Micaela Bastida’s Park

Introduction
The project is the result of a national competition held in 1996. Also included the recovery of the Costanera Sur and Puerto Madero boulevards (works already constructed).
It is named for the wife of Jose Gabriel Condorcanqui Tupac Amaru.
For architects who designed it, the reason for the construction of gullies is purely cosmetic reasons. They argue that “the best parks in Buenos Aires are built in canyons oriented north or east.
Location
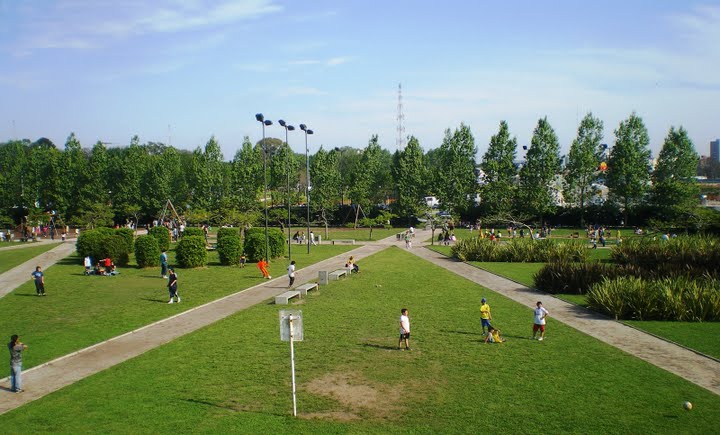
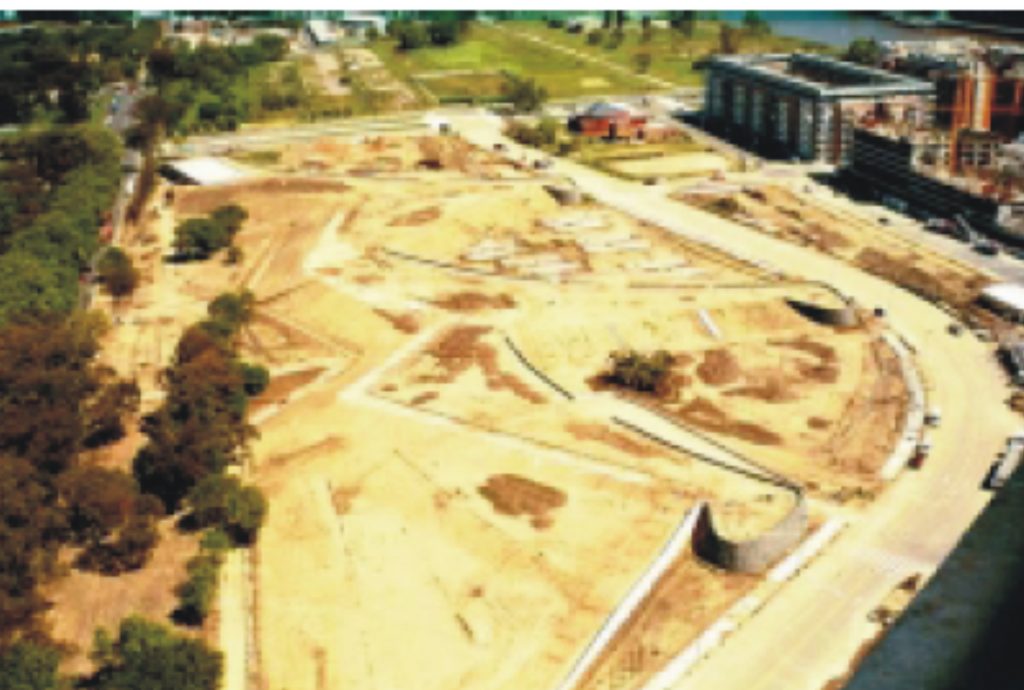
It is located in the eastern sector of the Dock 2 in Puerto Madero. It is the large park in the area and was first built. Opened in January 2003, covers an area of 72,000 m2.
The border: Av Rosario Vera Penaloza, Julieta Lanteri and Calabria Avenue,
The park is bordered on one side by the docks and canals where they formed a circuit exclusive luxury restaurants, prestigious office buildings and hotels. On the other side, the Paseo de la Costanera Sur, is visited by the middle and lower classes.
Concept
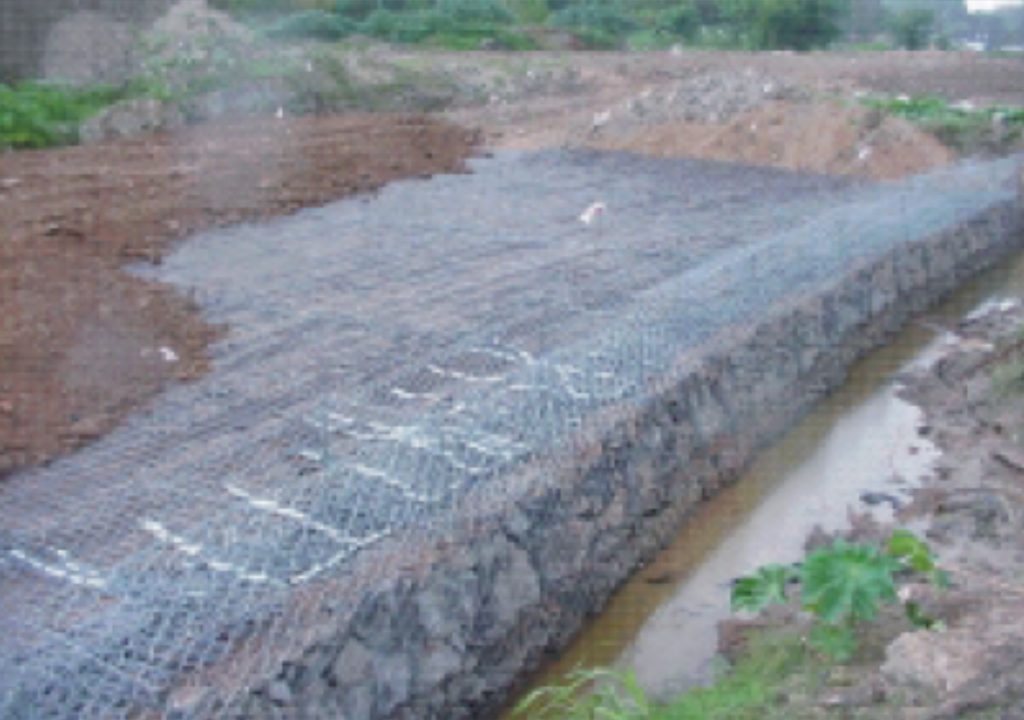
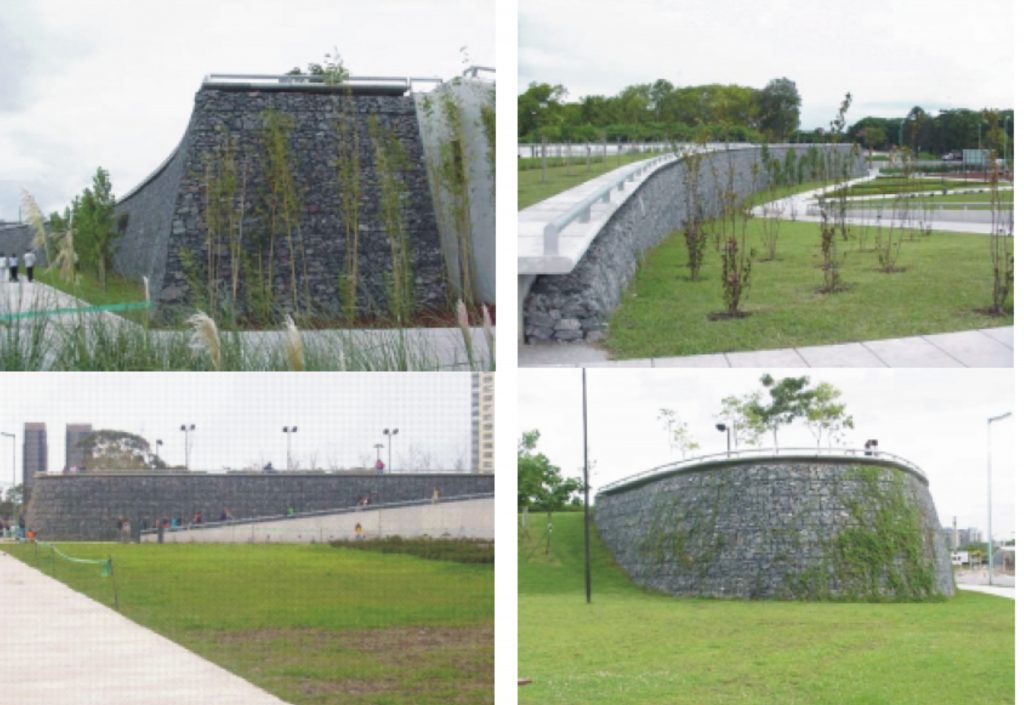
It is characterized by great dynamism that give the slopes of three hills, 5 feet high, contained by gabions (stones wrapped in wire mesh) and the zig-zag path which crosses from north to south, articulated by stairs and ramps.
Spaces
It is designed on two levels, one higher on the street Julieta Lanteri and a lower adjoining Costanera Sur. The upper part is divided into three areas: Plaza de los Niños, which features games, Central Square (south rose garden) and Plaza del Sol, separated by gabions.
In the Plaza of Children play area complies with innovative design using wood.
In the Plaza del Sol have provided large 2x2m wooden benches that are used by people to sit or lie down and sunbathe.
Ramps and paths through the park, offering travel alternatives.
Vegetation
In the park, forestry, landscape advice of an agronomist Fernando Gonzalez, was used as a design element spaces. Children’s Square, is protected from the street by a row of Leyland cypress, the central plaza or Rose Garden of the South, with 3884 rose bushes, color-sectored, and Plaza del Sol, was worked with grass.
It is mostly planted flowering trees, as though the use of worn out people’s gardens, flowers remain the same. Afforestation integrates with most native species: jacarandas ceibos, sticks drunken cow hooves, ibirá-Pita, lapachos, timber and tipa. The 40,000 trees and shrubs, 150 different species to create a great green mass that forms a forest (to the street Calabria) and places with little privacy, where among rows and rows of poplars little ones will be created. Towards the river, includes the planting of 2,500 new trees.
Levels
To access the upper stairs were built and three ramps. The upper area consists of a large square granite tiles dry, too zigzag.
The bottom is the most populated by plants and shrubs that give color to the sector. The lawn is interrupted by shell paths, accompanying each of the falls in the Coastal.
Furniture
It comprises: wooden benches and cement, and pallets, as well as bike racks, trash receptacles and drinking fountains. In all cases abound.
Chairs were also installed in a circle like to make friends told a mate, and trunks of trees for use as seats.
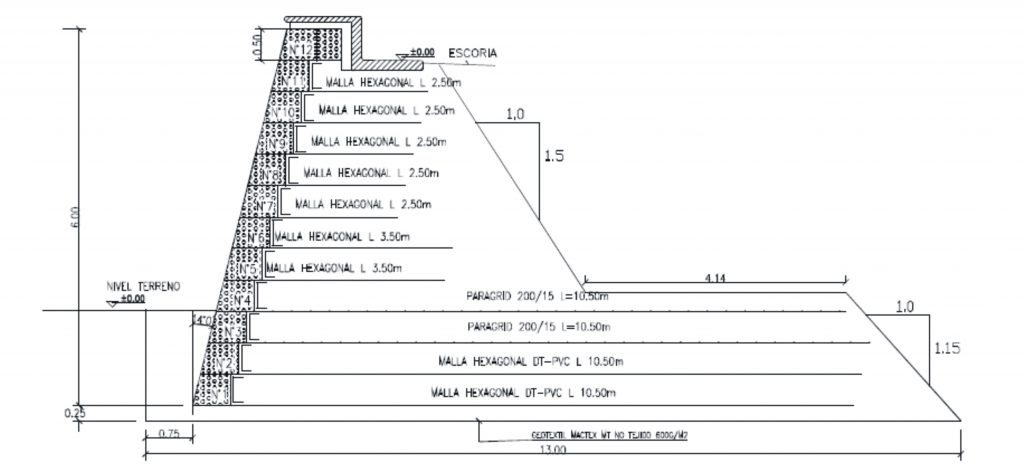
The retaining walls
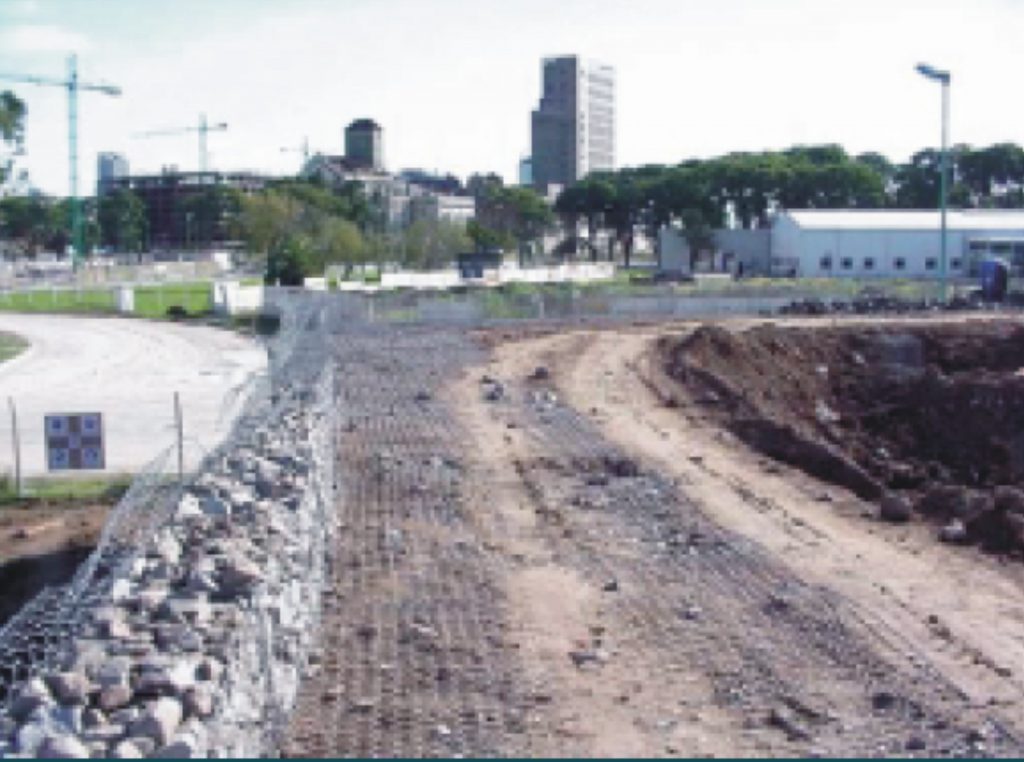
One problem was to break the monotony of a totally flat landscape. This was achieved in the 70,000 m2 of the park with the creation of different slopes formed by earth mounds. These are supported by soft ground and needed to be stabilized and content.
Is the solution through reinforced soil structures.
Because the will to achieve environmental integration, simplicity, speed and fitness constructive architectural external wall surfaces of the walls should be inclined 14 degrees from the vertical.
To support the soft soil of the terraces were not compromised by the load, were applied on the basis of these geogrillas resistance of 200 kN.