Hyperbuilding

Introduction
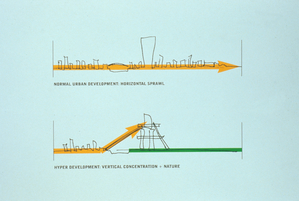
This theoretical project is the creation of a mega city-level structure. The proposal, which was planned as the next step in the world of architecture and urbanism, should not necessarily be a high-tech construction. Even need of technology for development, hyperbuilding should be based more on basic principles of architecture that try to solve all based on technology. The elemental simplicity should send over the implications of high-tech.
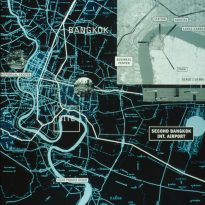
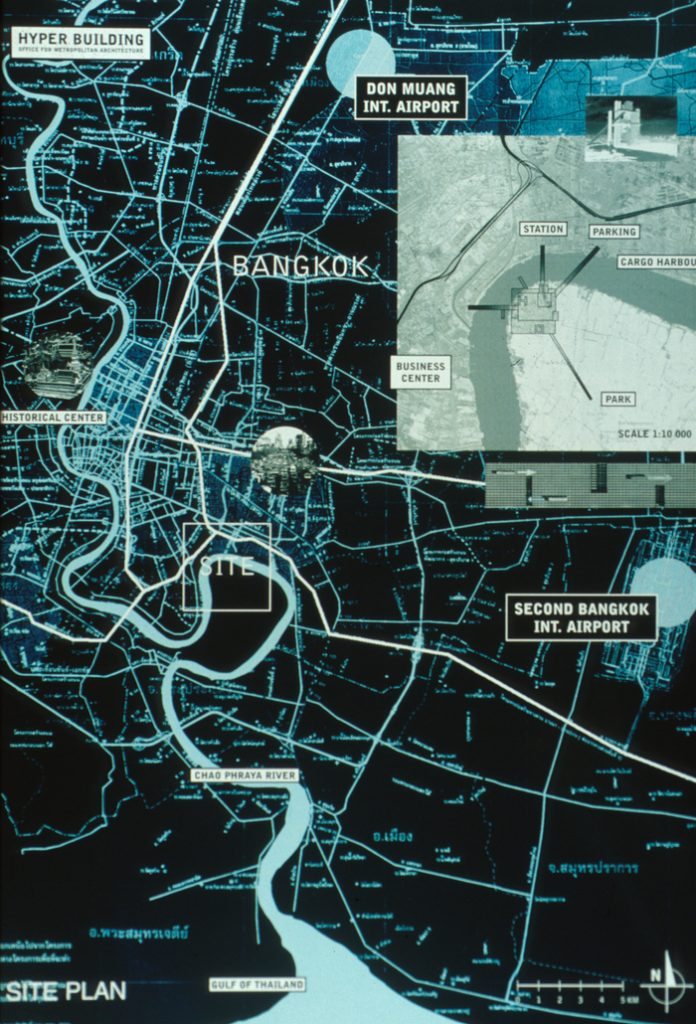
For commissioning work from this study virtual city was chosen Bangkok, Thailand. This location was suitable because of its extreme situation. From the point of view of traffic, the political circumstances and growth, Bangkok was a city in crisis susceptible host this type of intervention. The hyperbuilding could adjust to these circumstances, shortening, for example, travel time between the residence and workplace of its people, and creating a place to be.
“A city on the limit of what is tolerable (that) offers the perfect context in which to test these theories.” – OMA
Location
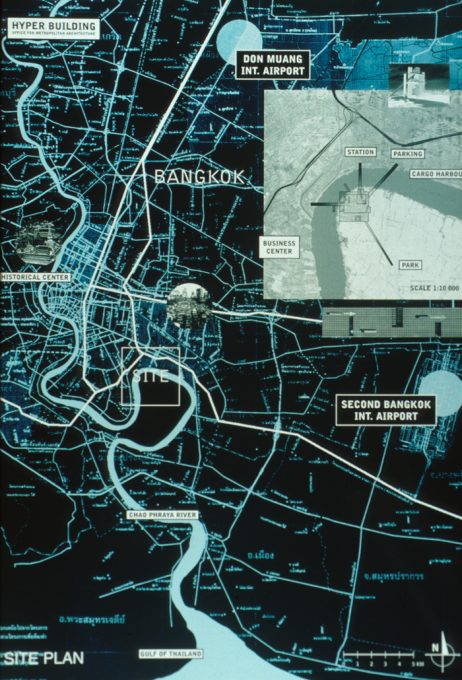
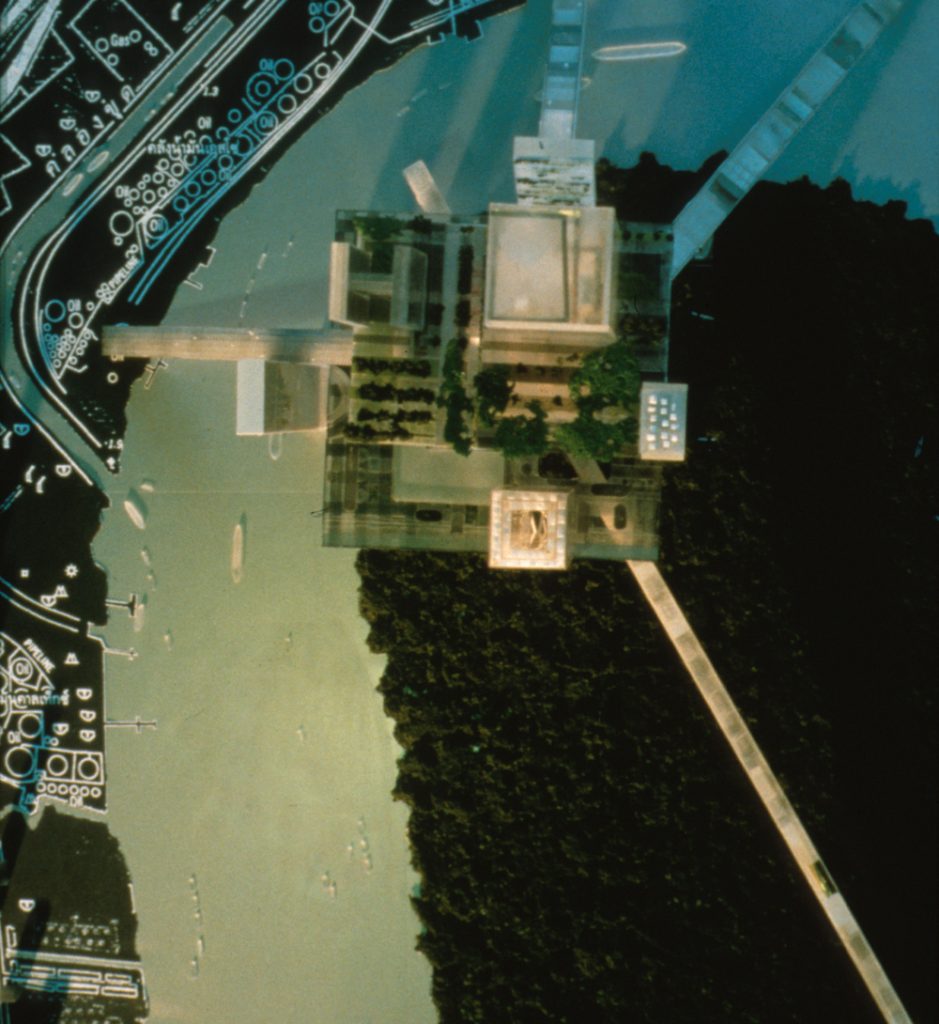
The hyperbuilding stood at Phra Pradaeng, a green reserve located on the west bank of the Chao Phraya River from the city of Bangkok. This pristine environment could work well with high density that the proposed hyperbuilding. He was also well connected with a new retail and office area through major urban infrastructure.
Concept
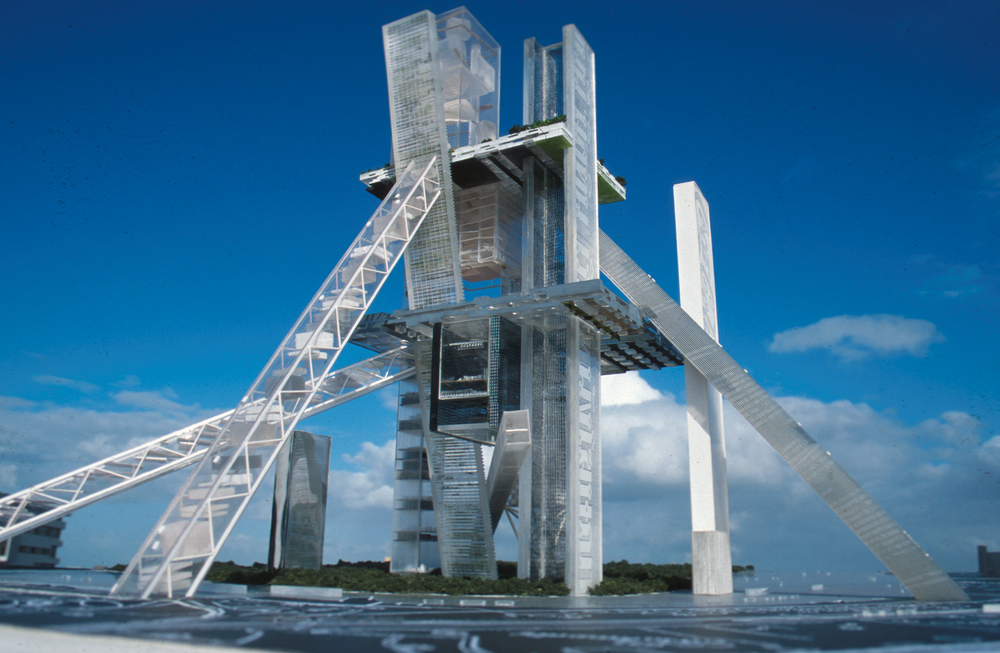
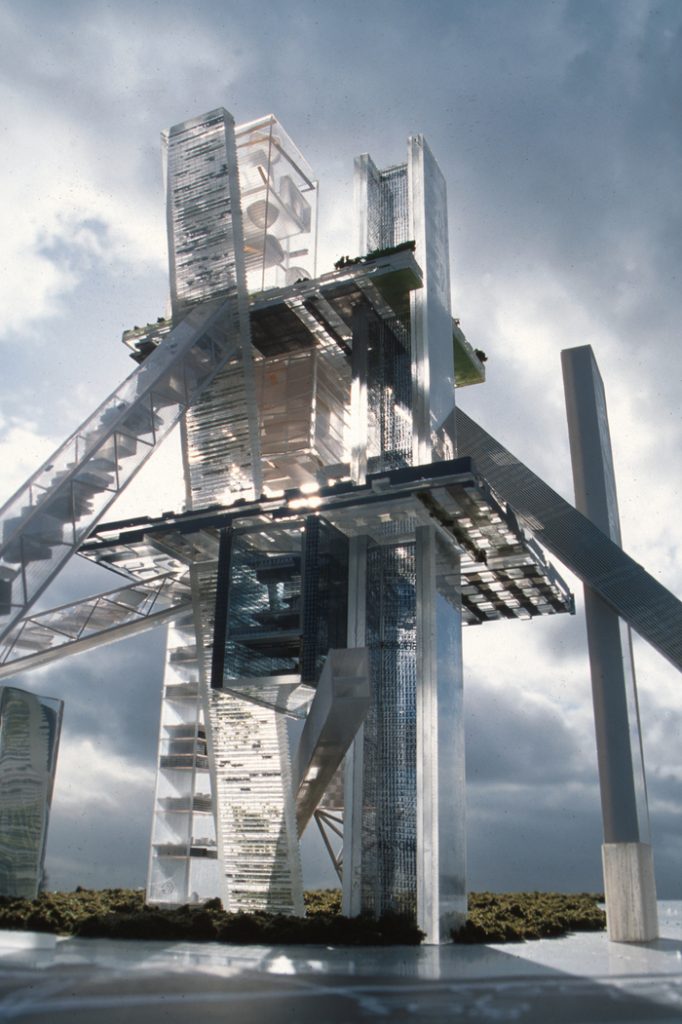
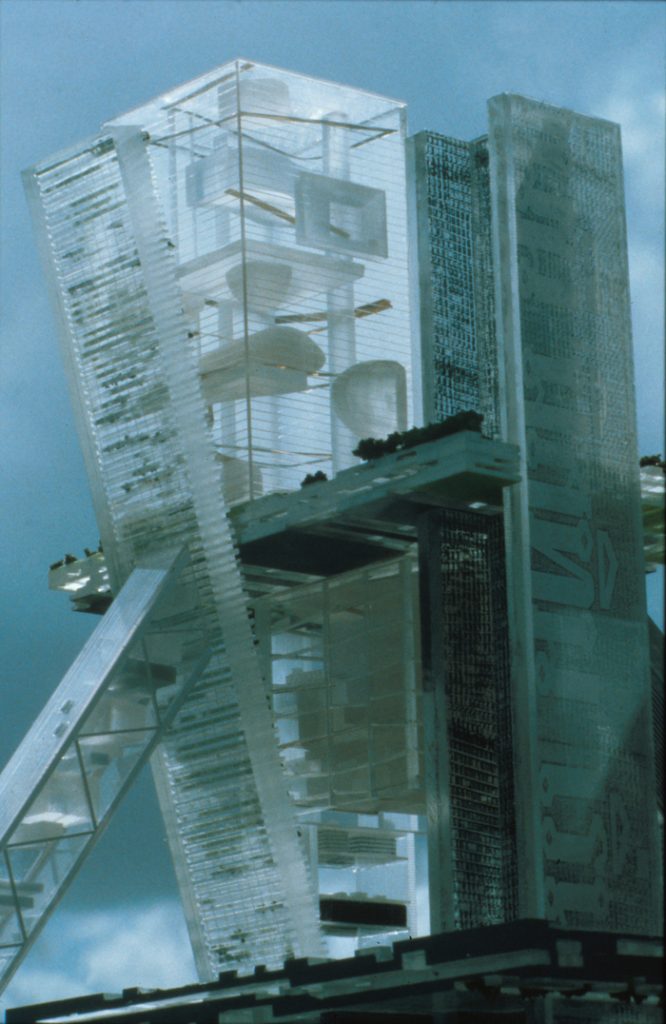
The hyperbuilding means architectural, urban and structurally as a whole. It seems the union of several buildings and systems into one larger in which all aspects are integrated together. Overall stability, access, circulation and services are organized collectively in this new neighborhood or city.
Spaces
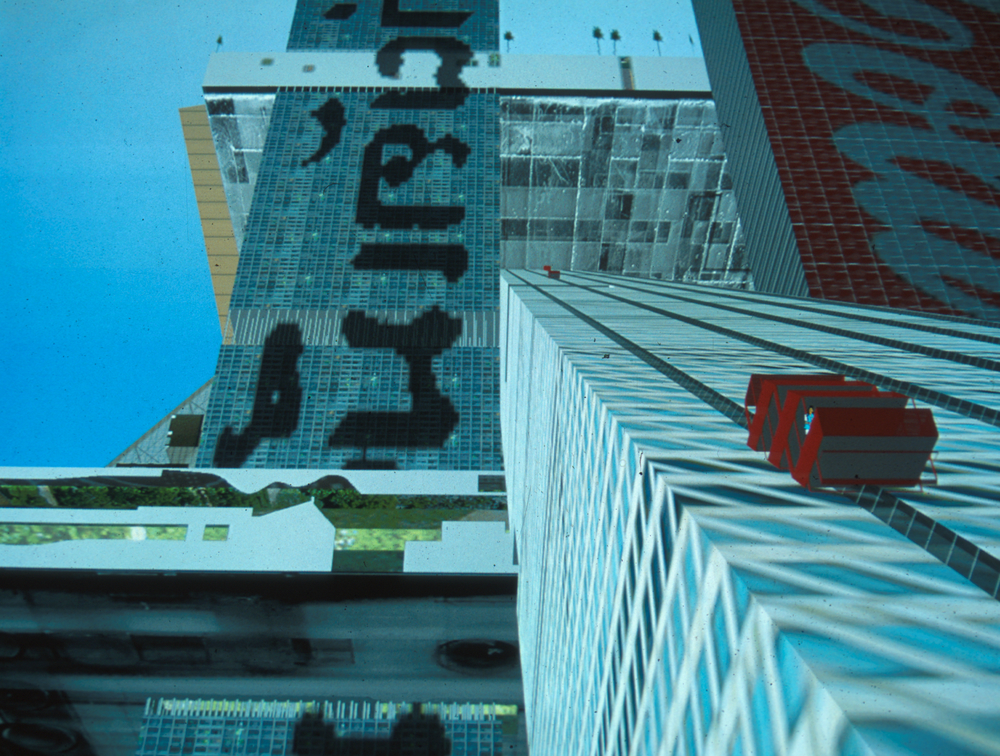
To achieve the complexity involved in a city, the hyperbuilding makes a metaphor for this, making construction elements in representative parts of the city. In this way, the towers could be seen as streets, parks and horizontal elements, volumes, neighborhoods; and diagonal boulevards.
Program
The hyperbuilding presents the scene of a self-contained city but in relation to the surrounding environment. It proposes a space in which 120,000 people would move daily from one place to another, from their residence to work. Through placement of a series of thin towers, the assembly prevents deep dark cores of conventional towers, creating space for the program nodules.
- Residential – 5,520,000 m²
- Public space – 3,500,000 m²
- Offices – 781,000 sqm
- Education – 432,000 sqm
- Theatre – 400,000 sqm
- Industrial – 371,000 sqm
- Commercial – 128,000 sqm
- Restaurant / Bar – 120,000 sqm
- Hotel – 88,000 m²
- Museum / gallery – 80,000 m²
- Total – 11,420,000 m²
Circulations
The hyperbuilding has several connection systems: between it and the street and between hyperbuilding own with its different levels. Boulevards has four ski lifts, gondolas and trains lift for connection to the city at ground level. For internal circulation has six streets with conventional and high-speed elevators, which are the main vertical connections, and twelve-kilometer pedestrian promenade connecting the base of the building with its summit.