Scottish Parliament

Introduction
In July 1998, the architects EMBT of Barcelona and Scottish partners RMJM Scotland, won a competition to design the new building for the Scottish Parliament at Holyrood. The team presented a series of charts showing where the design of Parliament: as a leaf and branch, with a strong symbolic meaning.
This drew the attention of the jury and led to winning the proposal, although no one term to understand.
Location
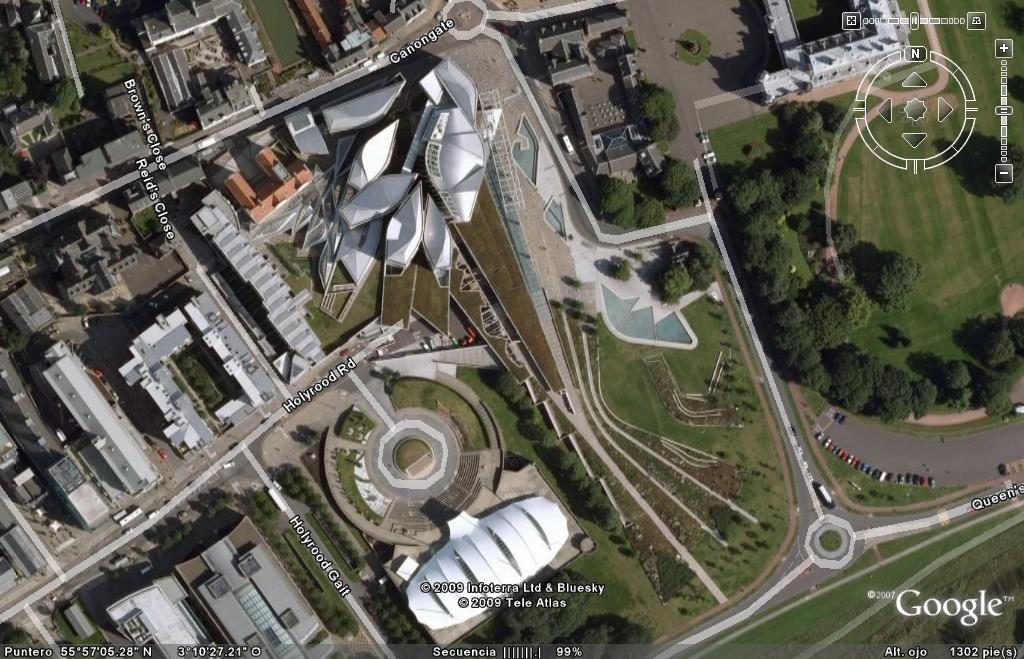
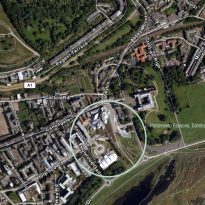
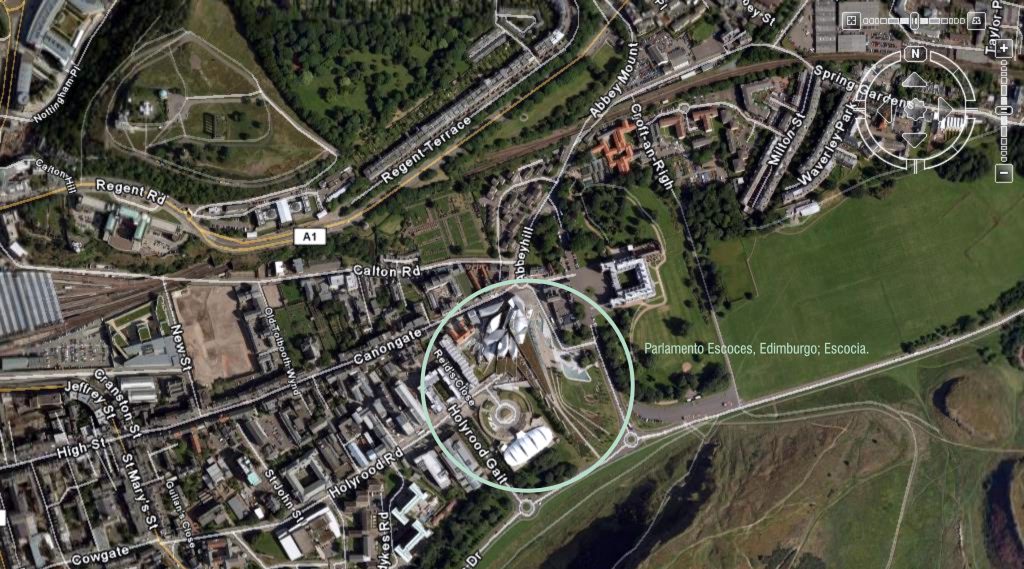
The building is located on land owned by a brewery of 1.6 hectares, where he was the Queensberry House (a historic mansion that is used as a military hospital) and is an area that is surrounded by Dutchman style buildings.
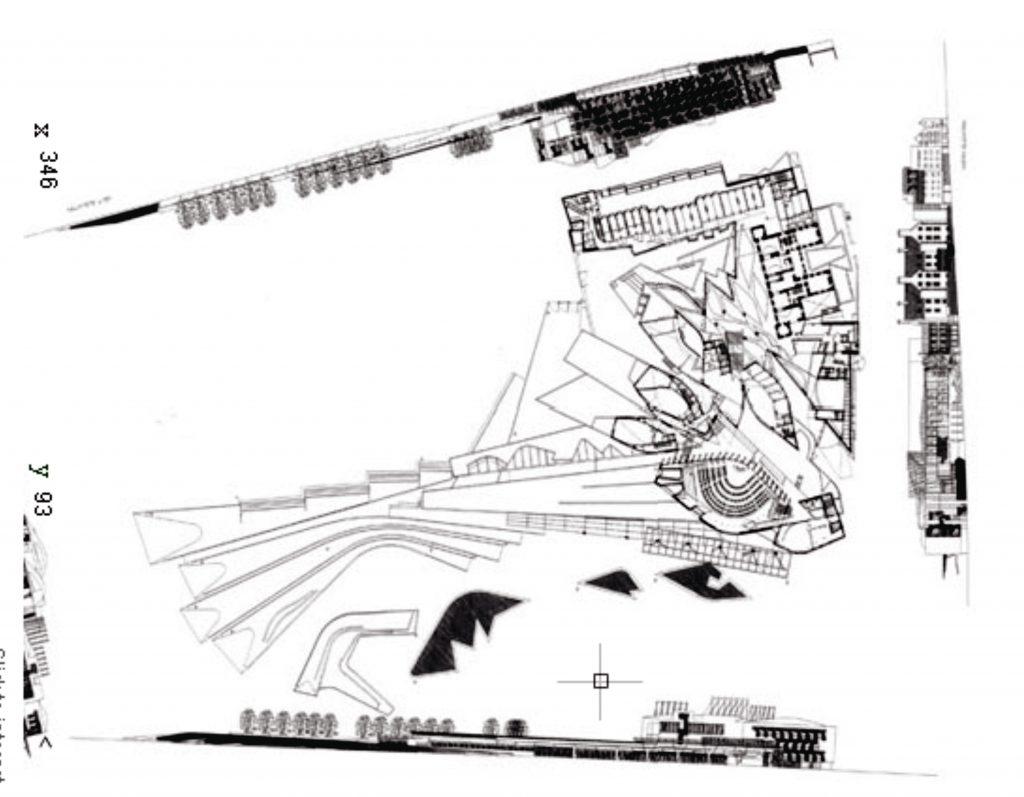
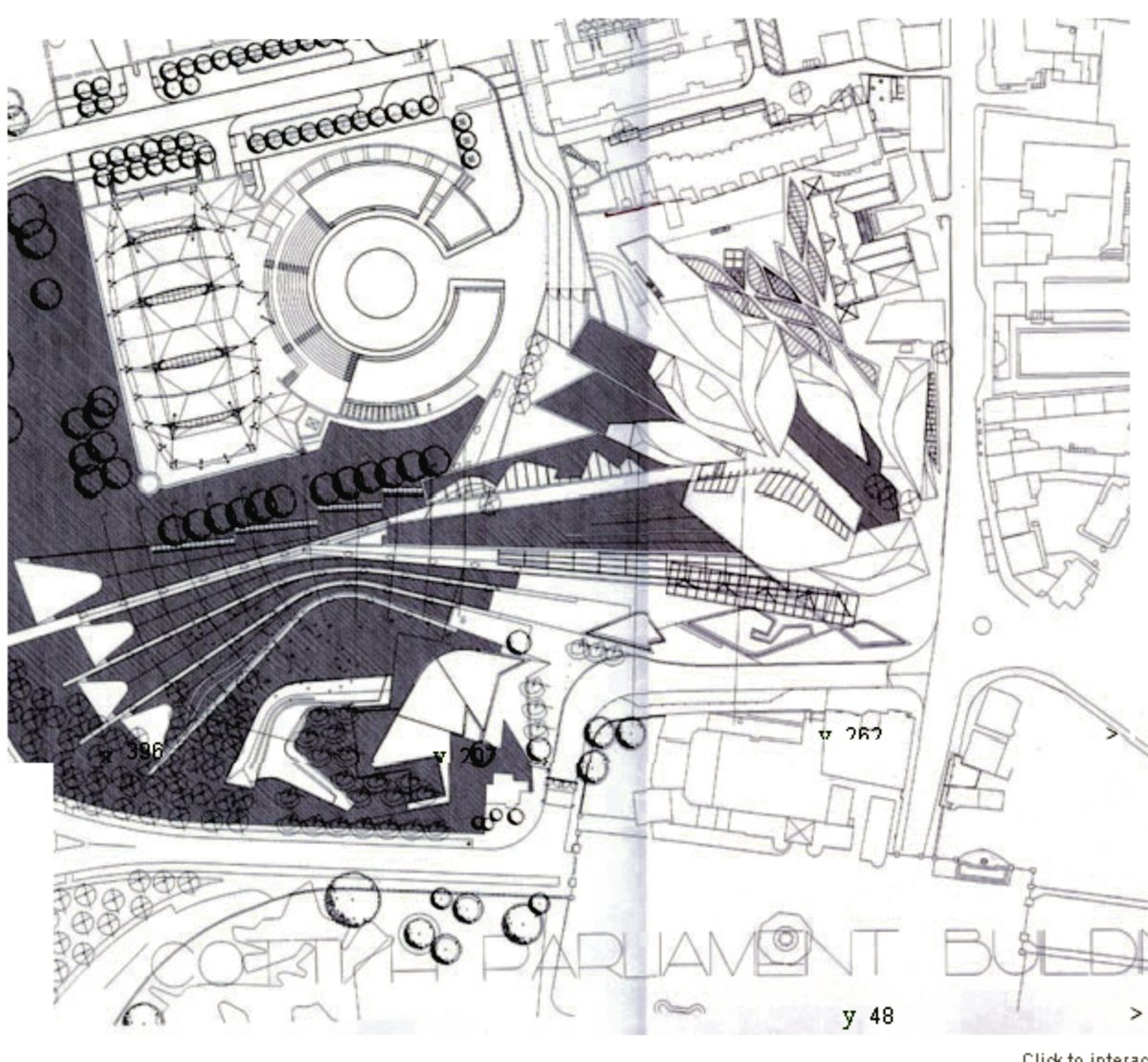
The building occupies an area of 1.45 hectares, which is added 1.86 acres of gardens. The building consists of a set of scattered units that form a whole.
Concept
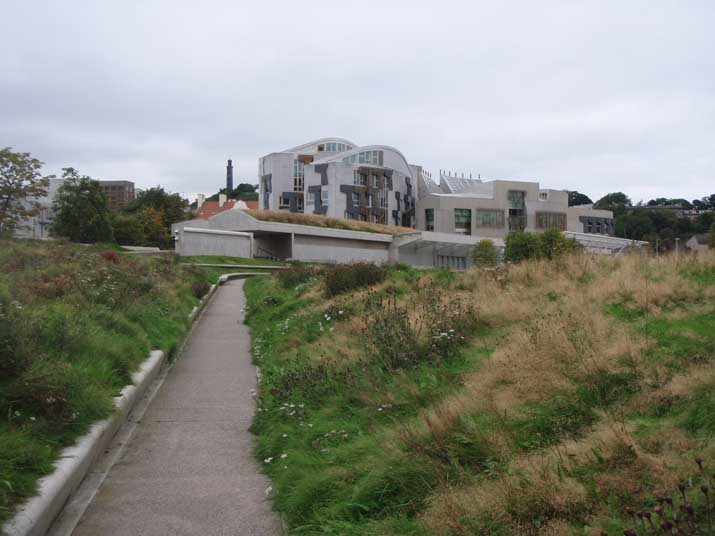
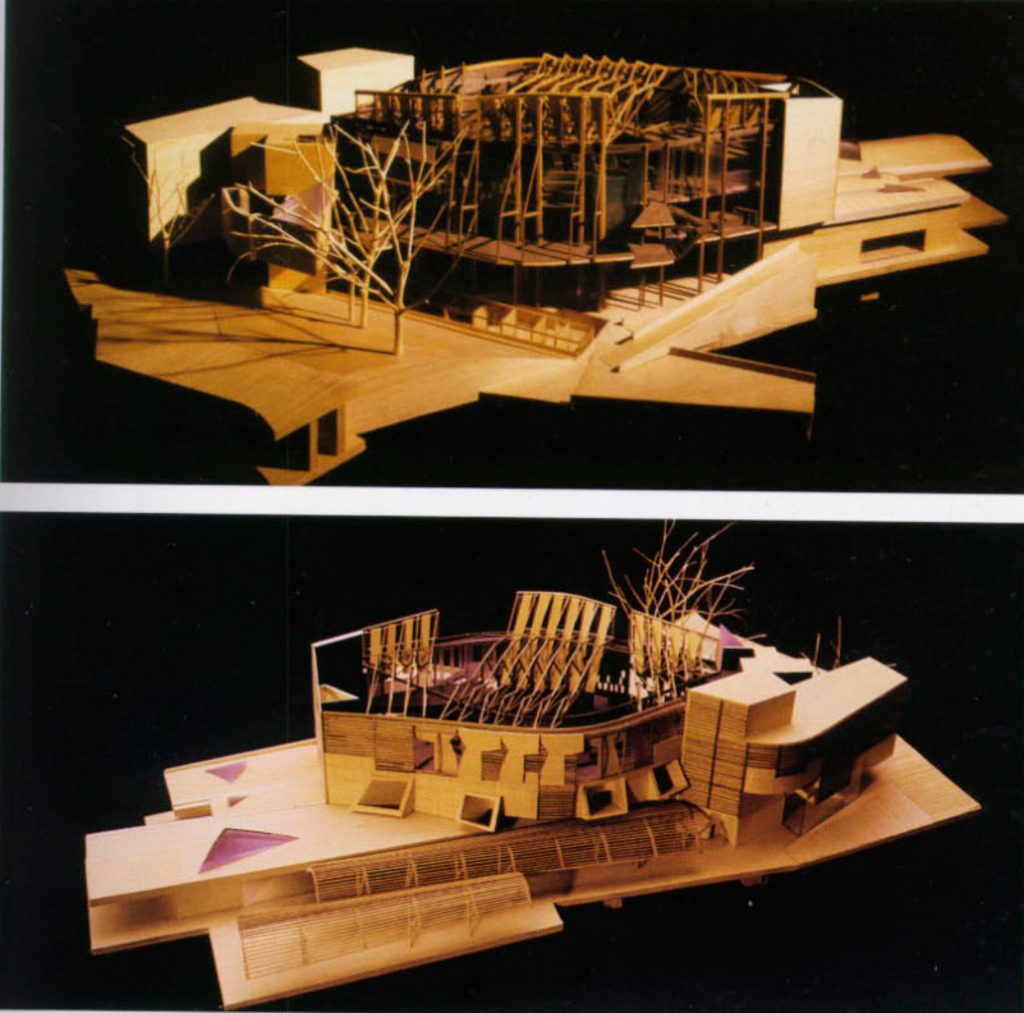
The design has a very strong symbolic basis: one thinks a building that reflects the land on which it arises.
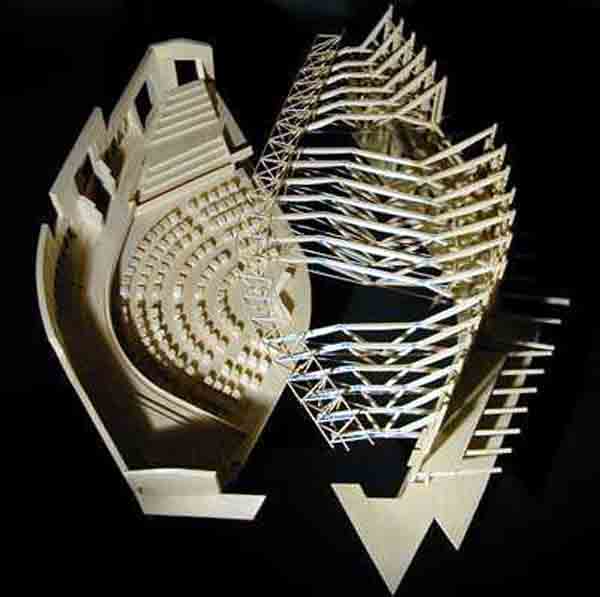
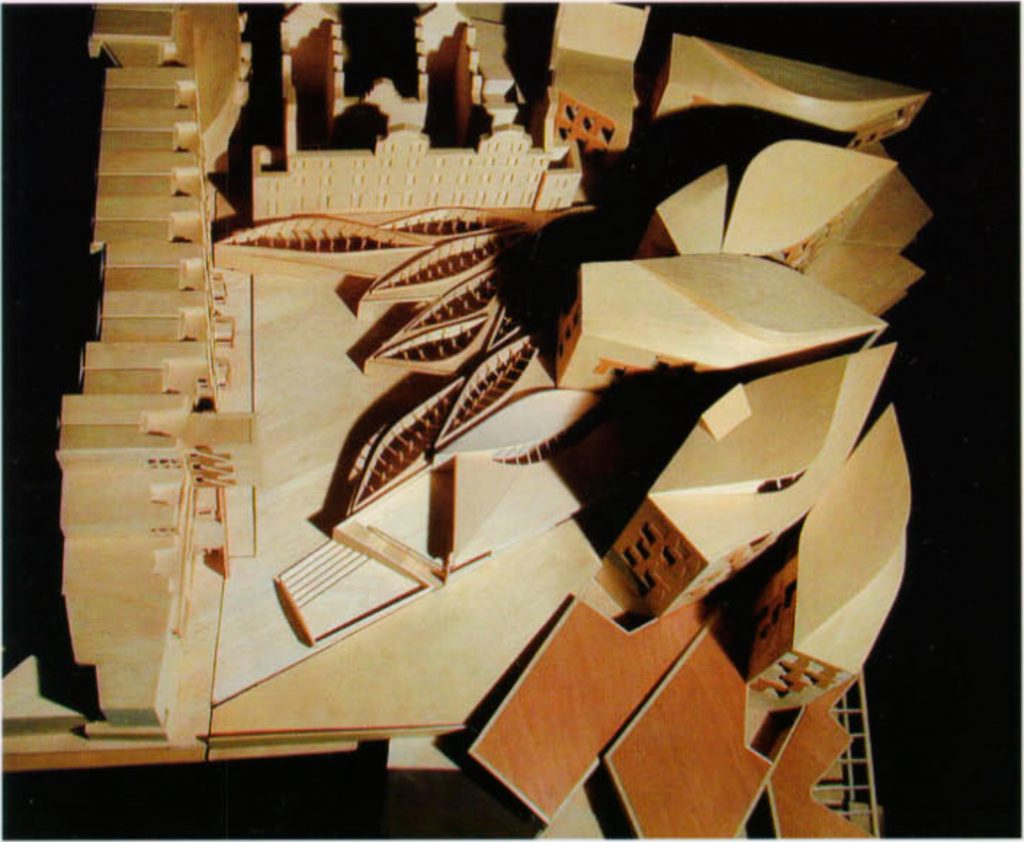
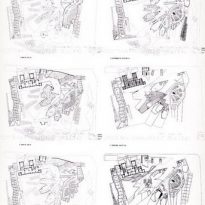
EMBT The study based its proposal on three points: the Scottish landscape, its people and its culture. That’s why the resort is situated like a small town, with streets and buildings of varying scale, and allowed to go through different feelings while it runs.
Spaces
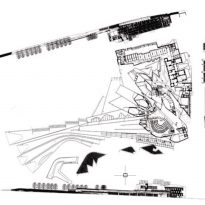
General provision
Most of all be seen in “towers” that are available to the city. The gardens and terraces are scattered towards the volcanic outcrop of Arthur’s Seat.
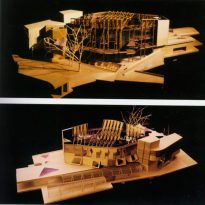
The buildings are arranged in two groups, container buildings, which form an “L” and contains a group of three buildings: the mansion Queensberry, the Royal Mile and Cannongate tower and theSouthwestby the contents of buildings ” L “: a series of leaf-shaped towers that house services for parliamentarians. Before them lies the great hall of parliament, crowned by a group of naturally lit skylights and give identity to space.
In theeastside are the most important buildings: the tower of the press and the House debates, and before they have a pergola that connects the building with the outside.
Towards the south,,will feature a series of gardens worked by Miralles.
New buildings
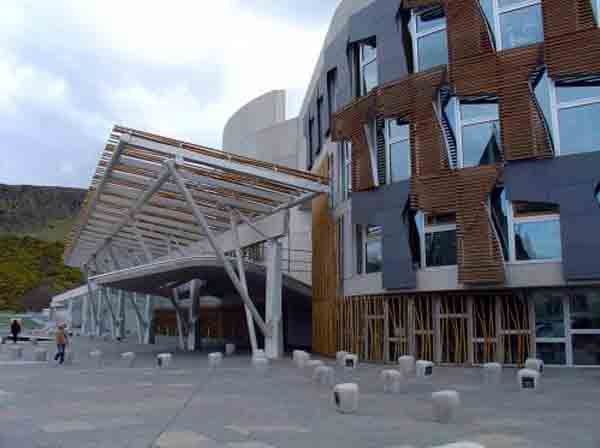
- The entrance building: Is located to the east. Contains information services (counters), restaurant and shops. The counter is made of wood and banana Scottish oak.
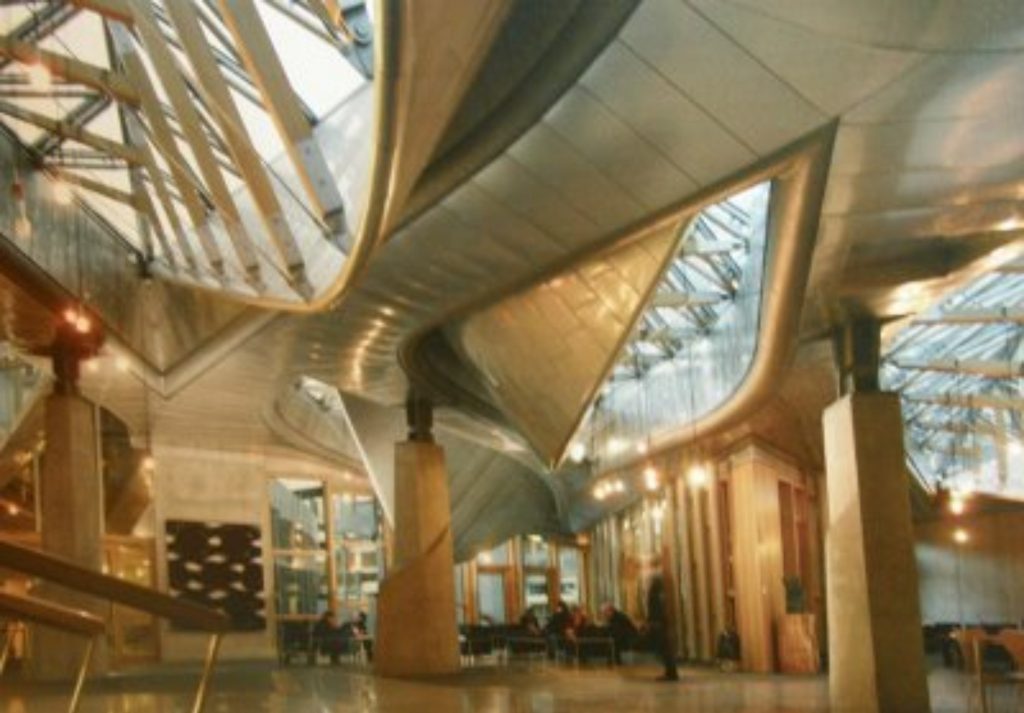
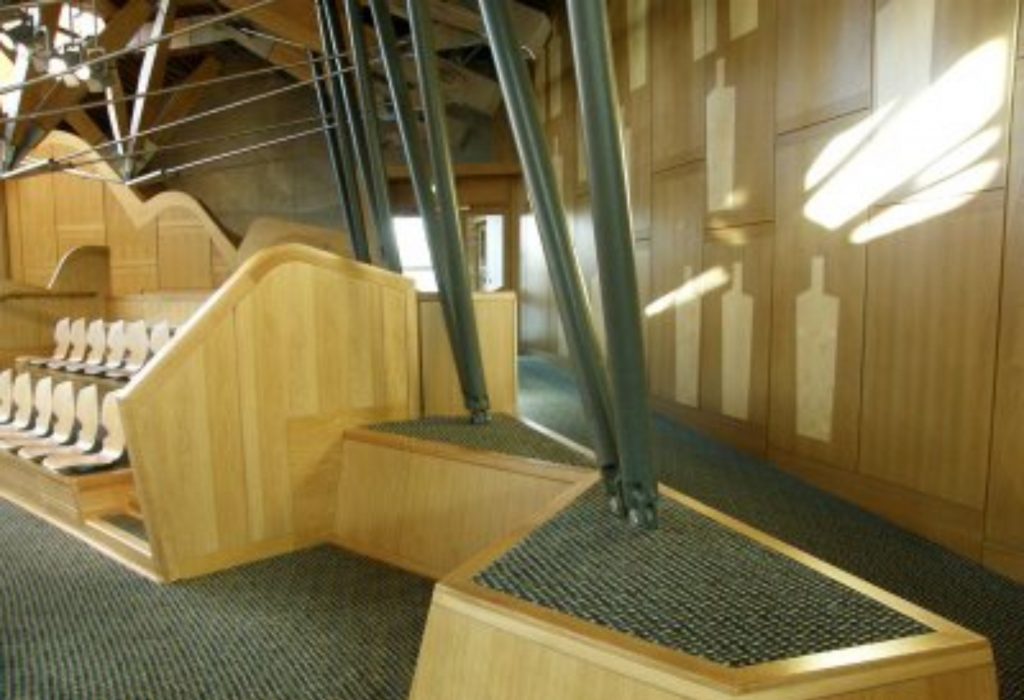
- The debating chamber: Located above the entrance foyer (public). There is here a clear symbolism: the basis of Representatives is the people who elected them.
The camera is used wooden structure, referring to former Parliament (1639). The floor is steel mesh which in turn acts as transfer loads to columns arbitrarily placed. Through it passed the installation of air conditioning and electricity.
The seats and desks were designed by Enric Miralles specifically in plantain and oak.
- Assembly building: Here are located the committee rooms and support services, which resolve most issues.
The appearance of this building resembles a Scottish boats moored to the dock. The roofs with overhangs of double curvature, materialized with steel elements, creating an atmosphere in the church roof.
- Torres assembly: There are four towers in total and around the chamber of deputies. Towers 1 and 2 house parliamentary committees and staff offices. In the towers 3 and 4 provide ministries are located, his staff and the chair of Parliament. Their roofs are shaped like boats.
- Tower of media: It is located on the corner of Horse Wynd, the Canongate building and debating chamber.
A building of 4 floors. The front conforms to boot-shaped pieces made of stone and oak.
- Canongate buildings: is earmarked to finance and management offices. The outer wall is precast concrete elements.
- The building of parliamentarians: 6-storey linear building located in the West. Inside offices are located-cells manufactured with a vaulted ceiling. Each module has 15 m2 and weighs 18 tons. The facade is defined by 114 windows bay window (cantilever and provided with a seat). The form of these is based on the profile of a famous painting by Raeburn.
The movement is located to the east, and overlooks a courtyard garden. The structure is concrete.
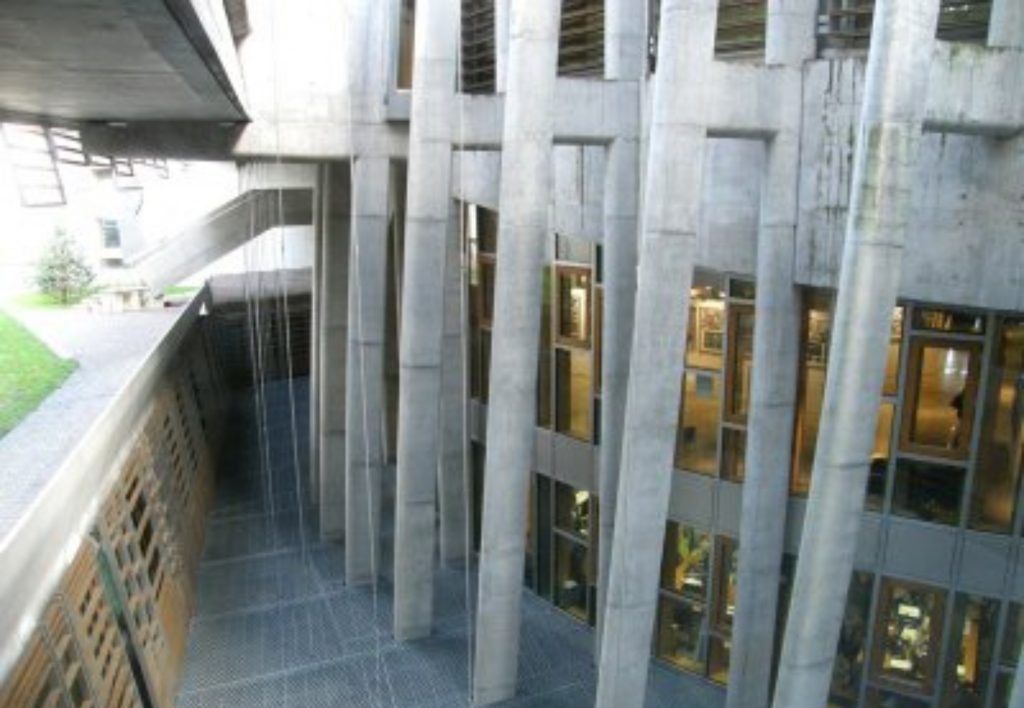
Structure
Each space has a different structure.
- The entrance buildingendings are characterized by their high quality concrete and has three domes dotted with crosses (taking the image of the Scottish flag). The COLUMNS invade apparently arbitrarily.
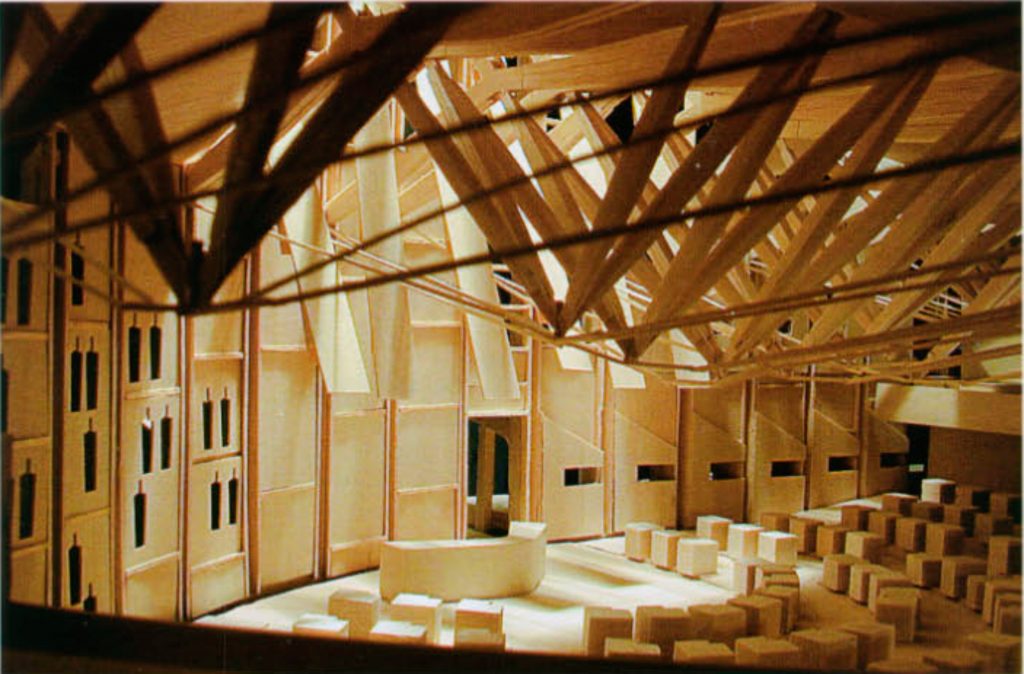
- In the debating chamber,The roof consists of three large wooden trusses with 120 knots, and fabricated stainless steel connectors in Aberdeen especially for the building.
The elements comprising the structure are laminated European oak compression elements and stainless steel for the elements in tension.
- Theassembly buildings have been designed in prestressed concrete to get lights for more than 14 m.
- The Canongate buildingshave within a metallic structure. Finally, thebuildinghas MPs in the office sector, prefabricated cells with a vaulted ceiling and the concrete structure movement.
Materials
It is used largely for banana timber Scottish European oak and banana, as well as concrete and stone. Although each sector has materials that characterize them:
In the towers of the assembly, using reinforced concrete frames, covered Kemnay granite, from Aberdeenshire. There are decorative panels made of oak and black and gray granite. The roofs are covered with stainless steel.
On the west side,the representative office,there are windows of stainless steel.
Some of the windows have exterior design with a lattice of oak.
In the debating chamber, all based coatings are made from European oak and banana. The western side of the camera has 1000 m2 of laminated glass panels. Each panel has a sheet of banana strips placed in horizontal layers between two glass and shaping the forms that mimic human forms. The furniture was held in banana and oak.