Central Park of Nou Barris


Introduction
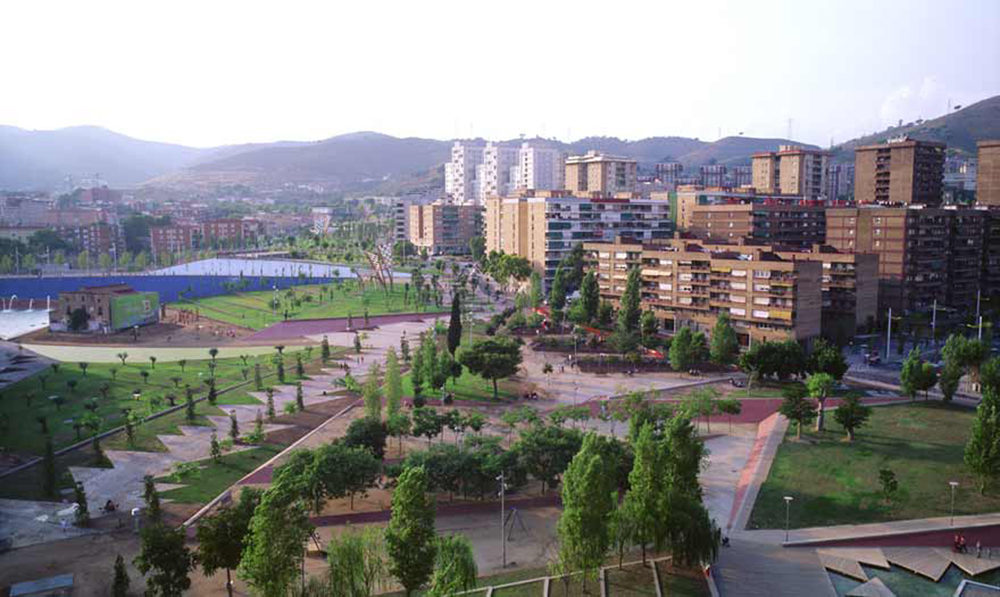
The construction of Parque de Nou Barris stands as the central operation in the renewal of the eastern outskirts of Barcelona. With the implementation of cubism into three dimensions is achieved by a fluid connection to the city center and a better relationship between the built environment and public space.
Location
Nou Barris district of Barcelona is not a part of town with its own identity. On the contrary, is a large area consisting of a conglomeration of different neighborhoods with an area of about eight square miles, very poorly communicated and different urban histories. It was not until the Olympics of 92, when they finally built the Belt Ronda de Dalt, that this area was connected with the rest of the city and its urban potential increased significantly. With only ten minutes drive through the roundabout at the Place de Karl Marx, were linked rich areas of the western part of the city with all the Nou Barris district.
Nou Barris district is the only sector of the city than in the nineties was the outskirts of Barcelona.
The Second Round Belt route finally to the beginning of the 90s was the essential infrastructure that supported the district to make a qualitative leap in potential and match the other boroughs.
Five years after the Olympic Games 92, in line with the international economic crisis, few operations planned were carried to term. 97 In accordance with the decentralization policy of the City Council to bring the centers of decision to the citizens, strengthens the idea of creating a new downtown district to the environment of the old Mental Hospital.
Concept
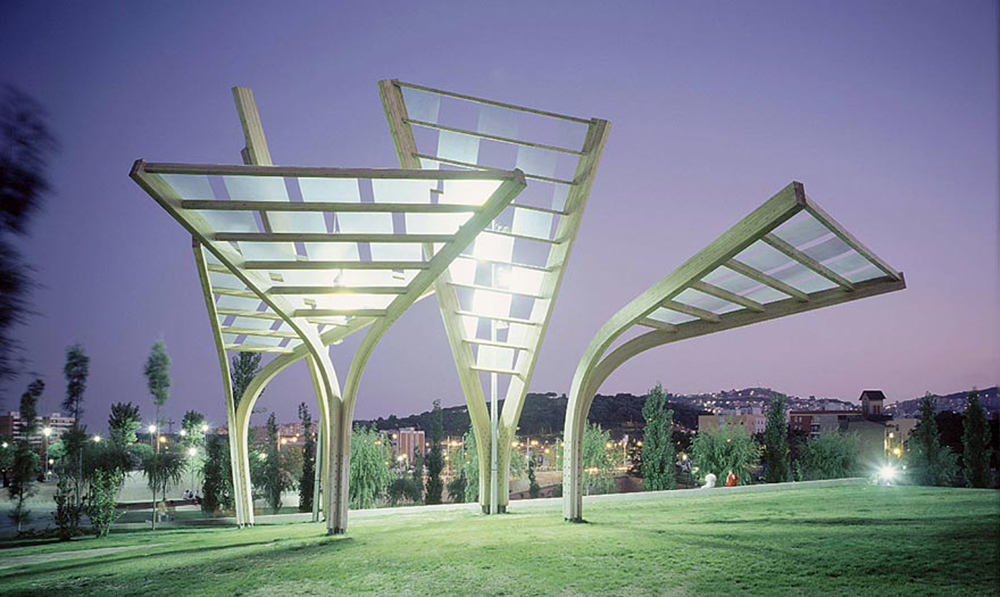
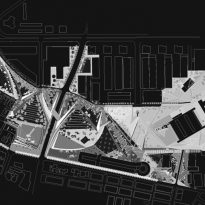
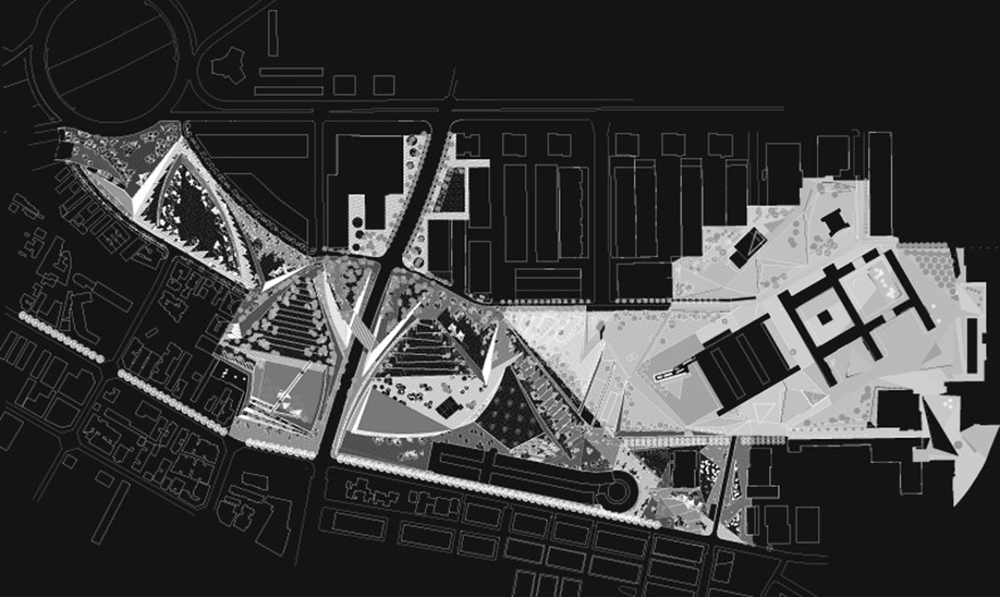
The Parque Central de Nou Barris expresses the desire of ownership of the street, open space, not a monumental primary language but with the intention to assess, for the most part, that which already exists. It is not a contextual view, in the sense that the project is the product of the site’s features, but the establishment of a new layer that changes the perception, organization and use of fitness.
The second phase of Nou Barris Central Park, opens to the public in September 2003 and becomes the large core district team.
If Barcelona in the 80s was known for the recovery of the historical city and the application of criteria similar to the periphery intervention, the change that has occurred in the district of Nou Barris in Barcelona in recent years, demonstrating the ability suburban areas of the contemporary city to be radically transformed through processes of project more in line with the bill for the real city.
Spaces
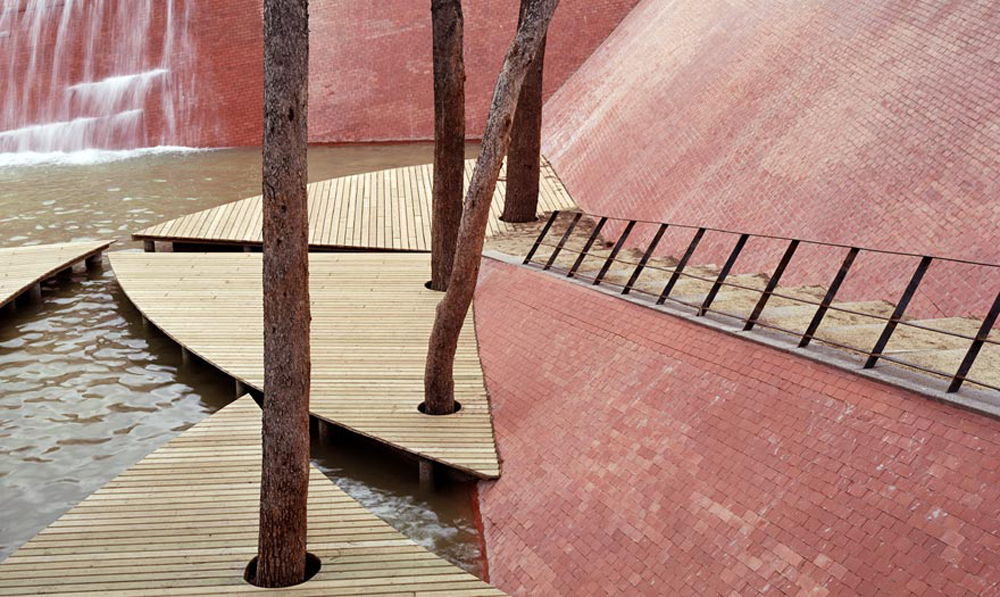
The Cubist landscape emerges from this organization of space rather than a particular formal approach. The establishment of triangular surfaces flat or sloping triangular sides forming with saving uneven slopes and connected together, allowing the establishment of a continuous faceted surface that extends to all the interstitial spaces.
Central Park is the manifestation of a way to project where the instrument does not determine a composition of laws closed but allows variations to suit the needs of the periphery connectives.
The real city is the block and passages, the belt, the tracks and the park, the towers and the wall. The intervention of design, it comes to continuity between housing and public space using these elements with procedures such as Cubist variations that emphasize the identity and uniqueness of the vacuum fragmented.
Materials
Materials used for the implementation of the work. From the basic materials of the structure to the interior finishes such as flooring, paints, coatings, etc..