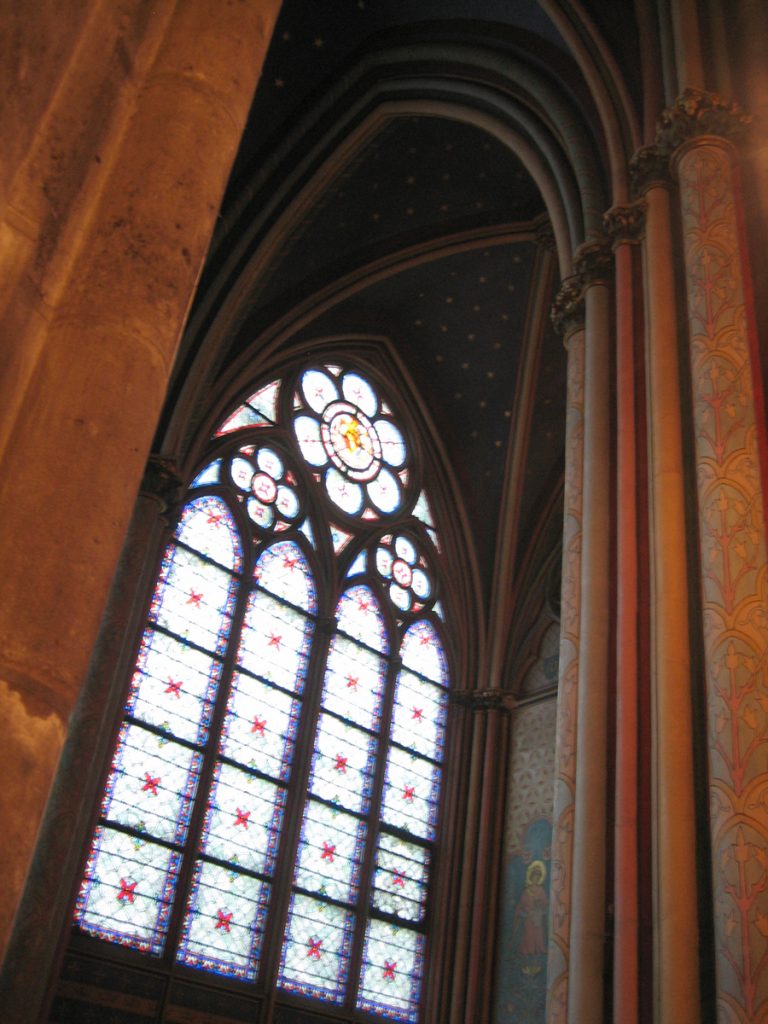
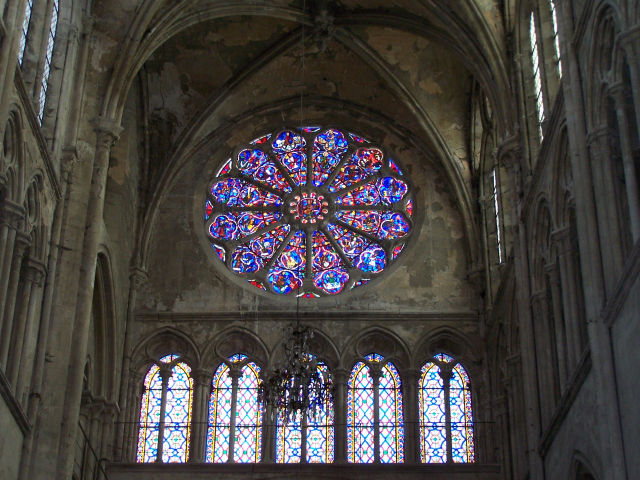
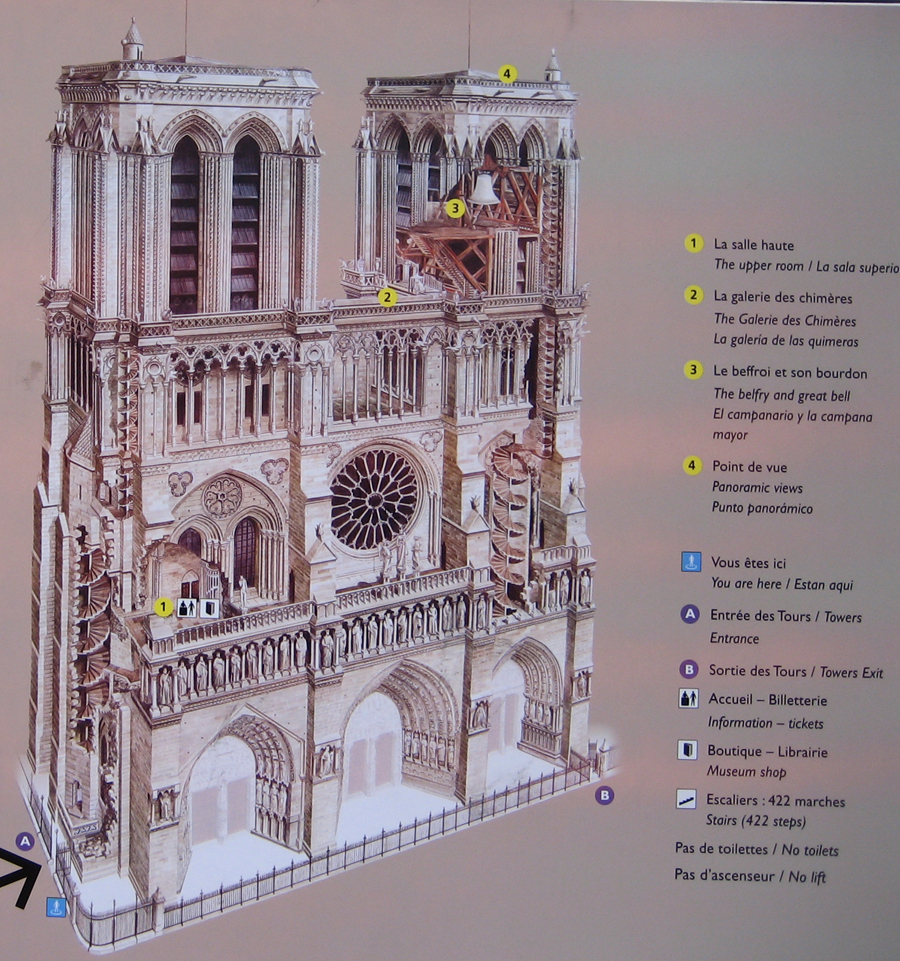
Besides the plant in the form of a cross, the cathedral has a facade of 40 meters wide, a length of 130 meters and a maximum height of 69 meters. Contains 5 ships, 37 chapels, rose 3 to 13.5 meters in diameter each and a total of 113 windows.
Facade
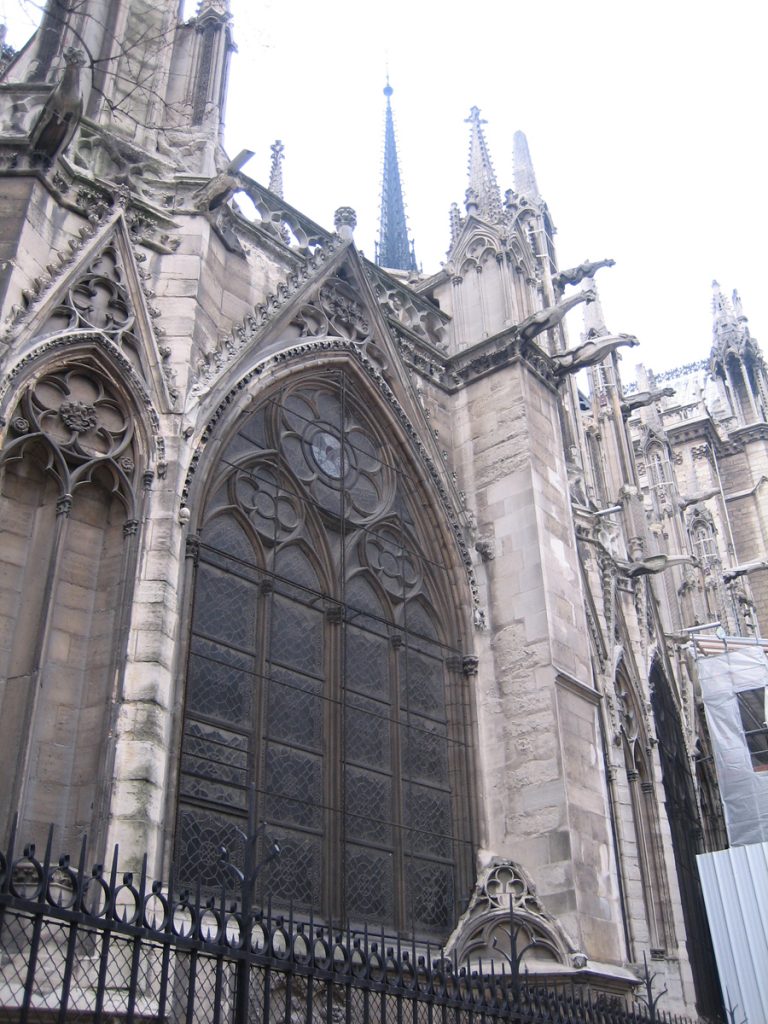
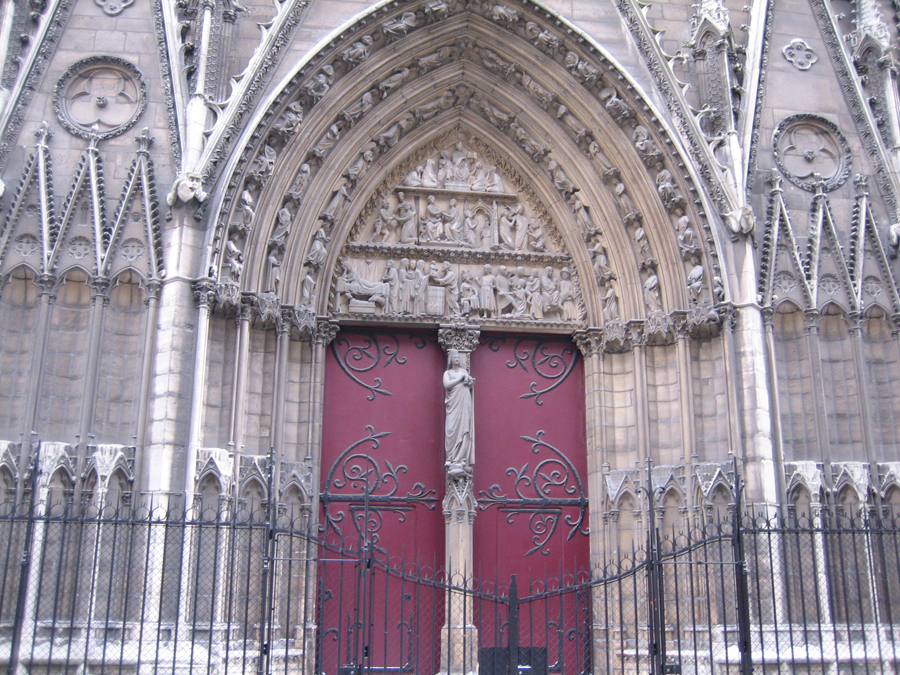
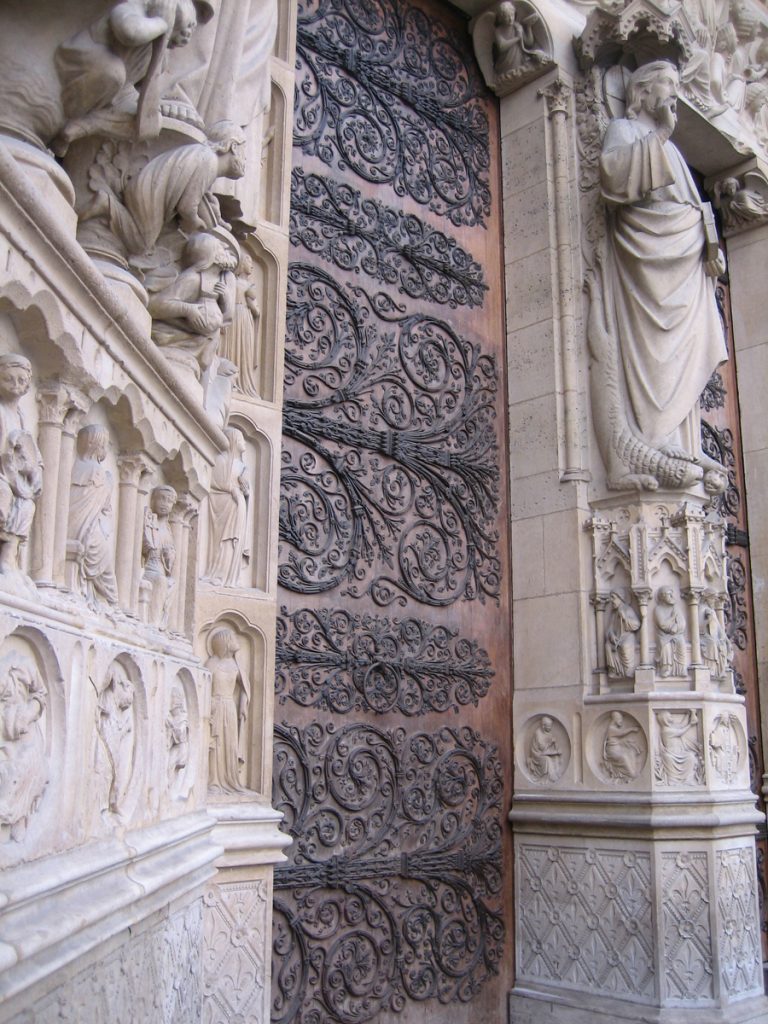
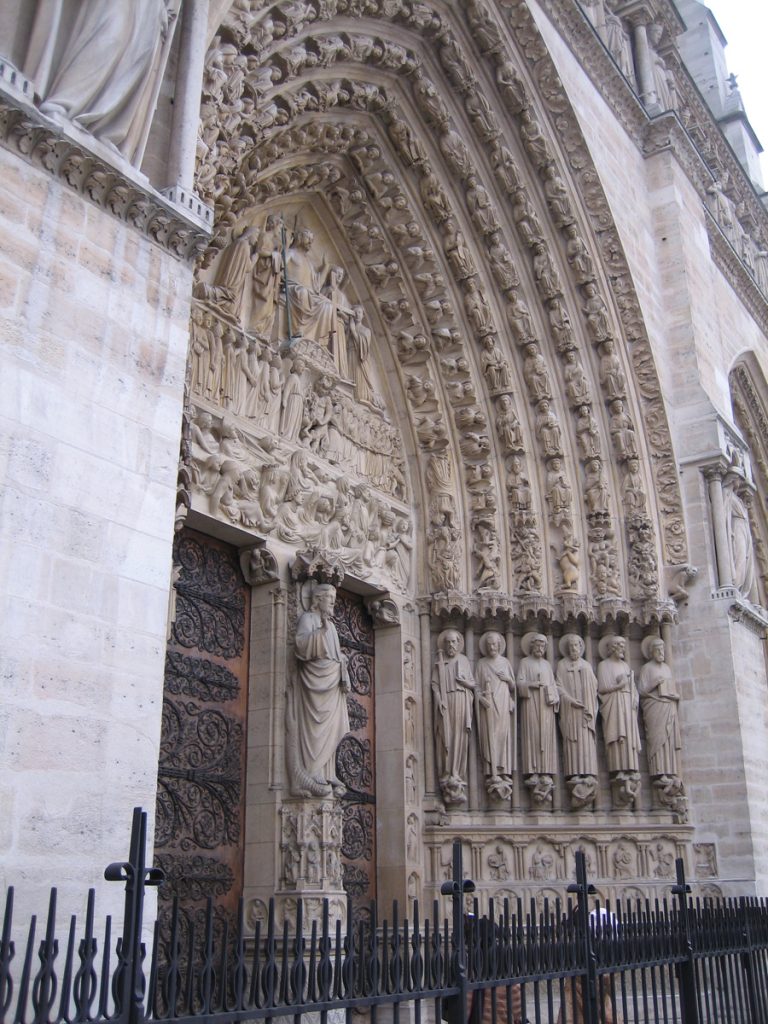
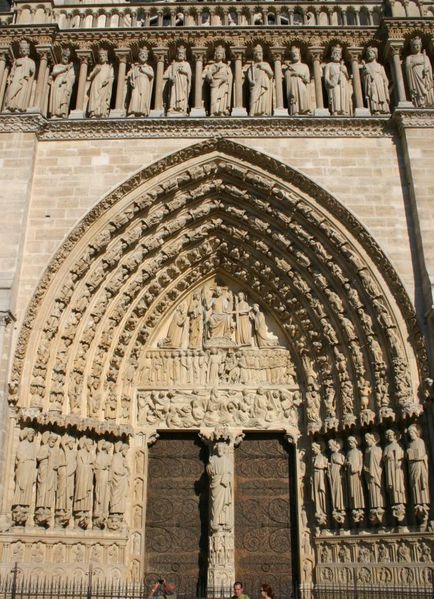
The facade has three big portals. The Portal of Reckoning, the most important center displays sculptures representing the resurrection of the dead, an angel with a scale to weigh sins and virtues and demons who steal the souls sinful images that undoubtedly will have great weight in the unconscious popular in the Middle Ages. The two sides were websites dedicated to the Virgin Mary and St. Anne, her mother.
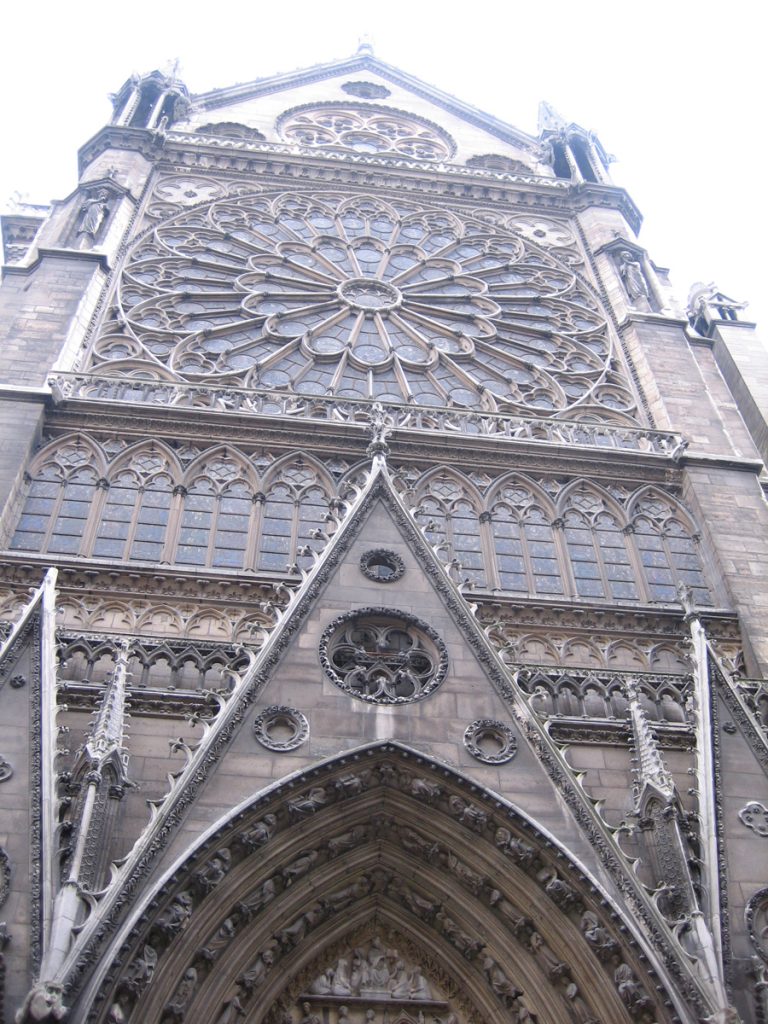
At the front are trying to balance the verticality of the two towers, which correspond with double aisles of the temple, with the horizontality of the bands and galleries decorated. Show, therefore, a tripartite standard when they are within the five ships of the church. Their share has two squares that stand in the middle of its height. The vertical axis of symmetry divides it into six squares and the height and width ratio is 3:2.
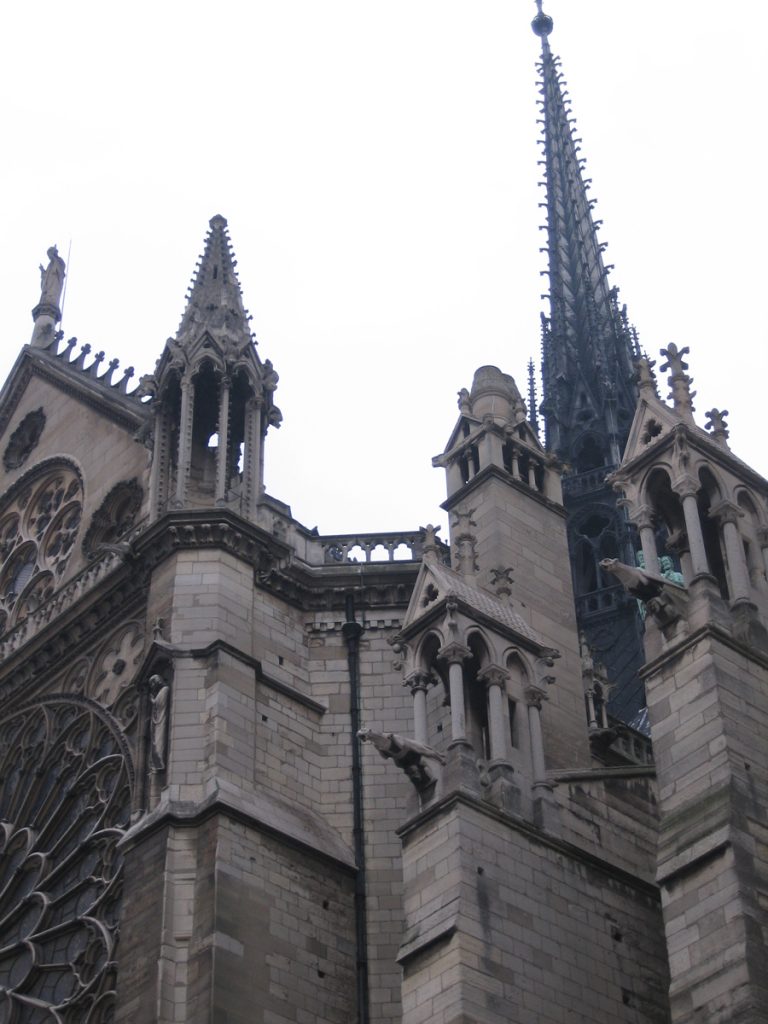
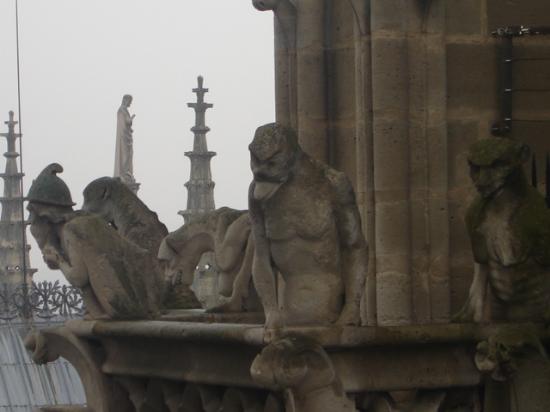
At about 20 meters above the ground, a gallery with 28 statues rises above the portals. Each statue, 3.5 meters in height, representing the 28 kings of Judea before the coming of Christ. Of the original medieval statues are only fragments, which were destroyed during the Revolution were to believe that French kings.
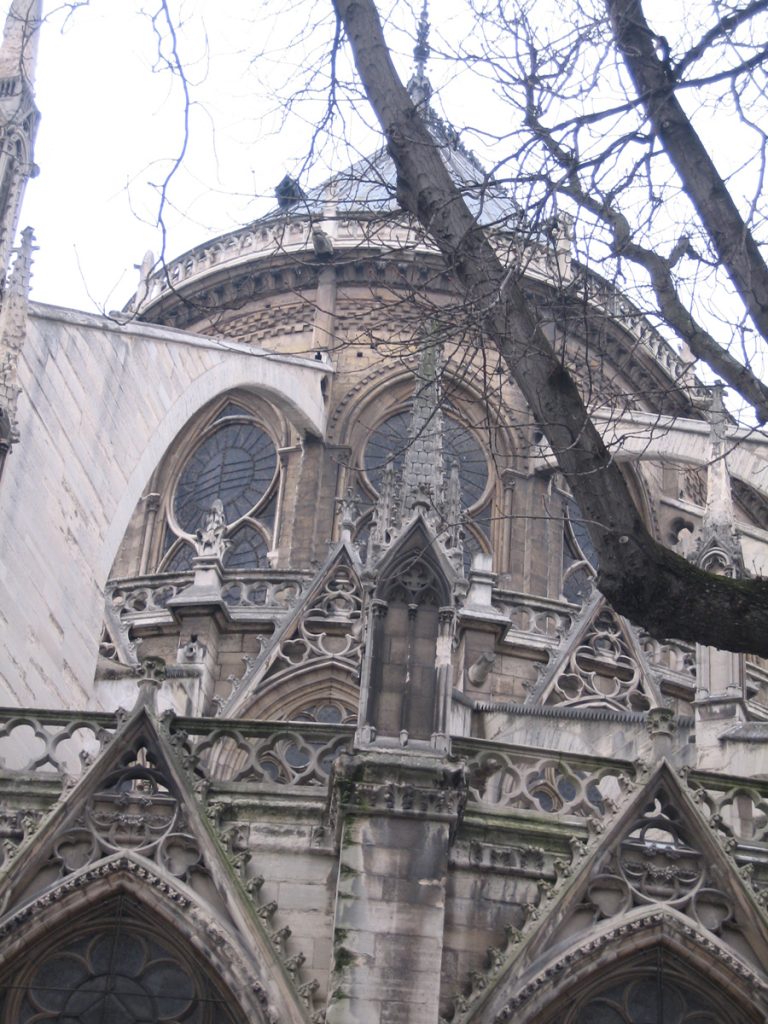
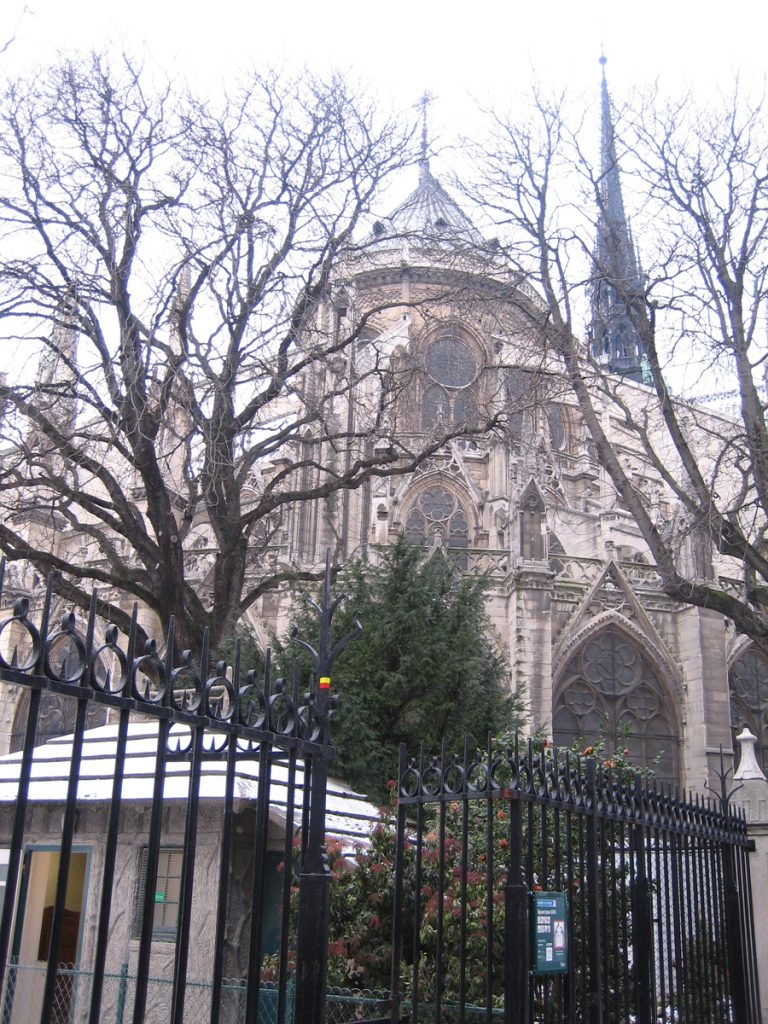
On the central portal highlights the large circular stained glass window of the rosette of nearly 10 meters in diameter, one of the most notorious of the facade. However, this window is not the biggest of the cathedral, as the north and south facades have windows of 13 meters in diameter. Above the wall, a row of columns and then the two bell towers to complete the west side.
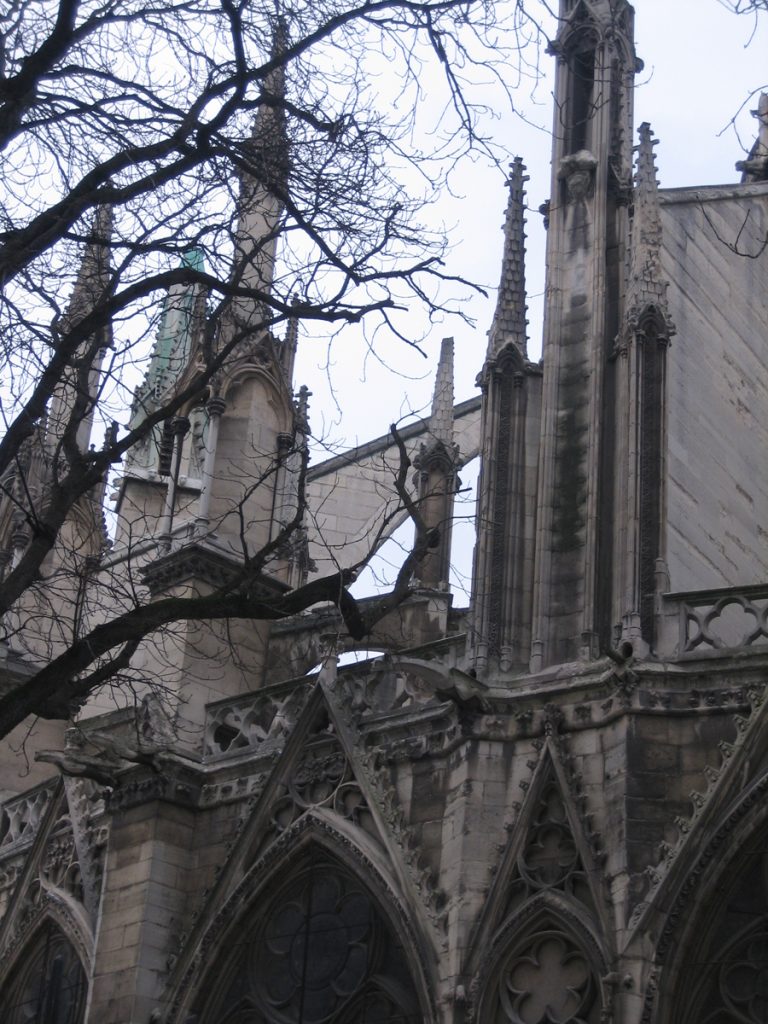
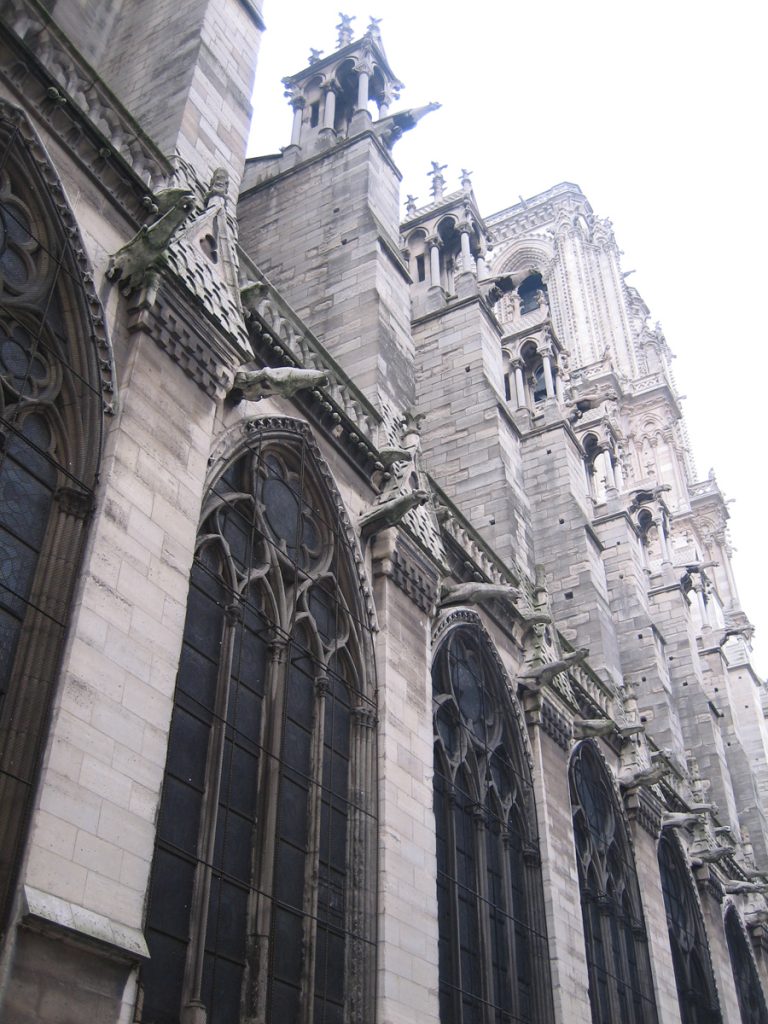
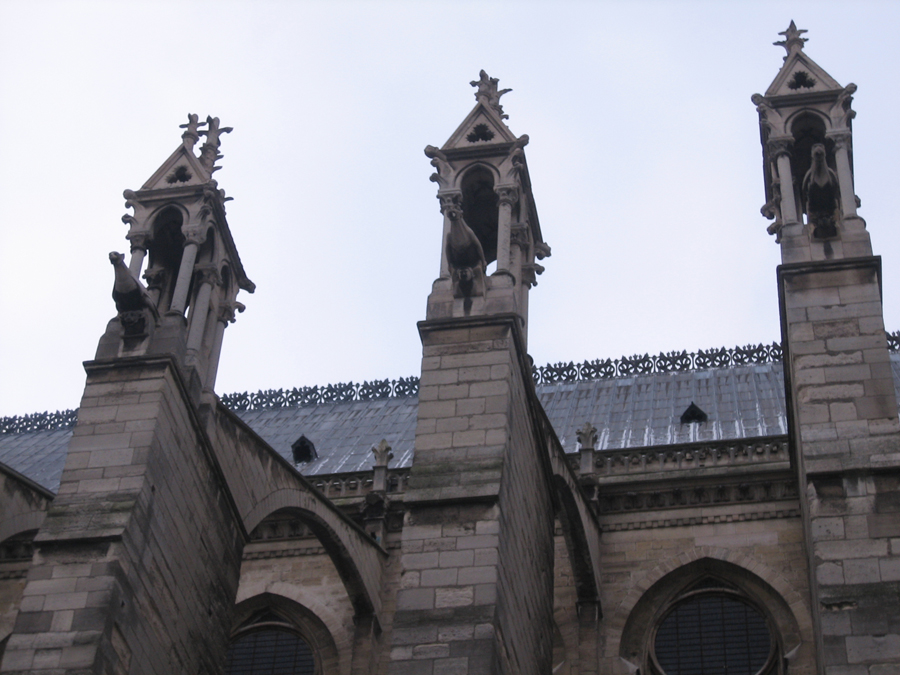
Also highlighted in this cathedral, the gargoyles of the facades.
Structure
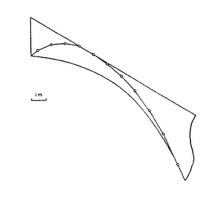
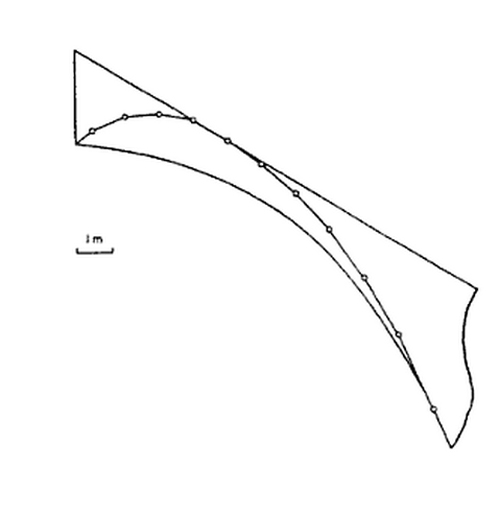
He joined the new system here Gothic flying buttresses and spurs, the only one capable of downloading the thrusts of the high nave.
The buttresses were introduced to 1175, when carrying out preparations to hold the vaults of the nave. At the start of the main hall, it was decided to increase its height over 2 meters. This caused the system to counter the main vault, through the roofs of the aisles, is inadequate. Solved by external buttresses and used early in the twelfth century.
The buttresses of the ambulatory holding the wall at two levels: the upper arm stabilizes the inner wall of the ambulatory, offsetting the thrust of the vaults. The lower arm under the exterior walls.
The height of the nave and the relative thinness of its walls (1 meter on average) demanded the placement of exterior buttresses to counter the lateral thrust of the vault. Thanks to the vault, the loads are concentrated in specific points, the pillars, allowing the wall and fill desmaterialice large glass surfaces. In the thirteenth century the windows were enlarged body height (claristorio) to get more natural light into the interior. This was made possible by the improvement of the Gothic structure.