Galileo Galilei Planetarium

Introduction
The idea that the City of Buenos Aires will feature a planetarium began to arise in 1958 at the initiative of the Socialist Councilman José Luis Pena and Secretary of Culture of the Municipality Aldo Cocca.
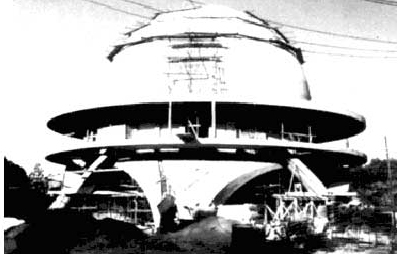
The construction of Galileo Galilei Planetarium began, under the direction of Argentine architect Enrique Jan, the Department of Architecture of the former Municipality of the City of Buenos Aires (MCBA) in 1962. The works were made by the Company Civil Constructions SA, the then Mayor Eugenio Schettini inaugurated the December 20, 1966.
The first performance took place on June 13, 1967. From the first show students Banfield No. 1 Commercial School and the College of the Holy Union of the Sacred Hearts, Capital Federal participated. Professor of Geography and Mathematics Antonio Cornejo showed them on that occasion as would the sky over Buenos Aires, Argentina Antarctica and the South Pole that night, and how to orient watching the Southern Cross. The definitive opening to the general public was held on April 5, 1968.
In addition to fulfilling his duties as Galileo Galilei Planetarium Planetarium has a small estate of collector which forms a small museum in the building itself. Among these related objects, all related to the world of astronomy, include small lunar rocks brought back by the Apollo 11 crew and the remains of the meteorite that fell in Campo del Cielo, Chaco, about 4,000 years ago. It also has the Copernican, a German instrument dating from 1901. It offers children’s shows, monitoring functions, educational lectures and special workshops for children.
Situation
The Planetarium Galileo Galilei is located at the intersection of Avenida General Sarmiento and Belisario Roldán, within the Tres de Febrero Park, in the neighborhood of Palermo, in the city of Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Concept
According to Enrique Jan this building is one of the few in the world designed and constructed based on the module equilateral triangle.
The architectural choice of this geometric figure holds a symbolism which was expressly sought. It is the most perfect flat surface can be performed with a minimum of equal sides, locking itself a primitive symbolic unit principle. These sequential conditions introduced throughout the development of the architectural project would be the guiding idea to accompany and would show the close relationship between the parts and the whole, suggesting developments since the first elementary particle (matter) to that cosmic development in which we operate. ”
The building form is symbolically structured around the figures of the equilateral triangle, rhombus, hexagon and circle, in an evolution from simple to complex.
Instrumental
Until 2011 the planetarium instrument was a device 5 meters high and 2.5 tons, with a hundred projectors. It consisted of a cylindrical shell with independent projectors for the moon, sun and planets visible to the naked Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn sight, and two spheres at the extremes which project 8,900 stars. A system of projectors and laser targeting devices that dome afforded various shows on the formation of the universe, with the exhibition of 8900 fixed stars, constellations and nebulae.
In 2011 a reform took place in Room Planetarium. The re-opening was held on Thursday, December 15, 2011.
Changes made during the reform were several:
- The MEGASTAR II A projector showing stars down to 11th magnitude was installed, which would be approximately a million stars over conventional planetary. In addition, over 140 projects clusters and nebulae and the Milky Way can be seen with a realism never before achieved. The projector is the first in the world to adopt LED lamps, replacing the previous lamps consuming far more electricity.
- The shows now have high-resolution images and have DigitalSky II, which is a system of full-dome video Advanced covering the entire dome.
- The amendment also added a new outer dome eco lighting and exchanged the normal 360 seats for a 4D type, incorporating a remote control that allows the viewer to interact during projection. Also the sound system was upgraded to digital 5.1
- The lake was in the park was recovered.
Spaces
Higher levels
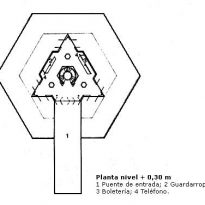
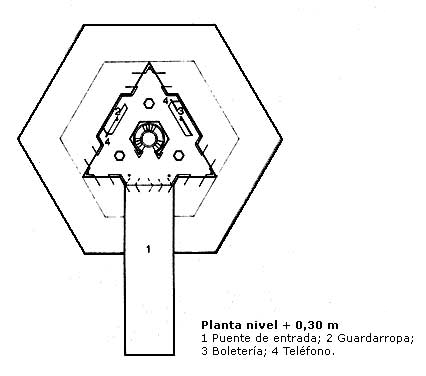
- Level + 0.30m
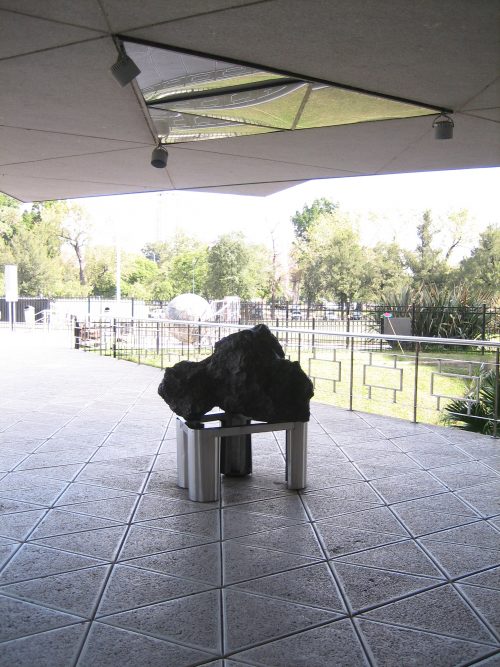
The entrance to the building is via a bridge, dodging the void of a big pot of 47 m. diameter of the bottom of architectural volumes isolated by a large water surface. In the slabs of the driveway, brought from Neuquén, you can find ammonites, extinct marine fossils around 100 million years ago. On the esplanade of access can see a metallic meteorite found in 1965 in the province of Chaco.

In the lobby (which has lockers and receiving) great triangular spherical cap, that beyond its structural features, creates an expressive limit, below which governs the triangular module and above it is seen, everything is sorted by module angular degrees.
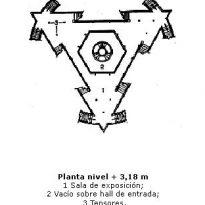
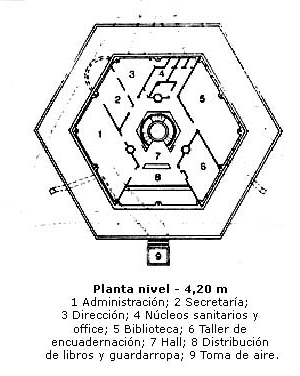
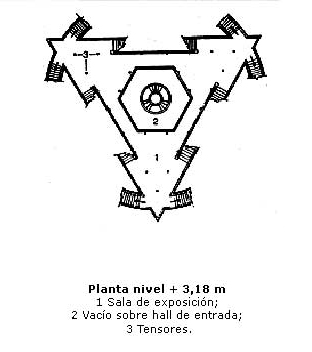
- Level + 3.18m
It ascending by wide stairs leads to the first floor exhibition whose plan shape is triangular. Here operates the Museum, where permanent or temporary exhibitions are offered and a moon rock brought to Earth Apollo XI mission to the Planetarium is displayed. In the center of this empty circle on the lower floor balconea triangular plant.
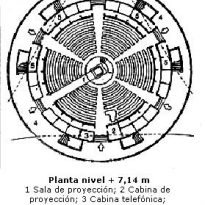
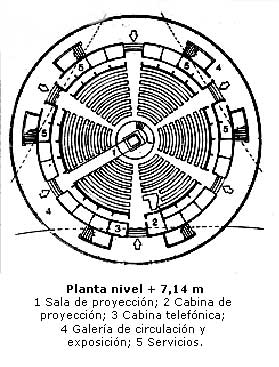
- Level + 7.14m
On the second floor room fully renovated in technology and facility level projections works: new planetarium projector model MEGASTAR II A; new system of full immersive dome video DigitalSky II of SKy Skan, new dome 4D projection and armchairs.
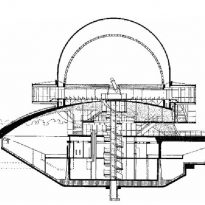
Subsoils
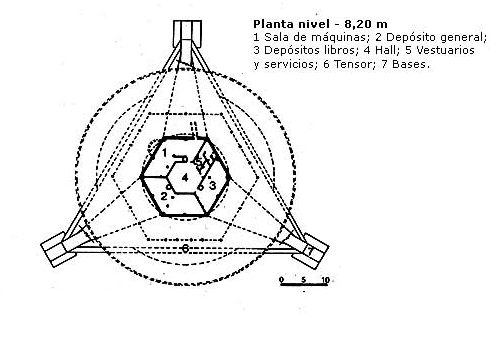
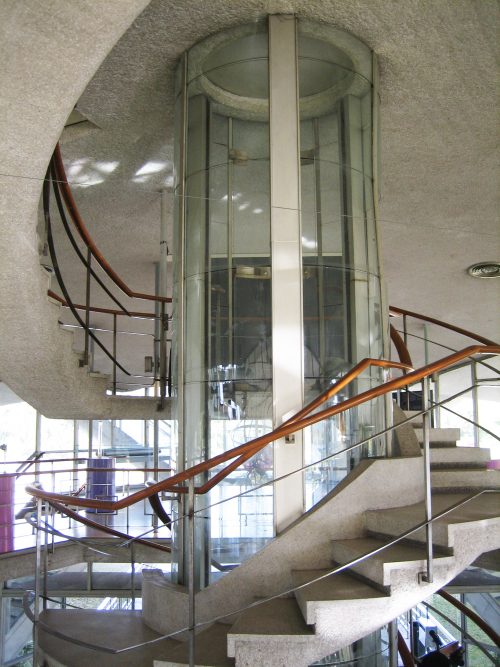
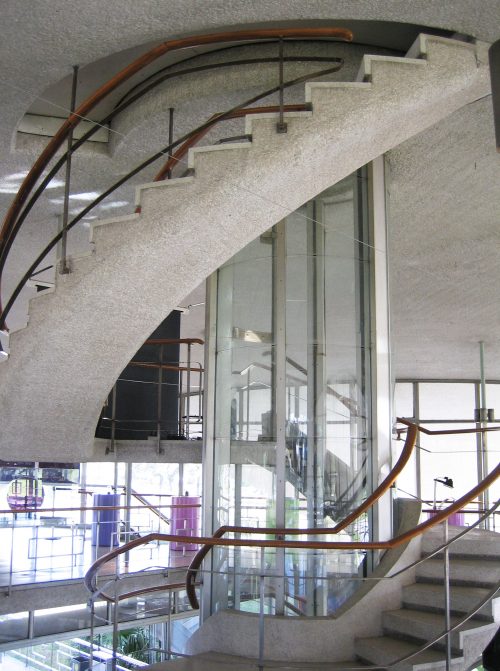
The building has two basements. It descends from the lobby by a spiral staircase.
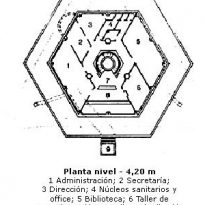
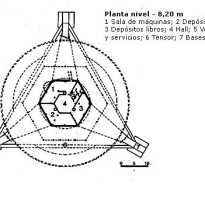
- Level -4.20m
In the first of them is a specialized library, administrative offices, restrooms, air intakes, bindery and address.
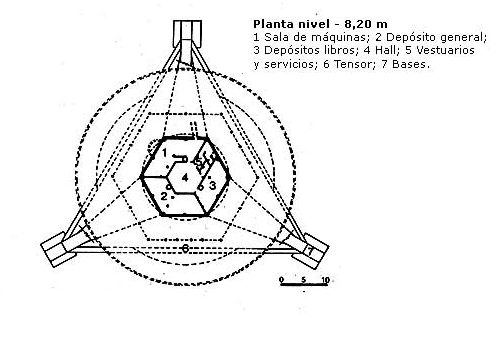
- Level -8.20m
For the same staircase you reach the second basement (and underground) where the tank, the engine room and audiovisual production department are located.
Structure and Materials
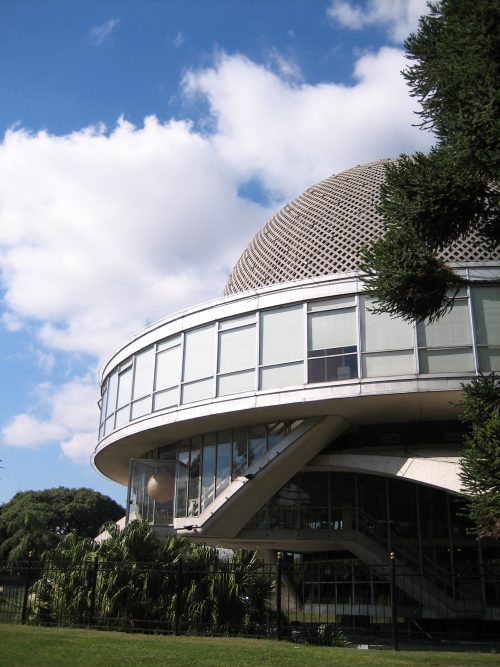
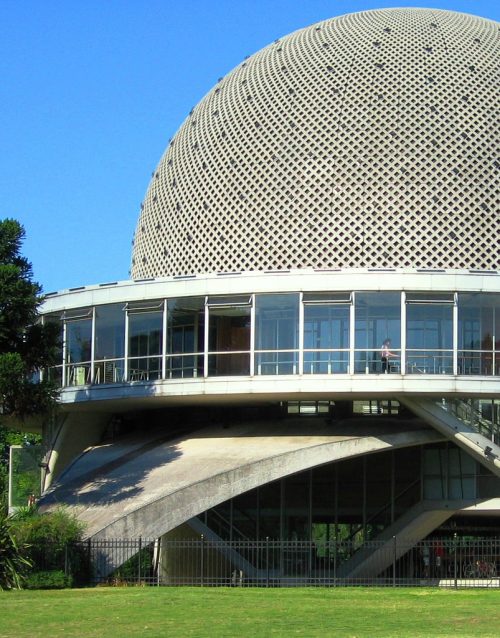
The building has five floors, six stairs (helical) and a circular room of 20 meters in diameter.
Your hemispherical dome is 20 meters in diameter and coated inside with aluminum sheets, which serves as a screen. In the center is housed his heart, the real planetarium.
The hemisphere is mounted on a network of interconnected steel rods 5,300, aluminum and wooden plates, curved glass and an iron core in a U shape, that is, six equilateral triangles whose vertices disposed inwards results in a circle.